Imaging Criteria for the Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Supportive or Mandatory?
Abstract
1. Introduction
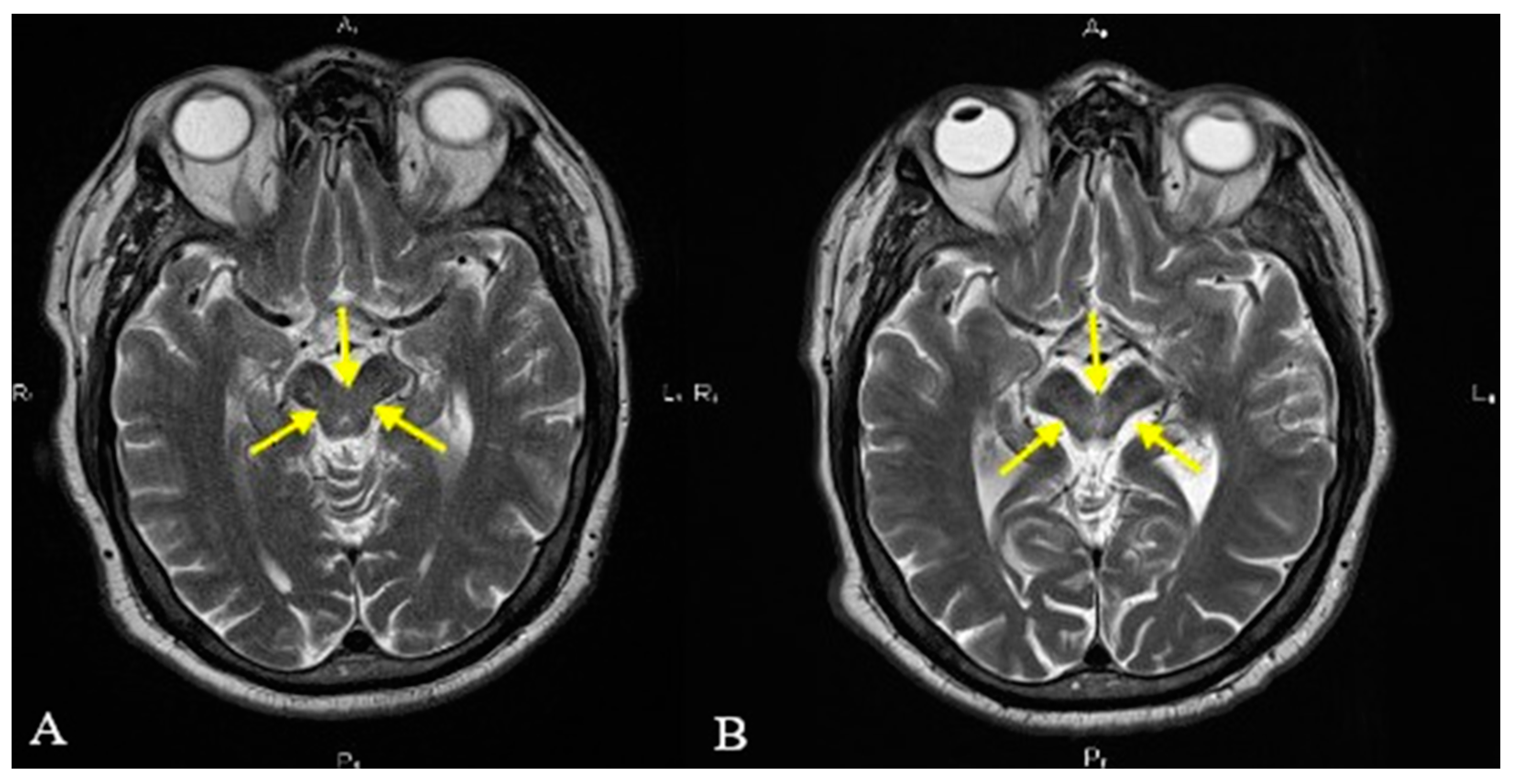
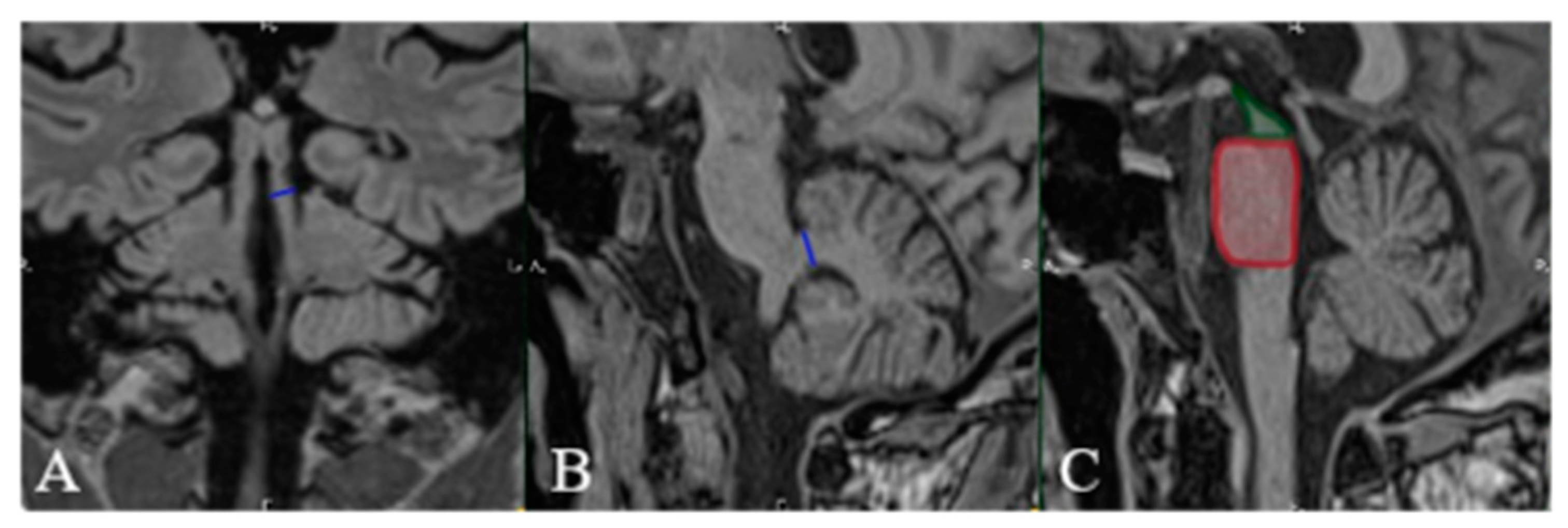
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, H.R.; Martin, A.S.; Joshua, P.K.; Sashank, P. (Eds.) Chapter 38: Degenerative Diseases of the Nervous System. In Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology; McGraw-Hill Educational: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1118–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.R. Chapter 14: Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Degeneration. In Oxford Textbook of Movement Disorders; Burn, D.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-endorsed PSP Study Group. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.B.; Holland, N.; Rittman, T. Progressive supranuclear palsy: Diagnosis and management. Pract. Neurol. 2021, 21, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosetto, P. CT in progressive supranuclear palsy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1987, 8, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonfeld, S.M.; Golbe, L.I.; Sage, J.I.; Safer, J.N.; Duvoisin, R.C. Computed tomographic findings in progressive supranuclear palsy: Correlation with clinical grade. Mov. Disord. 1987, 2, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, H.; Yoshii, F.; Shinohara, Y. Computed tomographic findings in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuroradiology 1987, 29, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Sato, S.; Yuasa, T.; Ito, J.; Miyatake, T. Computed tomographic findings of progressive supranuclear palsy compared with Parkinson’s disease. Jpn. J. Med. 1990, 29, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masucci, E.F.; Borts, F.T.; Smirniotopoulos, J.G.; Kurtzke, J.F.; Schellinger, D. Thin-section CT of midbrain abnormalities in progressive supranuclear palsy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1985, 6, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.J.; Stamelou, M.; Quinn, N.; Bhatia, K.P. Parkinson’s Disease and other Movement Disorders, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Filippi, M.; Agosta, F. Movement disorders: Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonisms. In Oxford Texbook of Neuroimaging; Filippi, M., Kennard, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Yagishita, A.; Oda, M. Progressive supranuclear palsy: MRI and pathological findings. Neuroradiology 1996, 38 (Suppl. S1), S60–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuth-Metz, M.; Naumann, M.; Csoti, I.; Solymosi, L. Measurement of the midbrain diameter on routine magnetic resonance imaging: A simple and accurate method of differentiating between Parkinson disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, A.; Antonini, A.; De Notaris, R.; Bianchini, E.; Meucci, N.; Sacilotto, G.; Canesi, M.; De Gaspari, D.; Triulzi, F.; Pezzoli, G. MR imaging of the superior profile of the midbrain: Differential diagnosis between progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, M.; Kawanami, T.; Ohshima, H.; Sugai, Y.; Hosoya, T. Morning glory sign: A particular MR finding in progressive supranuclear palsy. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2004, 3, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, L.A.; Micallef, C.; Paviour, D.C.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Ling, H.; Williams, D.R.; Kallis, C.; Holton, J.L.; Revesz, T.; Burn, D.; et al. Conventional magnetic resonance imaging in confirmed progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephs, K.A. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurol. Clin. 2007, 25, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, N.; Ray, S. The Hummingbird sign: A diagnostic clue for Steele-Richardson-Olszweski syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr2012006263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, U.; Lang, A.E.; Masellis, M. Neuroimaging Advances in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 572976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: An Update. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Höglinger, G.U.; Antonini, A.; Bordelon, Y.; Boxer, A.L.; Colosimo, C.; van Eimeren, T.; Golbe, L.I.; Kassubek, J.; Kurz, C.; et al. Radiological biomarkers for diagnosis in PSP: Where are we and where do we need to be? Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 955–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Kawanami, T.; Ohshima, F. The “morning glory sign” should be evaluated using thinly sliced axial images. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2007, 6, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, H.; Yagishita, A.; Terada, H.; Barkovich, A.J.; Kutomi, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Furui, S.; Shimizu, T.; Uchigata, M.; Matsumura, K.; et al. New and reliable MRI diagnosis for progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2005, 64, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, L.A.; Jäger, H.R.; Paviour, D.C.; O’sullivan, S.S.; Ling, H.; Williams, D.R.; Kallis, C.; Holton, J.; Revesz, T.; Burn, D.J.; et al. The midbrain to pons ratio: A simple and specific MRI sign of progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2013, 80, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrone, A.; Nicoletti, G.; Messina, D.; Fera, F.; Condino, F.; Pugliese, P.; Lanza, P.; Barone, P.; Morgante, L.; Zappia, M.; et al. MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Radiology 2008, 246, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Arabia, G.; Salsone, M.; Novellino, F.; Giofrè, L.; Paletta, R.; Messina, D.; Nicoletti, G.; Condino, F.; Gallo, O.; et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance parkinsonism index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from