Changes in Cystoscopic Findings after Intravesical Hyaluronic Acid Instillation Therapy in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Medical Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
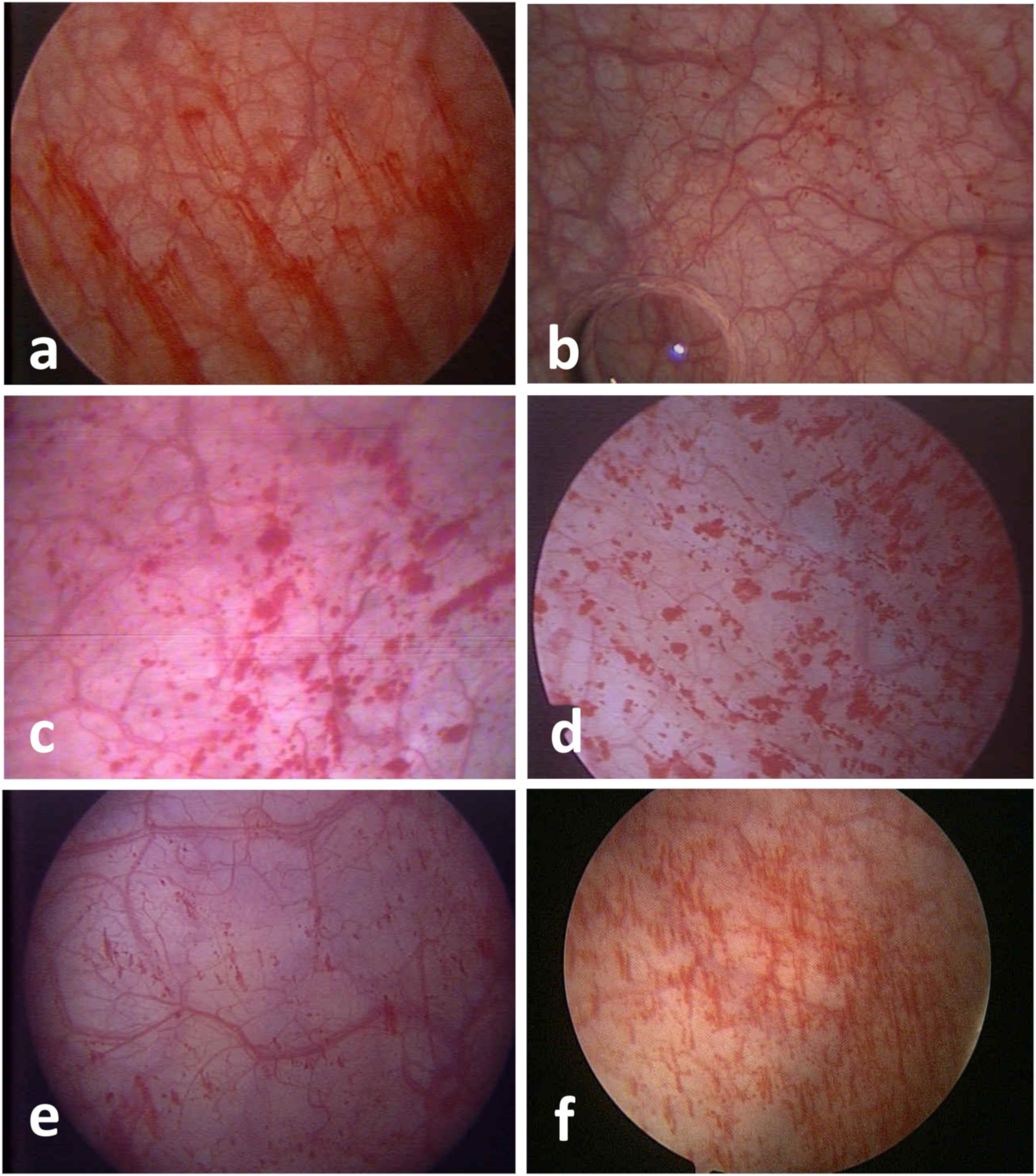
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; Van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology 2003, 61, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Erickson, D.; Moldwin, R.; Faraday, M.M. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messing, E.M.; Stamey, T.A. Interstitial cystitis: Early diagnosis, pathology, and treatment. Urology 1978, 12, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Nomiya, A.; Niimi, A.; Igawa, Y.; Ito, T.; Tomoe, H.; Takei, M.; Ueda, T.; Homma, Y. A survey on clinical practice of interstitial cystitis in Japan. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chuang, Y.C. Advances in intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome (BPS)/interstitial cystitis (IC). Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2018, 10, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.; Lin, A.; Nordling, J.; Nyberg, L.; van Ophoven, A.; Ueda, T.; Wein, A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Committee of the International Consultation on Incontinence. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2010, 29, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Srivastava, A.; Lee, R.; Tewari, A.K.; Te, A.E. Role of inflammation in bladder function and interstitial cystitis. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2011, 3, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.H.; Kuo, H.C. Higher levels of cell apoptosis and abnormal E-cadherin expression in the urothelium are associated with inflammation in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2011, 108, E136–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.J.; Tsai, C.P.; Lin, Y.H.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, G.D.; Shen, P.S. Hyaluronic acid improves pain symptoms more than bladder storage symptoms in women with interstitial cystitis. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 58, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallestrup, E.B.; Jorgensen, S.S.; Nordling, J.; Hald, T. Treatment of interstitial cystitis with Cystistat: A hyaluronic acid product. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2005, 39, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, C.R.; Engelhardt, P.F.; Daha, K.L.; Morakis, N.; Pflüger, H. Hyaluronan treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2007, 19, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porru, D.; Leva, F.; Parmigiani, A.; Barletta, D.; Choussos, D.; Gardella, B.; Dacco, M.D.; Nappi, R.E.; Allegri, M.; Tinelli, C.; et al. Impact of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate on bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2012, 23, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.F.; Brady, C.M.; Creagh, T. Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and evidence-based treatment options. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2014, 175, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Hoe, K.O.; Shin, J.H.; Choo, M.S. Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and the efficacy of antimuscarinic treatment. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2017, 58, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, I.F.; Soylu, H.; Ates, E.; Acar, N.; Ustunel, I.; Danisman, A. Impact of intravesical hyaluronic acid treatment on bladder inflammation in interstitial cystitis rat model. