Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma from Retinal Images Using Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
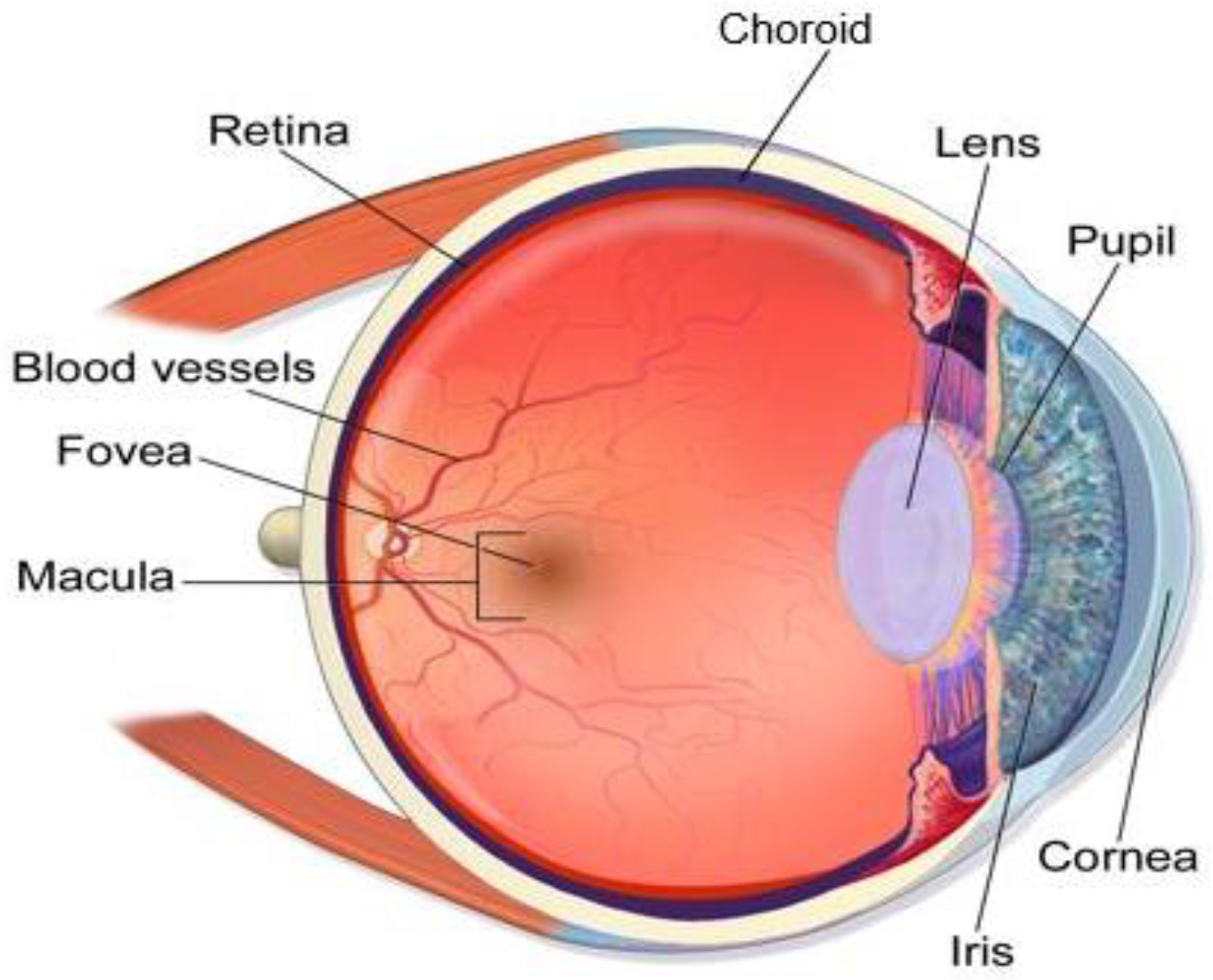
:1. Introduction
- The most notable recent machine learning and deep learning-based glaucoma detection research is thoroughly reviewed to define the problem, focusing on various features that can support an efficient diagnosis.