probable or possible Parkinson disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, M.; Arabia, G.; Novellino, F.; Salsone, M.; Giofrè, L.; Condino, F.; Messina, D.; Quattrone, A. MRI measurements predict PSP in unclassifiable parkinsonisms: A cohort study. Neurology 2011, 77, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szasz, J.A.; Jianu, D.C.; Simu, M.A.; Constantin, V.A.; Dulamea, A.O.; Onuk, K.; Popescu, D.; Vasile, M.-T.; Popescu, B.O.; Fasano, A.; et al. Characterizing Advanced Parkinson’s Disease: Romanian Subanalysis from the OBSERVE-PD Study. Park. Dis. 2021, 2021, 6635618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picillo, M.; Tepedino, M.F.; Abate, F.; Erro, R.; Ponticorvo, S.; Tartaglione, S.; Volpe, G.; Frosini, D.; Cecchi, P.; Cosottini, M.; et al. Midbrain MRI assessments in progressive supranuclear palsy subtypes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrone, A.; Morelli, M.; Nigro, S.; Quattrone, A.; Vescio, B.; Arabia, G.; Nicoletti, G.; Nisticò, R.; Salsone, M.; Novellino, F.; et al. A new MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy-parkinsonism from Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 54, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrone, A.; Morelli, M.; Vescio, B.; Nigro, S.; Le Piane, E.; Sabatini, U.; Caracciolo, M.; Vescio, V.; Quattrone, A.; Barbagallo, G.; et al. Refining initial diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease after follow-up: A 4-year prospective clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, S.; Arabia, G.; Antonini, A.; Weis, L.; Marcante, A.; Tessitore, A.; Cirillo, M.; Tedeschi, G.; Zanigni, S.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index: Diagnostic accuracy of a fully automated algorithm in comparison with the manual measurement in a large Italian multicentre study in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, E.; Holland, N.; Chelban, V.; Jones, P.S.; Lamb, R.; Rawlinson, C.; Guo, T.; Costantini, A.A.; Tan, M.M.X.; Heslegrave, A.J.; et al. Diagnosis Across the Spectrum of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grijalva, R.M.; Pham, N.T.T.; Huang, Q.; Martin, P.R.; Ali, F.; Clark, H.M.; Duffy, J.R.; Utianski, R.L.; Botha, H.; Machulda, M.M.; et al. Brainstem Biomarkers of Clinical Variant and Pathology in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Tosakulwong, N.; Botha, H.; Ali, F.; Clark, H.M.; Duffy, J.R.; Utianski, R.L.; Stevens, C.A.; Weigand, S.D.; Schwarz, C.G.; et al. Brain volume and flortaucipir analysis of progressive supranuclear palsy clinical variants. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 25, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Calne, D.; Campbell, G.; Dubois, B.; Duvoisin, R.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Golbe, L.I.; Grafman, J.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): Report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ocular motor dysfunction | Vertical gaze palsy (both upward and downward)—O1 |
