Abstract
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) is the second most common malignant neoplasm of the liver. In spite of the increasing incidence worldwide, it is relatively rare in Western countries. IHCC is relatively common in Eastern and Southeastern Asia. Patients with IHCC are usually diagnosed at an advanced stage, therefore, the clinical outcome is dismal. Dysregulation of urea cycle metabolic enzyme expression is found in different types of cancers. Nevertheless, a comprehensive evaluation of genes related to the urea cycle (i.e., GO:0000050) has not been conducted in IHCC. By performing a comparative analysis of gene expression profiles, we specifically examined genes associated with the urea cycle (GO:0000050) in a publicly accessible transcriptomic dataset (GSE26566). Interestingly, CPS1 was identified as the second most prominently down-regulated gene in this context. Tumor tissues of 182 IHCC patients who underwent curative-intent hepatectomy were enrolled. The expression level of CPS1 protein in our IHCC cohort was assessed by immunohistochemical study. Subsequent to that, statistical analyses were carried out to examine the expression of CPS1 in relation to various clinicopathological factors, as well as to assess its impact on survival outcomes. We noticed that lower immunoreactivity of CPS1 in IHCC was associated with tumor progression (pT status) with statistical significance (p = 0.003). CPS1 underexpression was not only negatively correlated to overall survival (OS), disease-specific survival (DSS), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and metastasis-free survival (MeFS) in univariate analysis but also an independent prognosticator to forecast poorer clinical outcome for all prognostic indices (OS, DSS, LRFS and MeFs) in patients with IHCC (all p ≤ 0.001). These results support that CPS1 may play a crucial role in IHCC oncogenesis and tumor progression and serve as a novel prognostic factor and a potential diagnostic and theranostic biomarker.
1. Introduction
Cholangiocarcinomas are primary malignant neoplasms arising in epithelial lining of biliary tracts. They can be divided into extrahepatic and intrahepatic counterparts. The latter is more common than the former. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) is the second most common primary hepatic malignancy after hepatocellular carcinoma [1]. The global incidence is higher in Eastern and Southeastern Asia, especially in Thailand, where 85 per 100,000 cases are diagnosed per year [2]. Due to asymptomatic disease in the early stage and the difficulty of early diagnosis, patients with IHCC are usually diagnosed in advanced disease with no possibility for surgical resection [3]. Since surgical resection with free margin remains the only potential curative therapy, the clinical outcome of IHCC is dismal [4]. The prognosis is still discouraging for patients undergoing curative-intent surgery, with a five-year survival rate of about 20% to 35% [5]. Hence, the search for new targetable treatment for IHCC patients is urgent.
Dysregulation of urea cycle metabolic enzyme expression is found in different types of cancers [6]. Among them, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) is the cardinal enzyme in ureagenesis in consideration of its anabolism in the first and rate-limiting step of the urea cycle [7]. Altered expression of the CPS1 gene and/or CPS1 protein in different malignancies has been investigated recently. Overexpression of CPS1 is found in glioblastoma [8], ovarian carcinoma [9], urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder [10], lung adenocarcinoma [11,12], breast cancer [13] and colorectal cancer [14]. By contrast, CPS1 down-regulation is noted in hepatocellular carcinoma [15], gastric adenocarcinoma [16] and adenocarcinoma of the small intestine [17]. The genes related to the Gene Ontology term urea cycle (GO:0000050) have not been systemically evaluated in IHCC. By analysis of the open-access transcriptomic gene expression data of IHCC (GSE26566) from the Gene Expression Omnibus, National Center for Biotechnology Information (GEO, NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA), we found that CPS1 mRNA is one of the most significantly down-regulated genes involved in the urea cycle (GO:0000050). However, there has been no systemic investigation of CPS1 expression and its clinical significance and prognostic value in IHCC. Therefore, we conducted the current study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles from Publicly Accessible Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Database
The transcriptomic profiles by array of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) (GSE26566) including 104 surgically resected IHCC and matched adjacent hepatic tissues from 59 patients from the Gene Expression Omnibus, National Center for Biotechnology Information (GEO, NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA) [18] were downloaded for analysis. The downloaded raw data were evaluated by comparative analysis by GeneChip™ Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). We focused on the transcriptomic levels of genes related to Gene Ontology term urea cycle (GO:0000050). The expression degree of genes was computed by probe combinations, which were settled without preselection or filtering. Following that, genes meeting the criteria of a p-value less than 0.01 and a log2-transformed expression fold change greater than ±0.2 were chosen for subsequent analysis.
2.2. Study Cohort of Patients, Tumor Tissue Samples and Histopathological Evaluation
Between 1990 to 2010, adequate paraffin-embedded tissue blocks from 182 patients diagnosed with IHCCs at Chi Mei Medical Center and undergoing surgical resection were collected. All patients were surgically resectable whilst those with distant metastasis at diagnosis were excluded from the study. All patients were subject to regular clinical follow-up after surgery, with monitoring continuing until either their death or their last appointment. The tissue sections from the blocks were routinely stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The important pathological parameters, such as surgical margins, vascular invasion, histopathological variants and grading, were re-evaluated by a pathologist (I.-W.C.). The histopathological grade and subtypes were evaluated according to the latest edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Digestive System Tumors [19]. Approvals were authorized by the Institutional Review Board of Chi Mei Medical Center (IRB09912003) and Joint Institutional Review Board of Taipei Medical University (N202304035).
