Multiple Faces of Cervical Lesions in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Justification of the Case Report
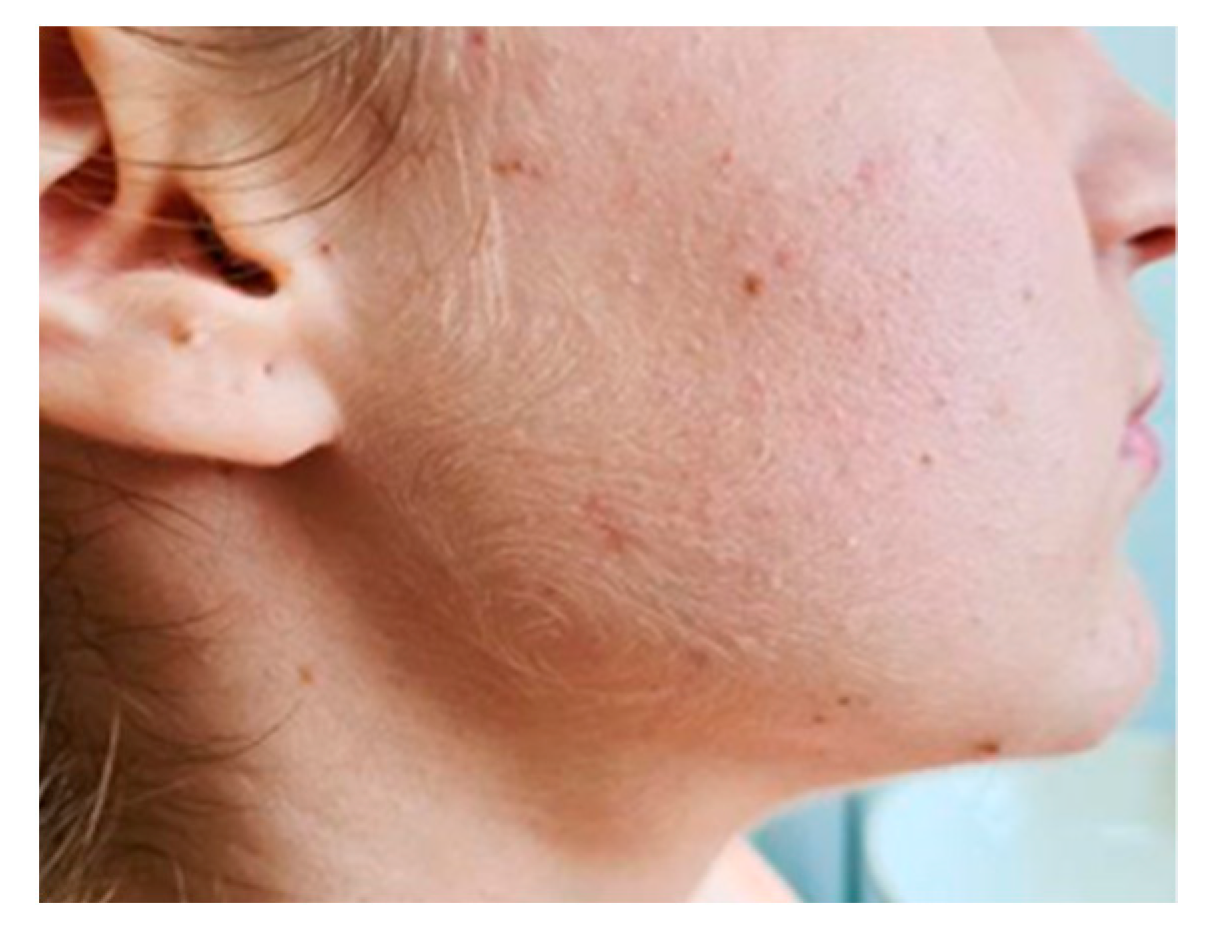
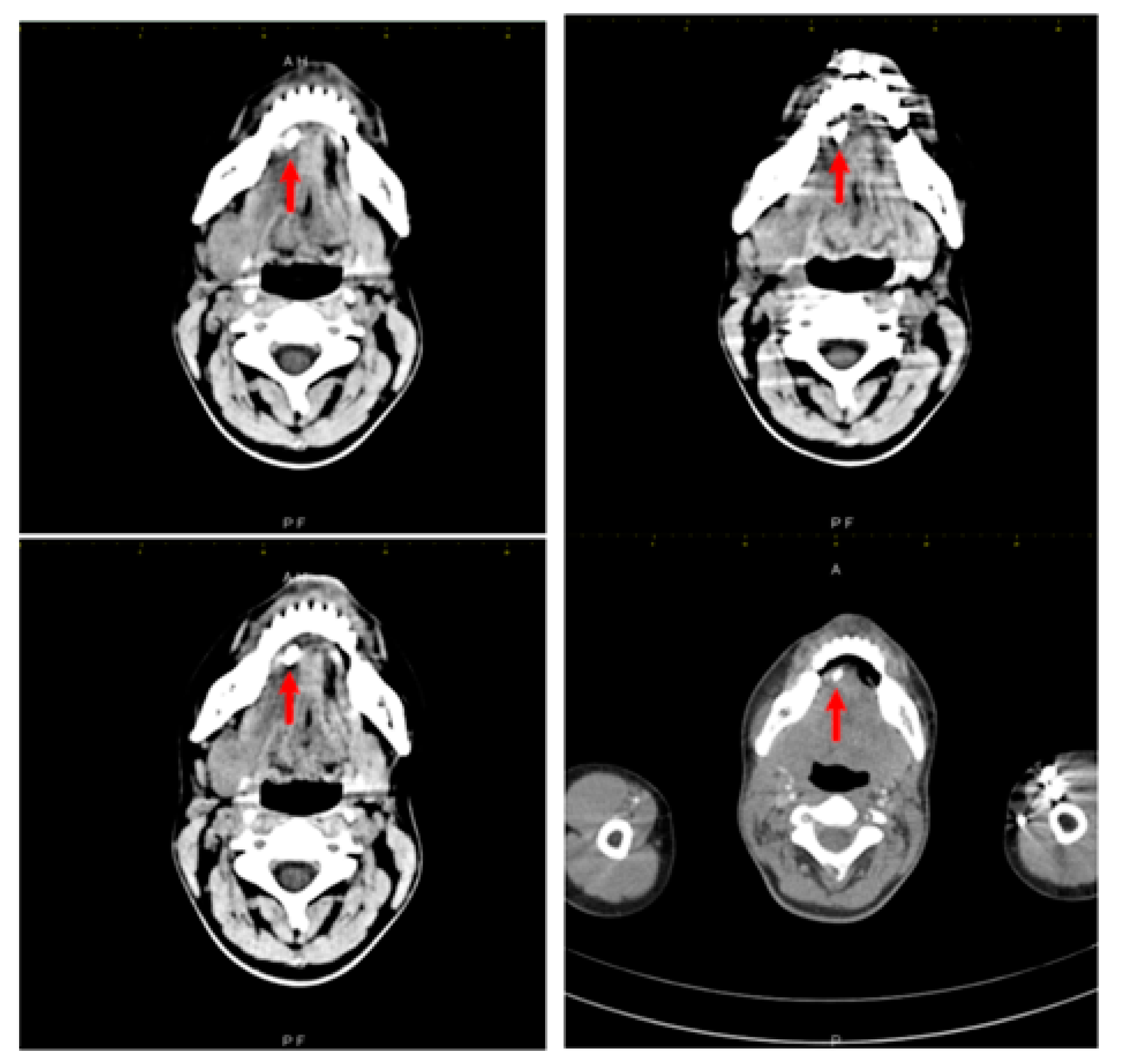
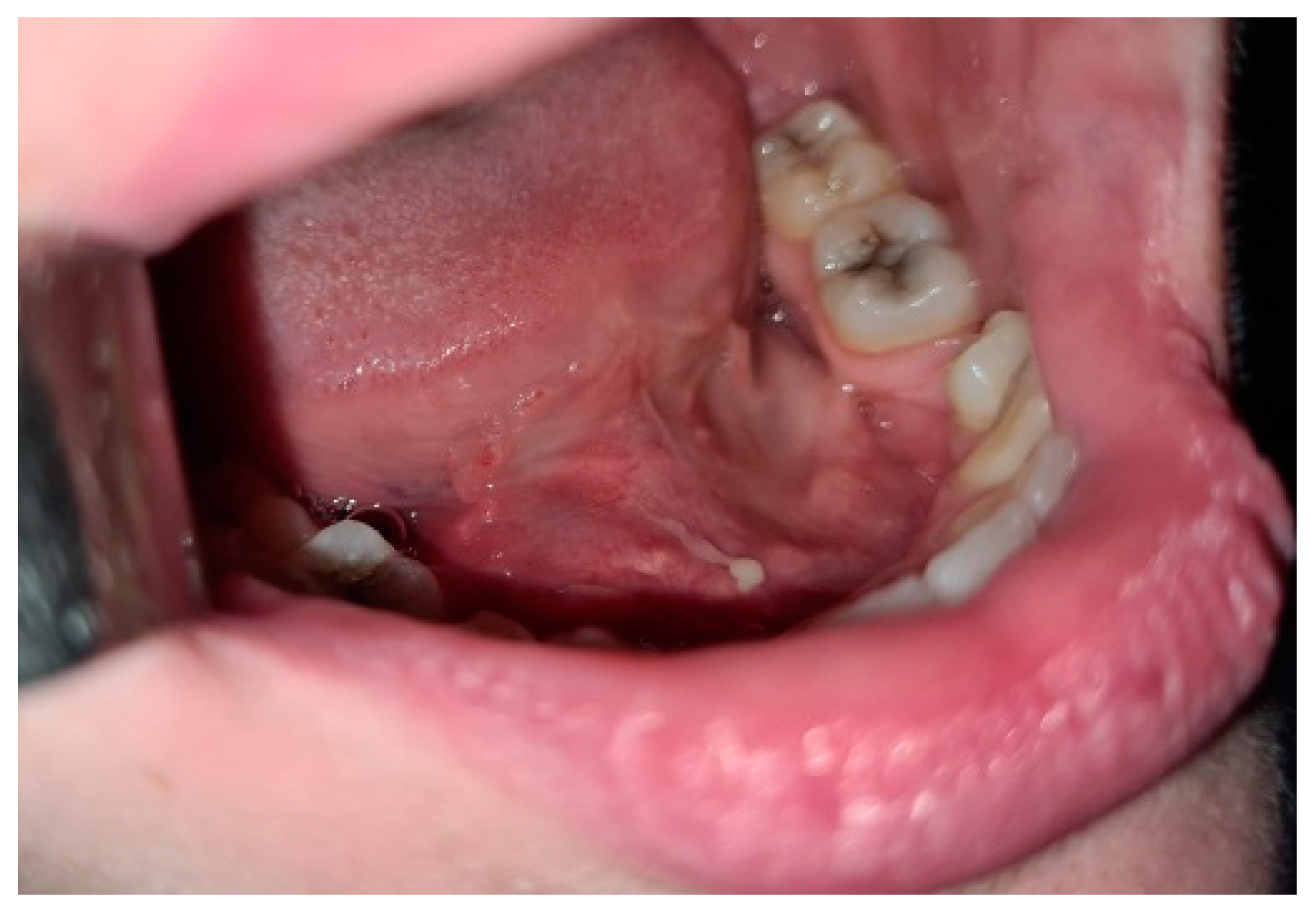
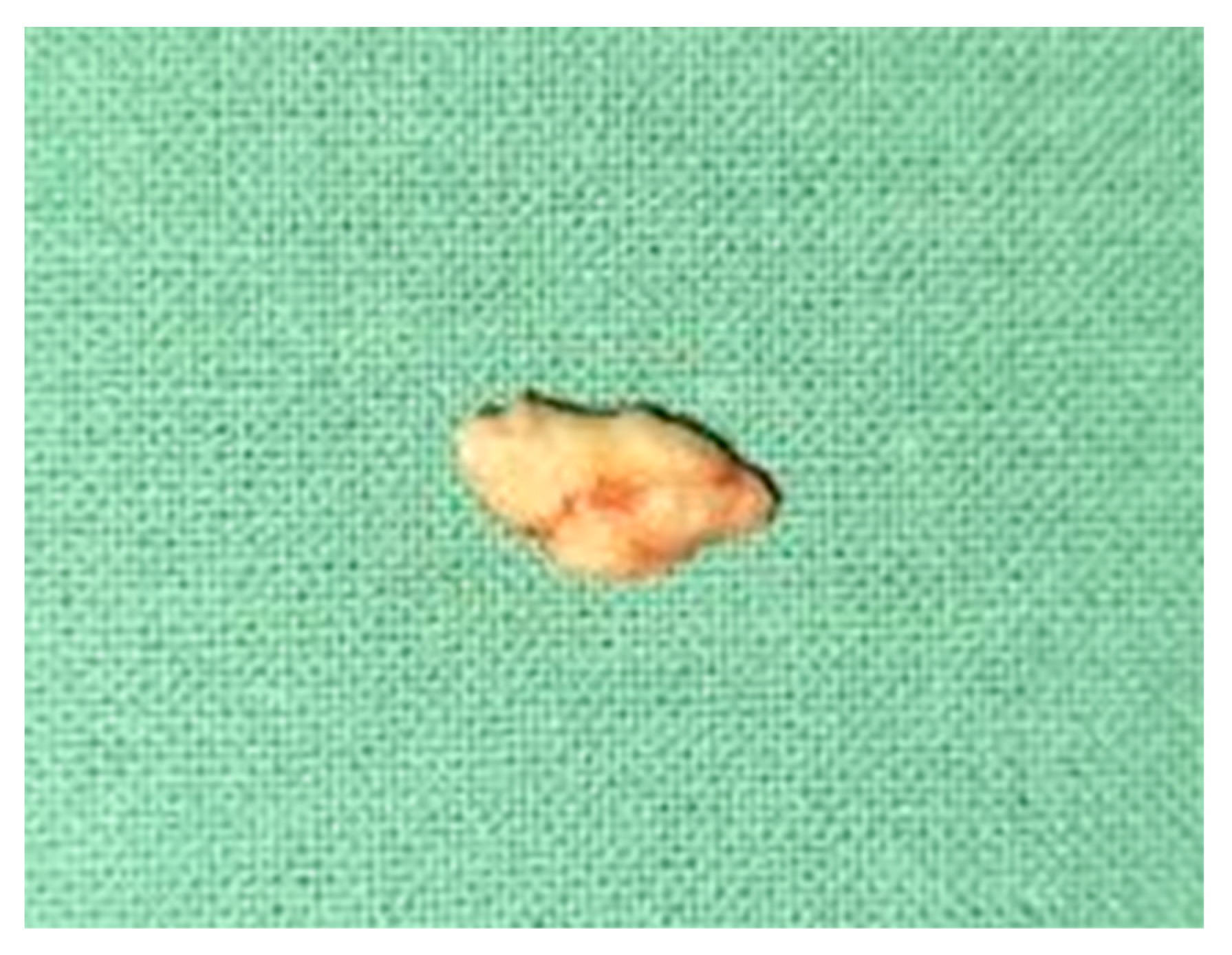
2. Case Report
3. Literature Review Methodology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bedros, A. Lymphadenopaty in children. Adv. Pediatr. 1981, 28, 341–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popescu, V. Evaluarea limfadenopatiilor la copil. Rev. Rom. Pediatr. 2006, 3, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, M. Evaluarea si managementul limfadenopatieila copil: Cand suspectam o malignitate? Rom. J. Pediatr. 2018, 67, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, L.; Fliss, D. Parotid and submandibular calculi in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1995, 31, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellies, M.; Laskawi, R. Diseases of the salivary glands in infants and adolescents. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escudier, M.; McGurk, M. Symptomatic sialoadenitis and sialolithiasis in the English population, an estimate of the cost of hospital treatment. Br. Dent. J. 1999, 186, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustman, J.; Regev, E.; Melamed, Y. Sialolithiasis: A survey on 245 patients and a review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1990, 19, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurk, M.; Escudier, M.; Brown, J. Modern management of salivary calculi. Br. J. Surg. 2005, 92, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.