The Impact of the Angulus Biopsy on the Detection of Staging and the Grading of Chronic Gastritis
Abstract
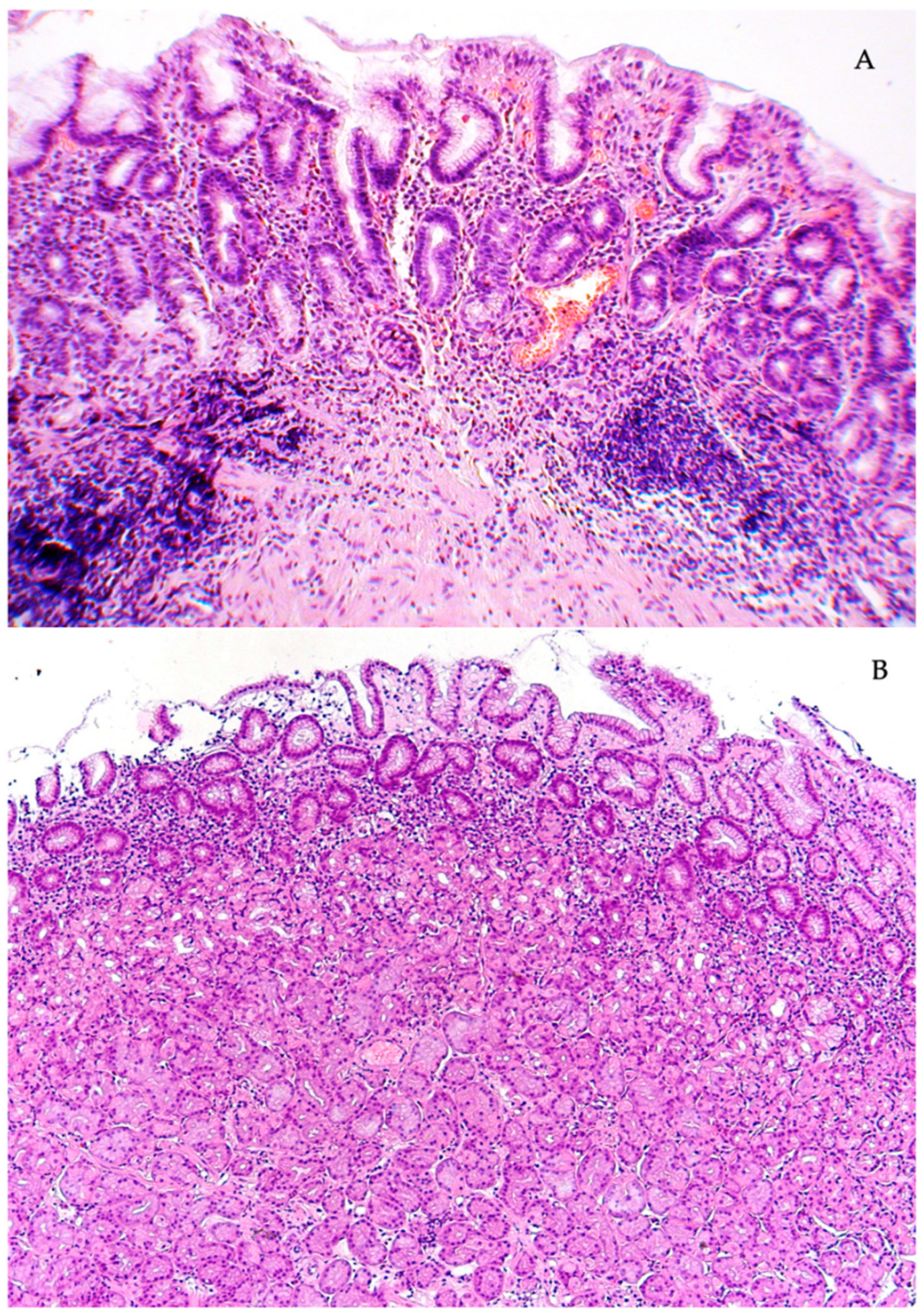
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Taking a biopsy from the incisura angularis with subsequent analysis of structural changes in the gastric mucosa in most cases does not play a decisive role in the integral assessment of the stage of gastritis in accordance with the OLGA-system;
- In persons with a long course of chronic gastritis associated with H. pylori, the assessment of the presence and severity of atrophy of the incisura angularis is appropriate for a more accurate assessment of the stage of gastritis.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Rugge, M.; Genta, R.M. Staging and grading of chronic gastritis. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, M.F.; Genta, R.M.; Yardley, J.H.; Correa, P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torun, C.; Yavuz, A.; Akan, K.; Seneldir, H.; Toksoz, A.N.; Ulasoglu, H.C.; Tuncer, I. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of the updated Sydney system and single biopsy. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, N.K.; Färkkilä, M.A.; Voutilainen, M.E.; Arkkila, P.E. The clinical value of taking routine biopsies from the incisura angularis during gastroscopy. Endoscopy 2005, 37, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddingham, W.; Nieuwenburg, S.A.V.; Carlson, S.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Spaander, M.; Kuipers, E.J.; Jansen, M.; Graham, D.G.; Banks, M. Recent advances in the detection and management of early gastric cancer and its precursors. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020, 12, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isajevs, S.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Janciauskas, D.; Moisejevs, G.; Funka, K.; Kikuste, I.; Vanags, A.; Tolmanis, I.; Leja, M. The effect of incisura angularis biopsy sampling on the assessment of gastritis stage. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Libânio, D.; Marcos-Pinto, R.; Areia, M.; Leja, M.; Esposito, G.; Garrido, M.; Kikuste, I.; Megraud, F.; Matysiak-Budnik, T.; et al. Management of epithelial precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS II): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group (EHMSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED) guideline update 2019. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 365–388. [Google Scholar]
- Bordin, D.S.; Voynovan, I.N.; Andreev, D.N.; Maev, I.V. Current Helicobacter pylori Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgessa, N.A.; Geethakumari, P.; Kampa, P.; Parchuri, R.; Bhandari, R.; Alnasser, A.R.; Akram, A.; Kar, S.; Osman, F.; Mashat, G.D.; et al. A Comparison Between Histology and Rapid Urease Test in the Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori in Gastric Biopsies: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e39360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livzan, M.A.; Gaus, O.V.; Mozgovoi, S.I.; Bordin, D.S. Chronic Autoimmune Gastritis: Modern Diagnostic Principles. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Stomach. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/7-Stomach-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Bordin, D.; Morozov, S.; Plavnik, R.; Bakulina, N.; Voynovan, I.; Skibo, I.; Isakov, V.; Bakulin, I.; Andreev, D.; Maev, I. Helicobacter pylori infection prevalence in ambulatory settings in 2017-2019 in RUSSIA: The data of real-world national multicenter trial. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.Y.; Xu, S.F.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Sang, H.M.; Zhang, G.X. Anatomical predilection of intestinal metaplasia based on 78,335 endoscopic cases. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I.; Kook, M.C.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.G.; Joo, J.; Choi, I.J. Effect of biopsy site on detection of gastric cancer high-risk groups by OLGA and OLGIM stages. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lash, J.G.; Genta, R.M. Adherence to the Sydney System guidelines increases the detection of Helicobacter gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in 400738 sets of gastric biopsies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbanova, M.; Wex, T.; Jechorek, D.; Röhl, F.W.; Langner, C.; Selgrad, M.; Malfertheiner, P. Impact of the angulus biopsy for the detection of gastric preneoplastic conditions and gastric cancer risk assessment. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, M.; Müller, H.; Talley, N.J.; O’morain, C.; Bolling-Sternevald, E.; Sundin, M.; Eriksson, S.; Blum, A. In patients with Helicobacter pylori gastritis and functional dyspepsia, a biopsy from the incisura angularis provides useful diagnostic information. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2006, 202, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, C.A.; Jaramillo, E.; Suzuki, G.; Lagergren, P.; Nesi, G. Antralization of the gastric mucosa of the incisura angularis and its gastrin expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 2, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.H.; Kalantar, J.S.; Talley, N.J.; Wyatt, J.M.; Adams, S.; Chueng, K.; Mitchell, H.M. Antral-type mucosa in the gastric incisura, body, and fundus (antralization): A link between Helicobacter pylori infection and intestinal metaplasia? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Z.; Deng, Z.; Yi, Z.; Tuo, B.; Li, T.; Liu, X. Role of spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia in gastric mucosal diseases. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yamada, N.; Wu, Y.L.; Wen, M.; Matsuhisa, T.; Matsukura, N. Helicobacter pylori infection, glandular atrophy and intestinal metaplasia in superficial gastritis, gastric erosion, erosive gastritis, gastric ulcer and early gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Jin, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Jin, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, B. Risk of progression in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis: A retrospective study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 942091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Etiology | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Chronic gastritis associated with H. pylori | 380 | 52.9 |
| Group 2 | Autoimmune gastritis | 209 | 29.1 |
| Group 3 | Autoimmune gastritis in combination with chronic gastritis associated with H. pylori | 129 | 18.0 |
| Total | 718 | 100 |
| Detection Methods | Group 1. Chronic Gastritis Associated with H. pylori (n = 380 Patients) | Group 3. Autoimmune Gastritis in Combination with Chronic H. pylori Gastritis (n = 129 Patients) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % | Total | % | |
| 13C urease breath test | 109 | 28.68% | 15 | 11.62% |
| Rapid urease test | 55 | 14.47% | 26 | 20.15% |
| Antibodies to H. pylori IgG | 64 | 16.84% | 25 | 19.38% |
| Morphological study | 118 | 31.05% | 4 | 3.1% |
| Monoclonal antigen in feces | 17 | 4.47% | 3 | 2.32% |
