Fetal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Associated with and without Fetal Growth Restriction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Prenatal Imaging Findings, Postnatal Clinical Findings, and Outcomes for Fetuses with Both cCMV and FGR
3.2. Prenatal Imaging Findings, Postnatal Clinical Findings, and Outcomes for Fetuses with cCMV without FGR
3.3. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics between the FGR and Non-FGR Groups
3.4. Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Prenatal US Findings between the FGR and Non-FGR Groups
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revello, M.G.; Gerna, G. Diagnosis and management of human cytomegalovirus infection in the mother, fetus, and newborn infant. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 680–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stagno, S.; Whitley, R.J. Herpesvirus infections of pregnancy. Part I: Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jester, P.M.; Sanchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, R.F.; et al. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morioka, I.; Kakei, Y.; Omori, T.; Nozu, K.; Fujioka, K.; Takahashi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Moriuchi, H.; Ito, Y.; Oka, A.; et al. Oral Valganciclovir Therapy in Infants Aged </=2 Months with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Disease: A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Open-Label Clinical Trial in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3582. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimura, K.; Tairaku, S.; Ebina, Y.; Morioka, I.; Nagamata, S.; Deguchi, K.; Morizane, M.; Deguchi, M.; Minematsu, T.; Yamada, H. Prediction of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in High-Risk Pregnant Women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imafuku, H.; Yamada, H.; Uchida, A.; Deguchi, M.; Shirakawa, T.; Sasagawa, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fujioka, K.; Morioka, I.; Tanimura, K. Clinical and ultrasound features associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection as potential predictors for targeted newborn screening in high-risk pregnancies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, G.; Bader, U.; Lindemann, L.; Schalasta, G.; Daiminger, A. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in 189 pregnancies with known outcome. Prenat. Diagn. 2001, 21, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicin; Hughes, B.L.; Gyamfi-Bannerman, C. Diagnosis and antenatal management of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, B5–B11. [Google Scholar]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Ren, S.; Magny, J.F.; Jacquemard, F.; Couderc, S.; Garcia, P.; Maillotte, A.M.; Benard, M.; Pinquier, D.; Minodier, P.; et al. Accuracy of prenatal ultrasound screening to identify fetuses infected by cytomegalovirus which will develop severe long-term sequelae. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Kazzi, S.N. Yield and costs of screening growth-retarded infants for torch infections. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Ishii, K.; Shimada, M.; Hayashi, S.; Hidaka, N.; Nakayama, M.; Mitsuda, N. Significance of maternal screening for toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus infection in cases of fetal growth restriction. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2013, 39, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voekt, C.A.; Rinderknecht, T.; Hirsch, H.H.; Blaich, A.; Hosli, I.M. Ultrasound indications for maternal STORCH testing in pregnancy. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2017, 147, w14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, D.; Holmes, N.E.; Hui, L. A systematic review of maternal TORCH serology as a screen for suspected fetal infection. Prenat. Diagn. 2022, 42, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Stirnemann, J.; Sellier, Y.; Guilleminot, T.; Dejean, A.; Magny, J.F.; Couderc, S.; Jacquemard, F.; Ville, Y. Feasibility of predicting the outcome of fetal infection with cytomegalovirus at the time of prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 342.e341–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leyder, M.; Vorsselmans, A.; Done, E.; Van Berkel, K.; Faron, G.; Foulon, I.; Naessens, A.; Jansen, A.; Foulon, W.; Gucciardo, L. Primary maternal cytomegalovirus infections: Accuracy of fetal ultrasound for predicting sequelae in offspring. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 638.e631–638.e638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipitz, S.; Yinon, Y.; Malinger, G.; Yagel, S.; Levit, L.; Hoffman, C.; Rantzer, R.; Weisz, B. Risk of cytomegalovirus-associated sequelae in relation to time of infection and findings on prenatal imaging. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, K.; Shi, Y.; Uchida, A.; Uenaka, M.; Imafuku, H.; Ikuta, T.; Fujioka, K.; Morioka, I.; Deguchi, M.; Minematsu, T.; et al. Immunoglobulin fetal therapy and neonatal therapy with antiviral drugs improve neurological outcome of infants with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 143, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, S.J.; Beune, I.M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.; Baschat, A.A.; Baker, P.N.; Silver, R.M.; Wynia, K.; Ganzevoort, W. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: A Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.C.G.; Odibo, L.; Zientara, S.; Obican, S.G.; Rodriguez, A.; Stout, M.; Odibo, A.O. Validation of Delphi procedure consensus criteria for defining fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervenak, F.A.; Jeanty, P.; Cantraine, F.; Chitkara, U.; Venus, I.; Berkowitz, R.L.; Hobbins, J.C. The diagnosis of fetal microcephaly. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1984, 149, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglioti, P.; Danelon, D.; Bontempo, S.; Mombro, M.; Cardaropoli, S.; Todros, T. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly: Outcome in 176 cases. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 25, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murao, F.; Takamori, H.; Hata, K.; Hata, T.; Kitao, M. Fetal liver measurements by ultrasonography. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 1987, 25, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.; Yarkoni, S.; Jeanty, P.; Grannum, P.; Hobbins, J.C. Sonographic measurements of the fetal spleen: Clinical implications. J. Ultrasound Med. 1985, 4, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoddick, W.K.; Mahony, B.S.; Callen, P.W.; Filly, R.A. Placental thickness. J. Ultrasound Med. 1985, 4, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Torre, R.; Nigro, G.; Mazzocco, M.; Best, A.M.; Adler, S.P. Placental enlargement in women with primary maternal cytomegalovirus infection is associated with fetal and neonatal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, Y.; Mishina, J.; Sato, N.; Watanabe, T.; Honma, Y. Developmental characteristics of very low-birthweight infants at 18 months’ corrected age according to birthweight. Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, K.; Tairaku, S.; Morioka, I.; Ozaki, K.; Nagamata, S.; Morizane, M.; Deguchi, M.; Ebina, Y.; Minematsu, T.; Yamada, H. Universal Screening With Use of Immunoglobulin G Avidity for Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Japanese Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Immunoglobulin Fetal Therapy Study Group. A trial of immunoglobulin fetal therapy for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 95, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoui, R.; Zodan-Marin, T.; Wisser, J. Marked splenomegaly in fetal cytomegalovirus infection: Detection supported by three-dimensional power Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 20, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Ghout, I.; Bussieres, L.; Stirnemann, J.; Magny, J.F.; Couderc, S.; Salomon, L.J.; Guilleminot, T.; Aegerter, P.; Benoist, G.; et al. In utero treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection with valacyclovir in a multicenter, open-label, phase II study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 462.e461–462.e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Kimura, H.; Torii, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Tanaka, T.; Tajiri, H.; Yoto, Y.; Tanaka-Taya, K.; Kanegane, H.; Nariai, A.; et al. Risk factors for poor outcome in congenital cytomegalovirus infection and neonatal herpes on the basis of a nationwide survey in Japan. Pediatr. Int. 2013, 55, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, T.; Petitt, M.; Zydek, M.; Fang-Hoover, J.; Larocque, N.; Tsuge, M.; Gormley, M.; Kauvar, L.M.; Pereira, L. Human cytomegalovirus infection interferes with the maintenance and differentiation of trophoblast progenitor cells of the human placenta. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5134–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doneda, C.; Parazzini, C.; Righini, A.; Rustico, M.; Tassis, B.; Fabbri, E.; Arrigoni, F.; Consonni, D.; Triulzi, F. Early cerebral lesions in cytomegalovirus infection: Prenatal MR imaging. Radiology 2010, 255, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, O.A.; Cuneo, A.A.; Barkovich, A.J.; Hashemi, Z.; Bartha, A.I.; Xu, D. Malformations of cortical development: Diagnostic accuracy of fetal MR imaging. Radiology 2012, 263, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannie, M.M.; Devlieger, R.; Leyder, M.; Claus, F.; Leus, A.; De Catte, L.; Cossey, V.; Foulon, I.; Van der Valk, E.; Foulon, W.; et al. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Contribution and best timing of prenatal MR imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipitz, S.; Elkan Miller, T.; Yinon, Y.; Weissbach, T.; De-Castro, H.; Hoffman, C.; Katorza, E.; Weisz, B. Revisiting short- and long-term outcome after fetal first-trimester primary cytomegalovirus infection in relation to prenatal imaging findings. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavoretto, P.I.; Fornara, C.; Baldoli, C.; Arossa, A.; Furione, M.; Candiani, M.; Rovere Querini, P.; Barera, G.; Poloniato, A.; Gaeta, G.; et al. Prenatal Management of Congenital Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in Seropositive Pregnant Patients Treated with Azathioprine. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltezou, P.G.; Kourlaba, G.; Kourkouni, E.; Luck, S.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Ville, Y.; Lilleri, D.; Dimopoulou, D.; Karalexi, M.; Papaevangelou, V. Maternal type of CMV infection and sequelae in infants with congenital CMV: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.B.; Mitchell, J.M.; McCowan, L.M.; Barker, S. Ultrasonographic measurement of liver length in the small-for-gestational-age fetus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 180, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins-Villarreal, A.; Moreno-Espinosa, A.L.; Martinez-Portilla, R.J.; Castillo, K.; Hahner, N.; Nakaki, A.; Trigo, L.; Picone, O.; Siauve, N.; Figueras, F.; et al. Fetal Liver Volume Assessment Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Fetuses with Cytomegalovirus Infection (dagger). Front. Med. 2022, 9, 889976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
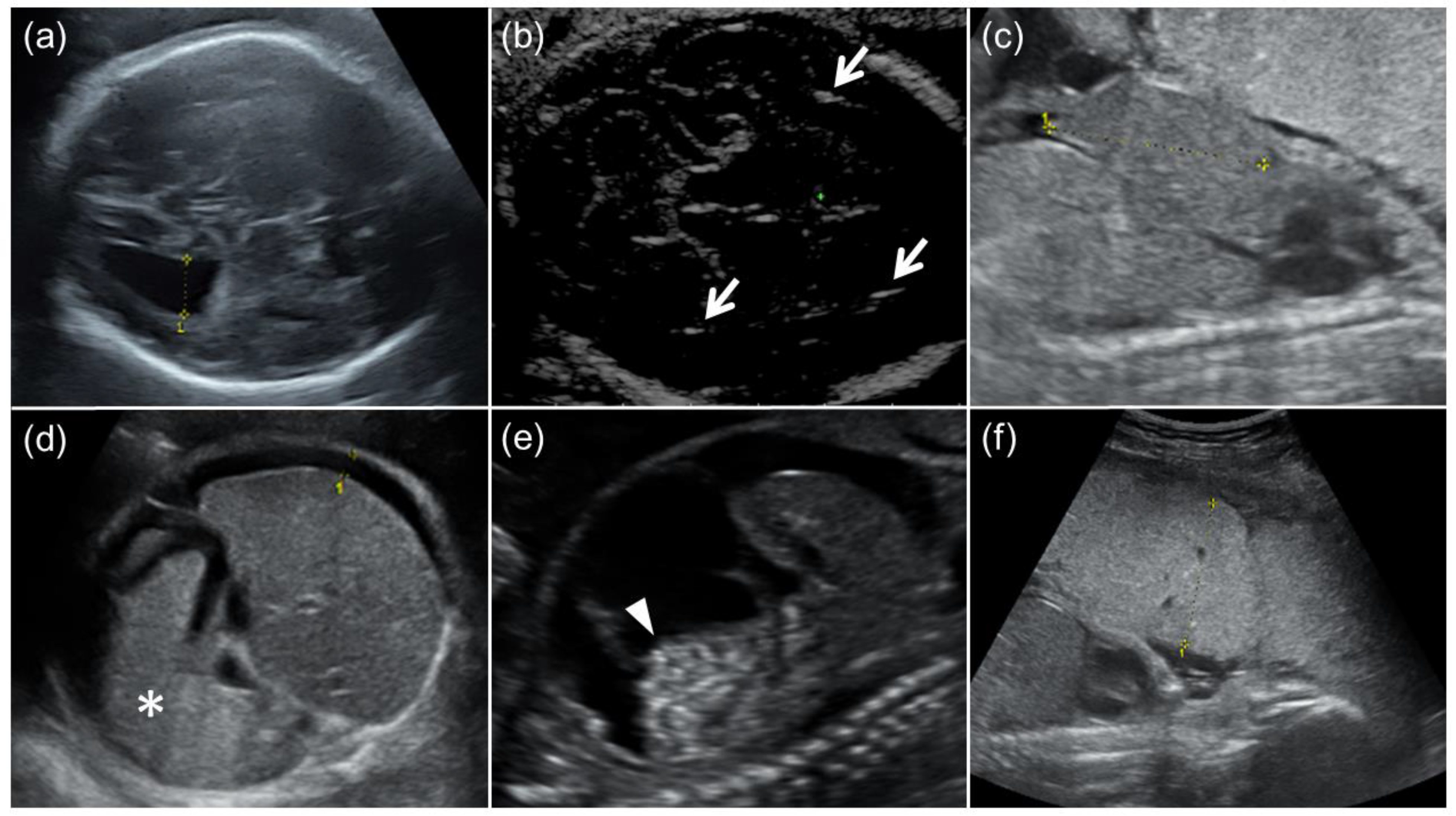
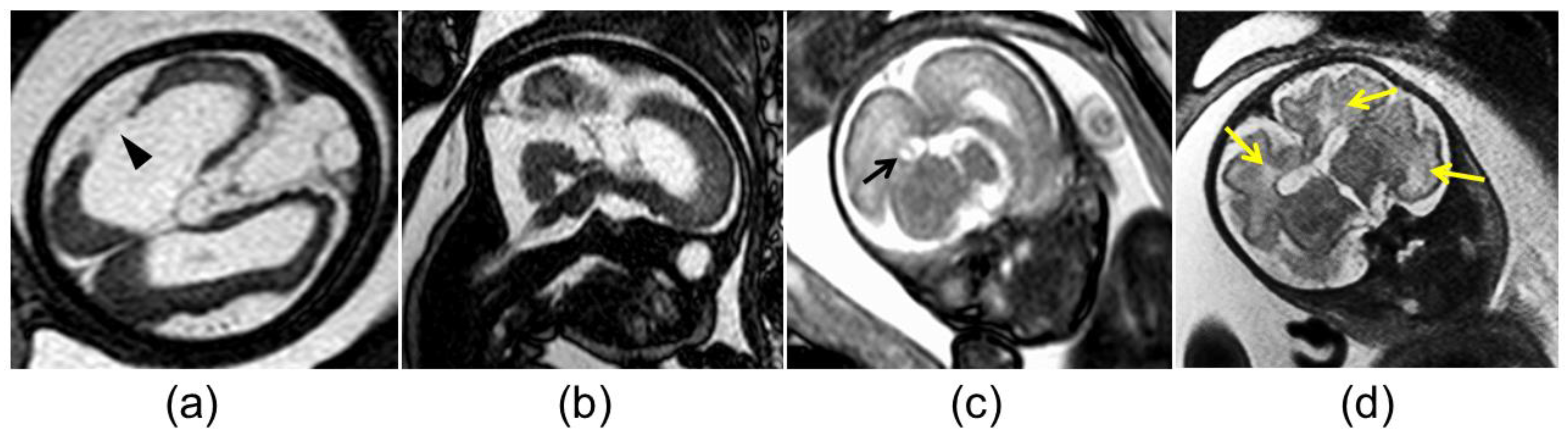
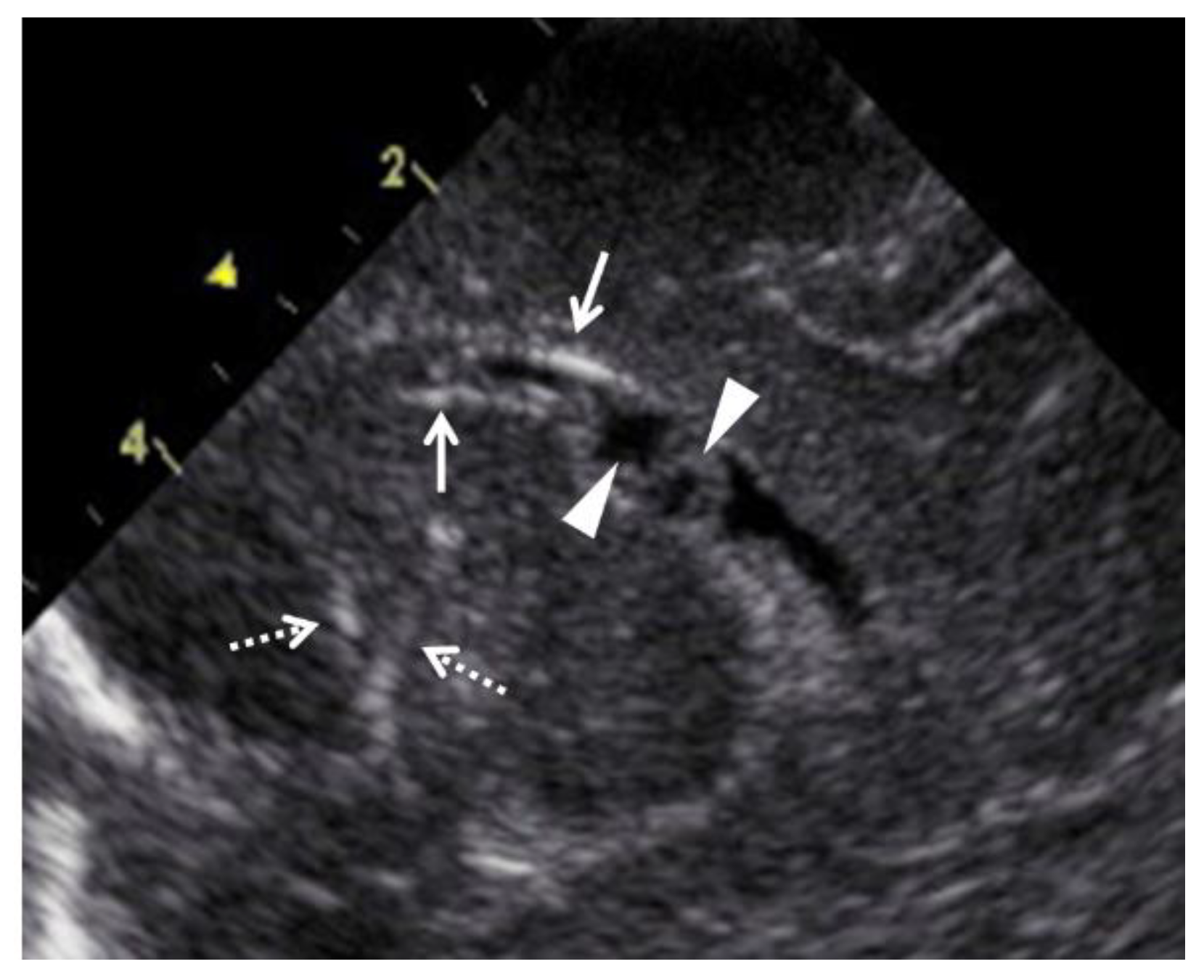
| Case | Age, Gravidity/Parity | Fetal US Findings | MRI Findings in the Fetal Brain | Clinical Findings at Birth | Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGR | Ventri-culo-megaly * | Intra-cranial Calcifi-cation | Cysts/Pseudo-cysts | Micro-cephaly | Ascites | Hepato-megaly | Spleno-megaly | Others | Birthweight, Delivery Mode, (GW) | Ventri-culo-megaly | Intra-Cranial Calcifi-ccation | Cysts/Pseudo-cysts | Micro-cephaly | Ascites | Hepato-megaly | Spleno-megaly | Others | Death | Hearling Impairment | Epilepsy | Cerebral Palsy | Overall-DQ | Age at Evalua-tion | |||