| Limited adduction of the right eye | |
| Preserved vestibulo-ocular reflex | |
| Postural instability | Absent postural reflex |
| Repeated unprovoked falls within three years—P1 | |
| Akinesia | Bradykinesia |
| Bilateral and axial rigidity | |
| Unresponsive to Levodopa—A2 | |
| Cognitive dysfunction | MMSE = 29/30 points (no cognitive impairment) |
| Author, Year | Age at Presentation | Duration of Disease | Clinical Characteristics | Radiological Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our case report | 54 years old | 3 years |
| Positive “hummingbird” sign. |
| Positive “Mickey mouse” sign. | ||||
| Positive “horning glory” sign. | ||||
| MRPI > 14. | ||||
| Midbrain-to-pons ratio = 0.37. | ||||
| Righini et al., 2004 [14] | 68.88 ± 6.48 years old | 5.3 ± 3.28 years |
| “Hummingbird” sign had 68% sensitivity and 88.8% specificity in discriminating between PSP and PD. |
| Sonthalia et al., 2012 [18] | 75 years old | 2 years |
|
|
| Adachi et al., 2007 [22] | 57 years-old | 2 years |
| “Morning glory” sign was present on slices of 3 mm thickness (but not on conventional slices of 7 mm thickness). |
| Massey et al., 2013 [24] | 69.4 ± 6.5 years old | 4.6 ± 3.1 years |
| Midbrain-to-pons ratio < 0.52 had a 100% specificity for PSP. |
| Picillo et al., 2020 [29] | 70 (52–84) years old | 4 (1–11) years |
|
|
| Quattrone et al., 2019 [31] |
|
|
|
|
| Jabbari et al., 2020 [33] | 70.6 ± 7.3 years old | 4.4 ± 2.7 years |
|
|
| Whitwell et al., 2020 [35] | 70 [66, 74] years old | 6.6 [4.8, 8.5] years |
|
|
| 68 [65, 72] years old | 3.4 [2, 4] years |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupascu, N.; Lupescu, I.C.; Caloianu, I.; Naftanaila, F.; Glogojeanu, R.R.; Sirbu, C.A.; Mitrica, M. Imaging Criteria for the Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Supportive or Mandatory? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111967
Lupascu N, Lupescu IC, Caloianu I, Naftanaila F, Glogojeanu RR, Sirbu CA, Mitrica M. Imaging Criteria for the Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Supportive or Mandatory? Diagnostics. 2023; 13(11):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111967
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupascu, Nicoleta, Ioan Cristian Lupescu, Ionuț Caloianu, Florin Naftanaila, Remus Relu Glogojeanu, Carmen Adella Sirbu, and Marian Mitrica. 2023. "Imaging Criteria for the Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Supportive or Mandatory?" Diagnostics 13, no. 11: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111967
APA StyleLupascu, N., Lupescu, I. C., Caloianu, I., Naftanaila, F., Glogojeanu, R. R., Sirbu, C. A., & Mitrica, M. (2023). Imaging Criteria for the Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Supportive or Mandatory? Diagnostics, 13(11), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111967







