Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Its Principle and Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
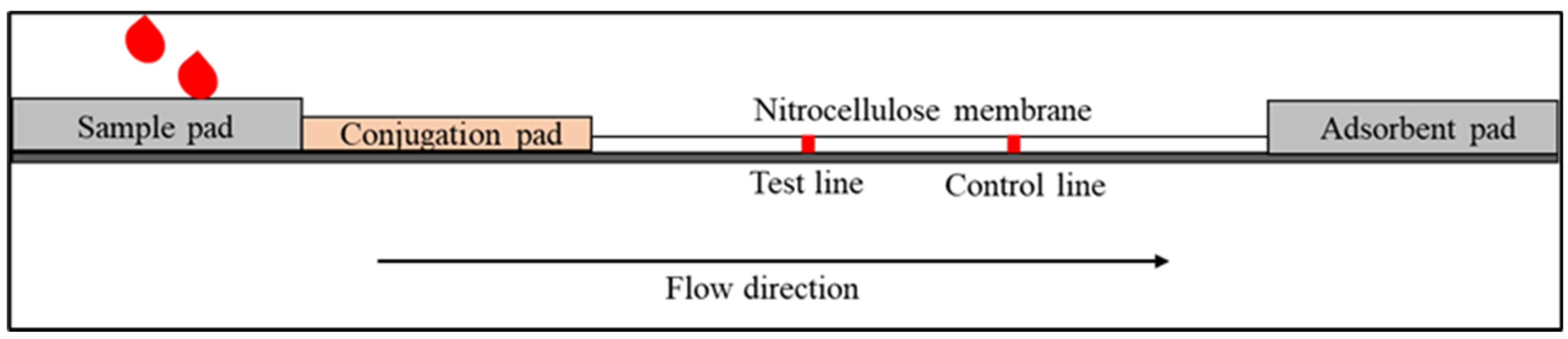
2. Lateral Flow Immunoassay
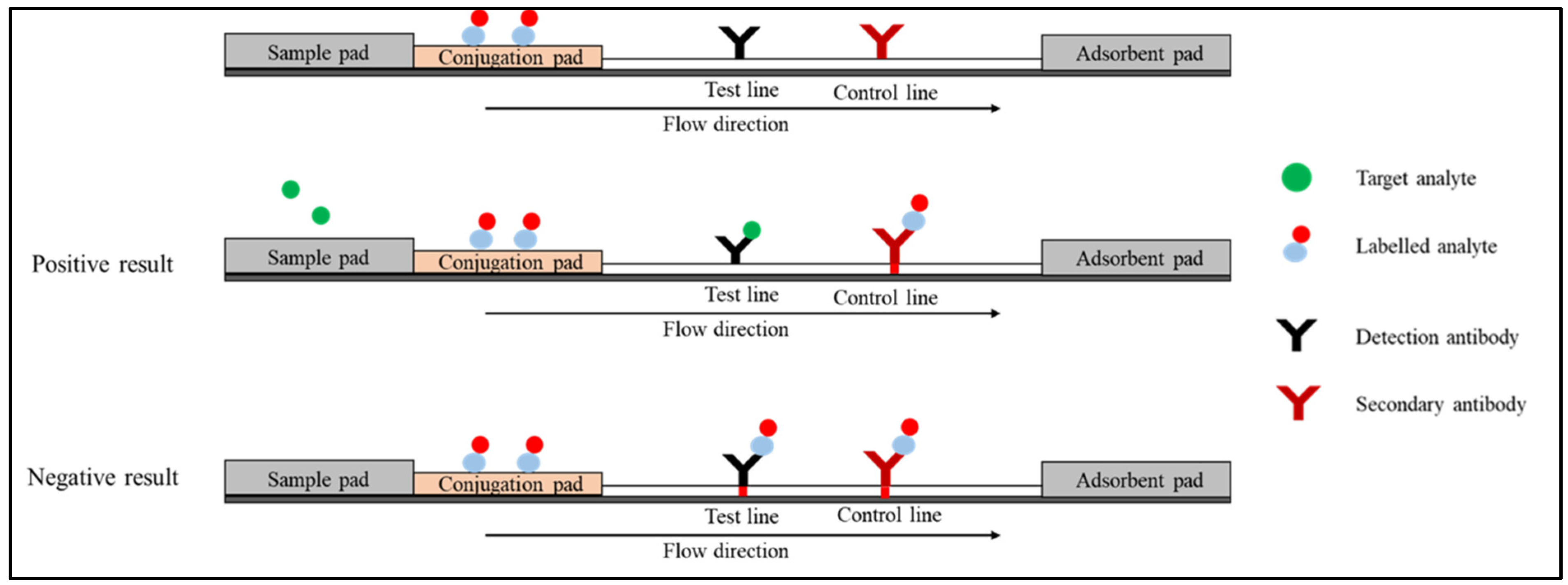
2.1. Sandwich Immunoassay
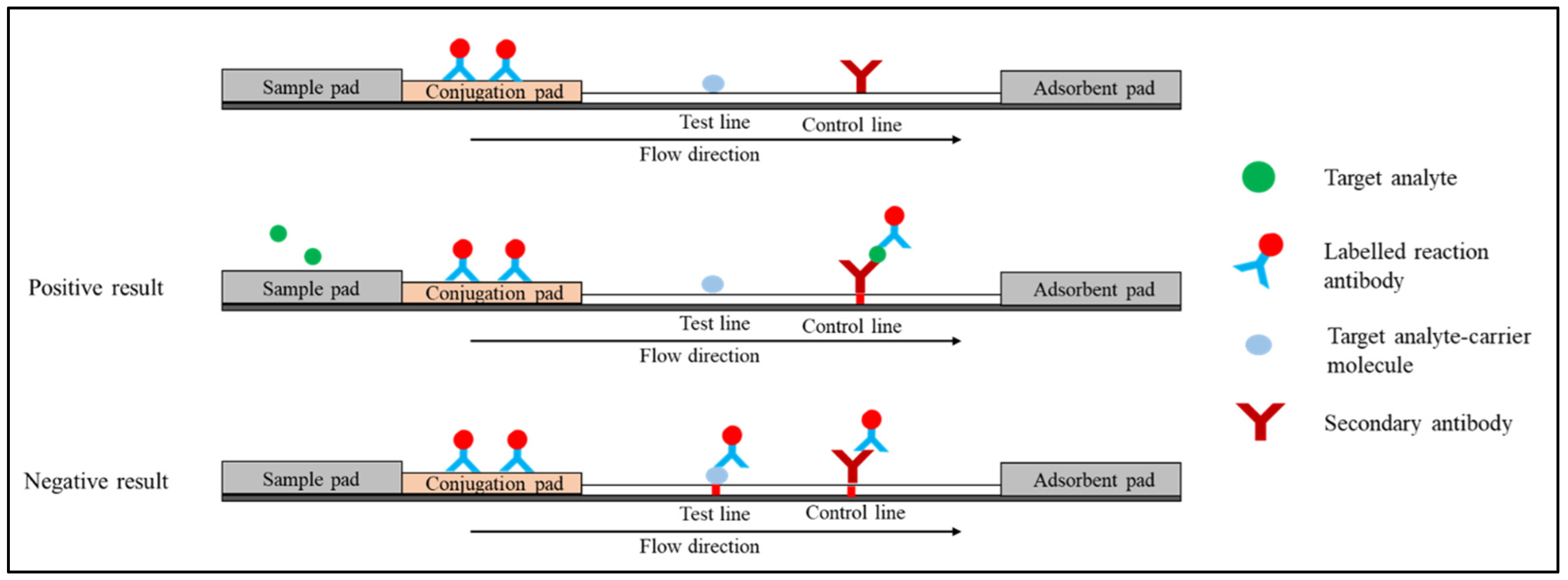
2.2. Competitive Immunoassay (or Inhibition Immunoassay)
3. Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay
3.1. Types of Quantum Dots
3.1.1. Core-Type Quantum Dots
3.1.2. Core–Shell Quantum Dots
3.1.3. Alloyed Quantum Dots
3.2. Strategies for Conjugating Quantum Dot with Antibodies
3.3. Performance of Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global Trends in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, X. A Generalized Infectious Model Induced by the Contacting Distance (CTD). Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2020, 54, 103113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Yin, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, X. Prediction Model for Infectious Disease Health Literacy Based on Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique Algorithm. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 8498159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; de Lima Kaminski Kaminski, V.; Chies, J.A.B. Emerging Infectious Disease Prevention: Where Should We Invest Our Resources and Efforts? J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Learoyd, T.P.; Gaut, R.M. Cholera: Under Diagnosis and Differentiation from Other Diarrhoeal Diseases. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, S46–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigl, B.H.; Neogi, T.; McGuire, H. Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Low-Resource Settings and Their Impact on Care in the Age of the Noncommunicable and Chronic Disease Epidemic. SLAS Technol. 2014, 19, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liang, Z.-Y.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Tao, Z.-Z. A Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid, Quantitative, and Sensitive Detection of Specific IgE for Mite Allergens in Sera from Patients with Allergic Rhinitis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppa, P.B. Point-of-Care Testing at the Interface of Emerging Technologies and New Clinical Applications. J. Lab. Med. 2020, 44, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assays for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Membrane-Based Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Strip with Nanoparticles as Reporters for Detection: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehringer, H.R.; O’Farrell, B.J. Lateral Flow Assays in Infectious Disease Diagnosis. Clin. Chem. 2021, 68, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Mihailescu, C.-M.; Matei, I.; Stan, D.; Moldovan, C.A.; Ion, M.; Baciu, I. A Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of Human Heart Fatty Acid Binding Protein (HFABP) in Human Serum. Talanta 2018, 178, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirica, A.-C.; Stan, D.; Chelcea, I.-C.; Mihailescu, C.M.; Ofiteru, A.; Bocancia-Mateescu, L.-A. Latest Trends in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) Detection Labels and Conjugation Process. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 922772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cao, X.E.; Finkelstein, J.L.; Cárdenas, W.B.; Erickson, D.; Mehta, S. A Two-Colour Multiplexed Lateral Flow Immunoassay System to Differentially Detect Human Malaria Species on a Single Test Line. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, E.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Europium Fluorescent Nanoparticles-Based Multiplex Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Simultaneous Detection of Three Antibiotic Families Residue. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Tu, Z.; Gu, B.; Wang, S. Ultrasensitive and Multiplex Detection of Four Pathogenic Bacteria on a Bi-Channel Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strip with Three-Dimensional Membrane-like SERS Nanostickers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takalkar, S.; Baryeh, K.; Liu, G. Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of DNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.-W.; Wang, Y.-B.; Fang, L.-L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.-Y.; Ge, S.-X.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.-Z.; Deng, X.-M.; et al. Rapid Fluorescent Lateral-Flow Immunoassay for Hepatitis B Virus Genotyping. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5173–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Oh, C.; An, J.; Baek, S.; Bock, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.-S.; Song, H.; Kim, J.-W.; Jo, A.; et al. Multi-Quantum Dots-Embedded Silica-Encapsulated Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Assay for Highly Sensitive Exosome Detection. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Taranova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Dzantiev, B.B. Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Detection of Chloramphenicol in Milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4997–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xiong, Q.-R.; Xu, H.-Y.; Xiong, Y.-H.; Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Lai, W.-H. Advantages of Fluorescent Microspheres Compared with Colloidal Gold as a Label in Immunochromatographic Lateral Flow Assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Wen, K.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Fluorescent Microspheres and Colloidal Gold as Labels in Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assays for the Detection of T-2 Toxin. Molecules 2015, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral Flow Assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, S.; Nara, S. Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticle Based Lateral Flow Assays for Diagnosis of Enterobacteriaceae Members in Food and Water. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Wang, W.; Du, T.-E. Rapid Quantitative Immunochromatographic Strip for Multiple Proteins Test. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, R.E.; Sammons, D.L.; Smith, J.P.; MacKenzie, B.A.; Striley, C.A.F.; Snawder, J.E.; Robertson, S.A.; Quinn, C.P. Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Lateral-Flow Immunochromatographic Device To Measure Anti-Anthrax Protective Antigen Immunoglobulin G in Serum and Whole Blood. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, Y.; Ghrera, A.S. Recent Advances in Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of Bacterial Infection. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3767–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemulapati, S.; Rey, E.; O’Dell, D.; Mehta, S.; Erickson, D. A Quantitative Point-of-Need Assay for the Assessment of Vitamin D3 Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral Flow Assays: Principles, Designs and Labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, G.L.; Pereira, D.Y.; Han, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Wu, C.M.; Wu, B.M.; Kamei, D.T. Improved Lateral-Flow Immunoassays for Chlamydia and Immunoglobulin M by Sequential Rehydration of Two-Phase System Components within a Paper-Based Diagnostic. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4055–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X. Rapid Detection of Hepatitis B Virus in Blood Samples Using a Combination of Polymerase Spiral Reaction With Nanoparticles Lateral-Flow Biosensor. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 578892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Yoo, Y.K.; Han, S.I.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.; Hwang, K.S.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, S.; Lee, J.H. Battery Operated Preconcentration-Assisted Lateral Flow Assay. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwyn, S.; Mitchell, A.; Dean, D.; Mkocha, H.; Handali, S.; Martin, D.L. Lateral Flow-Based Antibody Testing for Chlamydia Trachomatis. J. Immunol. Methods 2016, 435, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.-N.; Daud, M. Designs, Formats and Applications of Lateral Flow Assay: A Literature Review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussien, M.N.; Dang, A.K. Sensitive and Rapid Lateral-Flow Assay for Early Detection of Subclinical Mammary Infection in Dairy Cows. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danthanarayana, A.N.; Brgoch, J.; Willson, R.C. Photoluminescent Molecules and Materials as Diagnostic Reporters in Lateral Flow Assays. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Jaiswal, A. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Point-of-Care Diagnostic Tool for Infectious Agents and Diseases. Analyst 2018, 143, 1970–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.; Hwang, H.M.; Shin, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, H.; Yang, J.; Bak, S.; Lee, H. Chemically Modulated Graphene Quantum Dot for Tuning the Photoluminescence as Novel Sensory Probe. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.L.; Goreham, R.V.; Nann, T. Graphene Quantum Dots for Theranostics and Bioimaging. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2337–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tian, C.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, X. A Sensitive Lateral Flow Test Strip Based on Silica Nanoparticle/CdTe Quantum Dot Composite Reporter Probes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, R.J.; Beard, M.C.; Johnson, J.C.; Yu, P.; Micic, O.I.; Nozik, A.J.; Shabaev, A.; Efros, A.L. Highly Efficient Multiple Exciton Generation in Colloidal PbSe and PbS Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, D.; Gaddam, R.R.; Trinchi, A.; Cole, I. Core–Shell Quantum Dots: Properties and Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 636, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, K.; Lu, W.; Qin, W.; Cui, D.; He, J. CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot-Labeled Lateral Flow Strips for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Gastric Cancer Carbohydrate Antigen 72-4. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mao, M.; Wu, F.; Li, Q.; Wei, L.; Ma, L. Amino-Functionalized CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Huynh, K.-H.; Ha, Y.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, H.-M.; Kim, D.-M.; Kim, J.; Pham, X.-H.; Kim, D.-E.; Ho, J.-N.; et al. Surface Modification of a Stable CdSeZnS/ZnS Alloy Quantum Dot for Immunoassay. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 4937049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.S.; Mansur, A.A.P. CdSe Quantum Dots Stabilized by Carboxylic-Functionalized PVA: Synthesis and UV–Vis Spectroscopy Characterization. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 125, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Du, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zou, W. Fabrication of Carboxyl Group-Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots and Its Transparent and Luminescent Epoxy Matrix Nanocomposites for White LED Encapsulation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, G. Quantum-Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Detection of Neonicotinoid Residues in Tea Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10107–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Hua, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M. Quantum Dots-Based Fluoroimmunoassay for the Simultaneous Detection of Clothianidin and Thiacloprid in Environmental and Agricultural Samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 3039–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foubert, A.; Beloglazova, N.V.; Rajkovic, A.; Sas, B.; Madder, A.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; De Saeger, S. Bioconjugation of Quantum Dots: Review & Impact on Future Application. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 83, 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cimaglia, F.; Aliverti, A.; Chiesa, M.; Poltronieri, P.; De Lorenzis, E.; Santino, A.; Sechi, L.A. Quantum Dots Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Assay for Rapid Detection of Mycobacterium Species Using Anti-FprA Antibodies. Nanotechnol. Dev. 2012, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Sung, H.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, M.-N. A New Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Detection of Influenza Viruses. BioChip J. 2022, 16, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, H.-M.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qu, L.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y. Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Test Strips for Highly Sensitive Detection of the Tetanus Antibody. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6789–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, S.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. Ultrasensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Two Specific SARS-CoV-2 Antigens in Human Specimens Using Direct/Enrichment Dual-Mode Fluorescence Lateral Flow Immunoassay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40342–40353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, C.; Mao, M.; Liu, Q.; Shen, H.; Cen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ma, L.; Song Li, L. Multiplexed Detection of Influenza A Virus Subtype H5 and H9 via Quantum Dot-Based Immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, D.; He, R.; Guo, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, P.; Cui, D. A Novel Quantum Dots–Based Point of Care Test for Syphilis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J. Application of DNA Aptamers and Quantum Dots to Lateral Flow Test Strips for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens with Improved Sensitivity versus Colloidal Gold. Pathogens 2014, 3, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, D.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, K.; Guo, X.; Jin, M.; Han, H. A Fast and Sensitive Immunoassay of Avian Influenza Virus Based on Label-Free Quantum Dot Probe and Lateral Flow Test Strip. Talanta 2012, 100, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, J.P.; Posada-Martínez, E.L.; Saldarriaga, C.; Wyss, F.; Ponte-Negretti, C.I.; Alexander, B.; Miranda-Arboleda, A.F.; Martínez-Sellés, M.; Baranchuk, A. Tuberculosis and the Heart. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, D.; Huang, L.; Bonroy, K.; Muyldermans, S. Antibody Fragments as Probe in Biosensor Development. Sensors 2008, 8, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Strom, M.; Hammond, D.S.; Shigdar, S. Anything You Can Do, I Can Do Better: Can Aptamers Replace Antibodies in Clinical Diagnostic Applications? Molecules 2019, 24, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Pathogens | Targets | Samples | No of Samples | Capture Probes | Type of QDs | Size of QDs | Origin of QDs | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | FprA antigens | FprA antigens diluted in PBS | NR | anti-FprA antibodies | CdSe/ZnS | 15–20 nm | commercial | LoD of 12.5 pg/μL in less than 10 min | [51] |
| 2 | Influenza A and B | N antigens | Human nasopharyngeal swab | 394 | Influenza A and B antibodies | NR | NR | commercial | Sensitivity of 80.9% for influenza A and 83.7% for influenza B and 100% specificity | [52] |
| 3 | Clostridium tetani | Tetanus antibody | Human serum spiked with tetanus antibody | NR | Tetanus antigens | Cu:Zn−In−S/ZnS | NR | synthesized | LoD of 0.001 IU/mL in 30 min | [53] |
| 4 | SARS-CoV-2 | S and N antigens | Human saliva and nasal swab spiked with SARS-CoV-2 S and N antigens | NR | Monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 N antigens and S antigens | MagTQD | 160 nm | synthesized | LoD of 1 pg/mL for direct mode and 0.5 pg/mL for enrichment mode in 10 min | [54] |
| 5 | Influenza A | N antigens | Avian cloacal swab | 147 | Influenza A virus subtype H5 and H9 antibodies | CdSe/ZnS | 25 nm | synthesized | 100% accuracy and LoD of 0.016 HAU for H5 and 0.25 HAU for H9 in 15 min | [55] |
| 6 | Treponema pallidum | anti-TP47 polyclonal antibodies | Serum of syphilis patients and healthy individuals | 100 | TP47 antigen | CdTe | 3.5 nm | synthesized | 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity in 10 min, LoD of 2 ng/mL | [56] |
| 7 | Escherichia coli | Whole cells | E. coli diluted in PBS | NR | DNA aptamers | Qdot | NR | commercial | LoD of 300 bacterial cells | [57] |
| 8 | Influenza A | Influenza A virus subtype H5 antigens | Chicken serum samples | 20 | Influenza A virus subtype H5 antibodies | CdTe | NR | synthesized | LoD of 0.09 ng/mL. Turnaround time in 10 min. 100% sensitivity and 88.2% specificity. | [58] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad Najib, M.; Selvam, K.; Khalid, M.F.; Ozsoz, M.; Aziah, I. Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Its Principle and Performance. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092158
Ahmad Najib M, Selvam K, Khalid MF, Ozsoz M, Aziah I. Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Its Principle and Performance. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(9):2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092158
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad Najib, Mohamad, Kasturi Selvam, Muhammad Fazli Khalid, Mehmet Ozsoz, and Ismail Aziah. 2022. "Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Its Principle and Performance" Diagnostics 12, no. 9: 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092158
APA StyleAhmad Najib, M., Selvam, K., Khalid, M. F., Ozsoz, M., & Aziah, I. (2022). Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Its Principle and Performance. Diagnostics, 12(9), 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092158







