Utilizing Envelope Analysis of a Nasal Pressure Signal for Sleep Apnea Severity Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Signal Preprocessing
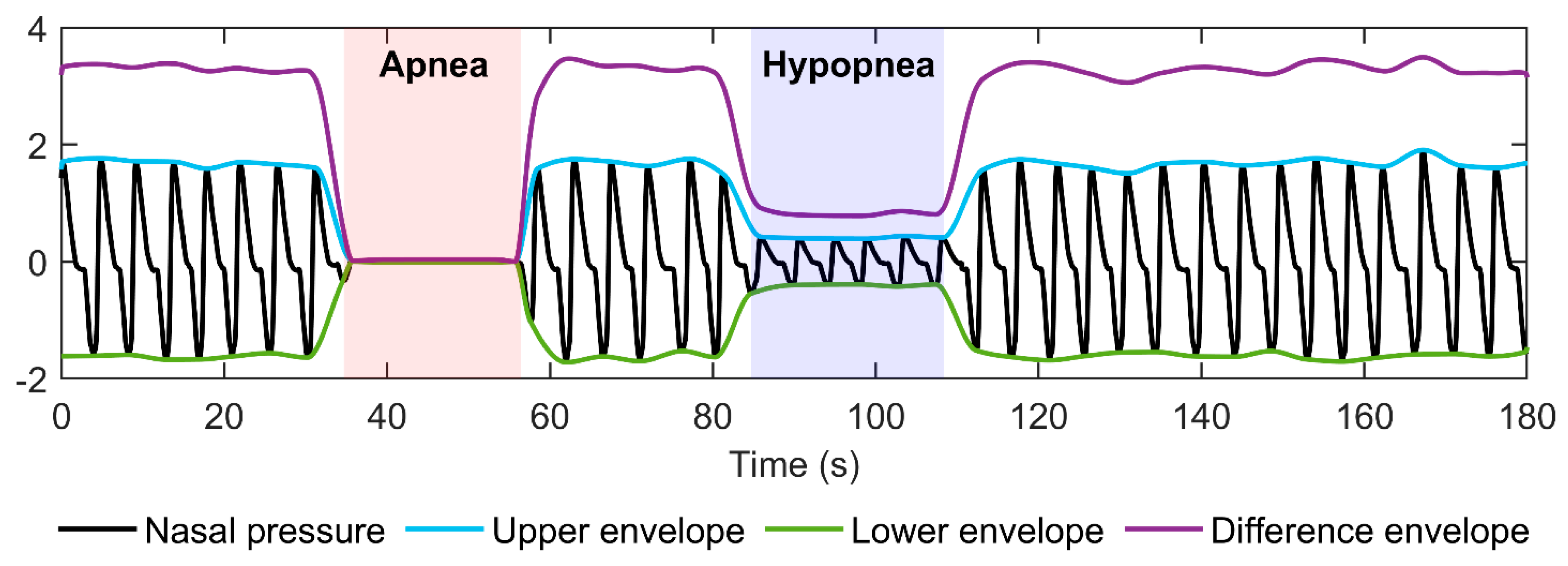
2.3. Envelope Algorithm
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
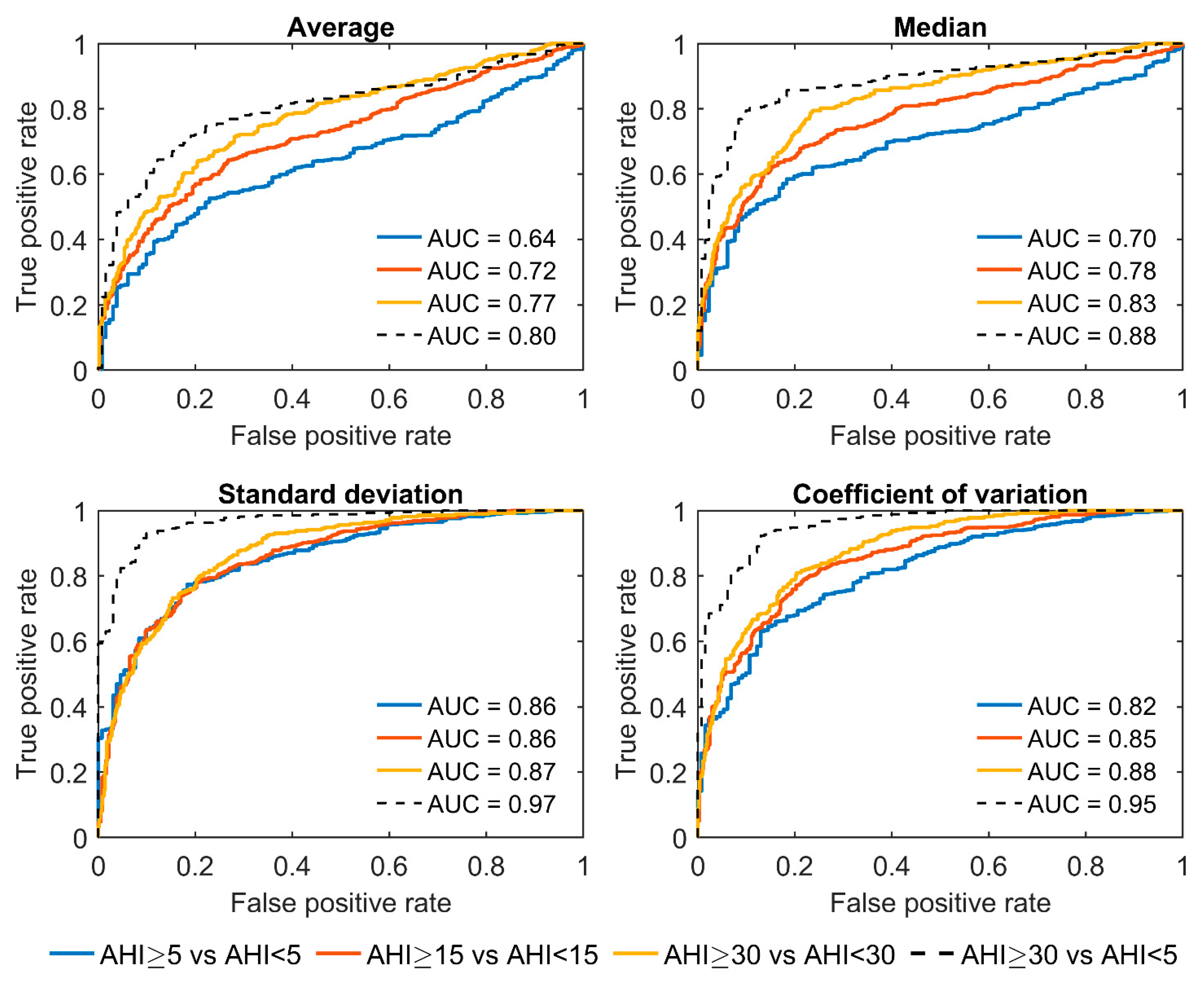
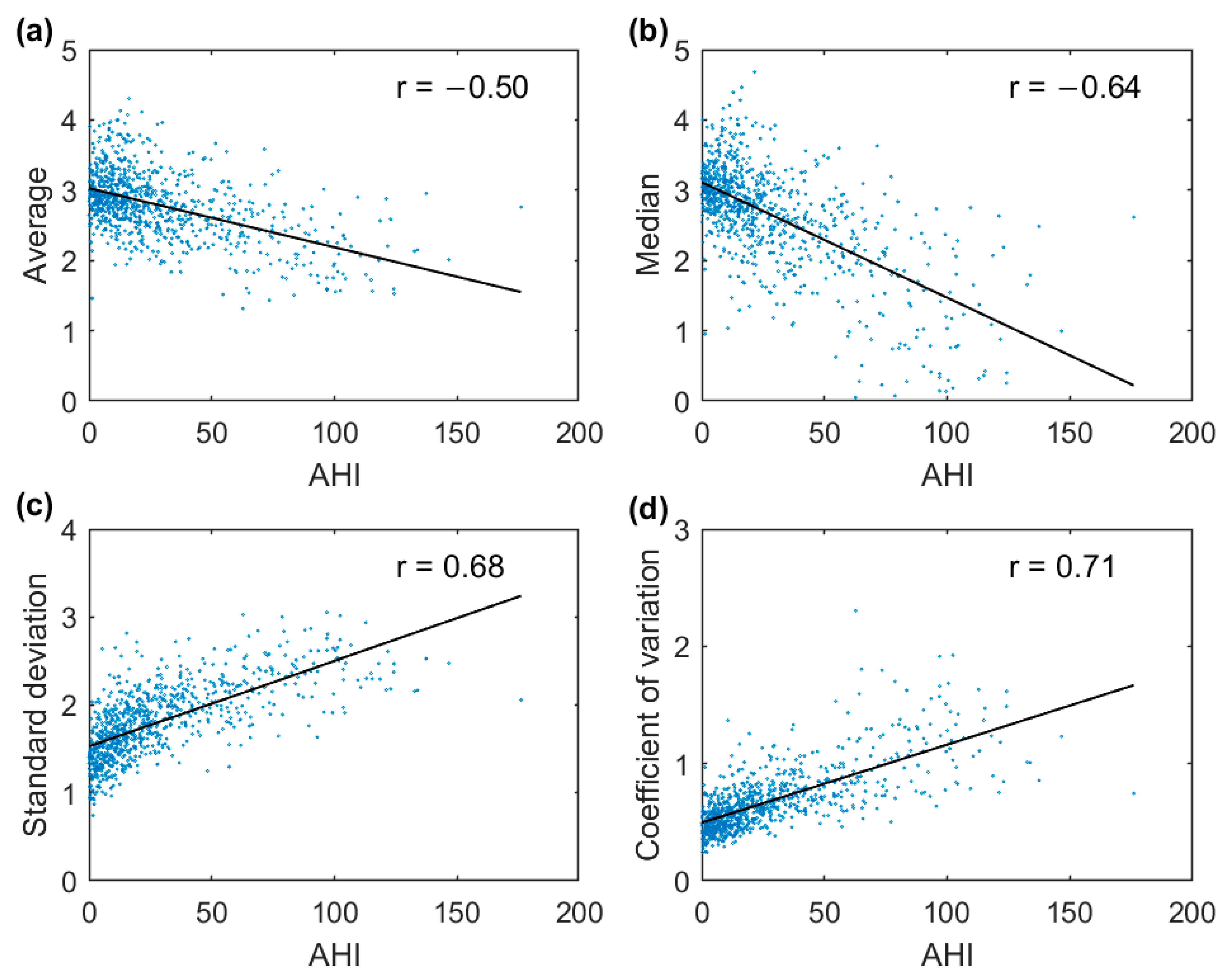
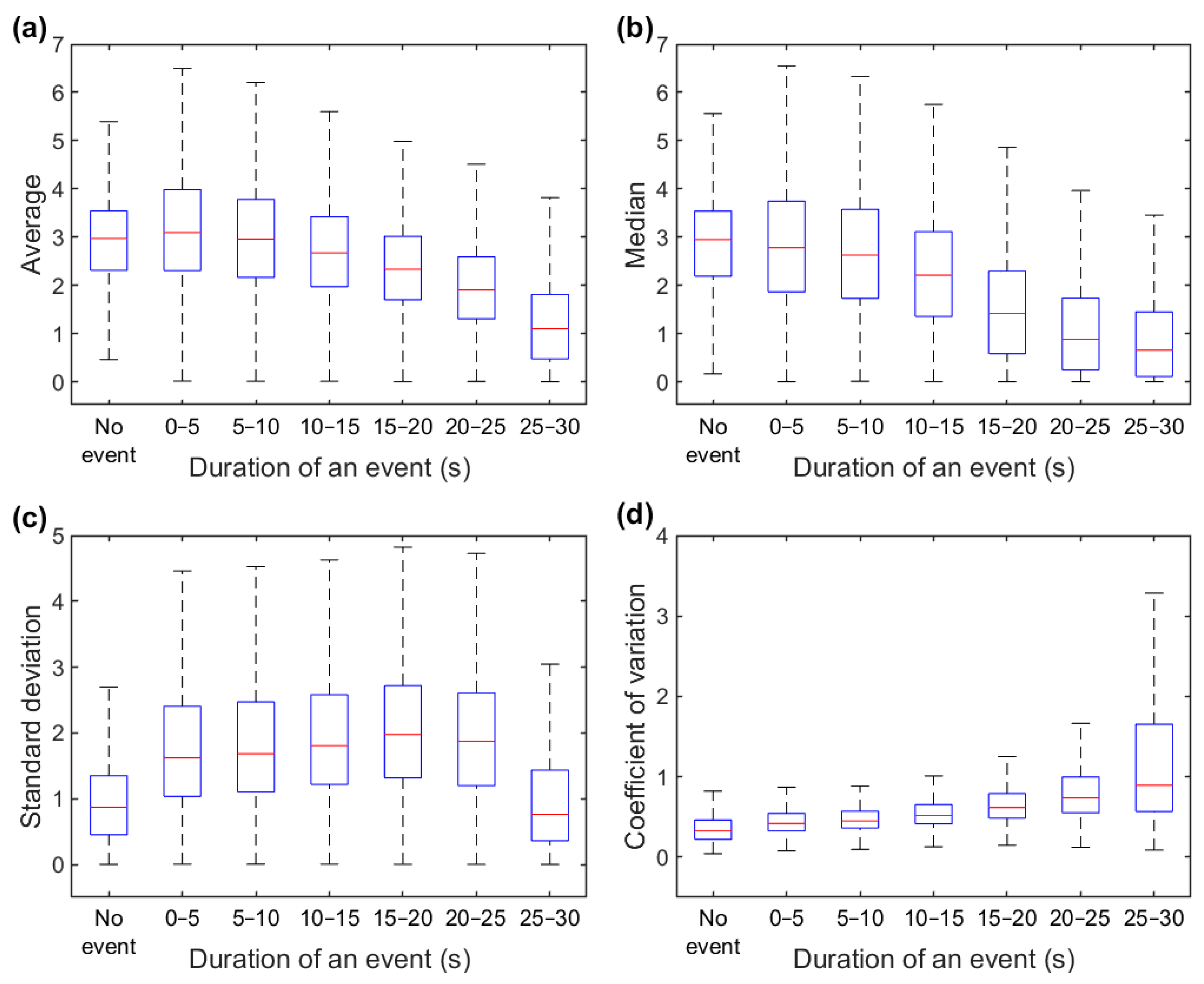
3.1. Full-Night Envelope Analyses
3.2. Epoch-by-Epoch Analyses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.-L.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence and Burden of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Literature-Based Analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sateia, M.J. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Adults: Recommendations for Syndrome Definition and Measurement Techniques in Clinical Research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 1999, 22, 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevernagie, D.A.; Gnidovec-Strazisar, B.; Grote, L.; Heinzer, R.; McNicholas, W.T.; Penzel, T.; Randerath, W.; Schiza, S.; Verbraecken, J.; Arnardottir, E.S. On the Rise and Fall of the Apnea-Hypopnea Index: A Historical Review and Critical Appraisal. J. Sleep Res. 2020, 29, e13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Quan, S.F.; Troester, M.M.; Vaughn, B. V AASM|Scoring Manual Version 2.4 The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications Version 2.4; AASM: Darien, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karhu, T.; Myllymaa, S.; Nikkonen, S.; Mazzotti, D.R.; Töyräs, J.; Leppänen, T. Longer and