Blood Slide Image Analysis to Classify WBC Types for Prediction Haematology Based on a Hybrid Model of CNN and Handcrafted Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Improving blood slide images using overlapping average filters and Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE);
- Classification of WBC types by SVM based on hybrid features of VGG19-ResNet101, ResNet101-MobileNet and VGG19-ResNet101-MobileNet;
- Classification of WBC types by FFNN based on hybrid features of CNN (VGG19, ResNet101 and MobileNet) and handcrafted features.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Description of the WBC Type Dataset
3.2. Enhancement Images of Blood Smears for WBC Type
3.3. CNN-SVM Technique
3.3.1. CNN Models for Feature Extraction
3.3.2. SVM Algorithm
3.4. FFNN with Fused CNN and Handcrafted Features
4. Results of Techniques Performance
4.1. Split of WBC Dataset
4.2. System Performance Metrics
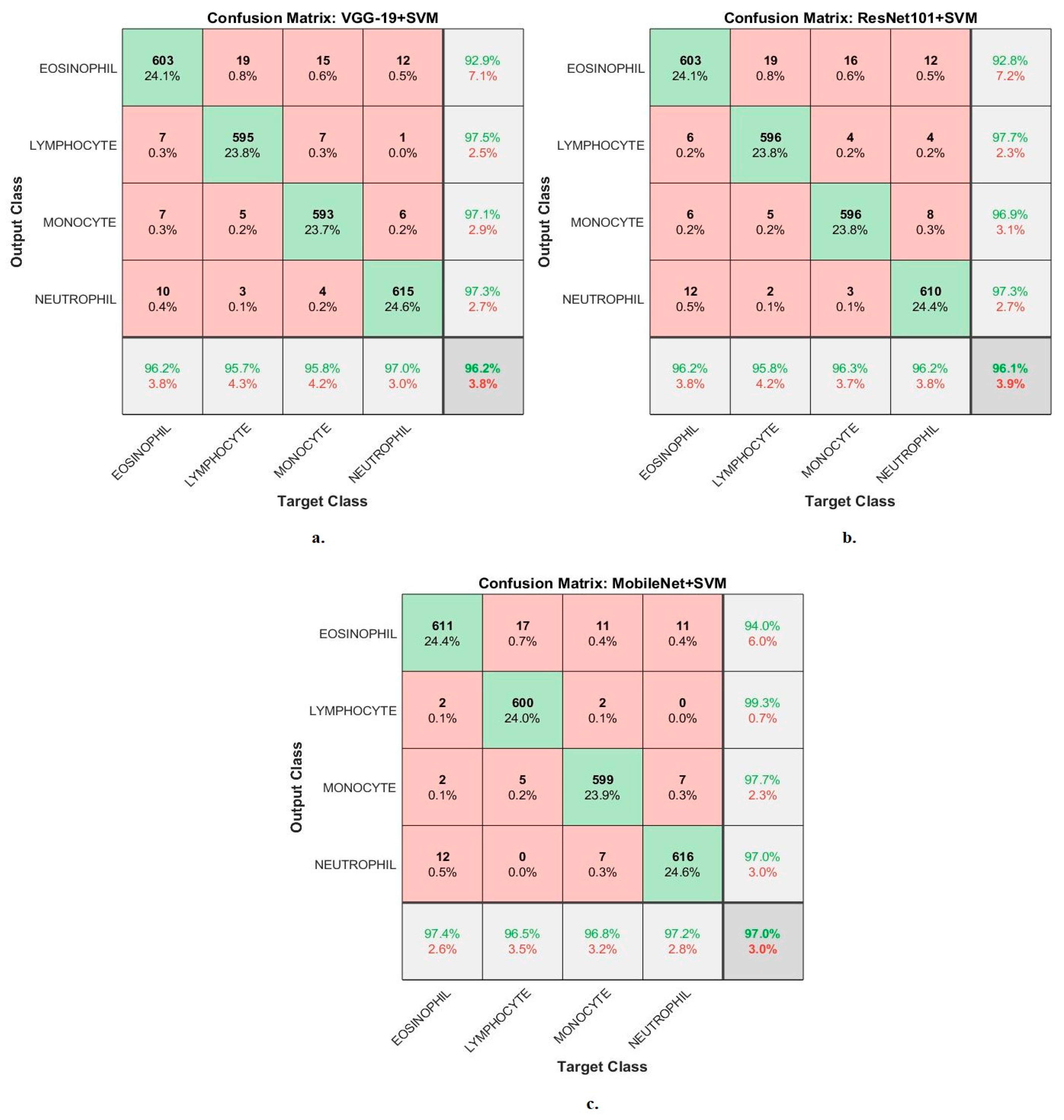
4.3. Results of CNN-SVM Technique
4.4. Results of FFNN with Fused Features of CNN and Handcrafted
4.4.1. Error Histogram
4.4.2. Cross-Entropy
4.4.3. Gradient and Validation Checks
5. Discussion of the Systems Performance for Classifying WBC Types
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blood Cells: A Practical Guide-Barbara, J. Bain-Google Books. Available online: https://books.google.co.in (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Almurayziq, T.S.; Senan, E.M.; Mohammed, B.A.; Al-Mekhlafi, Z.G.; Alshammari, G.; Alshammari, A.; Alturki, M.; Albaker, A. Deep and Hybrid Learning Techniques for Diagnosing Microscopic Blood Samples for Early Detection of White Blood Cell Diseases. Electronics 2023, 12, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, N.; Verma, U.; Nagwanshi, K.K. WBCs-Net: Type identification of white blood cells using convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 81, 42131–42147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M. Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Basophils, Eosinophils. In The Autoimmune Diseases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Haam, J.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Cross-Sectional and Time-Dependent Analyses on Inflammatory Markers following Natural Killer Cell Activity. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopleva, M.V.; Borisova, V.N.; Sokolova, M.V.; Semenenko, T.A.; Suslov, A.P. Recombinant HBsAg of the Wild-Type and the G145R Escape Mutant, included in the New Multivalent Vaccine against Hepatitis B Virus, Dramatically Differ in their Effects on Leukocytes from Healthy Donors In Vitro. Vaccines 2022, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, N.; Pittner, A.; Ramoji, A.; Mondol, A.S.; Dahms, M.; Rüger, J.; Kurzai, O.; Schie, I.W.; Bauer, M.; Popp, J.; et al. Detection and differentiation of bacterial and fungal infection of neutrophils from peripheral blood using Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10560–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouli, A.; Trab, S.S.; Alshaghel, S.; Mouti, M.B.; Hamdoun, H. Congenital nephrotic syndrome as a complication of whooping cough: A case report. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruses, Plagues, and History: Past, Present, and Future-Michael B. A. Oldstone-Google Books. Available online: https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=vRP0DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=HIV,+polio,+tuberculosis,+and+rubeola+decrease+lymphocytes+in+the+blood&ots=wQvEHcEi0z&sig=jXsOA9UWhL2PGtj38kDEpuJjzoA#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Théroude, C.; Reverte, M.; Heinonen, T.; Ciarlo, E.; Schrijver, I.T.; Antonakos, N.; Maillard, N.; Pralong, F.; Le Roy, D.; Roger, T. Trained Immunity Confers Prolonged Protection from Listeriosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Morio, T. Inborn errors of immunity with eosinophilia. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakovic, T.R.; Dolicanin, Z.C.; Babic, G.M.; Djordjevic, N.Z. The Maternal Leucocytes in Thrombophilia and Hypothyroidism and their Influence on Fetal Cells. Serb. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 21, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Sarkar, A.; Bhowmik, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Chakraborty, S. A portable spinning disc for complete blood count (CBC). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 150, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunadi, I.; Senan, E.M. Multi-Method Diagnosis of Blood Microscopic Sample for Early Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on Deep Learning and Hybrid Techniques. Sensors 2022, 22, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyurt, F. A fused CNN model for WBC detection with MRMR feature selection and extreme learning machine. Soft Comput. 2019, 24, 8163–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Patil, M.; Birajdar, G. White Blood Cells Image Classification Using Deep Learning with Canonical Correlation Analysis. IRBM 2020, 42, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydilli, Y.Y.; Atila, Ü. Classification of white blood cells using capsule networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2020, 80, 101699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, H.; Avci, E.; Özyurt, F. White blood cells detection and classification based on regional convolutional neural networks. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 135, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğaçar, M.; Ergen, B.; Cömert, Z. Classification of white blood cells using deep features obtained from Convolutional Neural Network models based on the combination of feature selection methods. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almezhghwi, K.; Serte, S. Improved Classification of White Blood Cells with the Generative Adversarial Network and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippeveld, M.; Knill, C.; Ladlow, E.; Fuller, A.; Michaelis, L.J.; Saeys, Y.; Filby, A.; Peralta, D. Classification of Human White Blood Cells Using Machine Learning for Stain-Free Imaging Flow Cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2019, 97, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlol, A.T.; Kollmannsberger, P.; Ewees, A.A. Efficient Classification of White Blood Cell Leukemia with Improved Swarm Optimization of Deep Features. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chola, C.; Muaad, A.Y.; Bin Heyat, B.; Benifa, J.V.B.; Naji, W.R.; Hemachandran, K.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Samee, N.A.; Al-Antari, M.A.; Kadah, Y.M.; et al. BCNet: A Deep Learning Computer-Aided Diagnosis Framework for Human Peripheral Blood Cell Identification. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, X.; Fan, H.; Lai, T.; Li, Z. WBC-Net: A white blood cell segmentation network based on UNet++ and ResNet. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 107006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, P.P.; Saha, R.; Kim, K.-D. An Automatic Nucleus Segmentation and CNN Model based Classification Method of White Blood Cell. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 149, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Raza, M.; Shah, J.H.; Sharif, M.; Nayak, R.S. Categorizing white blood cells by utilizing deep features of proposed 4B-AdditionNet-based CNN network with ant colony optimization. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3143–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benomar, M.L.; Chikh, A.; Descombes, X.; Benazzouz, M. Multi-feature-based approach for white blood cells segmentation and classification in peripheral blood and bone marrow images. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2021, 35, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydilli, Y.Y.; Atila, U.; Elen, A. Learn from one data set to classify all–A multi-target domain adaptation approach for white blood cell classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105645. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169260720314784 (accessed on 2 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Fast and robust segmentation of white blood cell images by self-supervised learning. Micron 2018, 107, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WBC Multiclass Dataset|Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/alifrahman/main-dataset (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Baig, R.; Rehman, A.; Almuhaimeed, A.; Alzahrani, A.; Rauf, H.T. Detecting Malignant Leukemia Cells Using Microscopic Blood Smear Images: A Deep Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hejri, A.M.; Al-Tam, R.M.; Fazea, M.; Sable, A.H.; Lee, S.; Al-Antari, M.A. ETECADx: Ensemble Self-Attention Transformer Encoder for Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Full-Field Digital X-ray Breast Images. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fati, S.M.; Senan, E.M.; ElHakim, N. Deep and Hybrid Learning Technique for Early Detection of Tuberculosis Based on X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lin, J.-W. Complete Blood Cell Detection and Counting Based on Deep Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tam, R.M.; Al-Hejri, A.M.; Narangale, S.M.; Samee, N.A.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Al-Masni, M.A.; Al-Antari, M.A. A Hybrid Workflow of Residual Convolutional Transformer Encoder for Breast Cancer Classification Using Digital X-ray Mammograms. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senan, E.M.; Jadhav, M.E.; Rassem, T.H.; Aljaloud, A.S.; Mohammed, B.A.; Al-Mekhlafi, Z.G. Early Diagnosis of Brain Tumour MRI Images Using Hybrid Techniques between Deep and Machine Learning. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 8300833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, S.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. Multi-Modal Brain Tumor Detection Using Deep Neural Network and Multiclass SVM. Medicina 2022, 58, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senan, E.M.; Abunadi, I.; Jadhav, M.E.; Fati, S.M. Score and Correlation Coefficient-Based Feature Selection for Predicting Heart Failure Diagnosis by Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 8500314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Marine Oil Spill Detection with X-Band Shipborne Radar Using GLCM, SVM and FCM. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubir, H.; Rguig, M.; El Aroussi, M.; Chehri, A.; Saadane, R. Concrete Bridge Crack Image Classification Using Histograms of Oriented Gradients, Uniform Local Binary Patterns, and Kernel Principal Component Analysis. Electronics 2022, 11, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fang, M.; Kaneko, S. Absent Color Indexing: Histogram-Based Identification Using Major and Minor Colors. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senan, E.M.; E Jadhav, M.; Kadam, A. Classification of PH2 Images for Early Detection of Skin Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Maharashtra, India, 2–4 April 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Lin, C.-W. A Study on Reversible Data Hiding Technique Based on Three-Dimensional Prediction-Error Histogram Modification and a Multilayer Perceptron. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.; Senan, E.M.; Shatnawi, H.S.A.; Alkhraisha, Z.M.; Al-Azzam, M.M.A. Multi-Techniques for Analyzing X-ray Images for Early Detection and Differentiation of Pneumonia and Tuberculosis Based on Hybrid Features. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
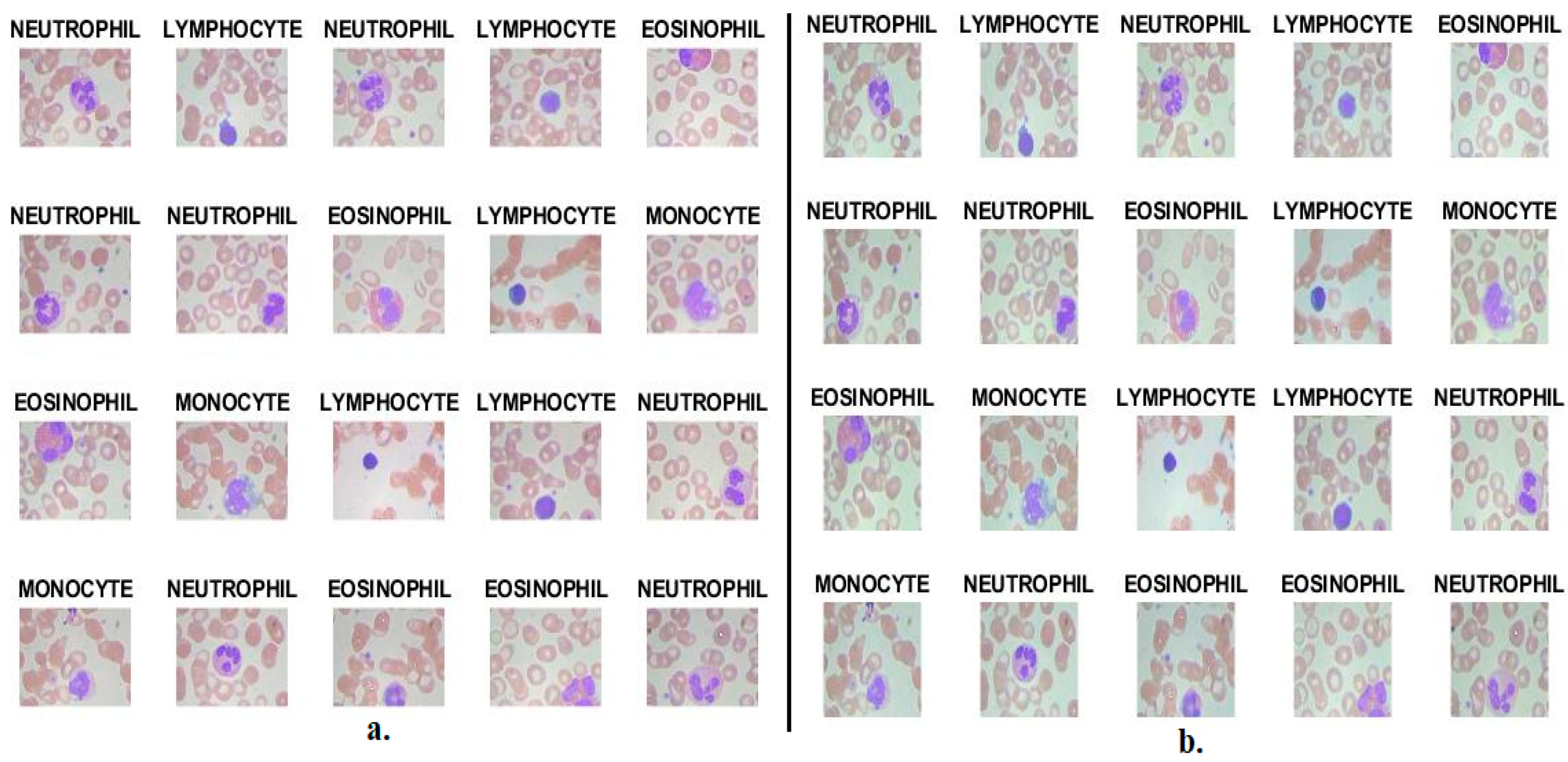















| Phase | 80% (80:20) | Testing 20% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | Training (80%) | Validation (20%) | |
| Eosinophil | 2005 | 501 | 627 |