2.3. Immunohistochemical Study and Interpretation
To assess the expression of the CPS1 protein, immunohistochemistry (IHC) was conducted using surgically resected formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks. The procedure involved cutting 4 μm sections from the blocks and placing them onto pre-coated glass slides. Deparaffinization of the slides was carried out using xylene, followed by rehydration with ethanol. Antigen retrieval was performed by heating the sections in a 10 mM citrate buffer (pH = 6) for 7 min using a microwave. Endogenous peroxidases were blocked using 3% H2O2. Subsequently, the slides were washed with TRIS-buffered saline (TBS) for 15 min and incubated with a primary antibody against CPS1 (rabbit polyclonal, dilution 1:500, Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA). The cytoplasmic immunoreactivity of CPS1 was evaluated using the H-score, calculated using the following equation: H-score = ΣPi (i + 1), where i represents the intensity of the stained tumor cells (ranging from 0 to 3+) and Pi represents the percentage of cytoplasmic immunoreactivity in tumor cells at different intensities. Low CPS1 expression was defined as having an H-score below the median of all scored cases.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The association between CPS1 expression and various clinicopathological features was assessed using Pearson’s chi-squared (χ2) test. Survival analysis, including overall survival (OS), disease-specific survival (DSS), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and metastasis-free survival (MeFS), was conducted using Kaplan–Meier plots. Univariate survival analyses were compared using log-rank tests. For the multivariate analysis, a Cox proportional hazards model was employed to identify independent prognostic factors. Statistical significance was defined as a p-value less than 0.05 using two-sided tests. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Result
3.1. Urea Cycle-Associated Gene CPS1 Is Significantly Down-Regulated in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas Compared with Non-Cancerous Counterparts
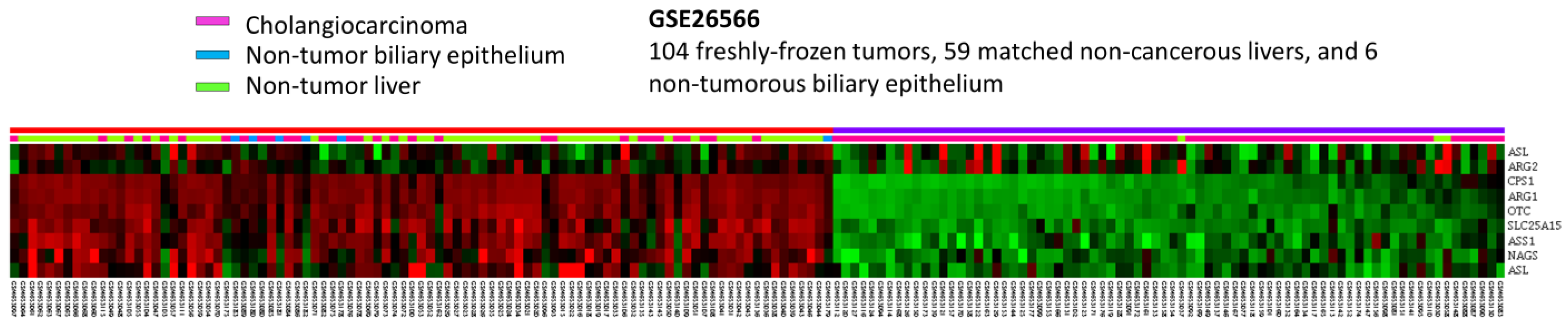
To develop the potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for IHCC patients, the public intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC) transcriptomic dataset (GSE26566) from GEO, NCBI, comprising 104 IHCC cancer tissues, 59 non-tumorous hepatic tissues and 9 normal intrahepatic bile duct tissues, was downloaded. By data mining and focus on genes linked to Gene Ontology term urea cycle (GO:0000050), ten probes covering eight mRNA transcripts were identified (Figure 1). As shown in Figure 1 and Table 1, by comparing IHCC to non-tumorous hepatic tissues, seven mRNA transcripts are significantly down-regulated, including ARG1, CPS1, OTC, SLC25A15, ASS1, ASL and NAGS genes (p ≤ 0.036). By comparing IHCC to normal intrahepatic bile duct tissues, four transcripts are significantly down-regulated, including ARG1, CPS1, OTC and SLC25A15 genes (p ≤ 0.0014). Among them, ARG1 and CPS1 genes exhibit the most significant down-regulation, whose log2 ratios by comparison between IHCC and non-tumor, as well as IHCC and normal bile duct, are −4.0505 and −2.9184 (p ≤ 0.0001) and −3.9435 and −2.8787 (p ≤ 0.0002), respectively. Taken together, these findings demonstrated that ARG1 and CPS1 gene alterations might play an essential role in IHCC cancer progression. However, the expression level and prognostic value of ARG1 in IHCC have been comprehensively evaluated [20]. In addition, arginase-1, encoded by the ARG1 gene, is also considered as a sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker of normal cells and benign and malignant neoplasms derived from hepatocytes [21]. Therefore, we focused on the expression of CPS1.
