Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- Type 1 (acute cardiorenal syndrome): acute decompensated heart failure causing acute kidney failure
- -
- Type 2 (chronic cardiorenal syndrome): chronic heart failure leading to kidney dysfunction
- -
- Type 3 (acute renocardiac syndrome): acute aggravation of kidney function causing heart dysfunction
- -
- Type 4 (chronic renocardiac syndrome): chronic kidney diseasegenerating heart dysfunction/disease
- -
2. Classification
2.1. CRS Type 1
2.2. CRS Type 2
2.3. CRS Type 3
2.4. CRS Type 4
2.5. CRS Type 5
3. Pathophysiology
3.1. Hemodynamic Pathways
3.1.1. Non-Hemodynamic Pathways
3.1.2. Endothelial Dysfunction
3.2. Epigenetics Implications
3.2.1. Role of Vascular Growth Factors
3.2.2. Megalin and Cubilin Receptors
3.2.3. Hipoxia Inducible Factors
3.2.4. Oxidative Stress
3.2.5. Chronic Inflammation
3.2.6. Other Mechanisms Involved
3.2.7. Biomarkers
4. Future Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortesi, C.; Ibrahim, M.; Rivera, F.C.; Hernandez, G.A. Cardiorenal Syndrome, Hemodynamics, and Noninvasive Evaluation. Clin. Med. Insights Ther. 2017, 9, 1179559X17742376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronco, C.; Haapio, M.; House, A.A.; Anavekar, N.; Bellomo, R. Cardiorenal syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tharaux, P.L. Histamine provides an original vista on cardiorenal syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5550–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Valente, M.A.E.; Voors, A.A. Renal impairment, worsening renal function, and outcome in patients with heart failure: An updated meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virzì, G.M.; Zhang, J.; Nalesso, F.; Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A. The Role of Dendritic and Endothelial Cells in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, L.; Bellasi, A.; Barbera, V.; Russo, D.; Russo, L.; Di Iorio, B.; Cozzolino, M.; Ronco, C. Pathophysiology of the cardio-renal syndromes types 1–5: An uptodate. Indian Heart J. 2017, 69, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembillo, G.; Visconti, L.; Giusti, M.A.; Siligato, R.; Gallo, A.; Santoro, D.; Mattina, A. Cardiorenal Syndrome: New Pathways and Novel Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restini, C.B.A.; Pereira, B.F.M.; Geleilete, T.M. Free Radicals and Biomarkers Related to the Diagnosis of Cardiorenal Syndrome. IntechOpen-Free Radic. Dis. 2016, 277–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, Z.; Romagnoli, S.; Ronco, C. Cardiorenal Syndrome. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peesapati, V.; Sadik, M.; Verma, S. Panoramic Dominance of the Immune System in Cardiorenal Syndrome Type I. Cureus 2020, 12, e9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Muller, C.; Damman, K.; Murray, P.T.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A. Pathogenesis of Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1 in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Workgroup Statements from the Eleventh Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 182, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Cicoira, M.; McCullough, P.A. Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1: Pathophysiological Crosstalk Leading to Combined Heart and Kidney Dysfunction in the Setting of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virzì, G.; Breglia, A.; Brocca, A.; DeCal, M.; Bolin, C.; Vescovo, G.; Ronco, C. Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Oxidative Stress, and Tissue Damage Markers in Patients with Acute Heart Failure with and without Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A.; Anker, S.D. Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Consensus Group Cardiorenal Syndromes: An executive summary from the Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Contrib Nephrol. 2010, 165, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ronco, C.; Bellasi, A.; Di Lullo, L. Cardiorenal Syndrome: An Overview. Adv. Chronic. Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.T.; Fonarow, G.C.; Costanzo, M.R.; Mathur, V.S.; Wigneswaran, J.R.; Wynne, J.; Committee, A.S.A. High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on out come in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: A report from the ADHERE database. J. Card. Fail. 2007, 13, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, R.; Nair, N.; Chakraborty, R.; Nemer, L.; Dasgupta, R.; Varian, K. An Update on the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiol. Res. 2020, 11, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.; Benouna, M.E.G.; Habbal, R. Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 2: A Strong Prognostic Factor of Survival. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Sci. 2017, 30, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, W.J.; Fu, G.P.; Li, Q.Q.; Min, X.C.; Guo, Y.F. Circulating miRNA-21 as a diagnostic biomarker in elderly patients with type 2 cardiorenal syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vecchis, R.; Baldi, C. Cardiorenal syndrome type 2: From diagnosis to optimal management. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Mei, Y.; Cui, S.; Feng, Z.; Chen, X. New insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiorenal syndrome. Aging 2020, 12, 12422–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, M.; Doi, K.; Ogasawara, E.; Yamashita, T.; Hamasaki, Y.; Kariya, T.; Takimoto, E.; Yahagi, N.; Nangaku, M.; Noiri, E. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by dynamin related protein-1 in acute cardiorenal syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.A.; Cozzi, M.; Bush, E.L.; Rabb, H. Distant Organ Dysfunction in Acute Kidney Injury: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, U.; Wettersten, N.; Garimella, P.S. Cardiorenal syndrome: Pathophysiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M. The pathophysiology of chronic cardiorenal disease based on central Hemodynamics. J. Cardiovasc. Med. Cardiol. 2018, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnanaraj, J.; Radhakrishnan, J. Cardio-renal syndrome. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, X.; Dekkers, I.A.; Lamb, H.J. Cardioneral Syndrome: Emerging Role of Medical Imaging for Clinical Diagnosis and Management. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiphilippou, S.; Kon, S.P. Cardiorenal syndrome: Review of our current understanding. J. R. Soc. Med. 2016, 109, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virzì, G.M.; Clementi, A.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C. Multi-Omics Approach: New Potential Key Mechanisms Implicated in Cardiorenal Syndromes. Cardiorenal Med. 2019, 9, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Firoz, A.; Garlapati, S. Emerging Treatments of Cardiorenal Syndrome: An Update on Pathophysiology and Management. Cureus 2021, 13, e17240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; Van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G. Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verbrugge, F.H.; Dupont, M.; Steels, P.; Grieten, L.; Malbrain, M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Mullens, W. Abdominal Contributions to Cardiorenal Dysfunction in Congestive Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redant, S.; Honoré, P.M.; De Bels, D. Fifty shades of central venous pressure in the cardiorenal syndrome. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2020, 8, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghionzoli, N.; Sciaccaluga, C.; Mandoli, G.E.; Vergaro, G.; Gentile, F.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Mondillo, S.; Emdin, M.; Valente, S.; Cameli, M. Cardiogenic shock and acute kidney injury: The rule rather than the exception. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Malvin, R.L. Stimulation of renal sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. 1977, 232, F298–F306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, P. Cardiorenal Syndrome An Important Subject in Nephrocardiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.A.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, A.; Virzì, G.M.