| A doctor’s entry in the medical records about the presence of H. pylori and the performed eradication therapy | 145 | 38.26% | 56 | 43.41% |
| Grade of OLGA | Total | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | I | II | III | IV | ||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| 1 | Chronic gastritis associated with H. pylori | 2 | 0.5 | 14 | 3.7 | 246 | 64.7 | 95 | 25 | 23 | 6.1 | 380 |
| 2 | Autoimmune gastritis | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 170 | 81.2 | 35 | 16.8 | 1 | 0.5 | 209 |
| 3 | Autoimmune gastritis in combination with H. pylori chronic gastritis | 0 | - | 1 | 0.8 | 103 | 79.8 | 23 | 17.8 | 2 | 1.6 | 129 |
| Total | 3 | 0.4 | 17 | 2.4 | 519 | 72.3 | 153 | 21.3 | 26 | 3.6 | 718 | |
| Stage of OLGA | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | I | II | III | IV | ||
| Cases considering the incisura angularis | 139 | 98 | 82 | 51 | 10 | 380 |
| Cases without considering the incisura angularis | 155 | 90 | 74 | 55 | 6 | 380 |
| Total discrepancies | +16 | +8/−15 | −8 | +4 | −4 | |
| Discrepancies with reduced atrophy stage | 0 | 15 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 27 (7.11%) |
| Stage of OLGA | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | I | II | III | IV | ||
| Cases considering the incisura angularis | 7 | 6 | 35 | 141 | 20 | 209 |
| Cases without considering the incisura angularis | 9 | 6 | 36 | 139 | 19 | 209 |
| Discrepancies of everything | +2 | +2/−2 | +3/−2 | +1/−3 | −1 | |
| Discrepancies with decreasing stage of atrophy | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 8 (3.83%) |
| Stage of OLGA | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | I | II | III | IV | ||
| Cases considering the incisura angularis | 9 | 7 | 22 | 84 | 7 | 129 |
| Cases without considering the incisura angularis | 10 | 7 | 21 | 85 | 6 | 129 |
| Discrepancies of everything | +1 | +1/−1 | −1 | +1 | −1 | |
| Discrepancies with decreasing stage of atrophy | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 (2.32%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khomeriki, S.G.; Bordin, D.S.; Khomeriki, N.M.; Parfenchikova, E.V.; Nikolskaya, K.A.; Ivanova, V.A.; Chebotareva, M.V.; Gretskaya, M.L.; Voynovan, I.N.; Kiriukova, M.A.; et al. The Impact of the Angulus Biopsy on the Detection of Staging and the Grading of Chronic Gastritis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182928
Khomeriki SG, Bordin DS, Khomeriki NM, Parfenchikova EV, Nikolskaya KA, Ivanova VA, Chebotareva MV, Gretskaya ML, Voynovan IN, Kiriukova MA, et al. The Impact of the Angulus Biopsy on the Detection of Staging and the Grading of Chronic Gastritis. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(18):2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182928
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhomeriki, Sergey G., Dmitry S. Bordin, Natalia M. Khomeriki, Elena V. Parfenchikova, Karine A. Nikolskaya, Valeria A. Ivanova, Margarita V. Chebotareva, Maria L. Gretskaya, Irina N. Voynovan, Mariia A. Kiriukova, and et al. 2023. "The Impact of the Angulus Biopsy on the Detection of Staging and the Grading of Chronic Gastritis" Diagnostics 13, no. 18: 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182928
APA StyleKhomeriki, S. G., Bordin, D. S., Khomeriki, N. M., Parfenchikova, E. V., Nikolskaya, K. A., Ivanova, V. A., Chebotareva, M. V., Gretskaya, M. L., Voynovan, I. N., Kiriukova, M. A., Livzan, M. A., & Khatkov, I. E. (2023). The Impact of the Angulus Biopsy on the Detection of Staging and the Grading of Chronic Gastritis. Diagnostics, 13(18), 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13182928








