Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Hepatic Uveal Melanoma Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
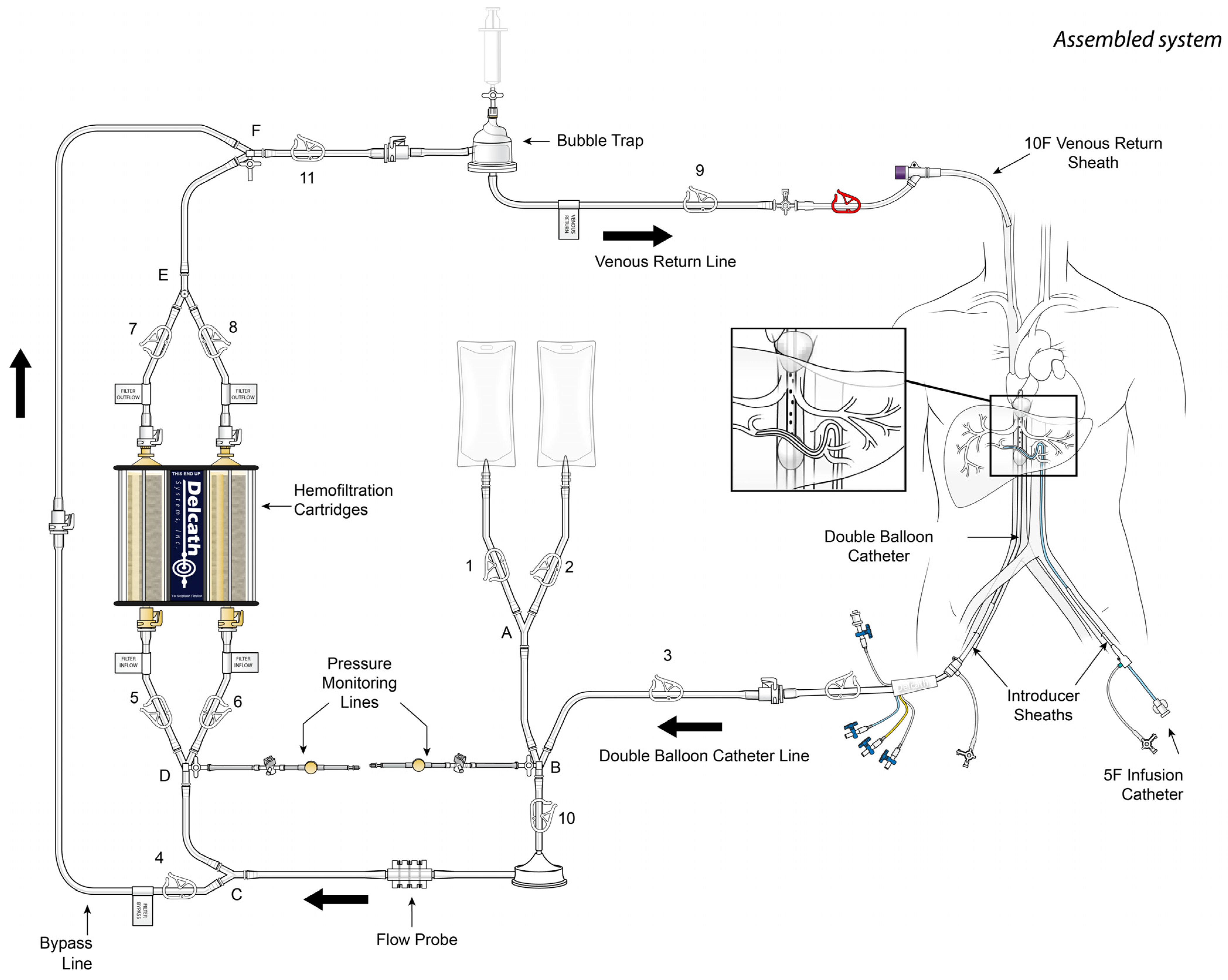
2. Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion
3. Immunoembolization
4. Transarterial Chemoembolization
5. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation
6. Radioembolization
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvajal, R.D.; Schwartz, G.; Tezel, T.; Marr, B.; Francis, J.H.; Nathan, P.D. Metastatic disease from uveal melanoma: Treatment options and future prospects. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 101, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A.B.; Preen, D.B.; McLenachan, S.; Gray, E.S.; Chen, F.K. Incidence and mortality of uveal melanoma in Australia (1982–2014). Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strashilov, S.; Yordanov, A. Aetiology and Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Melanoma: Current Concepts and Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.Z.; Uriel, M.; Porcu, A.; Manos, M.P.; Mercurio, A.C.; Caplan, M.M.; Hulse, L.; Seedor, R.; Holovatska, M.; Francis, J.; et al. Characterizing metastatic uveal melanoma patients who develop symptomatic brain metastases. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 961517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stålhammar, G.; Herrspiegel, C. Long-term relative survival in uveal melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, R.D.; Sacco, J.J.; Jager, M.J.; Eschelman, D.J.; Bagge, R.O.; Harbour, J.W.; Chieng, N.D.; Patel, S.P.; Joshua, A.M.; Piperno-Neumann, S. Advances in the clinical management of uveal melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.S.; Zager, J.; Faries, M.; Alexander, H.R.; Royal, R.E.; Wood, B.; Choi, J.; McCluskey, K.; Whitman, E.; Agarwala, S.; et al. Results of a Randomized Controlled Multicenter Phase III Trial of Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion Compared with Best Available Care for Patients with Melanoma Liver Metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, M.E.; Terai, M.; Eschelman, D.J.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Chervoneva, I.; Shields, J.A.; Shields, C.L.; Yamamoto, A.; Sullivan, K.L.; Laudadio, M.; et al. Double-blinded, randomized phase II study using embolization with or without granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in uveal melanoma with hepatic metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 523–532.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Sullivan, K.; Berd, D.; Mastrangelo, M.; Shields, C.L.; Shields, J.A.; Sato, T. Chemoembolization of the hepatic artery with BCNU for metastatic uveal melanoma: Results of a phase II study. Melanoma Res. 2005, 15, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doussot, A.; Nardin, C.; Takaki, H.; Litchman, T.D.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Postow, M.A.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Kingham, T.P. Liver resection and ablation for metastatic melanoma: A single center experience. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 111, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, C.F.; Eschelman, D.J.; Adamo, R.D.; Anne, P.R.; Orloff, M.M.; Terai, M.; Hage, A.N.; Yi, M.; Chervoneva, I.; Sato, T.; et al. A Prospective Phase II Trial of Radioembolization for Treatment of Uveal Melanoma Hepatic Metastasis. Radiology 2019, 293, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, T.S.; Dieters, J.H.N.; de Leede, E.M.; Geus-Oei, L.D.; Vuijk, J.; Martini, C.H.; Van Erkel, A.R.; Lutjeboer, J.; can der Meer, R.W.; Tijl, F.G.J.; et al. Prospective evaluation of percutaneous hepatic perfusion with melphalan as a treatment for unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, M.J.; Su, J.; Cohen, J.B.; Liu, J.; Serdiuk, A.A.; Stewart, S.R.; Doobay, N.; Duclos, A.; Deal, D.A.; Choi, J.; et al. Over 12 Years Single Institutional Experience Performing Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion for Unresectable Liver Metastases. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 1073274820983019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, K.K.; Zager, J.S. Intra-arterial perfusion-based therapies for regionally metastatic cutaneous and uveal melanoma. Melanoma Manag. 