Figure 1.
Analysis of gene expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by utilizing a previous publicly accessible transcriptomic dataset (GSE26566). Through a clustering analysis of genes specifically associated with the urea cycle (GO:0000050), it was observed that CPS1 is among the genes exhibiting the most significant down-regulation in cholangiocarcinoma when compared to non-tumor tissue. The heat map depicts cholangiocarcinoma (represented in pink), normal biliary epithelium (represented in blue) and normal liver (represented in green) at the top. The degree of up-regulation and down-regulation of gene expression is depicted by varying shades of red and green, respectively, with unchanged transcriptional levels indicated in black.

Table 1.
Summary of the alterations of genes associated with urea cycle (GO:0000050) in cholangiocarcinoma (GSE26566).
3.2. CPS1 Expression and the Associations with Clinical and Pathological Variables of Cholangiocarcinoma Patients
The aforementioned data suggested that low expression of CPS1 may be interrelated with carcinogenesis and tumor progression of IHCC. Accordingly, the correlation between CPS1 expression and the clinical and pathological features of IHCC patients was further scrutinized. The details of our patient cohort are revealed in Table 2. In total, we collected 182 cases of patients with primary localized IHCC, and 108 were male and 74 were female (M:F = 59.3%:40.7%), of which 41.2% patients (n = 75) were over 65 years old and 58.8% patients (n = 107) were younger than 65 years. Eighty patients (44.0%) had intrahepatic cholelithiasis. The resection margins of 19 IHCCs were positive (R1 resection, 10.4%). Histopathologically, the majority (57.7%, n = 105) were large duct type, while 42.3% of cases (n = 77) were small duct type. Sixty-one cases (33.5%) were grade 1 (well differentiated), sixty-six (36.3%) were grade 2 (moderately differentiated) and fifty-five (30.2%) were grade 3 (poorly differentiated). Furthermore, we analyzed clinicopathological parameters and found that lower expression of CPS1 in IHCCs was prominently related to more advanced primary tumor (pT1, pT2 and pT3) with statistical significance (Figure 2, p = 0.003). On the other hand, the expression of CPS1 was not significantly associated with gender, age, types of hepatitis, intrahepatic stones, surgical margins and histological variants and grading.