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.S.; Yao, Y.S.; Lin, M.E.; Rong, L.; Deng, B.H.; Huang, J.; Hao, W.P. Interleukin-6 levels in female rats with protaminesulfate-induced chronic cystitis treated with hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, P.; Srivastava, A.; Watson, L.; Quinlan, L.R.; Pandit, A. Hyaluronic acid decreases IL-6 and IL-8 secretion and permeability in an inflammatory model of interstitial cystitis. Acta Biomater. 2015, 19, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daha, L.K.; Riedl, C.R.; Lazar, D.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Pflüger, H. Do cystometric findings predict the results of intravesical hyaluronic acid in women with interstitial cystitis? Eur. Urol. 2005, 47, 393–397, discussion 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.R.; Jhang, J.F.; Ho, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Cystoscopic hydrodistention characteristics provide clinical and long-term prognostic features of interstitial cystitis after treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordling, J.; Anjum, F.H.; Bade, J.J.; Bouchelouche, K.; Bouchelouche, P.; Cervigni, M.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hald, T.; Hanus, T.; et al. Primary evaluation of patients suspected of having interstitial cystitis (IC). Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, E.; Lazzeri, M.; Pistolesi, D.; Del Zingaro, M.; Frumenzio, E.; Boni, A.; Pietropaolo, A.; Fragala, E.; Porena, M. 265 Morphological changes of bladder mucosa in patients who underwent instillation with combined sodium hyaluronic acid-chondroitin sulphate (Ialuril(R)). Urol. Int. 2013, 91, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, P.F.; Morakis, N.; Daha, L.K.; Esterbauer, B.; Riedl, C.R. Long-term results of intravesical hyaluronan therapy in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2011, 22, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervigni, M.; Natale, F.; Nasta, L.; Mako, A. Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate for bladder pain syn-drome/interstitial cystitis: Long-term treatment results. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2012, 23, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Emerson, L.; Nickel, J.C.; Lundie, M. Intravesical hyaluronic acid in the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.C.; Yueh-Hsia Chiu, S.; Feng, M.; Liang, C.C. The effect of intravesical hyaluronic acid therapy on urodynamic and clinical outcomes among women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 59, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shear, S.; Mayer, R. Development of glomerulations in younger women with interstitial cystitis. Urology 2006, 68, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Lee, W.C.; Chuang, Y.C. New Frontiers or the Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome—Focused on Stem Cells, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Low-Energy Shock Wave. Int. Neurourol. J. 2020, 24, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.J.; Tsai, C.P.; Ying, T.H.; Chen, G.D.; Su, H.L.; Tseng, C.J. Improved symptoms and signs of refractory interstitial cystitis in women after intravesical Nanofat plus platelet-rich plasma grafting: A pilot study. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2022, 85, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Han, J.Y.; Ryu, C.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, S.U.; Cho, Y.M.; Shin, D.M.; Choo, M.S. Histopathological characteristics of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome without Hunner lesion. Histopathology 2017, 71, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavazzo, C.; Athanasiou, S.; Pitsouni, E.; Falagas, M.E. Hyaluronic acid: An effective alternative treatment of interstitial cystitis, recurrent urinary tract infections, and hemorrhagic cystitis? Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 1534–1540, discussion 1540–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| General Data | Value (Mean ± SD) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 46.3 ± 12.3 | 18–68 |
