Progress in the Diagnostic and Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome
Abstract
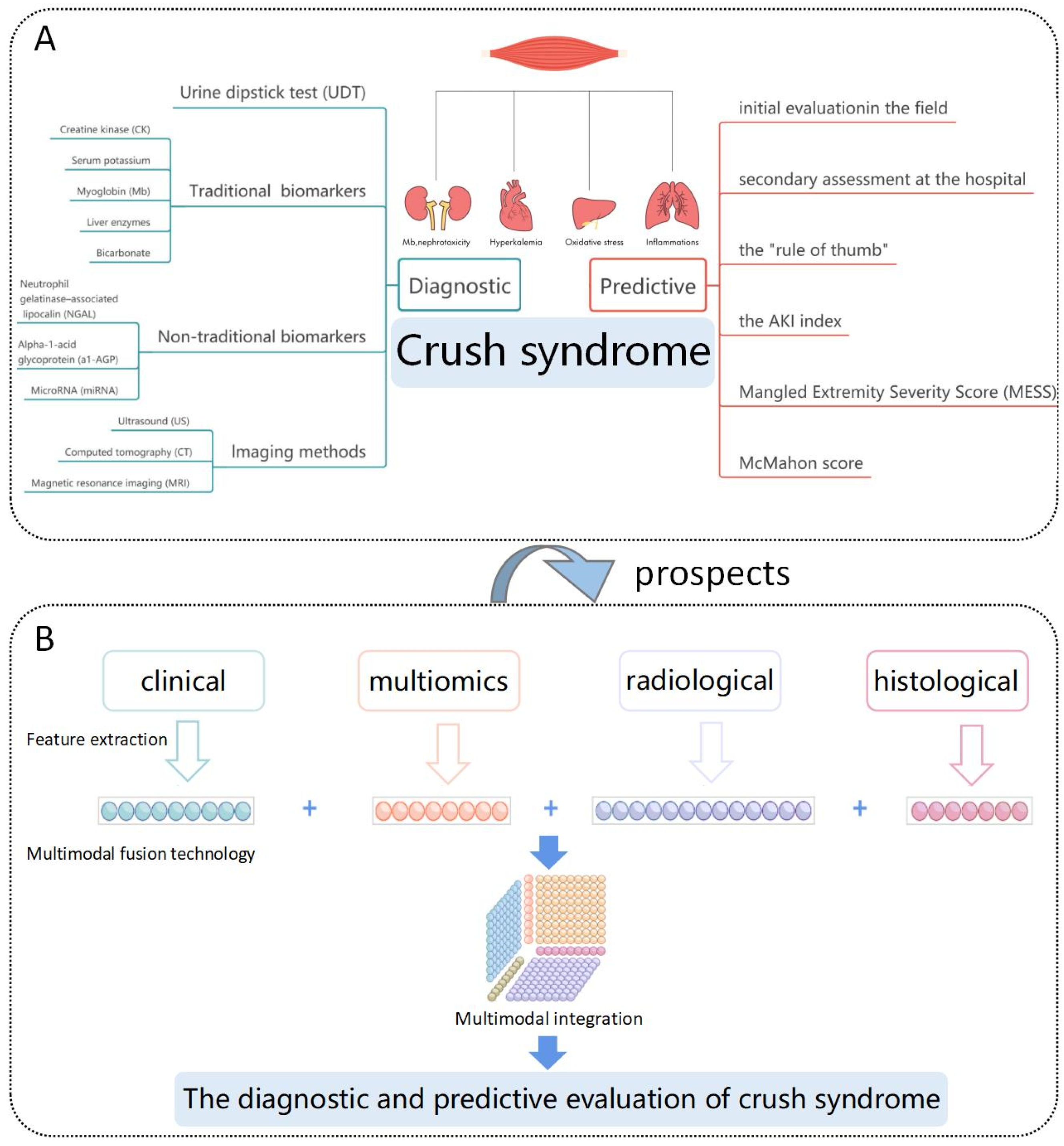
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Evaluation of Crush Syndrome
2.1. Urine Dipstick Test (UDT)
2.2. Traditional Biomarkers
2.2.1. Creatine Kinase (CK)
2.2.2. Serum Potassium
2.2.3. Myoglobin (Mb)
2.2.4. Liver Enzymes
2.2.5. Bicarbonate
2.3. Non-Traditional Biomarkers
2.3.1. Neutrophil-Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
2.3.2. Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein (a1-AGP)
2.3.3. MicroRNA (miRNA)
2.4. Imaging Methods
2.4.1. Ultrasound (US)
2.4.2. Computed Tomography (CT)
2.4.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
3. Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.; Greaves, I. Crush injury and crush syndrome: A review. J. Trauma 2003, 54, S226–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodadek, L.; Carmichael, S.P., II; Seshadri, A.; Pathak, A.; Hoth, J.; Appelbaum, R.; Michetti, C.P.; Gonzalez, R.P. Rhabdomyolysis: An American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Critical Care Committee Clinical Consensus Document. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2022, 7, e000836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Long, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Song, J.; Midgley, A.C.; Fan, H.; Hou, S. The Role of Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Crush Syndrome-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Shock 2021, 56, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, O.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Gong, Y. Ferroptosis in acute kidney injury following crush syndrome: A novel target for treatment. J. Adv. Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Liao, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Crush syndrome and acute kidney injury in the Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Trauma 2011, 70, 1213–1217; discussion 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, K.; Kurosawa, M.; Kamiya, M.; Urano, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Hase, K.; Homma, K.; Sasaki, J.; Miyauchi, H.; et al. Macrophage extracellular trap formation promoted by platelet activation is a key mediator of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meijer, A.R.; Fikkers, B.G.; de Keijzer, M.H.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Drenth, J.P.H. Serum creatine kinase as predictor of clinical course in rhabdomyolysis: A 5-year intensive care survey. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, V.; Noto, A.; Lacquaniti, A.; Bolignano, D.; Versaci, A.; David, A.; Spinelli, F.; Buemi, M. Levels of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in 2 patients with crush syndrome after a mudslide. Am. J. Crit. Care 2011, 20, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.; Cone, D.C.; Portereiko, J.V. Complex extrication and crush injury. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2010, 14, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleckovic-Halilovic, M.; Pjanic, M.; Mesic, E.; Storrar, J.; Woywodt, A. From quail to earthquakes and human conflict: A historical perspective of rhabdomyolysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bywaters, E.G.L.; Beall, D. Crush Injuries with Impairment of Renal Function. BMJ 1941, 1, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, D. A historical perspective on crush syndrome: The clinical application of its pathogenesis, established by the study of wartime crush injuries. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, M.S.; Lameire, N.; van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R. Disaster nephrology: A new concept for an old problem. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, M.S.; Vanholder, R. Management of crush victims in mass disasters: Highlights from recently published recommendations. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartal, C.; Zeller, L.; Miskin, I.; Sebbag, G.; Karp, E.; Grossman, A.; Engel, A.; Carter, D.; Kreiss, Y. Crush Syndrome: Saving More Lives in Disasters. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, A.; Yavuz, M.; Usta, M.; Ercan, I.; Aslanhan, I.; Güllülü, M.; Kurt, E.; Emir, G.; Dilek, K.; Yurtkuran, M. Survival analysis of the factors affecting in mortality in injured patients requiring dialysis due to acute renal failure during the Marmara earthquake: Survivors vs non-survivors. Clin. Nephrol. 