| 1 | 27, 2/1 | + (19) | − | − | − | − | + (19) | − | − | Cardiomegaly (22), poly-hydramnios (30) | None (27) | 1824 g, CS, (31) | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | Hypoplastic lung, anemia, thrombo- cytopenia | + | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 d |
| 2 | 28, 4/1 | + (25) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | Oligo-hydramnios (31) | None (31) | 1396 g, CS, (32) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | − | − | − | − | ≥80 | 5 y |
| 3 | 19, 3/0 | + (26) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | None (28) | 1378 g, CS, (31) | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | Petechia, anemia, thrombo-cytopenia, liver dysfunction | − | + Unilateral | − | − | ≥80 | 4 y |
| 4 | 36, 1/0 | + (23) | +++ (23) | − | − | + (30) | + (21) | − | − | None | Ventriculomegaly, pseudocyst, schizencephaly, cerebellar hypoplasia, WM hyperintensity (36) | 2184 g, CS, (36) | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | Schizencephaly, thrombocytopenia, liver dysfunction, chorioretinitis | − | + Bilateral | + | + | <70 | 3 y |
| 5 | 23, 2/1 | + (19) | ++ (25) | − | − | − | − | + (25) | − | Hyperechoic bowel (21), cardiomegaly (22) | Ventriculomegaly (30) | 2192 g, CS, (36) | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia, cholestasis | − | − | − | − | 70–79 | 5 y |
| 6 | 32, 8/2 | + (29) | ++ (33) | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | Ventriculomegaly, pseudocyst (34) | 2030 g, CS, (36) | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia, liver dysfunction | − | − | − | − | ≥80 | 4 y |
| 7 | 22, 2/0 | + (30) | + (35) | + (30) | − | + (30) | − | + (35) | − | None | Cerebellar hypoplasia (31) | 1860 g, CS, (36) | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia, liver dysfunction, retinal vascular malformation | − | + Bilateral | + | + | <70 | 3 y |
| 8 | 28, 1/0 | + (23) | + (34) | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | Ventriculomegaly, cerebellar hypoplasia, WM hyperintensity (31) | 1255 g, CS, (35) | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | WM lesion, cerebral atrophy, cholestasis, thrombocytopenia, liver dysfunction | − | + Bilateral | − | + | <70 | 3 y |
| Case | Age, Gravidity/Parity | Fetal US Findings | MRI Findings in the Fetal Brain | Clinical Findings at Birth | Outcomes | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGR | Ventri-culo-megaly * | Intra-cranial calcifi-cation | Cysts/Pseudo-cysts | Micro-cephaly | Ascites | Hepato-megaly | Spleno-megaly | Others | Birthweight, Delivery Mode, (GW) | Ventri-culo-megaly | Intra-cranial Calcifi-cation | Cysts/Pseudo-cysts | Micro-cephaly | Ascites | Hepato-megaly | Spleno-megaly | Others | Death | Hearling Impairment | Epilepsy | Cerebral Palsy | Overall-DQ | Age at Evalua-tion | |||