Table 2.
Correlations between CPS1 expression and other important clinicopathological parameters in primary localized IHCC.
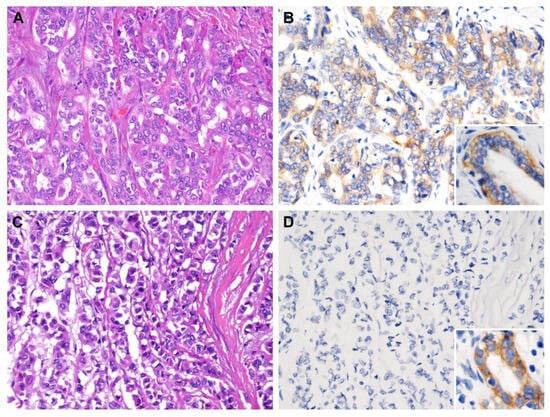
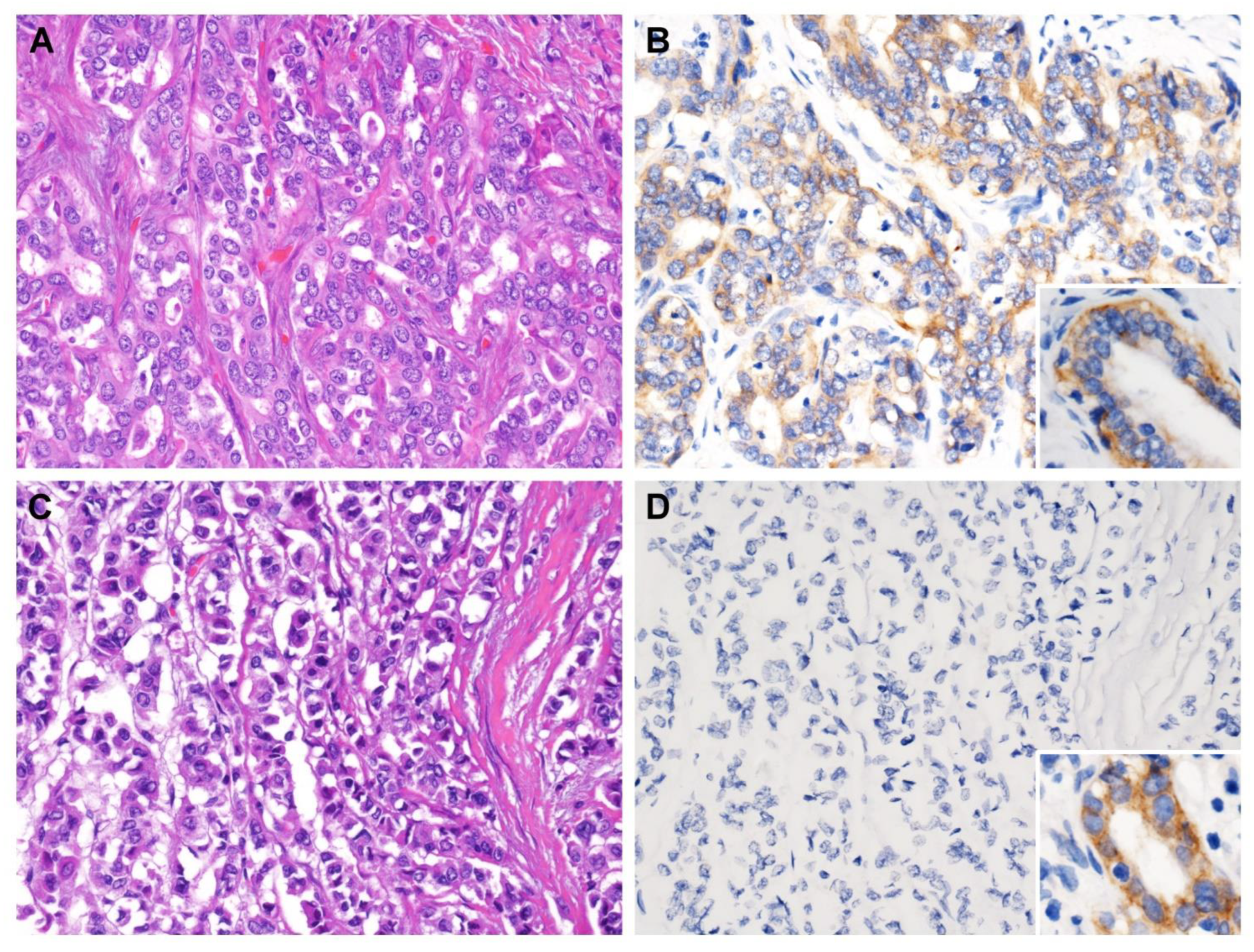
Figure 2.
CPS1 immunostaining of representative sections. (A) Solitary tumor without vascular invasion (pT1) exhibited (B) strong cytoplasmic immunoreactivity, while (C) tumor with visceral peritoneum perforation (pT3) was (D) negative for CPS1 immunostain. Note the strong expression in normal biliary epithelium (inset). ((A,C) hematoxylin and eosin stain, magnification 200×; (B,D) CPS1 immunostain, magnification 200×).
3.3. Survival Analyses for Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
The survival analyses are presented in Table 3 and Table 4. In the univariate log-rank test, male patients had better overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) compared to female patients (p = 0.0254 and 0.0072, respectively). Free surgical margin after hepatectomy (R0 resection) and less-advanced cancer disease (pT status) were positively linked to longer overall survival (OS), disease-specific survival (DSS), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and metastasis-free survival (MeFS) intervals (all p ≤ 0.0001). Small duct type and lower histological grade were significantly associated with improved LRFS rate (p = 0.0085 and 0.0299, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, only surgical margin was an independent prognostic factor for all survival indices, i.e., OS (relative risk = 3.013, 95% confidence interval = 1.517–5.985, p = 0.002), DSS (RR = 5.639, 95% CI = 2.472–12.863, p < 0.001), LRFS (RR = 4.209, 95% CI = 2.122–8.348, p < 0.001) and MeFS (RR = 3.034, 95% CI = 1.470–6.260, p = 0.003). Extension of primary tumor (pT status) was an independent indicator for DSS, LRFS and MeFS (p = 0.016, 0.041 and 0.032, respectively) but not OS (p = 0.055).

Table 3.
Univariate log-rank and multivariate analyses for overall and disease-specific survivals in primary localized IHCC.

Table 4.
Univariate log-rank and multivariate analyses for local recurrence-free and metastasis-free survivals in primary localized IHCC.