| Follow-up interval (months) | 26.9 ± 19.9 | 4.8–72.9 |
| Total HA dosage (vial) | 24.5 ± 16.2 | 4–61 |
| Average HA dosage per month (vial/months) | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.6–2 |
| Initial Cystoscopy | Follow-Up Cystoscopy | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max capacity (mL, Mean ± SD) | 620.6 ± 143.6 | 650 ± 130 | 0.135 * |
| Glomerulation grade (n) | 0.196 # | ||
| Grade 0 | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.9%) | |
| Grade 1 | 11 (31.4%) | 14 (40.0%) | |
| Grade 2 | 10 (28.6%) | 7 (20.0%) | |
| Grade 3 | 14 (40.0%) | 13 (37.1%) | |
| Hunner’s lesion | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (2.9%) | 1.000 ** |
| Terminal hematuria | 14 (40.0%) | 13 (37.1%) | 1.000 ** |
| Trabeculum | 23 (65.7%) | 18 (51.4%) | 0.180 ** |
| Pain | 25 (71.4%) | 22 (62.9%) | |
| LUTS | 29 (82.9%) | 17 (48.6%) | |
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 20) | Group 3 (n = 6) | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved | Similar | Worsened | |||||
| Mean age | 45.3 | ±13.6 | 44.2 | ±12.2 | 55 | ±7.5 | 0.121 |
| Mean initial capacity (mL) | 555.6 | ±164.8 | 642.1 | ±131.5 | 650 | ±141.4 | 0.357 |
| Mean follow-up capacity (mL) | 637.5 | ±176.8 | 652.6 | ±126.4 | 660.0 | ±54.8 | 0.978 |
| Mean follow-up time (months) | 44.8 | ±22.7 | 19.3 | ±12.4 | 25.1 | ±21.9 | 0.031 * |
| Mean HA dose (vial) | 35.9 | ±18.8 | 19.9 | ±11.5 | 23.0 | ±20.1 | 0.095 |
| Mean average HA dose(vial/m) | 0.9 | ±0.3 | 1.1 | ±0.3 | 1.0 | ±0.3 | 0.236 |
| Before HA pain | 9 | (100%) | 14 | (70%) | 2 | (33.3%) | |
| LUTS | 7 | (77.78%) | 17 | (85%) | 5 | (83.3%) | |
| HA for 1 year pain | 1 | (11.1%) | 6 | (31.6%) | 1 | (16.7%) | |
| LUTS | 2 | (22.2%) | 5 | (26.3%) | 1 | (16.7%) | |
| Before follow-up cystoscope pain | 6 | (66.7%) | 12 | (63.2%) | 4 | (66.7) | |
| LUTS | 5 | (55.6%) | 10 | (50%) | 2 | (33.3%) | |
| Group 2 (n = 20) Similar | Group 3 (n = 6) Worsened | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age | 44.2 | ±12.2 | 55 | ±7.5 | 0.037 * |
| Mean initial bladder capacity (mL) | 642.1 | ±131.5 | 650 | ±141.4 | 0.831 |
| Mean follow-up time (months) | 19.3 | ±12.4 | 25.1 | ±21.9 | 0.689 |
| Mean HA dose (vial) | 19.9 | ±11.5 | 23.0 | ±20.1 | 0.822 |
| Mean average HA dose (vial/m) | 1.1 | ±0.3 | 1.0 | ±0.3 | 0.487 |
| Mean follow-up bladder capacity(mL) | 652.6 | ±126.4 | 660.0 | ±54.8 | 0.836 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-J.; Liu, C.-K.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Tsai, C.-P. Changes in Cystoscopic Findings after Intravesical Hyaluronic Acid Instillation Therapy in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12082009
Lin C-J, Liu C-K, Hsieh H-Y, Chen M-J, Tsai C-P. Changes in Cystoscopic Findings after Intravesical Hyaluronic Acid Instillation Therapy in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(8):2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12082009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chia-Ju, Chih-Ku Liu, Hsiao-Yun Hsieh, Ming-Jer Chen, and Ching-Pei Tsai. 2022. "Changes in Cystoscopic Findings after Intravesical Hyaluronic Acid Instillation Therapy in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis" Diagnostics 12, no. 8: 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12082009
APA StyleLin, C. -J., Liu, C. -K., Hsieh, H. -Y., Chen, M. -J., & Tsai, C. -P. (2022). Changes in Cystoscopic Findings after Intravesical Hyaluronic Acid Instillation Therapy in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis. Diagnostics, 12(8), 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12082009