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C. Neurohormonal, Endocrine, and Immune Dysregulation and Inflammation in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiorenal Med. 2019, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavlovsky, P.J.; Tonnerre, P.; Guitton, C.; Charreau, B. Expression of MHC class I-related molecules MICA, HLA-E and EPCR shape endothelial cells with unique functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, H.A.; Carr, C.S.; Al, S.J. Endothelial dysfunction: Cardiovascular risk factors, therapy, and outcome. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bottiglieri, T.; McCullough, P.A. The Central Role of Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Cardiorenal Med. 2017, 7, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kooijmans, S.A.; Vader, P.; Van Dommelen, S.M.; Van Solinge, W.W.; Schiffelers, R.M. Exosome mimetics: A novel class of drug delivery systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L. Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cellto-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Kuroda, M. Roles of exosomes and microvesicles in disease pathogenesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Ishrat, R.; Tazyeen, S.; Alam, A.; Farooqui, A.; Ali, R.; Imam, N.; Tamkeen, N.; Ali, S.; Malik, M.D.; et al. In Silico Integrative Approach Revealed Key MicroRNAs and Associated Target Genes in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2021, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Clementi, A.; Brocca, A.; Cal, M.; Ronco, C. Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cardiorenal Cross Talk. Pathobiology 2016, 83, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Yang, M.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, J. MicroRNA-21-containing microvesicles from tubular epithelial cells promote cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Renal Fail. 2021, 43, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-K.; Bar, C.; Thum, T. miR-21, Mediator, and Potential Therapeutic Target in the Cardiorenal Syndrome. Front. Fharmacology 2020, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, C.A.; Gnudi, L. Vascular growth factors as potential new treatment in cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, S.; Hosojima, M.; Kaseda, R.; Kabasawa, H.; Yamamoto-Kabasawa, K.; Kurosawa, H.; Sato, H.; Iino, N.; Takeda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Significance of urinary full-length and ectodomain forms of megalin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, A.; Kaseda, R.; Hosojima, M.; Sato, H. Proximal tubule cell hypothesis for cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes. Int. J. Nephrol. 2010, 2011, 957164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzolo, M.P.; Farfán, P. New Insights into the Roles of Megalin/LRP2 and the Regulation of its Functional Expression. Biol. Res. 2011, 44, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Cano, C.; Gutiérrez-Carrasquilla, L.; Barbé, F.; Sánchez, E.; Hernández, M.; Martí, R.; Ceperuelo-Mallafre, V.; Dalmases, M.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Vendrell, J.; et al. Effect of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha Expression. Is There a Relationship with the Clock Genes? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Mutual Antagonism of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Isoforms in Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Disorders. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Basic Trans. Sci. 2020, 5, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, S.; Maruyama, Y.; Honda, H. A new insight into the treatment of renal anemia with HIF stabilizer. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2020, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J. Contribution of aldosterone to cardiovascular and renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, I.S.; Woodside, J.V. Antioxidants in health and disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siwik, D.A.; Pagano, P.J.; Colucci, W.S. Oxidative stress regulates collagen synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C53–C60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, F.; Wang, J.F.; Tang, W.; Huang, H. Apocynin Attenuates Cardiac Injury in Type 4 Cardiorenal Syndrome via Suppressing Cardiac Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 with Oxidative Stress Inhibition. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kingma, J.G.; Simard, D.; Rouleau, J.R.; Drolet, B.; Simard, C. The Physiopathology of Cardiorenal Syndrome: A Review of the Potential Contributions of Inflammation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, P.C.; Ganda, A.; Lin, J. Inflammatory activation: Cardiac, renal, and cardio-renal interactions in patients with the cardiorenal syndrome. Heart Fail Rev. 2012, 17, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düsing, P.; Zietzer, A.; Goody, P.R. Vascular pathologies in chronic kidney disease: Pathophysiological mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhart, C.; Ulrich, C.; Greinert, D.; Dambeck, S.; Wienke, A.; Girndt, M.; Pliquett, R.U. Systemic inflammation in acute cardiorenal syndrome: An observational pilot study. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Bargues, C.; Alique, M.; Barrús-Ortiz, M.T.; Borrás, C.; Rodrigues-Díez, R. Exploring New Kingdoms: The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Oxi-Inflamm-Aging Related to Cardiorenal Syndrome. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schunk, S.J.; Triem, S.; Schmit, D.; Zewinger, S.; Sarakpi, T.; Becker, E.; Hütter, G.; Wrublewsky, S.; Küting, F.; Hohl, M.; et al. Interleukin-1α Is a Central Regulator of Leukocyte-Endothelial Adhesion in Myocardial Infarction and in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2021, 144, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grune, T.; Sommerburg, O.; Siems, W.G. Oxidative stress in anemia. Clin. Nephrol. 2000, 53, S18–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, S.J.; Choudhary, A.; Kalsi, A.K.; Zhao, S.; Alex, R.; Abraham, N.G. OX-HDL: A Starring Role in Cardiorenal Syndrome and the Effects of Heme Oxygenase-1 Intervention. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petreski, T.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R.; Bevc, S. Hyperuricemia the heart, and the kidneys—To treat or not to treat? Renal Fail. 2020, 42, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A. Anemia of cardiorenal syndrome. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2021, 11, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, F. Range of adiposity and cardiorenal syndrome. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 322–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P. Cardiorenal Syndrome Revisited. Circulation 2018, 138, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savira, F.; Magaye, R.; Liew, D.; Reid, C.; Kelly, D.J.; Kompa, A.R.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Burnett, J.C.; Kaye, D.; Wang, B.H. Cardiorenal syndrome: Multi-organ dysfunction involving the heart, kidney and vasculature. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2906–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Zhao, S.; Ye, P.; Luo, L. Biomarkers in Cardiorenal Syndromes. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9617363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, N.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Toscano, M.A.; Rabinovich, G.A. The role of galectins in the initiation, amplification and resolution of the inflammatory response. Tissue Antigens 2004, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.C.; Pokharel, S.; Van Brakel, T.J.; Van Berlo, J.H.; Cleutjens, J.P.; Schroen, B.; André, S.; Crijns, H.J.; Gabius, H.J.; Maessen, J. Galectin-3 Marks Activated Macrophages in Failure-Prone Hypertrophied Hearts and Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation 2004, 110, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, G.; Barone, R.; Di Terlizzi, V.; Correale, M.; Brunetti, N.D.; Iacoviello, M. Biomarkers in Cardiorenal Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthahar, N.; Meijers, W.C.; Silljé, H.H.W.; Ho, J.E.; Liu, F.T.; De Boer, R.A. Galectin-3 Activation and Inhibition in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Theranostics 2018, 8, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Staessen, J.A.; Mischak, H.; Latosinska, A.; Beige, J. Proteomic Biomarkers in the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Toward Deciphering Molecular Pathophysiology. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottone, S.; Mule, G.; Guarneri, M.; Palermo, A.; Lorito, M.C.; Riccobene, R.; Arsena, R.; Vaccaro, F.; Vadala, A.; Nardi, E.; et al. Endothelin-1 and F2-isoprostane relate to and predict renal dysfunction in hypertensive patients. Nephrol. Dial Transpl. 2009, 24, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavi, S.; Yang, E.H.; Prasad, A.; Mathew, V.; Barsness, G.W.; Rihal, C.S.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. The interaction between coronary endothelial dysfunction, local oxidative stress, and endogenous nitric oxide in humans. Hypertension 2008, 51, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, P.C.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, Y.C. Biomarkers for acute cardiorenal syndrome. Nephrology 2018, 23, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
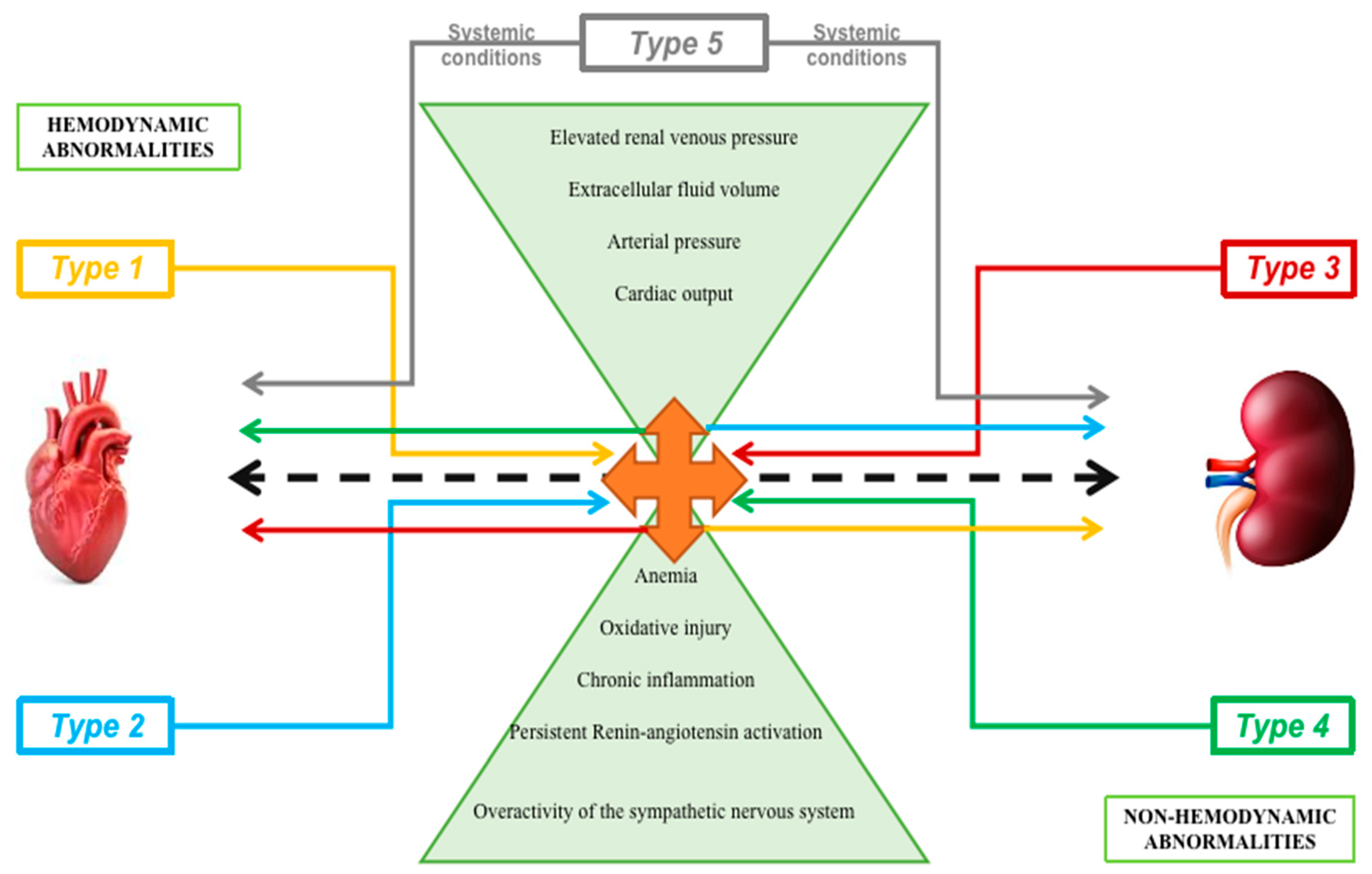
| Cardiorenal Types | Known as | Characteristics and Mechanisms | Etiology/Clinical Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Acute cardiorenal syndrome | Acute worsening of cardiac function cause acute kidney injury (AKI) | Acute ischemic heart disease, cardiogenic shock, acute decompensated heart failure |
| Type 2 | Chronic cardiorenal syndrome | Chronic cardiac dysfunction leading to progressive renal impairment | Chronic heart failure |
| Type 3 | Acute renocardiac syndrome | Acute kidney injury leads to acute cardiac dysfunction | AKI, uremia, kiperkaliemia, volume overload leading to pulmonary edema |
| Type 4 | Chronic renocardiac syndrome | Chronic kidney disease contributes to decreased cardiac function | CKD-associated cardiomyopathy |
| Type 5 | Secondary cardiorenal syndrome | Acute/chronic systemic condition leading to cardiac and renal impairment | Diabetes mellitus, sepsis, amyloidosis, cirrhosis |
| Pathophysiological Mechanism | Biomarkers | |
|---|---|---|
| Hemodynamic pathways | Cardiac output | BNP, copeptin, cardiac troponin-I |
| Arterial pressure | CRP, TNF alpha, ox-LDL, | |
| Extracellular fluid volume | NT-proBNP, cardiac troponin-I, copeptin | |
| Elevated renal venous pressure | Creatinine | |
| Non hemodynamic pathways | Fibrosis | Gal-3, NGAL, sST-2, cardiotrophin-1 |
| Oxidative stress | MMP, Ox-HDL, MR-proADM, 8-epi-isoprostanes | |
| Obesity | Aldosteron | |
| Endothelial dysfunction | sFLT-1, VEGF, PDGF soluble thrombomodulin, angiopoietin-2, anti-endothelial cell antibodies | |
| Chronic Inflammation | C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, NGAL, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-alpha | |
| Epigenetics | microRNAs, miR-21 |
| Cardiorenal Type | Biomarkers |
|---|---|
| 1 | BNP, NT-proBNP, creatinine, cystatin C, KIM-1, NGAL, MR-proADM, IL-6, IL-18, |
| 2 | BNP, NT-proBNP, creatinine, cystatin C, microalbuminuria, aldosterone, miRNA-21,NGAL, KIM-1 |
| 3 | BNP, NT-proBNP, creatinine, cystanin C, NGAL, KIM-1, netrin-1, IL-6, IL-18, |
| 4 | BNP, NT-proBNP, creatinine, cystatin C, troponins, CRP, homocysteine, uric acid, microalbumineria, aldosterone |
| 5 | BNP, creatinine, procalcitonin, CRP, IL-6, TGF-beta, Gal-3, sST2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buliga-Finis, O.N.; Ouatu, A.; Badescu, M.C.; Dima, N.; Tanase, D.M.; Richter, P.; Rezus, C. Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040773
Buliga-Finis ON, Ouatu A, Badescu MC, Dima N, Tanase DM, Richter P, Rezus C. Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040773
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuliga-Finis, Oana Nicoleta, Anca Ouatu, Minerva Codruta Badescu, Nicoleta Dima, Daniela Maria Tanase, Patricia Richter, and Ciprian Rezus. 2022. "Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040773
APA StyleBuliga-Finis, O. N., Ouatu, A., Badescu, M. C., Dima, N., Tanase, D. M., Richter, P., & Rezus, C. (2022). Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk. Diagnostics, 12(4), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040773