-J.; Lee, E.; Kim, H.; Oh, H.; Jeong, H. Pediatric sialolithiasis is not related to oral or oropharyngeal infection: A population-based case control study using the Korean National Health Insurance Database. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhynolaringol. 2017, 97, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doku, H.; Berkman, M. Submaxillary Salivary Calculus in Children. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1967, 114, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.; Jeong, H.; Ko, M. Pediatric sialolithiasis: What is different from adult sialolithiasis? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 71, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, R.; Lombardi, T. Submandibular sialolithiasis with concurrent sialoadenitis in a child. J. Clin. Pediatri. Dent. 1995, 20, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Lim, H. Association between cholelithiasis and sialolithiasis: Two longitudinal follow-up studies. Medicine 2019, 98, e16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodner, L.; Azaz, B. Submandibular sialolithiasis in children. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1982, 40, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskawi, R.; Schaffranietz, F.; Aglebe, C.; Ellies, M. Inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands in infants and adolescents. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldin, H.; Seldin, S.; Rakower, W. Conservative surgery for the removal of salivary calculi. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1953, 6, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomomichi, O.; Jouji, N.; Yoshihiko, M.; Shigeaki, Y.; Takayuki, N.; Shiori, U.; Toshiro, T. A Case of Sialolithiasis in a Child. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2007, 31, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.