- For the diagnosis, a model is developed employing advanced deep learning methods along with transfer learning, and the model is tuned using various techniques to lower the likelihood of model overfitting.
- Multiple datasets of glaucomatous retinal images are adopted to train and test the model to achieve higher diagnostic accuracy.
- An end-to-end learning system that overcomes the drawbacks of current glaucoma screening methods is developed.
2. Literature Review
3. Proposed Methodology
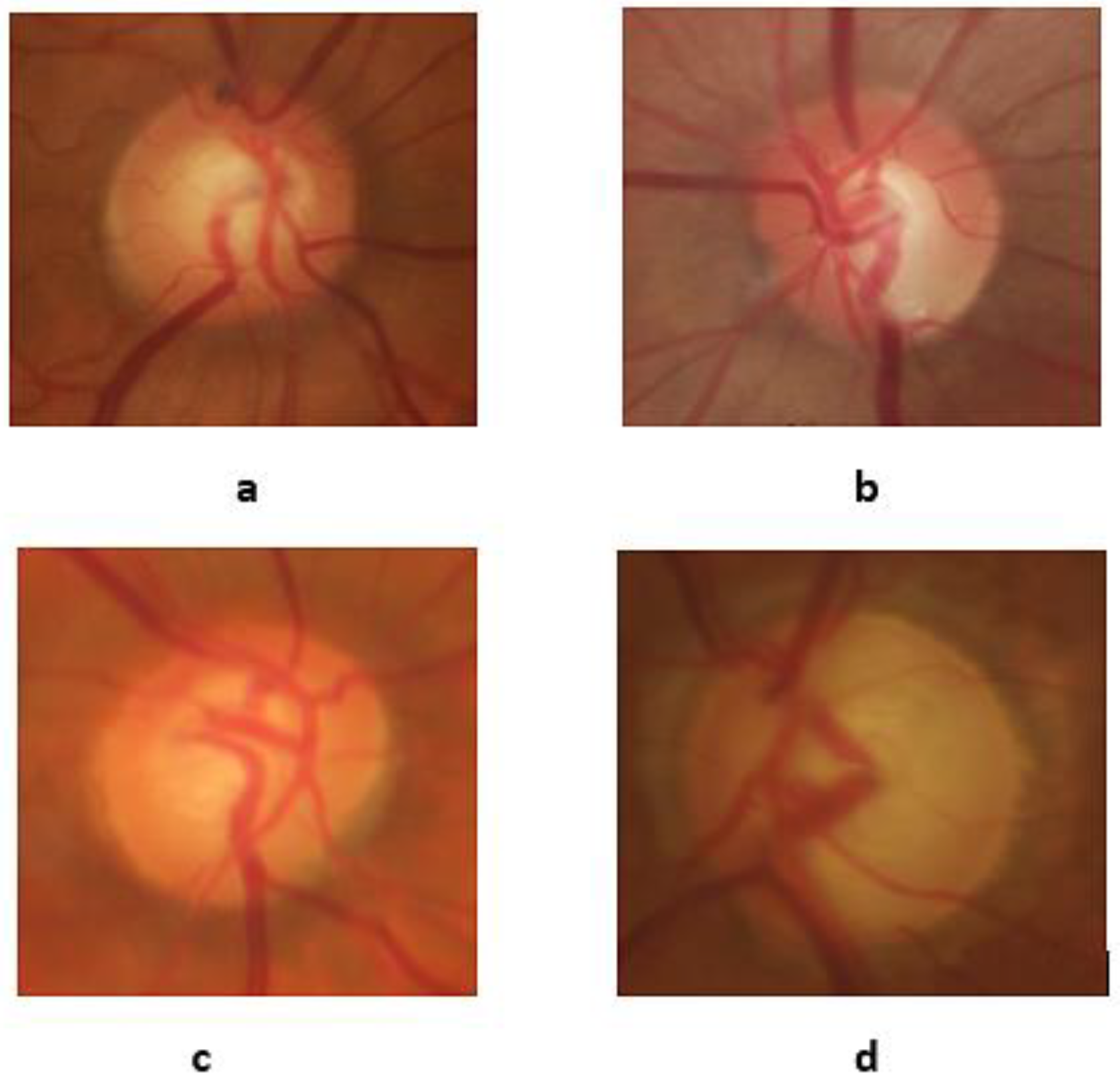
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Image Preprocessing
3.3. Data Augmentation
3.4. Transfer Learning
3.5. Convolutional Neural Network
3.6. ResNet-50 Architecture
- Acquire the fundus images from different publicly available datasets.