2003, 59, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, I.; Porter, K.; Smith, J.E. Consensus statement on the early management of crush injury and prevention of crush syndrome. J. R. Army Med. Corp. 2003, 149, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratalla, M.B.; Braun, P.; Fornas, G.M. Importance of MRI in the diagnosis and treatment of rhabdomyolysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 65, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Garrett, J.; Bhargava, P.; Aguilar, G.; Simoncini, A.; Sangster, G. Multimodality imaging findings in rhabdomyolysis and a brief review of differential diagnoses. Emerg. Radiol. 2017, 24, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadi, S.A.; Ruegner, R.; Snowden, B.; Hendey, G.W. Urinalysis is an inadequate screen for rhabdomyolysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.E.; Miller, M.A.; Docherty, M. Urine dipstick testing to rule out rhabdomyolysis in patients with suspected heat injury. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi-Moghaddam, M.; Safari, S.; Najafi, I.; Hosseini, M. Accuracy of urine dipstick in the detection of patients at risk for crush-induced rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 19, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, Y.; Shindoh, M.; Yukioka, H.; Nishi, S.; Fujumori, M.; Asada, A. Crush Syndrome Sustained in the 1995 Kobe, Japan, Earthquake; Treatment and Outcome. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1997, 30, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.; Sharifi, A.; Najafi, I.; Eghtesadi-Araghi, P.; Rasouli, M.R. Role of dipstick in detection of haeme pigment due to rhabdomyolysis in victims of Bam earthquake. EMHJ-East. Mediterr. Health J. 2009, 16, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, S.; Yousefifard, M.; Hashemi, B.; Baratloo, A.; Forouzanfar, M.M.; Rahmati, F.; Motamedi, M.; Najafi, I. The Role of Scoring Systems and Urine Dipstick in Prediction of Rhabdomyolysis-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 10, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y. Urine-an untapped goldmine for biomarker discovery? Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Ceresa, F.; Campo, S.; Barbera, G.; Caruso, D.; Palazzo, E.; Patanè, F.; Monardo, P. Acute Kidney Injury and Sepsis after Cardiac Surgery: The Roles of Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2, Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7, and Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Gao, Y. Early disease biomarkers can be found using animal models urine proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2021, 18, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntornsuk, W.; Suntornsuk, L. Recent applications of paper-based point-of-care devices for biomarker detection. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, C.; Fenwick, R. Rhabdomyolysis: A case-based critical reflection on its causes and diagnosis. Emerg. Nurse 2020, 28, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. An evidence-based narrative review of the emergency department evaluation and management of rhabdomyolysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, L.O.; Leon, M.; Einav, S.; Varon, J. Beyond muscle destruction: A systematic review of rhabdomyolysis for clinical practice. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, A.; Brusher, K.; Hall, V.; Howard, R.S.; Clark, P.A. Diagnosis and Management of Rhabdomyolysis in the Absence of Creatine Phosphokinase: A Medical Record Review. Mil. Med. 2019, 184, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nance, J.R.; Mammen, A.L. Diagnostic evaluation of rhabdomyolysis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Tsang, Y.-M.; Yu, C.-W.; Wu, M.-Z.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Shih, T.T.-F. Rhabdomyolysis: Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography Findings. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2007, 31, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.; Tanaka, H.; Masutani, K.; Yanagida, T.; Kashiwagi, M.; Mizumasa, T.; Masuda, K.; Hirakata, H.; Fujishima, M. The value of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose rhabdomyolysis in acute renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sever, M.S.; Vanholder, R.; Lameire, N. Management of crush-related injuries after disasters. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genthon, A.; Wilcox, S.R. Crush syndrome: A case report and review of the literature. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 46, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, S.; Yousefifard, M.; Hashemi, B.; Baratloo, A.; Forouzanfar, M.M.; Rahmati, F.; Motamedi, M.; Najafi, I. The value of serum creatine kinase in predicting the risk of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.P.; Taylor, A.; Sudhan, N.; Menon, D.K.; Lavinio, A. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury: Creatine kinase as a prognostic marker and validation of the McMahon Score in a 10-year cohort: A retrospective observational evaluation. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, S.-H. Case report: Severe rhabdomyolysis and acute liver injury in a high-altitude mountain climber. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 917355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, S.; Eshaghzade, M.; Najafi, I.; Baratloo, A.; Hashemi, B.; Forouzanfar, M.M.; Rahmati, F. Trends of Serum Electrolyte Changes in Crush syndrome patients of Bam Earthquake; a Cross sectional Study. Emergency 2017, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D. Crush syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, S34–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, M.S.; Erek, E.; Vanholder, R.; Kantarci, G.; Yavuz, M.; Turkmen, A.; Ergin, H.; Tulbek, M.Y.; Duranay, M.; Manga, G.; et al. Serum potassium in the crush syndrome victims of the Marmara disaster. Clin. Nephrol. 2003, 59, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T. Structure of myoglobin refined at 2-0 A resolution. II. Structure of deoxymyoglobin from sperm whale. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 110, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.; Ibounig, T.; Lyth, J.; Alkner, B.; von Walden, F.; Fornander, L.; Rämö, L.; Schmidt, A.; Schilcher, J. BioFACTS: Biomarkers of rhabdomyolysis in the diagnosis of acute compartment syndrome—Protocol for a prospective multinational, multicentre study involving patients with tibial fractures. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, H.U.; Balasubramaniyan, T.; Thirumavalavan, S.; Vasudevan, C.; Senthil Kumar, R.P.; Murugesan, V.; Abraham, A. Rhabdomyolysis with myoglobin-induced acute kidney injury: A case series of four cases. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizo, N.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Amaro-Villalobos, J.M.; Egido, J.; Moreno, J.A. Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2015, 40, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Pevzner, I.B.; Chupyrkina, A.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Silachev, D.N.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Zorov, D.B. The role of myoglobin degradation in nephrotoxicity after rhabdomyolysis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 256, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, E.Y.; Chupyrkina, A.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Isaev, N.K.; Zorov, D.B. Myoglobin causes oxidative stress, increase of NO production and dysfunction of kidney’s mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitselart, P.; Derely, J.; Daban, J.-L.; de Rudnicki, S.; Libert, N. Relationship between creatine kinase and liver enzymes in war wounded with rhabdomyolysis. Injury 2022, 53, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, V.; Figueiredo, S.; Hamada, S.; Pochard, J.; Haines, R.W.; Prowle, J.R.; Duranteau, J.; Vigué, B.; Harrois, A. Admission serum myoglobin and the development of acute kidney injury after major trauma. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premru, V.; Kovač, J.; Ponikvar, R. Use of myoglobin as a marker and predictor in myoglobinuric acute kidney injury. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2013, 17, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, Y.; Fu, P.; Cao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, F.; Hu, Z.; Su, B.; Tang, W.; Qin, W. Myoglobin clearance by continuous venous-venous haemofiltration in rhabdomyolysis with acute kidney injury: A case series. Injury 2012, 43, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.K. Abnormal liver function tests associated with severe rhabdomyolysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.B.; Algren, D.A.; Chenoweth, J.A.; Owen, K.P.; Ford, J.B.; Albertson, T.E.; Sutter, M.E. Transaminase and Creatine Kinase Ratios for Differentiating Delayed Acetaminophen Overdose from Rhabdomyolysis. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 19, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raurich, J.M.; Llompart-Pou, J.A.; Rodríguez-Yago, M.; Ferreruela, M.; Royo, C.; Ayestarán, I. Role of Elevated Aminotransferases in ICU Patients with Rhabdomyolysis. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.N.; Desai, P.V. Aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase activities of rat brain during crush syndrome. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 447, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zen, P.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Jiang, W.; Peng, G. Serum enzyme profile characteristics of victims following the Wenchuan earthquake in China. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibrecht, K.; Dayno, M.; Darling, C.; Bird, S.B. Liver aminotransferases are elevated with rhabdomyolysis in the absence of significant liver injury. J. Med. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.K.H.; Arumugananthan, C.; Lau Hing Yim, C.; Jellie, L.J.; Wong, E.W.W.; Junckerstorff, R.K. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Relationship between Serum Creatine Kinase and Liver Biochemistry in Patients with Rhabdomyolysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akmal, M.; Massry, S.G. Reversible hepatic dysfunction associated with rhabdomyolysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 1990, 10, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, S.; Fagan, E.; Williams, R.; Dewhurst, I.; Cory, C.E. Heatstroke and rhabdomyolysis presenting as fulminant hepatic failure. Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dufour, D.R.; Lott, J.A.; Nolte, F.S.; Gretch, D.R.; Koff, R.S.; Seeff, L.B. Diagnosis and monitoring of hepatic injury. II. Recommendations for use of laboratory tests in screening, diagnosis, and monitoring. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 2050–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muckart, D.J.; Moodley, M.; Naidu, A.G.; Reddy, A.D.; Meineke, K.R. Prediction of acute renal failure following soft-tissue injury using the venous bicarbonate concentration. J. Trauma 1992, 33, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, D.L.; Laing, G.L.; Bruce, J.; Biccard, B.; Muckart, D.J.J. Validating the utilisation of venous bicarbonate as a predictor of acute kidney injury in crush syndrome from sjambok injuries. S. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 107, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitendag, J.J.P.; Patel, M.Q.; Variawa, S.; Fichardt, J.; Mostert, B.; Goliath, A.; Clarke, D.L.; Oosthuizen, G.V. Venous bicarbonate and creatine kinase as diagnostic and prognostic tools in the setting of acute traumatic rhabdomyolysis. S. Afr. Med. J. 2021, 111, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Rousselle, A.; Klocke, J.; Bachmann, S.; Popovic, S.; Bontscho, J.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Siffrin, V.; Jerke, U.; Ashraf, M.I.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Protects from ANCA-Induced GN by Inhibiting TH17 Immunity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Bellomo, R.; Devarajan, P.; Schlattmann, P.; Haase-Fielitz, A. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonafine, M.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Jaisser, F. More than a simple biomarker: The role of NGAL in cardiovascular and renal diseases. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Coppolino, G.; Lacquaniti, A.; Nicocia, G.; Buemi, M. Pathological and prognostic value of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in macroproteinuric patients with worsening renal function. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2008, 31, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragas, N.; Qiu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Samstein, B.; Deng, S.-X.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Viltard, M.; Yu, W.; Forster, C.S.; Gong, G.; et al. The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Prada, A.