-F.; Meier, J.-D.; Ward, P.-D. Salivary gland disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 89, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gellrich, D.; Bichler, M.; Reichel, C.; Schrötzlmair, F.; Zengel, P. Salivary Gland Disorders in Children and Adolescents: A 15-year Experience. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 24, e31–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yiu, A.; Kalejaiye, A.; Amdur, R.; Hesham, T.-H.; Bandyopadhyay, B. Association of serum electrolytes and smoking with salivary gland stone formation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraaij, S.; Karagozoglu, K.; Forouzanfar, T.; Veerman, E.; Brand, H. Salivary stones: Symptoms, aetiology, biochemical composition and treatment. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 217, E23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraaij, S.; Hakki Karagozoglu, K.; Kenter, Y.; Pijpe, J.; Gilijamse, M.; Brand, H. Systemic diseases and the risk of developing salivary stones: A case control study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, A.; Choi, M.; Wagner, G. Multiple sialoliths and a sialolith of unusual size in the submandibular duct. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 1999, 87, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachisia, S.; Mandal, G.; Sahu, S.; Ghosh, S. Submandibular sialolithiasis: A series of three case reports with review of literature. Clin. Pract. 2019, 9, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ţarcă, E.; Cojocaru, E.; Luca, A.-C.; Trandafir, L.-M.; Roşu, S.-T.; Munteanu, V.; Țarcă, V.; Budacu, C.-C.; Costea, C.-F. Unusual Case of Masseter Muscle Hypertrophy in Adolescence-Case Report and Literature Overview. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ţarcă, E.; Cojocaru, E.; Roşu, S.-T.; Butnariu, L.-I.; Plămădeală, P.; Moisă, Ş.-M. Differential diagnosis difficulties related to infantile hemangioma—Case report and literature review. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butnariu, A.; Sas, V.; Gheban, D. Boala Kikuchi-Fujimoto—Probleme diagnostice. Rev. Rom. Pediatr. 2021, 3, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman, R.; Jenson, H.; Behrman, R.; Staton, B. Lymphadenopathy. In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics; Kliegman, R., Jenson, H., Behrman, R., Staton, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2093–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Nahlieli, O.; Eliay, E.; Hasson, O.; Zagury, A.; Baruchin, A. Pediatric sialolithiasis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2000, 90, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karengera, D.; Yousefpour, A.; Sadeghi, H.; Reychler, H. Sialolithiasis in children as a diagnostic dilemma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2000, 257, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, F.; Dulguerov, P.; Becker, M.; Barki, G.; Disant, F.; Lehmann, W. Specificity of parotid sialendoscopy. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zenk, J.; Hosemann, W.; Iro, H. Diameters of the main excretory ducts of the adult human submandibular and parotid gland: A histologic study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 1998, 5, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Remine, W.; Devine, K. Salivary gland calculi. Pain, swelling associated with eating. JAMA 1962, 181, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, G.; Harper, F. Chronic inflammation of the salivary glands with or without calculi. Int. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. Radiogr. 1931, 17, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresh, A.; Kutler, D.; Kacher, A. Sialoendoscopy in the diagnosis and management of obstructive sialadenitis. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, P.; Zenk, J.; Koch, M.; Schapher, M.; Rudes, M.; Iro, H. Nearly 3000 salivary stones: Some clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iro, H.; Zenk, J.; Koch, M. Modern concepts for the diagnosis and therapy of sialolithiasis. HNO 2010, 58, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.; Robson, W. Spontaneous passage of a submandibular salivary calculus in a child. J. Laringol. Otol. 1988, 102, 1052–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccio, P.; Canzi, P.; Gaffuri, M.; Occhini, A.; Benazzo, M.; Ottaviani, F.; Pignataro, L. Modern management of paediatric obstructive salivary disorders: Long-term clinical experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawas, B.; Beutner, D.; Geisthoff, U. The new S2k AWMF guideline for the treatment of obstructive sialadenitis in commented short form. Laryngorhinootologie 2014, 93, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Bang, W.; Park, B. Lack of evidence that nephrolithiasis increases the risk of sialolithiasis: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Type | Subtype | Diagnostic Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious causes | Viral causes: Citomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, HIV, mumps, rubella Bacterial causes: group A Streptococus pyogenes, Staphilococcus aureus, Tularemia, Brucellosis, Bartonela henslae Fungi: Cryptococcus, Aspergilus, Hystoplasmosis, Coccidiomycosis Mycobacteria: M. tuberculosis, M. avium Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Malaria |