| Lymphocyte | 1989 | 497 | 622 |
| Monocyte | 1981 | 495 | 619 |
| Neutrophil | 2030 | 507 | 634 |
| Techniques | Classes of WBC | AUC % | Accuracy % | Precision % | Specificity % | Sensitivity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG19-SVM | Eosinophil | 96.4 | 96.2 | 92.9 | 97.6 | 95.8 |
| Lymphocyte | 93.9 | 95.7 | 97.5 | 98.7 | 96.1 | |
| Monocyte | 94.5 | 95.8 | 97.1 | 99.2 | 95.5 | |
| Neutrophil | 96.1 | 97 | 97.3 | 99.4 | 97.2 | |
| average ratio | 95.23 | 96.20 | 96.20 | 98.73 | 96.15 | |
| ResNet101-SVM | Eosinophil | 97.1 | 96.2 | 92.8 | 97.1 | 96.2 |
| Lymphocyte | 96.8 | 95.8 | 97.7 | 98.6 | 96 | |
| Monocyte | 98.2 | 96.3 | 96.9 | 99.2 | 95.8 | |
| Neutrophil | 95.6 | 96.2 | 97.3 | 98.7 | 96.3 | |
| average ratio | 96.93 | 96.10 | 96.18 | 98.40 | 96.08 | |
| MobileNet-SVM | Eosinophil | 98.3 | 97.4 | 93.8 | 98.4 | 97.3 |
| Lymphocyte | 97.9 | 96.5 | 99.3 | 99.5 | 95.8 | |
| Monocyte | 97.5 | 96.8 | 97.7 | 99.2 | 96.8 | |
| Neutrophil | 96.8 | 97.2 | 96.8 | 98.6 | 97.2 | |
| average ratio | 97.63 | 97.00 | 96.90 | 98.93 | 96.78 |
| Techniques | Classes of WBC | AUC % | Accuracy % | Precision % | Specificity % | Sensitivity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG19-ResNet101-SVM | Eosinophil | 98.6 | 97.4 | 95.8 | 98.1 | 97.2 |
| Lymphocyte | 97.9 | 97.7 | 98.5 | 99.6 | 98.4 | |
| Monocyte | 99.1 | 97.7 | 98.5 | 99.8 | 98.1 | |
| Neutrophil | 98.8 | 97.3 | 97.5 | 98.8 | 96.7 | |
| Average ratio | 98.60 | 97.60 | 97.58 | 99.08 | 97.60 | |
| ResNet101-MobileNet-SVM | Eosinophil | 97.9 | 98.4 | 96.9 | 99.1 | 97.7 |
| Lymphocyte | 98.5 | 96.8 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 97.3 | |
| Monocyte | 99.4 | 98.1 | 98.7 | 99.5 | 98.1 | |
| Neutrophil | 99.1 | 99.2 | 97.5 | 98.8 | 99.2 | |
| Average ratio | 98.73 | 98.10 | 98.15 | 99.25 | 98.08 | |
| VGG19-ResNet101-MobileNet-SVM | Eosinophil | 98.5 | 97.8 | 98.8 | 100 | 98.4 |
| Lymphocyte | 98.8 | 98.7 | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.2 | |
| Monocyte | 99.5 | 98.1 | 97.9 | 99.1 | 97.8 | |
| Neutrophil | 98.7 | 98.9 | 97.4 | 99.3 | 98.9 | |
| Average ratio | 98.88 | 98.40 | 98.33 | 99.53 | 98.58 |
| Techniques | Classes of WBC | AUC % | Accuracy % | Precision % | Specificity % | Sensitivity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN-handcrafted features | Eosinophil | 92.5 | 89.8 | 90.4 | 96.8 | 90.4 |
| Lymphocyte | 93.6 | 98.4 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 98.1 | |
| Monocyte | 94.1 | 99 | 97.1 | 98.7 | 99.3 | |
| Neutrophil | 92.8 | 90.7 | 91.4 | 97.2 | 90.8 | |
| Average ratio | 93.25 | 94.40 | 94.45 | 98.05 | 94.65 |
| Techniques | Classes of WBC | AUC % | Accuracy % | Precision % | Specificity % | Sensitivity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN with VGG19-handcrafted | Eosinophil | 99.2 | 99.7 | 99.4 | 99.7 | 99.7 |
| Lymphocyte | 99.6 | 98.9 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 98.8 | |