2019, 6, MMT26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingpank, J.F.; Libutti, S.K.; Chang, R.; Wood, B.J.; Neeman, Z.; Kam, A.W.; Figg, W.D.; Zhai, S.; Beresneva, T.; Seidel, G.D.; et al. Phase I study of hepatic arterial melphalan infusion and hepatic venous hemofiltration using percutaneously placed catheters in patients with unresectable hepatic malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3465–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydis, I.; Gangi, A.; Wheater, M.J.; Choi, J.; Wilson, I.; Thomas, K.; Pearce, N.; Takhar, A.; Gupta, S.; Hardman, D.; et al. Percutaneous hepatic perfusion with melphalan in uveal melanoma: A safe and effective treatment modality in an orphan disease. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, J.S.; Orloff, M.M.; Ferrucci, P.F.; Glazer, E.S.; Ejaz, A.; Richtig, E.; Ochsenreither, S.; Lowe, M.C.; Reddy, S.A.; Beasley, G.; et al. FOCUS phase 3 trial results: Percutaneous hepatic perfusion (PHP) with melphalan for patients with ocular melanoma liver metastases (PHP-OCM-301/301A). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, J.S.; Orloff, M.M.; Ferrucci, P.F.; Glazer, E.S.; Ejaz, A.; Richtig, E.; Ochsenreither, S.; Lowe, M.C.; Reddy, S.A.; Beasley, G.; et al. Percutaneous hepatic perfusion (PHP) with melphalan for patients with ocular melanoma liver metastases: Preliminary results of FOCUS (PHP-OCM-301/301A) phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), 9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewald, C.L.A.; Warnke, M.; Bruning, R.; Schneider, M.A.; Wohlmuth, P.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Saborowski, A.; Vogel, A.; Wacker, F.K. Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion (PHP) with Melphalan in Liver-Dominant Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: The German Experience. Cancers 2022, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Khani, A.T.; Ortiz, A.S.; Swaminathan, S. GM-CSF: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 901277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terai, M.; Mastrangleo, M.J.; Sato, T. Immunological aspect of the liver and metastatic uveal melanoma. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017, 3, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Eschelman, D.J.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Terai, M.; Chervoneva, I.; McCue, P.A.; Shields, J.A.; Shields, C.L.; Yamamoto, A.; Berd, D.; et al. Immunoembolization of malignant liver tumors, including uveal melanoma, using granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5436–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Chervoneva, I.; Sullivan, K.L.; Eschelman, D.J.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Mastrangelo, M.J.; Berd, D.; Shields, J.A.; Shields, C.L.; Terai, M.; et al. High-dose immunoembolization: Survival benefit in patients with hepatic metastases from uveal melanoma. Radiology 2009, 252, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffolo, L.I.; Jackson, K.M.; Kuhlers, P.C.; Dale, B.S.; Guilliani, N.M.F.; Ullman, N.A.; Burchard, P.R.; Qin, S.S.; Juviler, P.G.; Keilson, J.M.; et al. GM-CSF drives myelopoiesis, recruitment and polarisation of tumour-associated macrophages in cholangiocarcinoma and systemic blockade facilitates antitumour immunity. Gut 2022, 71, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aedo-Lopez, V.; Gerard, C.L.; Boughdad, S.; Moura, B.G.; Berthod, G.; Digklia, A.; Homickso, K.; Schaefer, N.; Duran, R.; Cuendet, M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Ipilimumab plus Nivolumab and Sequential Selective Internal Radiation Therapy in Hepatic and Extrahepatic Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Y. Recent Advances on Polymeric Beads or Hydrogels as Embolization Agents for Improved Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE). Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Li, H.; Ma, C.; Xiao, Y. Conventional versus drug-eluting beads chemoembolization for infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparison of efficacy and safety. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagari, K.; Pomoni, M.; Kelekis, A.; Pomoni, A.; Dourakis, S.; Spyridopoulos, T.; Moschouris, H.; Emmanouil, E.; Rizos, S.; Kelekis, D. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with BeadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, F.; Duan, M.; Zhang, G. Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) vs. conventional TACE in treating hepatocellular carcinoma patients with multiple conventional TACE treatments history: A comparison of efficacy and safety. Medicine 2019, 98, e15314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavligit, G.M.; Charnsangavej, C.; Carrasco, C.H.; Patt, Y.Z.; Benjamin, R.S.; Wallace, S. Regression of ocular melanoma metastatic to the liver after hepatic arterial chemoembolization with cisplatin and polyvinyl sponge. JAMA 1988, 260, 974–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Johnson, M.M.; Murthy, R.; Ahrar, K.; Wallace, M.J.; Madoff, D.C.; McRae, S.E.; Hicks, M.E.; Rao, S.; Vauthey, J.; et al. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: Variables affecting response rates and survival. Cancer 2005, 104, 1590–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowcroft, A.; Loveday, D.P.T.; Thomson, B.N.J.; Banting, S.; Knowles, B. Systematic review of liver directed therapy for uveal melanoma hepatic metastases. HPB 2020, 22, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonsalves, C.F.; Eschelman, D.J.; Thornburg, B.; Frangos, A.; Sato, T. Uveal Melanoma Metastatic to the Liver: Chemoembolization With 1,3-Bis-(2-Chloroethyl)-1-Nitrosourea. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bedikian, A.Y.; Ahrar, J.; Ensor, J.; Ahrar, K.; Madoff, D.C.; Wallace, M.J.; Murthy, R.; Tam, A.; Hwu, P. Hepatic artery chemoembolization in patients with ocular melanoma metastatic to the liver: Response, survival, and prognostic factors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 33, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, R.; Lindner, M.; Wacker, F.; Krössin, M.; Bechrakis, N.; Foerster, M.H.; Thiel, E.; Keilholz, U.; Schmittel, A. Transarterial chemoembolization of liver metastases from uveal melanoma after failure of systemic therapy: Toxicity and outcome. Melanoma Res. 2010, 20, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, P.E.; Fierlbeck, G.; Pereira, P.; Schanz, S.; Duda, S.H.; Wietholtz, H.; Rozeik, C.; Claussen, C.D. Transarterial chemoembolization of liver metastases in patients with uveal melanoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 74, e38–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatli, S.; Tapan, U.; Morrison, P.R.; Silverman, S.G. Radiofrequency ablation: Technique and clinical applications. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 18, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, J.W.; Prologo, J.D.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A.; Buy, X.; Palussière, J.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.; Genshaft, S.; Abtin, F.; et al. Cryoablation for Palliation of Painful Bone Metastases: The MOTION Multicenter Study. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e200101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagla, S.; Sayed, D.; Smirniotopoulos, J.; Brower, J.; Neal Rutledge, J.; Dick, B.; Carlisle, J.; Lekht, I.; Georgy, B. Multicenter Prospective Clinical Series Evaluating Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Painful Spine Metastases. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, N.; Arai, Y.; Yamakado, K.; Aramaki, T.; Inaba, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Matsui, O.; Miyazaki, M.; Kodama, Y.; Anai, H.; et al. Phase I/II Study of Radiofrequency Ablation for Painful Bone Metastases: Japan Interventional Radiology in Oncology Study Group 0208. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puijk, R.S.; Ruarus, A.H.; Vroomen, L.G.P.H.; van Tilborg, A.A.J.M.; Scheffer, H.J.; Nielsen, K.; de Jong, M.C.; de Vries, J.J.J.; Zonderhuis, B.M.; Eker, H.H.; et al. Colorectal liver metastases: Surgery versus thermal ablation (COLLISION)—A phase III single-blind prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietti Violi, N.; Duran, R.; Guiu, B.; Cercueil, J.P.; Aubé, C.; Digklia, A.; Pache, I.; Deltenre, P.; Knebel, J.F.; Denys, A. Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: A randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosevic, A.; Quesada, R.; Serlavos, C.; Sánchez, J.; Zugazaga, A.; Sierra, A.; Coll, S.; Busto, M.; Aguilar, G.; Flores, D.; et al. Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver malignancies: A randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.-Z.; Li, J.-L.; Xu, K.-C. Percutaneous Cryoablation for Liver Cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2014, 2, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ní Eochagáin, A. Cryoshock following cryoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Anesth. 2022, 77, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P.; Maher, M.M.; O’Connor, O.J. Abdominal ablation techniques. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W495–W502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qu, J.; Lou, M.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Long-term outcomes of percutaneous cryoablation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Hu, K.; Xie, H.; Hu, K.Q.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Multicenter randomized controlled trial of percutaneous cryoablation versus radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombesi, P.; Di Vece, F.; Sartori, S. Resection vs. thermal ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: What’s the first choice? World J. Radiol. 2013, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, O.; Jaberi, A.; Kachura, J.R. Thermal Ablation versus Surgical Resection for the Treatment of Stage T1 Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database Population. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Mao, Y. Recent Advances and Challenges in Uveal Melanoma Immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonsalves, C.F.; Adamo, R.D.; Eschelman, D.J. Locoregional Therapies for the Treatment of Uveal Melanoma Hepatic Metastases. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 37, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derek, E.; Matsuoka, L.; Alexopoulos, S.; Fedenko, A.; Genyk, Y.; Selby, R. Combined surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation as treatment for metastatic ocular melanoma. Surg. Today 2013, 43, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuz, M.; Yazici, P.; Dural, C.; Yigitbas, H.; Okoh, A.; Bucak, E.; McNamara, M.; Singh, A.; Berber, E. Laparoscopic management of liver metastases from uveal melanoma. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 2567–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, P.; Almubarak, M.M.; Kollen, M.; Wagner, M.; Plancher, C.; Audollent, R.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Cassoux, N.; Servois, V. Radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection of liver metastases from uveal melanoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servois, V.; Bouhadiba, T.; Dureau, S.; Da Costa, C.; Almubarak, M.M.; Foucher, R.; Savignoni, A.; Cassoux, N.; Pierron, G.; Mariani, P. Iterative treatment with surgery and radiofrequency ablation of uveal melanoma liver metastasis: Retrospective analysis of a series of very long-term survivors. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozeman, E.A.; Prevoo, W.; Meier, M.A.J.; Sikorska, K.; Van, T.M.; van de Wiel, B.A.; van der Wal, J.E.; Mallo, H.A.; Grijpink-Ongering, L.G.; Broeks, A.; et al. Phase Ib/II trial testing combined radiofrequency ablation and ipilimumab in uveal melanoma (SECIRA-UM). Melanoma Res. 2020, 30, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterbis, E.; Gonalves, C.; Shaw, C.; Orloff, M.; Sato, T.; Eschelman, D.; Adamo, R. 03:45 P.M. Abstract No. 184 Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation for uveal melanoma metastatic to the liver. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Qi, H.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y.; Ma, W.; Song, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, T.; et al. Cryoablation combined with transarterial infusion of pembrolizumab (CATAP) for liver metastases of melanoma: An ambispective, proof-of-concept cohort study. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.P.; Cohalan, C.; Kopek, N.; Enger, S.A. A guide to (90)Y radioembolization and its dosimetry. Phys. Med. 2019, 68, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, K.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Kulik, L.; Riaz, A.