Deeper Desaturations Are Associated With the Worsening of Mild Sleep Apnea: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 657126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, S.; Töyräs, J.; Oksenberg, A.; Korkalainen, H.; Sefa, S.; Kulkas, A.; Leppänen, T. Severity of Desaturations Reflects OSA-Related Daytime Sleepiness Better Than AHI. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarbarzin, A.; Sands, S.A.; Stone, K.L.; Taranto-Montemurro, L.; Messineo, L.; Terrill, P.I.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Ensrud, K.; Purcell, S.; White, D.P.; et al. The Hypoxic Burden of Sleep Apnoea Predicts Cardiovascular Disease-Related Mortality: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study and the Sleep Heart Health Study. Eur. Heart. J. 2019, 40, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraja-Murro, A.; Kulkas, A.; Hiltunen, M.; Kupari, S.; Hukkanen, T.; Tiihonen, P.; Mervaala, E.; Töyräs, J. The Severity of Individual Obstruction Events Is Related to Increased Mortality Rate in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Sleep Res. 2013, 22, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkas, A.; Tiihonen, P.; Eskola, K.; Julkunen, P.; Mervaala, E.; Töyräs, J. Novel Parameters for Evaluating Severity of Sleep Disordered Breathing and for Supporting Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2013, 37, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, G. A Novel Parameter Is Better than the AHI to Assess Nocturnal Hypoxaemia and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkonen, S.; Afara, I.O.; Leppänen, T.; Töyräs, J. Artificial