- Convert the fundus images into grayscale.
- Apply the data augmentation approach to multiply the number of images by flipping, rescaling, and rotation after dividing the dataset into training and testing sets. Further, 80% of the images in the dataset are used for training, 10% of images for validation, and the remaining 10% for testing.
- Pre-trained DL architecture, such as the ResNet-50, is used for classification.
- The model classifies an image as either a healthy or glaucomatous image.
4. Experiments and Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vision. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21204-vision (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Optic Nerve, Healthline. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/optic-nerve#1 (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Coiner, B.; Pan, H.; Bennett, M.L.; Bodien, Y.G.; Iyer, S.; O’Neil-Pirozzi, T.M.; Leung, L.; Giacino, J.T.; Stern, E. Functional neuroanatomy of the human eye movement network: A review and atlas. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Xiao, D.; Frost, S.; Kanagasingam, Y. Robust optic disc and cup segmentation with deep learning for glaucoma detection. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 74, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, H.; Akram, M.U.; Khawaja, S.G.; Arslan, M.; Ramzan, A.; Nazir, N. Data on OCT and fundus images for the detection of glaucoma. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WikiJournal of Medicine. Available online: https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/WikiJournal_of_Medicine/Medical_galery_of_Blausen_Medical_2014#/media/File:Blausen_0389_EyeAnatomy_02.png (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Asano, S.; Asaoka, R.; Murata, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Miki, A.; Mori, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kanamoto, T.; Yamagami, J.; Inoue, K. Predicting the central 10 degrees visual field in glaucoma by applying a deep learning algorithm to optical coherence tomography images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H. Attention based glaucoma detection: A large-scale database and CNN Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10571–10580. [Google Scholar]
- World Report on Vision. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1257940/retrieve&ved=2ahUKEwjGy4js3pPrAhWMEBQKHWUQCFMQFjAAegQIARAB&usg=AOvVaw3DSQZJ6aFidsEgDH4nsz8X (accessed on 17 July 2021).
- Eyes on Eyecare. Available online: https://www.eyesoneyecare.com/resources/glaucoma-systemic-medications-friends508or-foes-with-cheat-sheet/. (accessed on 17 July 2021).