| Monocyte | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 99.5 | 99.6 | |
| Neutrophil | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.2 | |
| Average ratio | 99.40 | 99.40 | 99.45 | 99.65 | 99.33 | |
| FFNN with ResNet101-handcrafted | Eosinophil | 99.2 | 99.7 | 97.4 | 99.2 | 99.7 |
| Lymphocyte | 99.7 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 98.8 | |
| Monocyte | 99.4 | 98.4 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 98.5 | |
| Neutrophil | 99.6 | 98.7 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.2 | |
| Average ratio | 99.48 | 98.90 | 98.95 | 99.50 | 99.05 | |
| FFNN with MobileNet-handcrafted | Eosinophil | 99.6 | 100 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 100 |
| Lymphocyte | 99.5 | 99.2 | 99.8 | 99.5 | 99.5 | |
| Monocyte | 99.7 | 99.8 | 100 | 99.7 | 99.7 | |
| Neutrophil | 98.9 | 100 | 99.7 | 100 | 99.8 | |
| Average ratio | 99.43 | 99.80 | 99.75 | 99.75 | 99.68 |
| Techniques | Features | Eosinophil | Lymphocyte | Monocyte | Neutrophil | Accuracy % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | VGG19-PCA | 96.2 | 95.7 | 95.8 | 97 | 96.2 | |
| ResNet101-PCA | 96.2 | 95.8 | 96.3 | 96.2 | 96.1 | ||
| MobileNet-PCA | 97.4 | 96.5 | 96.8 | 97.2 | 97 | ||
| Fusion features | VGG19-ResNet101 | 97.4 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.3 | 97.6 | |
| ResNet101-MobileNet | 98.4 | 96.8 | 98.1 | 99.2 | 98.1 | ||
| VGG19-ResNet101-MobileNet | 97.8 | 98.7 | 98.1 | 98.9 | 98.4 | ||
| FFNN | Handcrafted features | 89.8 | 98.4 | 99 | 90.7 | 94.4 | |
| Fusion features | VGG19-hancrafted | 99.7 | 98.9 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.4 | |
| ResNet-101-handcrafted | 99.7 | 98.9 | 98.4 | 98.7 | 98.9 | ||
| MobileNet-handcrafted | 100 | 99.2 | 99.8 | 100 | 99.8 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olayah, F.; Senan, E.M.; Ahmed, I.A.; Awaji, B. Blood Slide Image Analysis to Classify WBC Types for Prediction Haematology Based on a Hybrid Model of CNN and Handcrafted Features. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111899
Olayah F, Senan EM, Ahmed IA, Awaji B. Blood Slide Image Analysis to Classify WBC Types for Prediction Haematology Based on a Hybrid Model of CNN and Handcrafted Features. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(11):1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111899
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlayah, Fekry, Ebrahim Mohammed Senan, Ibrahim Abdulrab Ahmed, and Bakri Awaji. 2023. "Blood Slide Image Analysis to Classify WBC Types for Prediction Haematology Based on a Hybrid Model of CNN and Handcrafted Features" Diagnostics 13, no. 11: 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111899
APA StyleOlayah, F., Senan, E. M., Ahmed, I. A., & Awaji, B. (2023). Blood Slide Image Analysis to Classify WBC Types for Prediction Haematology Based on a Hybrid Model of CNN and Handcrafted Features. Diagnostics, 13(11), 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111899