Neural Network Analysis of the Oxygen Saturation Signal Enables Accurate Diagnostics of Sleep Apnea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkonen, S.; Korkalainen, H.; Leino, A.; Myllymaa, S.; Duce, B.; Leppanen, T.; Toyras, J. Automatic Respiratory Event Scoring in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using a Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Ji, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q. Classification of Sleep Apnea Based on EEG Sub-Band Signal Characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, H.; Leske, V.; Gaultier, C. Use of Nasal Cannula for Detecting Sleep Apneas and Hypopneas in Infants and Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.B.; Chow, C.M.; Ling, S.H.; Su, S.W. A Novel Algorithm for Automatic Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea from Airflow and Oximetry Signals. Physiol. Meas. 2021, 42, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciołek, M.; Niedźwiecki, M.; Sieklicki, S.; Drozdowski, J.; Siebert, J. Automated Detection of Sleep Apnea and Hypopnea Events Based on Robust Airflow Envelope Tracking in the Presence of Breathing Artifacts. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, J.A.; Arancibia, J.M.; Bassi, A.; Vivaldi, E.A. Envelope Analysis of the Airflow Signal to Improve Polysomnographic Assessment of Sleep Disordered Breathing. Sleep 2014, 37, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redline, S.; Budhiraja, R.; Kapur, V.; Marcus, C.L.; Mateika, J.H.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarthy, S.; Somers, V.K.; Strohl, K.P.; Sulit, L.G.; et al. The Scoring of Respiratory Events in Sleep: Reliability and Validity. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, F.N.; Carlson, R.E. Monotone Piecewise Cubic Interpolation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1980, 17, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchuk, A.; Yaggi, H.K. Sleep Apnea Heterogeneity, Phenotypes, and Cardiovascular Risk. Implications for Trial Design and Precision Sleep Medicine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, P.K.; Westerman, D.E.; Dedhia, R.C. The Longest Obstructive Apnea You Have Ever Seen: A Patient With New-Onset Autonomic Dysfunction. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkalainen, H.; Töyräs, J.; Nikkonen, S.; Leppänen, T. Mortality-Risk-Based Apnea-Hypopnea Index Thresholds for Diagnostics of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Sleep Res. 2019, 28, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkas, A.; Tiihonen, P.; Julkunen, P.; Mervaala, E.; Töyräs, J. Novel Parameters Indicate Significant Differences in Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Patients Having Similar Apnea-Hypopnea Index. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsini, E.; Nogueira, F.; Nigro, C. Apnea-Hypopnea Index in Sleep Studies and the Risk of over-Simplification. Sleep Sci. 2018, 11, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Whole Population | Non-OSA (AHI < 5) | Mild OSA (5 ≤ AHI < 15) | Moderate OSA (15 ≤ AHI < 30) | Severe OSA (AHI ≥ 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (N, (male%)) | 847 (53.8) | 131 (32.8) | 239 (45.2) | 204 (55.9) | 273 (70.0) |