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zahedi, K.; Yang, J.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerico, A.; Galli, C.; Fortunato, A.; Ronco, C. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as biomarker of acute kidney injury: A review of the laboratory characteristics and clinical evidences. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarajan, P. Review: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: A troponin-like biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Nephrology 2010, 15, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochepied, T.; Berger, F.G.; Baumann, H.; Libert, C. α1-Acid glycoprotein: An acute phase protein with inflammatory and immunomodulating properties. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daemen, M.A.; Heemskerk, V.H.; van’t Veer, C.; Denecker, G.; Wolfs, T.G.; Vandenabeele, P.; Buurman, W.A. Functional protection by acute phase proteins alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein and alpha(1)-antitrypsin against ischemia/reperfusion injury by preventing apoptosis and inflammation. Circulation 2000, 102, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, B.; Walter, S.J.; Wolfs, T.G.A.M.; Hochepied, T.; Räbinä, J.; Heeringa, P.; Parkkinen, J.; Libert, C.; Buurman, W.A. Exogenous alpha-1-acid glycoprotein protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etheridge, A.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat. Res. 2011, 717, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laterza, O.F.; Lim, L.; Garrett-Engele, P.W.; Vlasakova, K.; Muniappa, N.; Tanaka, W.K.; Johnson, J.M.; Sina, J.F.; Fare, T.L.; Sistare, F.D.; et al. Plasma MicroRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers of tissue injury. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, W.J.; Barnum, J.E.; Erdos, Z.; LaFranco-Scheuch, L.; Lane, P.; Vlasakova, K.; Sistare, F.D.; Glaab, W.E. A Performance Evaluation of Liver and Skeletal Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Rat Plasma to Detect Drug-Induced Injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-D.; Lv, F.-Q.; Li, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.-Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Tang, J. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the diagnosis of skeletal muscle crush injury in rabbits. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Tian, M.; Xia, J.; Zhu, W.; Yang, L. Application of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Rhabdomyolysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 3349–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.-H.; Qiu, L.; Fu, P.; Luo, Y.; Tao, Y.; Peng, Y.-L. Ultrasonic appearance of rhabdomyolysis in patients with crush injury in the Wenchuan earthquake. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 1872–1876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Renal Perfusion in Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: An Experimental Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamminen, A.E.; Hekali, P.E.; Tiula, E.; Suramo, I.; Korhola, O.A. Acute rhabdomyolysis: Evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging compared with computed tomography and ultrasonography. Br. J. Radiol. 1989, 62, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, P.D.; Dillingham, M. Demonstration of CT hyperdensity in patients with acute renal failure associated with rhabdomyolysis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1991, 15, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Shimamoto, S.; Kishi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Ishida, T.; Tomoda, K.; Nakamura, H. CT, MR imaging and muscle biopsy in severe crush injury. Acta Radiol. 1997, 38, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, Z.-J.; Liu, F.; Fu, P.; Tao, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Song, B. Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography in severe crush syndrome with consideration of fasciotomy or amputation: A novel diagnostic tool. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 2068–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Shintani, S.; Shiigai, T. Repeat MRI in acute rhabdomyolysis: Correlation with clinicopathological findings. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1993, 17, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuler, M.S.; Reisman, W.M.; Cole, A.L.; Whitesides, T.E.; Moore, T.J. Near-infrared spectroscopy in acute compartment syndrome: Case report. Injury 2011, 42, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, N.; Demsar, J.; Zupan, B.; Mozina, M.; Pretto, E.A.; Oda, J.; Tanaka, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Fukui, T. Predictive model for estimating risk of crush syndrome: A data mining approach. J. Trauma 2007, 62, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, P.; Wang, L.; Cai, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Guo, D.; Sun, X.; Chen, F.; Bi, W.; et al. The clinical features and outcome of crush patients with acute kidney injury after the Wenchuan earthquake: Differences between elderly and younger adults. Injury 2012, 43, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, I.; van Biesen, W.; Sharifi, A.; Hoseini, M.; Rashid Farokhi, F.; Sanadgol, H.; Vanholder, R. Early detection of patients at high risk for acute kidney injury during disasters: Development of a scoring system based on the Bam earthquake experience. J. Nephrol. 2008, 21, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; John, B.; Pawar, B.; Sadiq, S. Renal profile in patients with orthopaedic trauma: A prospective study. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2009, 75, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McMahon, G.M.; Zeng, X.; Waikar, S.S. A risk prediction score for kidney failure or mortality in rhabdomyolysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Zhao, S.; Aishanjiang, K.; Cai, H.; Wei, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Han, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning for differential diagnosis of malignant hepatic tumors based on multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT and clinical data. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, S.K.; Madugundu, A.K.; Garapati, K.; Ramarajan, M.G.; Saraswat, M.; Kumar-M, P.; Hughes, T.; Shah, R.; Patnaik, M.M.; Chia, N.; et al. Development of a multiomics model for identification of predictive biomarkers for COVID-19 severity: A retrospective cohort study Development of a multiomics model for identification of predictive biomarkers for COVID-19 severity: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e632–e645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheerla, A.; Gevaert, O. Deep learning with multimodal representation for pancancer prognosis prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, i446–i454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Categories | Diagnostic Evaluation | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Biomarkers | UDT | Screening test, easy to operate [23,24,25] |
| CK | Easy, sensitive [3,34] | |
| Serum potassium | Combined ECG to monitor cardiac function [9] | |
| Mb | Cause of renal unit damage, early sign of muscle damage [46] | |
| Liver enzymes | Indicator of liver injury, elevated AST more common [55,56] | |
| Bicarbonate | Predict the risk of renal failure in CS patients [65] | |
| Non-Traditional Biomarkers | NGAL | A noninvasive, early biomarker of AKI and already in clinical application [72,73] |
| a1-AGP | Predict the severity of CS (animal studies) [3] | |
| miRNA | Distinguish between muscle damage and liver damage (animal studies) [80,81] | |
| Imaging Methods | US | Simple, fast, and bedside accessible [82,83,84] |
| CT | Detect occult rhabdomyolysis [87] | |
| MRI | Good soft tissue contrast, higher sensitivity than US and CT [18,36,86,89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Shi, J.; Guo, X.; Fan, H.; Lv, Q. Progress in the Diagnostic and Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193034
Luo Y, Liu C, Li D, Yang B, Shi J, Guo X, Fan H, Lv Q. Progress in the Diagnostic and Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(19):3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yu, Chunli Liu, Duo Li, Bofan Yang, Jie Shi, Xiaoqin Guo, Haojun Fan, and Qi Lv. 2023. "Progress in the Diagnostic and Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome" Diagnostics 13, no. 19: 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193034
APA StyleLuo, Y., Liu, C., Li, D., Yang, B., Shi, J., Guo, X., Fan, H., & Lv, Q. (2023). Progress in the Diagnostic and Predictive Evaluation of Crush Syndrome. Diagnostics, 13(19), 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193034