3.4. CPS1 Expression as an Independent Prognosticator in Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
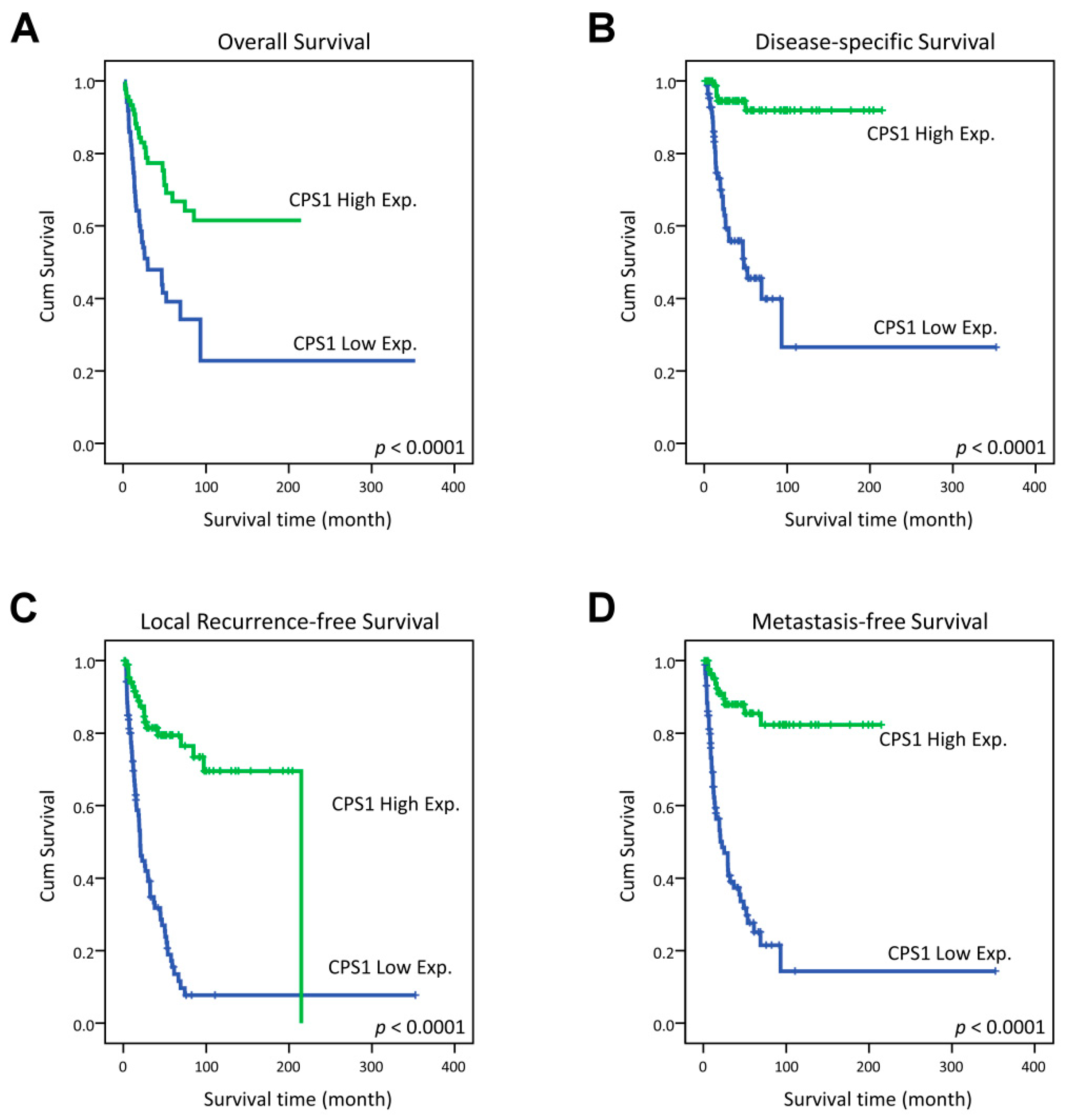
In the univariate analysis, CPS1 underexpression was significantly linked to poorer clinical outcome of all survival indices, including OS, DSS, LRFS and MeFS (all p < 0.0001, Figure 3). Remarkably, low expression of CPS1 even independently predicted adverse OS (relative risk = 2.378, 95% confidence interval = 1.424–3.971, p = 0.001), DSS (RR = 9.957, 95% CI = 3.817–25.975, p < 0.001), LRFS (RR = 5.519, 95% CI = 3.214–9.477, p < 0.001) and MeFS (RR = 7.417, 95% CI = 3.814–14.422, p < 0.001) in multivariate analysis (Table 3 and Table 4).
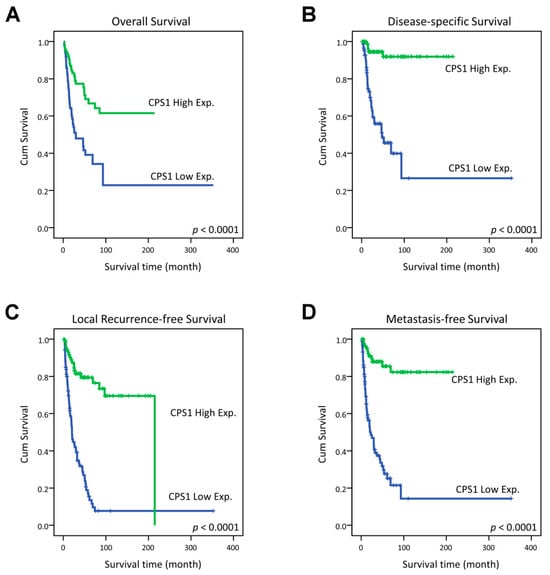
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier estimator demonstrated the significantly poorer clinical outcomes, including (A) overall survival (OS), (B) disease-specific survival (DSS), (C) local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and (D) distant metastasis-free survival (MeFS) in relation to the low expression of CPS1 (all p < 0.0001).