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Salem, R. Radioembolization for primary and metastatic liver cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 21, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.S.; Nutting, C.; Jakobs, T.; Cianni, R.; Notarianni, E.; Ofer, A.; Beny, A.; Dezarn, W.A. A first report of radioembolization for hepatic metastases from ocular melanoma. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonsalves, C.F.; Eschelman, D.J.; Sullivan, K.L.; Anne, P.R.; Doyle, L.; Sato, T. Radioembolization as salvage therapy for hepatic metastasis of uveal melanoma: A single-institution experience. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenstein, A.; Haug, A.R.; Zech, C.J.; Schaller, U.C. Radioembolization as locoregional therapy of hepatic metastases in uveal melanoma patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulokas, S.; Mäenpää, H.; Peltola, E.; Kivelä, T.; Vihinen, P.; Virta, A.; Mäkelä, S.; Kallio, R.; Hernberg, M. Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) as treatment for hepatic metastases of uveal melanoma: A Finnish nation-wide retrospective experience. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Irani, Z.; Lawrence, D.; Flaherty, D.; Arellano, R. Combined Effects of Yttrium-90 Transarterial Radioembolization around Immunotherapy for Hepatic Metastases from Uveal Melanoma: A Preliminary Retrospective Case Series. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.O.; Elsayed, M.; Lawson, D.H.; Ermentrout, R.M.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Bercu, Z.L.; Yushak, M.L.; Newsome, J.; Kokabi, N. Predictors of Overall and Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Ocular Melanoma Metastatic to the Liver Undergoing Y90 Radioembolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, D.R.; Kim, K.B.; Tong, R.T.; Wu, M.C.; Kshani-Sabet, M.; Orloff, M.; Eschelman, D.J.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Adamo, R.D.; Anne, P.R.; et al. A Pilot Study of Hepatic Irradiation with Yttrium-90 Microspheres Followed by Immunotherapy with Ipilimumab and Nivolumab for Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2022, 37, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Fine, G.C.; Adema, G.J.; Ahmed, M.; Chapiro, J.; Brok, M.; Duran, R.; Hunt, S.J.; Johnson, D.T.; Ricke, J.; et al. Immunotherapy and the Interventional Oncologist: Challenges and Opportunities-A Society of Interventional Oncology White Paper. Radiology 2019, 292, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Phase | n | Type of Therapy | Comparative Treatment | ORR (%) | Median hPFS (95% CI) | Median OS Months (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hughes et al. [7] | III | 93 | PHP-Mel | BAC | 27.4% | 5.4 | 10.6 |
| Valsecchi et al. [8] | II | 52 | Immunoembolization with GM-CSF | Bland embolization | 21.2% | 3.9 | 21.5 |
| Patel et al. [9] | II | 24 | BCNU-chemoembolization | None | 16.7% | NA | 5.2 |
| Doussot et al. [10] | R * | 48 | Percutaneous ablation with liver resection | Liver resection | N/A | 7.1 | 18 |
| Gonsalves et al. [11] | II | 24 | Y-90 Radioembolization | None | NA | 8.1 | 18.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajan, A.; Fordyce, S.; Sideris, A.; Liou, C.; Toor, Z.; Filtes, J.; Krishnasamy, V.; Ahmad, N.; Reis, S.; Brejt, S.; et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Hepatic Uveal Melanoma Metastases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111836
Sajan A, Fordyce S, Sideris A, Liou C, Toor Z, Filtes J, Krishnasamy V, Ahmad N, Reis S, Brejt S, et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Hepatic Uveal Melanoma Metastases. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(11):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111836
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajan, Abin, Samuel Fordyce, Andrew Sideris, Connie Liou, Zeeshan Toor, John Filtes, Venkatesh Krishnasamy, Noor Ahmad, Stephen Reis, Sidney Brejt, and et al. 2023. "Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Hepatic Uveal Melanoma Metastases" Diagnostics 13, no. 11: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111836
APA StyleSajan, A., Fordyce, S., Sideris, A., Liou, C., Toor, Z., Filtes, J., Krishnasamy, V., Ahmad, N., Reis, S., Brejt, S., Baig, A., Khan, S., Caplan, M., Sperling, D., & Weintraub, J. (2023). Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Hepatic Uveal Melanoma Metastases. Diagnostics, 13(11), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111836