- Fumero, F.; Alayón, S.; Sanchez, J.L.; Sigut, J.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M. RIM-ONE: An open retinal image database for optic nerve evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2011 24th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Bristol, UK, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- de Moura Lima, A.C.; Maia, L.B.; dos Santos, P.T.C.; Junior, G.B.; de Almeida, J.D.; de Paiva, A.C. Evolving Convolutional Neural Networks for Glaucoma Diagnosis. Braz. J. Health Rev. 2020, 3, 9224–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Vyas, A.; Parashar, L.; Singh, U. A Glaucoma Detection using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 2–4 July 2020; pp. 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Thakoor, K.A.; Li, X.; Tsamis, E.; Sajda, P.; Hood, D.C. Enhancing the Accuracy of Glaucoma Detection from OCT Probability Maps using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2036–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, S.; Kanhangad, V.; Pachori, R.B. CNN-based approach for glaucoma diagnosis using transfer learning and LBP-based data augmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.08013. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Khan, M.A.; Saba, T.; Mehmood, Z.; Tariq, U.; Ayesha, N. Microscopic brain tumor detection and classification using 3D CNN and feature selection architecture. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2021, 84, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, J.; Zeebaree, S. Skin lesion classification based on deep convolutional neural networks architectures. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2021, 2, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobecki, P.; Jóźwiak, R.; Sklinda, K.; Przelaskowski, A. Effect of domain knowledge encoding in CNN model architecture—A prostate cancer study using mpMRI images. PeerJ 2021, 9, 11006–11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Jammal, A.A.; Mariottoni, E.B. Detection of progressive glaucomatous optic nerve damage on fundus photographs with deep learning. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Cho, K.J.; Oh, S. Development of machine learning models for diagnosis of glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 177726–177742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Akram, M.U.; Sharif, M.; Tariq, A.; ullah Yasin, U. Arteriovenous ratio and papilledema based hybrid decision support system for detection and grading of hypertensive retinopathy. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 154, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Akram, M.U.; Sharif, M.; Tariq, A.; Khan, S.A. Decision support system for detection of hypertensive retinopathy using arteriovenous ratio. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 90, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.U.; Akbar, S.; Hassan, T.; Khawaja, S.G.; Yasin, U.; Basit, I. Data on fundus images for vessels segmentation, detection of hypertensive retinopathy, diabetic retinopathy and papilledema. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Hassan, M.; Akram, U.; Yasin, U.U.; Basit, I. AVRDB: Annotated dataset for vessel segmentation and calculation of arteriovenous ratio. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision, and Pattern Recognition (IPCV), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 17 July 2017; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, S.; Satoh, S.I.; Yoda, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Oshika, T.; Group, J.O.I.R.R. Evaluation of deep convolutional neural networks for glaucoma detection. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Sohail, A.; Zahoora, U.; Qureshi, A.S. A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5455–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sircar, P.; Pachori, R.; Bhandary, S.V.; Acharya, U.R. Automated glaucoma detection using center slice of higher order statistics. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2019, 19, 1940011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Tanito, M.; Mitsuhashi, K.; Fujino, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Murata, H.; Asaoka, R. Development of a deep residual learning algorithm to screen for glaucoma from fundus photography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dutta, M.K.; ParthaSarathi, M.; Uher, V.; Burget, R. Image processing based automatic diagnosis of glaucoma using wavelet features of segmented optic disc from fundus image. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 124, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Ran, A.R.; Luo, L.; Chan, P.P.; Tham, C.C.; Chang, R.T.; Mannil, S.S.; Cheung, C.Y.; Heng, P.A. Towards multi-center glaucoma OCT image screening with semi-supervised joint structure and function multi-task learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101695–101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, T.; Akbar, S.; Kolivand, H.; Ali Bahaj, S. Automatic detection of papilledema through fundus retinal images using deep learning. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2021, 84, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.A.; Akbar, S.; Rehman, A.; Saba, T.; Kolivand, H.; Bahaj, S.A. Recent Developments in Detection of Central Serous Retinopathy Through Imaging and Artificial Intelligence Techniques–A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 168731–168748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.E.; Akbar, S.; Gull, S.; Rehman, A.; Alaska, H. Deep Learning-Based Automatic Detection of Central Serous Retinopathy using Optical Coherence Tomographic Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics (CAIDA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–7 April 2021; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Heuvelmans, M.A.; van Ooijen, P.M.; Ather, S.; Silva, C.F.; Han, D.; Heussel, C.P.; Hickes, W.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Novotny, P.; Peschl, H. Lung cancer prediction by Deep Learning to identify benign lung nodules. Lung Cancer 2021, 154, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gull, S.; Akbar, S. Artificial Intelligence in Brain Tumor Detection through MRI Scans: Advancements and Challenges. In Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 241–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Zaki, W.M.D.W.; Hussain, A. An automated glaucoma screening system using cup-to-disc ratio via Simple Linear Iterative Clustering superpixel approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 53, 101454–101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, A.; Akram, M.U.; Shaukat, A.; Khawaja, S.G.; Yasin, U.U.; Butt, W.H. Automated glaucoma detection using retinal layers segmentation and optic cup-to-disc ratio in optical coherence tomography images. IET Image Process. 2018, 13, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Singh, A.; Leopold, H.A.; Gulati, T.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Ophthalmic diagnosis using deep learning with fundus images–A critical review. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 102, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemelings, R.; Elen, B.; Barbosa-Breda, J.; Lemmens, S.; Meire, M.; Pourjavan, S.; Vandewalle, E.; Van de Veire, S.; Blaschko, M.B.; De Boever, P. Accurate prediction of glaucoma from colour fundus images with a convolutional neural network that relies on active and transfer learning. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serte, S.; Serener, A. A Generalized Deep Learning Model for Glaucoma Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 10–12 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, P.K.; Pachori, R.B. Automatic diagnosis of glaucoma using two-dimensional Fourier-Bessel series expansion based empirical wavelet transform. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102237–102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Hou, B.; Liu, L.; Gordon, M.; Kass, M.; Wang, F.; Van Tassel, S.H.; Peng, Y. Automated diagnosing primary open-angle glaucoma from fundus image by simulating human’s grading with deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14080–14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zou, B.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, M. Clinical Interpretable Deep Learning Model for Glaucoma Diagnosis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, M.; Singh, S.; Agarwal, N.; Bali, S.; Gupta, S.; Thakur, N.; Jindal, P. Automated detection of Glaucoma using deep learning convolution network (G-net). Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15531–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetschke, S.; Antony, B.; Ishikawa, H.; Wollstein, G.; Schuman, J.; Garnavi, R. A feature agnostic approach for glaucoma detection in OCT volumes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 219126–219137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Goldbaum, M.; Yousefi, S. Predicting Glaucoma before Onset Using Deep Learning. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2020, 3, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.A.; de Carvalho Araújo, A.C.; de Moura Lima, A.C.; de Sousa, J.A.; de Almeida, J.D.S.; de Paiva, A.C.; Júnior, G.B. Mask Overlaying: A Deep Learning Approach for Individual Optic Cup Segmentation from Fundus Image. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Niterói, Brazil, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Elangovan, P.; Nath, M.K. Glaucoma assessment from color fundus images using convolutional neural network. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 955–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Irfan, M.; Ali, T.; Ali, G.; Shaf, A.; Al-Beshri, A.; Alasbali, T.; Mahnashi, M.H. An adoptive threshold-based multi-level deep convolutional neural network for glaucoma eye disease detection and classification. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, H.; Akram, M.U.; Shaukat, A.; Khan, S.A.; Alghamdi, N.; Khawaja, S.G.; Nazir, N. Extraction of retinal layers through convolution neural network (CNN) in an OCT image for glaucoma diagnosis. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sales Carvalho, N.R.; Rodrigues, M.d.C.L.C.; de Carvalho Filho, A.O.; Mathew, M.J. Automatic method for glaucoma diagnosis using a three-dimensional convoluted neural network. Neurocomputing 2021, 438, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, S.; Shariflou, S.; Phu, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Agar, A.; Kalloniatis, M.; Golzan, S.M. A combined convolutional and recurrent neural network for enhanced glaucoma detection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, H.N.; Muruganandham, A.; Senthil Kumaran, T. A novel optic disc and optic cup segmentation technique to diagnose glaucoma using deep learning convolutional neural network over retinal fundus images. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6187–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Alipour, K.; Bowd, C.; Christopher, M.; Brye, N.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Belghith, A.; Girkin, C.A.; Fazio, M.A.; et al. Detecting Glaucoma from Fundus Photographs Using Deep Learning without Convolutions: Transformer for Improved Generalization. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2023, 3, 100233–100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanki, R. A deep neural network and machine learning approach for retinal fundus image classification. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 3, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bo, W.; Hu, C.; Kang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Applications of deep learning in fundus images: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101971–101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, M.N.; Singh, G.A.P.; Neumeier, W.; Malik, M.I.; Dengel, A.; Ahmed, S. G1020: A Benchmark Retinal Fundus Image Dataset for Computer-Aided Glaucoma Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.09158. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaswamy, J.; Krishnadas, S.; Joshi, G.D.; Jain, M.; Tabish, A.U.S. Drishti-gs: Retinal image dataset for optic nerve head (onh) segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 11th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), Beijing, China, 29 April–2 May 2014; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, F.S.; Liu, J.; Wong, W.K.; Tan, N.M.; Lee, B.H.; Cheng, J.; Wong, T.Y. Origa-light: An online retinal fundus image database for glaucoma analysis and research. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 3065–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiknakis, N.; Theodoropoulos, D.; Manikis, G.; Ktistakis, E.; Boutsora, O.; Berto, A.; Scarpa, F.; Scarpa, A.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Marias, K. Deep Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and Classification Based on Fundus Images: A Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Understanding ResNet50 Architecture. Available online: https://iq.opengenus.org/resnet50-architecture/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Juan, PR, USA, 17–19 June 1997; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Valverde, J.J.; Antón, A.; Fatti, G.; Liefers, B.; Herranz, A.; Santos, A.; Sánchez, C.I.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J. Automatic glaucoma classification using color fundus images based on convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 892–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, M.; Belghith, A.; Bowd, C.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Weinreb, R.N.; Girkin, C.A.; Liebmann, J.M.; Zangwill, L.M. Performance of deep learning architectures and transfer learning for detecting glaucomatous optic neuropathy in fundus photographs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sr. No. | Authors | Year | Model | Datasets | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yu et al. [4] | 2019 | Pre-trained U-Net, ResNet | RIGA, DRISHTI-GS, RIM-ONE | Dice 97.38% (Disc) Dice 88.77% (Cup) |
| 2 | Li et al. [6] | 2019 | CNN | LAG, RIM-ONE | Accuracy 95.3% |