4. Discussion
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IHCC), also known as bile duct carcinoma, is the second most common primary cancer of the liver. It accounts for about 10–15% of primary hepatic malignancies [22]. It is relatively rare in Western countries, however, it is more common in Southeastern Asia owing to endemic liver fluke infection, e.g., Opisthorchis viverrini [23]. Histologically, it is divided into two main subtypes: large duct and small duct types [24]. The risk factors differ between these two subtypes. Large duct IHCC exhibits similar risk factors to extrahepatic and perihilar cholangiocarcinoma, including liver fluke infection, biliary lithiasis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, Caroli disease, etc., while small duct IHCC shares the same risk factors as hepatocellular carcinoma, such as chronic hepatitis B and C, alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, as well as non-biliary cirrhosis [25]. Generally, both large duct and small duct types of IHCC are associated with chronic inflammation of the biliary tree and cholestasis [26]. In spite of the improvement of treatment modality, the prognosis of IHCC is still dismal [27]. Five-year survival rate and overall survival after surgical excision range from 15% to 40% for resectable cases [27]. Accordingly, the search for new targetable treatment for IHCC patients is critical.
The urea cycle, also called the ornithine cycle, was first discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit in 1932 [28,29,30]. Ordinarily, the urea cycle primarily takes place in the liver [31]. It is a critical biochemical reaction for mammals to convert highly toxic ammonia to urea for elimination and also the principal route to excrete excess nitrogen in ureotelic animals, including humans. Urea cycle dysregulation is commonly found in different cancer types. In contrast with nitrogen disposal in normal hepatocytes, cancer cells tend to redirect urea cycle intermediates to anabolic pathways. An aberrance results in reduced production of nitrogen waste and increased alteration of carbon and nitrogen biosynthesis to fulfill nutrition demand of cancer cells and their growth [6]. Abnormal utilization of nitrogen in cancer cells also leads to increased synthesis of pyrimidine and subsequent nucleotide pool imbalance and transversion mutations [32].
There are six enzymes involved in the urea cycle, including carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1), N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS), ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC), argininosuccinate synthase (ASS1), argininosuccinate lyase (ASL) and arginase-1 (ARG1). Among them, CPS1 administers the first step and the rate-limiting reaction of the urea cycle. CPS1 catalyzes transfer of ammonia to phosphorylated bicarbonate with the production of carbamoyl phosphate [33]. Afterward, carbamoyl phosphate enters the urea cycle. Normally, the enzyme CPS1 is predominantly located in the mitochondria of the hepatocytes and is also detected in the mucosa of the small bowel [34]. Diseases associated with genetic alteration of the CPS1 gene have been discovered. For example, germline mutation of the CPS1 gene causes CPS1 deficiency, a rare lethal urea cycle disorder with autosomal recessive inheritance, causing the death of newborns owing to hyperammonemia [35].
There has been increasing evidence that CPS1 is involved in tumorigenesis. In 2002, Kinoshita et al. firstly identified a down-regulated transcriptomic level of the CPS1 gene in 15 out of 20 (75%) human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues compared with adjacent non-cancerous hepatitis tissues [15]. After that, Cao et al. also discovered that CPS1 was significantly underexpressed in HCCs with macrovascular invasion by an iTRAQ-based proteomic study [36]. The mechanism of dysregulated CPS1 in HCCs may contribute to hypermethylation of the two CpG sites of the promoter of the CPS1 gene [37]. In the study of gastric carcinogenesis by Fang et al., the immunoreactivity of CPS1 protein reveals gradually lower expression from intestinal metaplasia, low-grade dysplasia and high-grade dysplasia to intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma [16]. In the same research, lower expression of CPS1 was also significantly associated with unfavorable overall survival in both univariate and multivariate analyses [16]. Similarly, we identified CPS1 as one of the highly down-regulated genes associated with the Gene Ontology term “urea cycle” (GO:0000050) by analysis of the open-access transcriptomic gene expression data of IHCC (GSE26566). Lower immunoreactivity of CPS1 in IHCC was associated with tumor progression (pT status) with statistical significance (p = 0.003) in the current study. Furthermore, CPS1 underexpression was not only negatively correlated to overall survival (OS), disease-specific survival (DSS), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and metastasis-free survival (MeFS) in univariate analysis but also an independent prognosticator to forecast poorer clinical outcome for all prognostic indices (OS, DSS, LRFS and MeFs) in patients with IHCC (all p ≤ 0.001). Conversely, up-regulation of the CPS1 gene and overexpression of CPS1 protein are described in glioblastoma and carcinomas of the urinary bladder, ovary, lung and colon [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Overexpression of CPS1 is usually associated with adverse clinical outcome in patients with these cancer types. The discrepancies of CPS1 expression between two groups of cancers may be due to different mechanisms in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. In the former cancers, the low expression of CPS1 leads to exaggerated production of ammonia, which may result in reactive oxygen species (ROS) creation, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and hyperactivation of the AMPK–fatty acid oxidation (FAO)–forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) axis. Finally, fatty acid oxidation (FAO) supplies plentiful ATP for cancer cell proliferation [38]. In the latter cancer cells, overexpression of CPS1 increases nucleotide synthesis, as well as increases the pyrimidine to purine ratio, which may induce progression of the S phase of the cell cycle [11,39].