| Age (years) | 55.8 (44.8–65.7) | 44.8 (31.4–58.3) | 54.4 (44.8–64.1) | 56.8 (48.2–66.5) | 59.0 (48.0–68.5) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 34.0 (29.0–40.2) | 30.0 (25.0–35.3) | 33.6 (28.3–38.9) | 33.7 (30.3–39.9) | 36.2 (31.8–43.1) |
| AHI (events/h) | 18.0 (8.2–38.4) | 2.5 (1.3–3.6) | 9.8 (7.2–12.2) | 21.3 (17.9–25.0) | 56.0 (39.4–78.0) |
| Duration of analyzed period (h) | 7.3 (6.7–7.8) | 7.4 (6.8–7.8) | 7.3 (6.7–7.9) | 7.3 (6.7–7.8) | 7.3 (6.7–7.8) |
| Number of analyzed epochs (n) | 737,992 | 114,522 | 208,467 | 177,958 | 237,045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varis, M.; Karhu, T.; Leppänen, T.; Nikkonen, S. Utilizing Envelope Analysis of a Nasal Pressure Signal for Sleep Apnea Severity Estimation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101776
Varis M, Karhu T, Leppänen T, Nikkonen S. Utilizing Envelope Analysis of a Nasal Pressure Signal for Sleep Apnea Severity Estimation. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(10):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101776
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaris, Mikke, Tuomas Karhu, Timo Leppänen, and Sami Nikkonen. 2023. "Utilizing Envelope Analysis of a Nasal Pressure Signal for Sleep Apnea Severity Estimation" Diagnostics 13, no. 10: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101776
APA StyleVaris, M., Karhu, T., Leppänen, T., & Nikkonen, S. (2023). Utilizing Envelope Analysis of a Nasal Pressure Signal for Sleep Apnea Severity Estimation. Diagnostics, 13(10), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13101776