|
| Malignancies | Leukemias, lymphomas Solid tumors: neuroblastoma, rhabdomiosarcoma, carcinoma |
|
| Autoimmune diseases | Juvenile idiopathic arthritis Systemic lupus erithematosus |
|
| Histiocitosis | Malignant histiocytosis Langerhans histiocytosis, hemophagocitic syndromes |
|
| Stocking diseases | Niemann Pick disease Gaucher disease |
|
| Others | Sarcoidosis Kikuchi disease Castelman disease |
|
| Vaccinations Immunodeficiencies | Variole, tuberculosis Chronic granulomatous disease |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moisa, S.M.; Andrei, N.; Balcan, R.-D.; Miron, I.; Țarcă, E.; Butnariu, L.; Cojocaru, E.; Leon-Constantin, M.M.; Budacu, C.C.; Trandafir, L.M. Multiple Faces of Cervical Lesions in Children. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040792
Moisa SM, Andrei N, Balcan R-D, Miron I, Țarcă E, Butnariu L, Cojocaru E, Leon-Constantin MM, Budacu CC, Trandafir LM. Multiple Faces of Cervical Lesions in Children. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040792
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoisa, Stefana Maria, Nicolau Andrei, Raluca-Daniela Balcan, Ingrith Miron, Elena Țarcă, Lăcrămioara Butnariu, Elena Cojocaru, Maria Magdalena Leon-Constantin, Cristian Constantin Budacu, and Laura Mihaela Trandafir. 2022. "Multiple Faces of Cervical Lesions in Children" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040792
APA StyleMoisa, S. M., Andrei, N., Balcan, R.-D., Miron, I., Țarcă, E., Butnariu, L., Cojocaru, E., Leon-Constantin, M. M., Budacu, C. C., & Trandafir, L. M. (2022). Multiple Faces of Cervical Lesions in Children. Diagnostics, 12(4), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040792







