A Systematic Review of the Relationship between Chest CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings and Clinical Parameters in COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
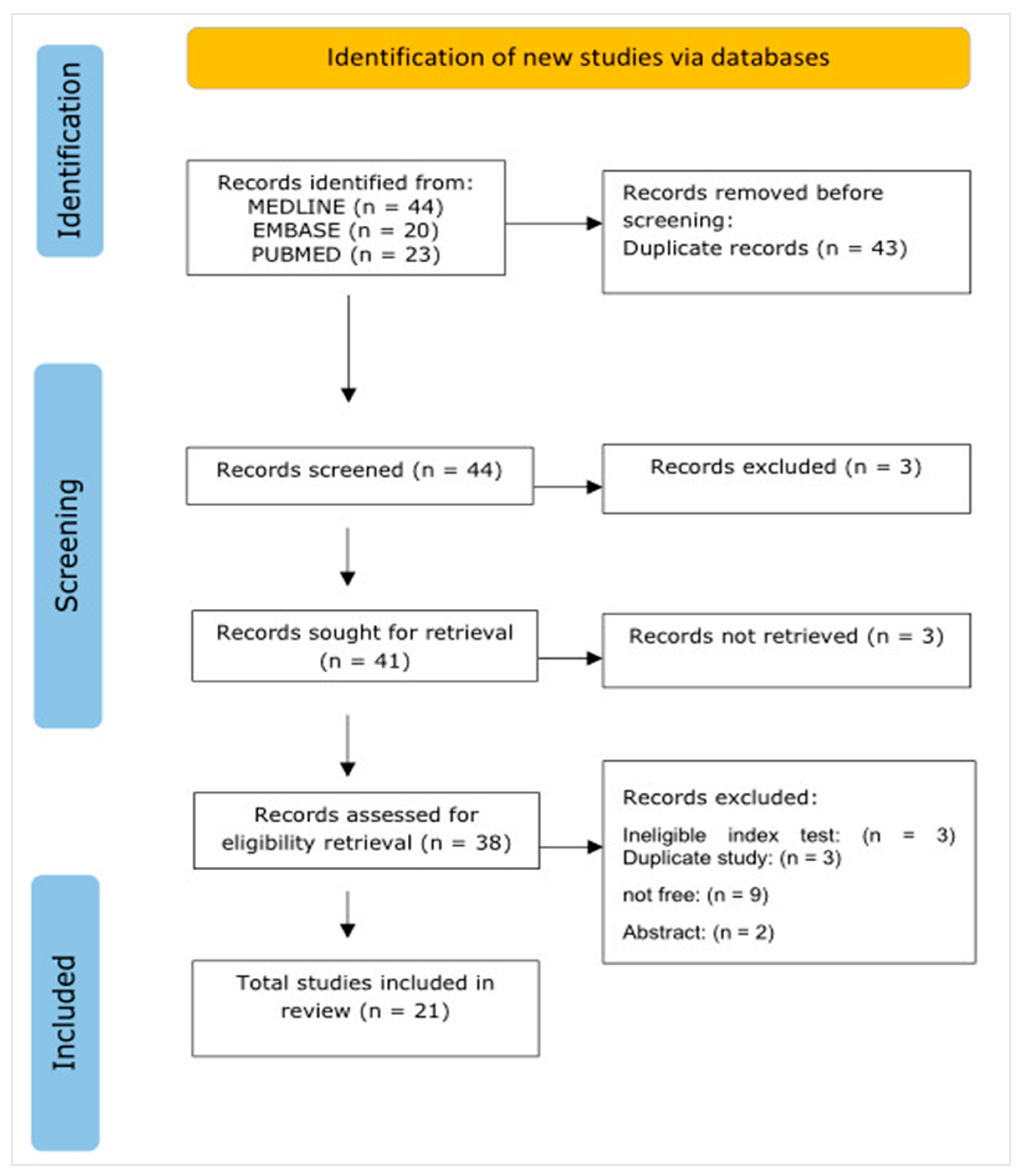
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Studies
3.2.1. Summary of Results Related to the Association between the CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings
3.2.2. Summary of Results Related to the Association between the CT Severity Score and Clinical Parameters
3.3. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Ethical Consideration
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, K.B.; Karade, S.; Sen, S.; Gupta, R.M. SARS-CoV-2: Camazotz’s Curse. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2020, 76, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Geng, D.; Mei, N.; Wu, P.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Jia, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, A.; et al. Cerebral Micro-Structural Changes in COVID-19 Patients—An MRI-based 3-month Follow-up Study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100484. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(20)30228-5/abstract (accessed on 7 April 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brielle, E.S.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Linial, M. The SARS-CoV-2 Exerts a Distinctive Strategy for Interacting with the ACE2 Human Receptor. Viruses 2020, 12, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxi, S.C.; Dailey, G.E.; Hypervitaminosis, A. A cause of hypercalcemia. West. J. Med. 1982, 137, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomo, S.; Karli, S.; Dharmalingam, K.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, P. The Clinical Laboratory: A Key Player in Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19. EJIFCC 2020, 31, 326–346. [Google Scholar]
- Mardani, R.; Vasmehjani, A.A.; Zali, F.; Gholami, A.; Nasab, S.D.M.; Kaghazian, H.; Kaviani, M.; Ahmadi, N. Laboratory Parameters in Detection of COVID-19 Patients with Positive RT-PCR; a Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Geng, S.; Han, B.; Xiao, J.; Wan, Y. Differences between COVID-19 and suspected then confirmed SARS-CoV-2-negative pneumonia: A retrospective study from a single center. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Micco, P.; Russo, V.; Carannante, N.; Imparato, M.; Rodolfi, S.; Cardillo, G.; Lodigiani, C. Clotting Factors in COVID-19: Epidemiological Association and Prognostic Values in Different Clinical Presentations in an Italian Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, X.; Xia, G.; Chen, H.-G.; Chen, F.; Geng, Z.; Xu, L.; Lei, S.; Pan, A.; Wang, L.; et al. Eosinopenia and elevated C-reactive protein facilitate triage of COVID-19 patients in fever clinic: A retrospective case-control study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 23, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Diagnostic utility of clinical laboratory data determinations for patients with the severe COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.-H.; Cai, L.; Cheng, Z.-S.; Cheng, H.; Deng, T.; Fan, Y.-P.; Fang, C.; Huang, D.; Huang, L.-Q.; Huang, Q.; et al. A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version). Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; Zhang, N.; Diao, K.; Lin, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, K.; et al. Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology 2020, 295, 200463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xia, L. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of Chest CT in Diagnosis and Management. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majrashi, N.A.A. The value of chest X-ray and CT severity scoring systems in the diagnosis of COVID-19: A review. Front. Med. 2023, 9. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.1076184 (accessed on 12 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mosawe, A.M.; Mohammed Abdulwahid, H.; Fayadh, N.A.H. Spectrum of CT appearance and CT severity index of COVID-19 pulmonary infection in correlation with age, sex, and PCR test: An Iraqi experience. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francone, M.; Iafrate, F.; Masci, G.M.; Coco, S.; Cilia, F.; Manganaro, L.; Panebianco, V.; Andreoli, C.; Colaiacomo, M.C.; Zingaropoli, M.A.; et al. Chest CT score in COVID-19 patients: Correlation with disease severity and short-term prognosis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6808–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, G.A.; Gaba, W.; Shah, A.; Al Helali, A.A.; Raidullah, E.; Al Ali, A.B.; Elghazali, M.; Ahmed, D.Y.; Al Kaabi, S.G.; Almazrouei, S. Correlation between Chest CT Severity Scores and the Clinical Parameters of Adult Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, e6697677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, A.; Saboo, B. IDF21-0411 Correlation of Chest CT severity score with blood glucose levels in patients with COVID-19. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 186 (Suppl. S1), 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Cau, S.; Babudieri, S.; Perra, R.; Ruzzittu, G.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules 2020, 25, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; De Vito, A.; Scano, V.; Paliogiannis, P.; Fiore, V.; Madeddu, G.; Maida, I.; Zinellu, E.; Mangoni, A.A.; Arru, L.B.; et al. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio on admission is independently associated with prolonged hospitalization in COVID-19 patients. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcari, L.; Ciolina, F.; Cacciotti, L.; Danti, M.; Camastra, G.; Manzo, D.; Musarò, S.; Pironi, B.; Marazzi, G.; Santini, C.; et al. Semiquantitative Chest CT Severity Score Predicts Failure of Noninvasive Positive-Pressure Ventilation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atre, A.L.; Atre, A.; Panchawagh, S.; Khamkar, R.; Chandorkar, A.; Patil, S. Association between Chest CT Severity Scores and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination among COVID-19 patients: A Cross-sectional Study from Pune, India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2022, 16, TC11–TC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanaban, U.B.; Kumar, G.S.; Chundeli, M.I.; Afroze, M.K.H. Clinical Spectrum Of COVID19 Patients Admitting To A Tertiary Care Hospital And Their Outcome Based On Ct Severity Score And Blood Sugar. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Patras, E.; Singhal, A. Correlation of chest CT severity score with clinical parameters in COVID-19 pulmonary disease in a tertiary care hospital in Delhi during the pandemic period. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, T.T.; Rajalakshmi, B.R.; Sadananda, K.S.; Manjunath, C.N. Association of Chest CT Severity Scores and Vaccination Status in COVID-19 Disease: A Cross-sectional Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2022, 16, TC17–TC20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, S.; Maqsood, H.; Sattar, A.; Younas, A.; Shakeel, H.A. A novel chest CT severity score in COVID-19 and its correlation with severity and prognosis of the lung disease: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 82, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wu, L.; Lin, W.; Zhu, L.; Hu, Y.; Lin, G.; Lin, J.; Tu, H. Correlation between chest CT severity score and laboratory indicators in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, C.; Hu, Y.; Lv, W.; Ai, T.; Xia, L. Chest CT imaging features and severity scores as biomarkers for prognostic prediction in patients with COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.; Akhavan, R.; Ghamari Khameneh, A.; Zandi, B.; Farrokh, D.; Pezeshki Rad, M.; Feyzi Laein, A.; Darvish, A.; Bijan, B. Evaluation of the relationship between inpatient COVID-19 mortality and chest CT severity score. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 45, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, J. Even Mild COVID-19 May Change the Brain. JAMA 2022, 327, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz-Ahari, A.; Keyhanian, M.; Mamishi, S.; Mahmoudi, S.; Bastani, E.E.; Asadi, F.; Khaleghi, M. Chest CT severity score: Assessment of COVID-19 severity and short-term prognosis in hospitalized Iranian patients. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2022, 172, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Megid, A.G.I.; El Shabrawy, M.; El-Hamid Mohamed Abdalla, A.A. Correlation between chest CT severity scoring system with oxygen saturation and laboratory inflammatory markers in adult patients with COVID-19 infection. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, D.; De Smet, K.; Herroelen, P.; Gryspeerdt, S.; Martens, G.A. Serum 25(OH)D Level on Hospital Admission Associated With COVID-19 Stage and Mortality. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 155, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk, C.; Zimatore, C.; Mazzinari, G.; Pierrakos, C.; Sivakorn, C.; Dechsanga, J.; Grasso, S.; Beenen, L.; Bos, L.; Paulus, F.; et al. The RALE-score versus the CT Severity Score in Invasively Ventilated COVID-19 patients—A retrospective study comparing their prognostic capacities. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmaciu, I.; Arbănași, E.M.; Kaller, R.; Mureșan, A.V.; Arbănași, E.M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Suciu, B.A.; Cojocaru, I.I.; Runcan, A.I.; Grosu, F.; et al. Chest CT Severity Score and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of the Need for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and of COVID-19 Patients’ Mortality. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padelli, M.; Gueye, P.; Guilloux, D.; Banydeen, R.; Campana, V.; Cabie, A.; Neviere, R. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor levels are predictive of COVID-19 severity in Afro-Caribbean patients. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, A. Correlation of chest CT score with baseline SPO2 on room air and laboratory findings in COVID 19 patients. Respirology 2021, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeed, S.; Faiz, B.Y.; Aslam, S.; Masood, L.; Saeed, R. CT chest severity score for covid 19 pneumonia: A quantitative imaging tool for severity assessment of disease. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2021, 31, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, N.A.; Ghadery, A.H.; Seyedalinaghi, S.A.; Jafari, F.; Jafari, S.; Hasannezad, M.; Koochak, H.E.; Salehi, M.; Manshadi, S.A.D.; Meidani, M.; et al. Predictors of the chest CT score in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional study. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.P.; Surekha, A.; Renuka devi, A.; Nagajyothi, B. Asssessing the Disease Severity in Patiens with Covid19 by Comparing Cycle Threshold Value of Rtpcr and Severity Score of Chest CT scan In A Teritiary Care Hospital. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wu, J.; Wu, F.; Guo, D.; Chen, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, C. The Clinical and Chest CT Features Associated With Severe and Critical COVID-19 Pneumonia. Invest. Radiol. 2020, 55, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J. Relation Between Chest CT Findings and Clinical Conditions of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pneumonia: A Multicenter Study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, A.; Zigliani, A.; Masciullo, R.; Golemi, S.; Maculotti, P.; Farina, D.; Maroldi, R. Radiographic severity index in COVID-19 pneumonia: Relationship to age and sex in 783 Italian patients. Radiol. Med. Torino 2020, 125, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmokadem, A.H.; Mounir, A.M.; Ramadan, Z.A.; Elsedeiq, M.; Saleh, G.A. Comparison of chest CT severity scoring systems for COVID-19. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3501–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, M.C.; Gambini, G.; Savastano, A.; Falsini, B.; De Vico, U.; Sanguinetti, M.; Cattani, P.; Marchetti, S.; Larici, A.R.; Franceschi, F.; et al. Evidence-based of conjunctival COVID-19 positivity: An Italian experience: Gemelli Against COVID Group. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 2886–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Zeng, W. Chest CT Severity Score: An Imaging Tool for Assessing Severe COVID-19. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Study | Inclusion Criteria | Description of Subjects and Setting | Validity of Exposure | Measurement of Condition | Confounding Factors | Strategies of Confounding Factors | Validity of Outcome | Statistical Analysis | Score (Out of 8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinellu et al., 2021 [22] | ☹ | ☺ | ? | ? | ☺ | ☹ | ☹ | ☺ | 3 |
| Padmanaban et al., 2022 [25] | ? | ☹ | ? | ☺ | ? | ☹ | ? | ☺ | 2 |
| Fois et al., 2020 [21] | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Younus et al., 2022 [28] | ☺ | ☺ | ? | ☺ | ? | ☹ | ? | ☺ | 4 |
| Vishwanath et al., 2022 [27] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 8 |
| Lin et al., 2021 [29] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ? | ? | ☺ | ☺ | 5 |
| Smet et al., 2020 [35] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Yazdi et al., 2021 [41] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Abd El Megid et al., 2022 [34] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Arcari et al., 2022 [23] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ? | ? | ☺ | ☺ | 6 |
| Inamdar and Saboo, 2022 [19] | ☹ | ☹ | ? | ? | ? | ? | ☺ | ? | 1 |
| Zhou et al., 2020 [30] | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Valk et al., 2022 [36] | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Abbasi et al., 2021 [31] | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Halmaciu et al., 2022 [37] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ? | ☺ | ☺ | 7 |
| Atre et al., 2022 [24] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 8 |
| Aziz-Alhari et al., 2022 [33] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | 6 |
| Saeed et al., 2021 [18] | ☺ | ☺ | ? | ? | ☹ | ☹ | ☹ | ☺ | 3 |
| Padelli et al., 2021 [38] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 8 |
| Sharma et al., 2022 [26] | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☹ | ☺ | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majrashi, N.A.; Alhulaibi, R.A.; Nammazi, I.H.; Alqasi, M.H.; Alyami, A.S.; Ageeli, W.A.; Abuhadi, N.H.; Kharizy, A.A.; Khormi, A.M.; Ghazwani, M.G.; et al. A Systematic Review of the Relationship between Chest CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings and Clinical Parameters in COVID-19 Pneumonia. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132223
Majrashi NA, Alhulaibi RA, Nammazi IH, Alqasi MH, Alyami AS, Ageeli WA, Abuhadi NH, Kharizy AA, Khormi AM, Ghazwani MG, et al. A Systematic Review of the Relationship between Chest CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings and Clinical Parameters in COVID-19 Pneumonia. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132223
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajrashi, Naif A., Rakan A. Alhulaibi, Ibrahim H. Nammazi, Mohammed H. Alqasi, Ali S. Alyami, Wael A. Ageeli, Nouf H. Abuhadi, Ali A. Kharizy, Abdu M. Khormi, Mohammed G. Ghazwani, and et al. 2023. "A Systematic Review of the Relationship between Chest CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings and Clinical Parameters in COVID-19 Pneumonia" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132223
APA StyleMajrashi, N. A., Alhulaibi, R. A., Nammazi, I. H., Alqasi, M. H., Alyami, A. S., Ageeli, W. A., Abuhadi, N. H., Kharizy, A. A., Khormi, A. M., Ghazwani, M. G., Alqasmi, A. A., & Refaee, T. A. (2023). A Systematic Review of the Relationship between Chest CT Severity Score and Laboratory Findings and Clinical Parameters in COVID-19 Pneumonia. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132223