Over the past few years, a significant number of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been discovered as essential contributors to the progression of different cancers, including IHCC [40]. In 2015, Ma et al. observed that the CPS1 transcript and its long non-coding RNA, CPS1 intronic transcript 1 (CPS1-IT1), were co-up-regulated in IHCC tissue from 31 patients compared with paired non-tumorous tissues, as well as in an IHCC cell line (ICC-9810) compared with a human fetal hepatocyte line (L-02) [41]. In addition, the authors addressed that 4-fold/5-fold up-regulation of the CPS1 transcript in IHCCs compared with benign counterparts was significantly correlated to worse disease-free survival and overall survival by a univariate log-rank test (p = 0.034 and 0.032, respectively) [41]. However, the difference in ΔCt values of CPS1 mRNA was not significantly lower in patients’ IHCC tissue (p = 0.09) and the IHCC cell line (p = 0.05). Moreover, multivariate survival analysis was not performed in that study. The divergent results of the investigation of Ma et al. compared to the current study may also have arisen from the intricate transcription and translation processes, leading to variations in mRNA and protein expression levels.
Small-molecule inhibitors of CPS1 have been discovered recently [42,43]. In the initial stage of carbamoyl phosphate synthesis, small-molecule inhibitors of CPS1 bind to an allosteric pocket, effectively inhibiting ATP hydrolysis. These CPS1 inhibitors have demonstrated activity in cellular assays by blocking both urea synthesis and the support provided by CPS1 to the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway [42]. These discoveries suggest potential theranostic implications of small-molecule compounds targeting CPS1.
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, the current study is the first one systemically evaluating the relationship between CPS1 expression and the important clinicopathological parameters and clinical outcomes in a large intrahepatic cholagiocarcinoma (IHCC) patient cohort. We mined the public-access transcriptomic database and identified CPS1 as one of the most significant down-regulated genes in IHCCs compared with normal counterparts. Furthermore, we recognized that underexpression of CPS1, the rate-limiting enzyme that regulates the first reaction of the urea cycle, was not only significantly associated with tumor progression (pT status) of IHCC but also an independent prognosticator predicting lower overall survival (OS), disease-specific survival (DSS), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS) and metastasis-free survival (MeFS) rate in patients with IHCC. It may serve as a novel prognostic factor and potential theranostic biomarker for patients with IHCC. Further investigations to clarify the complete molecular mechanisms of CPS1 in the oncogenesis of IHCC are obligatory for developing a promising CPS1-targeting therapy for high-risk patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.-W.C.; Methodology, Y.-L.S. and I.-W.C.; Formal Analysis, Y.-Y.H., D.-P.S. and S.K.-H.H.; Resources, K.H.O., Y.-F.T. and C.-L.C.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, K.H.O. and K.J.; Writing—Review and Editing, Y.-Y.H. and I.-W.C.; Supervision, I.-W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chi Mei Medical Center (IRB09912003) and Joint Institutional Review Board of Taipei Medical University (N202304035, 25 April 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to anonymized samples from Biobank.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Antwi, S.O.; Mousa, O.Y.; Patel, T. Racial, Ethnic, and Age Disparities in Incidence and Survival of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in the United States; 1995–2014. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.C.; Coburn, N.G.; Baxter, N.N.; Kiss, A.; Law, C.H. Surgical management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma--a population-based study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaib, Y.; El-Serag, H.B. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavros, M.N.; Economopoulos, K.P.; Alexiou, V.G.; Pawlik, T.M. Treatment and Prognosis for Patients With Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshet, R.; Szlosarek, P.; Carracedo, A.; Erez, A. Rewiring urea cycle metabolism in cancer to support anabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.I.; Perez-Arellano, I.; Pekkala, S.; Barcelona, B.; Cervera, J. Genetic, structural and biochemical basis of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 101, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Ou, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z. Expression and clinical significance of CPS1 in glioblastoma multiforme. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2019, 67, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seborova, K.; Kloudova-Spalenkova, A.; Koucka, K.; Holy, P.; Ehrlichova, M.; Wang, C.; Ojima, I.; Voleska, I.; Daniel, P.; Balusikova, K.; et al. The Role of TRIP6, ABCC3 and CPS1 Expression in Resistance of Ovarian Cancer to Taxanes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Bi, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, C. Caspase recruitment domain family member 10 regulates carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 and promotes cancer growth in bladder cancer cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 8128–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celiktas, M.; Tanaka, I.; Tripathi, S.C.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Aguilar-Bonavides, C.; Villalobos, P.; Delgado, O.; Dhillon, D.; Dennison, J.B.; Ostrin, E.J.; et al. Role of CPS1 in Cell Growth, Metabolism and Prognosis in LKB1-Inactivated Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Ou, C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; et al. CPS1 expression and its prognostic significance in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, P.; Halada, P.; Jelinek, M.; Balusikova, K.; Kovar, J. Differentially Expressed Mitochondrial Proteins in Human MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells Resistant to Paclitaxel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniappan, A.; Ramar, K.; Ramalingam, S. Computational Identification of Novel Stage-Specific Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, M.; Miyata, M. Underexpression of mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma focusing on eight loci. Hepatology 2002, 36, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wu, X.; Xiang, E.; Luo, F.; Li, Q.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, F.; Chen, P. Expression profiling of CPS1 in Correa’s cascade and its association with gastric cancer prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Loss of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I in small-intestinal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.B.; Spee, B.; Blechacz, B.R.; Avital, I.; Komuta, M.; Barbour, A.; Conner, E.A.; Gillen, M.C.; Roskams, T.; Roberts, L.R.; et al. Genomic and genetic characterization of cholangiocarcinoma identifies therapeutic targets for tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1021–1031.e1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Tumours: Digestive System Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2019; pp. 254–259.
- Qiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jin, S.; Yan, C.; Li, Z.; Tao, L.; Yu, H. The prognostic value of arginase-1 and glypican-3 expression levels in patients after surgical intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma resection. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.C.; Gong, C.; Song, J.; Krausz, T.; Tretiakova, M.; Hyjek, E.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Alves, V.; Xiao, S.Y.; Anders, R.A.; et al. Arginase-1: A new immunohistochemical marker of hepatocytes and hepatocellular neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, G.L.; Ilyas, J.A.; Duan, Z.; Green, L.K.; Younes, M.; El-Serag, H.B.; Davila, J.A. Secular trends in the incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in the USA and the impact of misclassification. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 3103–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Okanurak, K.; Lv, Z. Liver fluke infection and cholangiocarcinoma: A review. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishima, S.; Oda, Y. Pathogenesis and classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Different characters of perihilar large duct type versus peripheral small duct type. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massarweh, N.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control 2017, 24, 1073274817729245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Tavolari, S.; Brandi, G. Cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology and risk factors. Liver Int. 2019, 39 (Suppl. 1), 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, J.; Galle, P.R.; Khan, S.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Park, J.W.; Patel, T.; Pawlik, T.M.; Gores, G.J. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajaj, E.; Sciacovelli, M.; Frezza, C.; Erez, A. The context-specific roles of urea cycle enzymes in tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, H.A. The history of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1970, 14, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.L. Hans Krebs and the discovery of the ornithine cycle. Fed. Proc. 1980, 39, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Gaasbeek Janzen, J.W.; Lamers, W.H.; Moorman, A.F.; de Graaf, A.; Los, J.A.; Charles, R. Immunohistochemical localization of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (ammonia) in adult rat liver; evidence for a heterogeneous distribution. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1984, 32, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Adler, L.; Karathia, H.; Carmel, N.; Rabinovich, S.; Auslander, N.; Keshet, R.; Stettner, N.; Silberman, A.; Agemy, L.; et al. Urea Cycle Dysregulation Generates Clinically Relevant Genomic and Biochemical Signatures. Cell 2018, 174, 1559–1570.e1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; Cervera, J. The carbamoyl-phosphate synthase family and carbamate kinase: Structure-function studies. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1995, 23, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryall, J.; Nguyen, M.; Bendayan, M.; Shore, G.C. Expression of nuclear genes encoding the urea cycle enzymes, carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I and ornithine carbamoyl transferase, in rat liver and intestinal mucosa. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 152, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Fernandez, C.; Haberle, J. Targeting CPS1 in the treatment of Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) deficiency, a urea cycle disorder. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q.; Yang, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, Z.; Fang, L.; Du, R. Significant Down-Regulation of Urea Cycle Generates Clinically Relevant Proteomic Signature in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Macrovascular Invasion. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dong, H.; Robertson, K.; Liu, C. DNA methylation suppresses expression of the urea cycle enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Luo, G.; Lian, Q.; Sui, C.; Tang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Discovery of a Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1-Deficient HCC Subtype With Therapeutic Potential Through Integrative Genomic and Experimental Analysis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3249–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hu, Z.; Cai, L.; Li, K.; Choi, E.; Faubert, B.; Bezwada, D.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Villalobos, P.; Lin, Y.F.; et al. CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells. Nature 2017, 546, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Miao, L.; Jiang, Q. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNAs in cholangiocarcinoma: Advances and challenges. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 655–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.L.; Li, A.J.; Hu, Z.Y.; Shang, F.S.; Wu, M.C. Co-expression of the carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 gene and its long non-coding RNA correlates with poor prognosis of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7915–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Nguyen, T.V.; Rolfe, A.; Agrawal, A.A.; Ke, J.; Peng, S.; Colombo, F.; Yu, S.; Bouchard, P.; Wu, J.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibition of CPS1 Activity through an Allosteric Pocket. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 259–268.e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfe, A.; Yao, S.; Nguyen, T.V.; Omoto, K.; Colombo, F.; Virrankoski, M.; Vaillancourt, F.H.; Yu, L.; Cook, A.; Reynolds, D.; et al. Discovery of 2,6-Dimethylpiperazines as Allosteric Inhibitors of CPS1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).