| 3 | Phan et al. [25] | 2019 | ResNet-152, DenseNet201, VGG19 | Local dataset of 3777 images | AUC 0.9 |
| 4 | Liao et al. [43] | 2019 | ResNet | ORIGA | Accuracy 0.88 |
| 5 | Serte et al. [40] | 2019 | ResNet-50, ResNet-152, and GoogleNet (ensemble method) | HRF, DRISHTI-GS1, RIMONE, sjchoi86-HRF, ACRIMA | Accuracy 53%, AUC 83%, specificity 100% |
| 6 | Juneja et al. [44] | 2019 | U-Net | DRISHTI-GS | Accuracy 95.8% (OD segmentation), 93.0% (OC segmentation) |
| 7 | Maetschke et al. [45] | 2019 | CNN | Local dataset of 1110 images | AUC 0.94 |
| 8 | Thakoor et al. [14] | 2019 | Pre-trained CNN | Local dataset of 737 images | Accuracy 96.27% |
| 9 | Maheshwari et al. [15] | 2020 | AlexNet | RIM-ONE | Accuracy: 98.90% Sensitivity: 100% Specificity: 97.50% |
| 10 | Lima et al. [12] | 2020 | CNN | RIM-ONE r3 | Accuracy 91% |
| 11 | Saxena et al. [13] | 2020 | CNN | ORIGA, SCES | AUC 0.822 (ORIGA) AUC 0.882 (SCES) |
| 12 | Thakur et al. [46] | 2020 | MobileNet v2 | Local datasets of 45,301, 42,601, and 42,498 images | AUC 0.97 |
| 13 | Hemelings et al. [39] | 2020 | Pre-trained ResNet 128 | Local dataset of 1424 images | AUC 0.995 Sensitivity 99.2% Specificity 93% |
| 14 | Elangovan and Nath [48] | 2020 | CNN | RIM-ONE, DRISHTI–GS1, ORIGA, LAG, ACRIMA | Accuracy 96.64%, sensitivity 96.07%, specificity 97.39%, precision 97.74% |
| 15 | Aamir et al. [49] | 2020 | ML-DCNN | Local dataset of 1338 fundus images | Sensitivity 97.04%, specificity 98.99%, accuracy 99.39%, PRC 98.2% |
| 16 | Raja et al. [50] | 2020 | CNN | Local dataset of 196 OCT images | Accuracy 94%, sensitivity 94.4%, specificity 93.75% |
| 17 | Gheisari et al. [52] | 2021 | CNN, RNN | 295 videos and local dataset of 1810 fundus images | F-measure 96.2% |
| 18 | Chaudhary and Pachori [41] | 2021 | Ensemble ResNet Models | RIM-ONE, ORIGA, and DRISHTI-GS | Accuracy 91.1%, sensitivity 91.1%, specificity 94.3%, AUC 83.3%, ROC 96% |
| 19 | Carvalho et al. [51] | 2021 | 3DCNN | RIM-ONE and DRISHTI-GS | Accuracy 83.23%, sensitivity 85.54%, specificity 80.95%, AUC 83.2%, and Kappa 66.45% |
| 20 | Lin et al. [42] | 2022 | CNN | OHTS and LAG | Accuracy 0.930 (OHTS) and 0.969 (LAG) |
| 21 | Veena et al. [53] | 2022 | CNN | DRISHTI-GS | Accuracy 98% (OD), 97% (OC) |
| 22 | Fan et al. [54] | 2023 | CNN | Custom assembled from 5 public datasets | AUC 0.91 |
| 23 | Thanki [55] | 2023 | Deep NN | DRISHTI-GS and ORIGA | Accuracy 100% |
| Sr # | Authors | Dataset | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lima et al. [12] | RIM-ONE r3 | 91% | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | Saxena et al. [13] | SCES | 88.2% | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | Thakoor et al. [14] | Local dataset of 737 images | - | 96.27% | - | - | - |
| Fan et al. [54] | OHTS | - | 91% | - | - | - | |
| DIGS | 74% | ||||||
| ACRIMA | 74% | ||||||
| LAG | 79% | ||||||
| RIM-ONE | 90% | ||||||
| ORIGA | 55% | ||||||
| Lin et al. [42] | OHTS LAG | 90.4% | 93% | 49% | |||
| Thanki [49] | ORIGA | 69.7% | 76.2% | 100% | 73% | ||
| Veena et al. [53] | DRISHTI–GS | 98% | 95.41% | ||||
| 4 | Gomez-Valverde et al. [64] | Local dataset of 2313 images | 94% | 87.01% | 89.01% | 89.01% | - |
| 5 | Christopher et al. [65] | Local dataset of 14,822 images | 97% | 88% | 95% | 95% | - |
| 6 | Thakur et al. [46] | Local datasets of 45,301, 42,601, and 42,498 images | 97% | - | - | - | - |
| Proposed Method | RIM-ONE | 94.2% | 96.15% | 97.85% | 92.38% | 97% | |
| ORIGA | 93% | 92.59% | 98.39% | 79.26% | 95% | ||
| G1020 | 97% | 98.48% | 99.30% | 96.52% | 98% | ||
| DRISHTI-GS | 96% | 97.03% | 93.75% | 98.55% | 97% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shoukat, A.; Akbar, S.; Hassan, S.A.; Iqbal, S.; Mehmood, A.; Ilyas, Q.M. Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma from Retinal Images Using Deep Learning Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101738
Shoukat A, Akbar S, Hassan SA, Iqbal S, Mehmood A, Ilyas QM. Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma from Retinal Images Using Deep Learning Approach. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(10):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101738
Chicago/Turabian StyleShoukat, Ayesha, Shahzad Akbar, Syed Ale Hassan, Sajid Iqbal, Abid Mehmood, and Qazi Mudassar Ilyas. 2023. "Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma from Retinal Images Using Deep Learning Approach" Diagnostics 13, no. 10: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101738
APA StyleShoukat, A., Akbar, S., Hassan, S. A., Iqbal, S., Mehmood, A., & Ilyas, Q. M. (2023). Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma from Retinal Images Using Deep Learning Approach. Diagnostics, 13(10), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101738