| 1 | 35, 2/1 | − | +++ (30) | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | Ventriculomegaly, pseudocyst (33) | 2956 g, VD, (38) | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | None | − | + Unilateral | − | − | ≥ 80 | 5 y |
| 2 | 30, 3/1 | − | + (24) | − | − | − | + (22) | + (24) | + (24) | Cardiomegaly (24), peri-cardial effusion (24), palacento-megaly (24) | None (30) | 2236 g, CS, (31) | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | Hypoplastic lung, petechia, anemia, thrombo-cytopenia, liver dysfunction | + | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0 d |
| 3 | 21, 1/0 | − | ++ (28) | − | − | − | + (28) | + (28) | − | Hyperechoic bowel (28) | Ventriculomegaly, pseudocyst (31) | 2688 g, CS, (33) | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia, cholestasis | − | + Bilateral | − | − | ≥80 | 3 y |
| 4 | 29, 1/0 | − | + (28) | − | − | − | − | + (35) | − | None | Ventriculomegaly (32) | 2996 g, CS, (37) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | Liver dysfunction | − | − | − | − | ≥80 | 3 y |
| 5 | 37, 2/1 | − | +++ (30) | − | − | − | − | − | − | None | Ventriculomegaly, cortical malformation (32) | 2646 g, VD, (38) | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | None | − | − | − | − | ≥80 | 3 y |
| 6 | 29, 2/0 | − | ++ (24) | + (24) | − | − | + (20) | + (24) | − | Placento- megaly (24) | Ventriculomegaly, MW hyperintensities, cerebellar hypoplasia (34) | 2848 g, CS, (34) | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia | − | − | − | − | ≥80 | 3 y |
| 7 | 29, 1/0 | − | + (24) | − | − | − | + (21) | + (22) | − | None | Ventriculomegaly (31) | 2312 g, CS, (33) | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia | − | + Unilateral | − | − | ≥80 | 3 y |
| 8 | 19, 1/0 | − | + (24) | − | − | − | + (23) | + (24) | − | Hyperechoic bowel (24), placento-megaly (24) | U/D (24) | 1660 g, CS, (32) | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | Petechia, neutropenia, thrombo-cytopenia | − | − | − | − | 70–79 | 3 y |
| 9 | 32, 2/1 | − | − | − | − | − | + (20) | + (27) | − | Hyperechoic bowel (20), placento-megaly (22) | Ventriculomegaly (30) | 1860 g, CS, (30) | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | Petechia, thrombo-cytopenia, liver dysfunction | − | − | − | + | <70 | 1.5 y |
| 10 | 30, 3/2 | − | + (23) | − | − | − | + (20) | + (34) | − | None | Ventriculomegaly (30) | 3216 g, VD, (38) | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | None | − | + Bilateral | − | N/D | N/D | Dropped out before 1.5y |
| All n = 18 | cCMV with FGR n = 8 | cCMV without FGR n = 10 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |||||
| Age | 29 (19–37) | 28 (19–36) | 30 (19–37) | 0.3 | |
| Gravidity | 2 (1–8) | 2 (1–8) | 2 (1–3) | 0.3 | |
| Parity | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1.0 | |
| US findings of the fetuse or placenta | |||||
| Ventriculomegaly | |||||
| ≥mild | 14 (77.8%) | 5 (62.5%) | 9 (90.0%) | 0.3 | |
| ≥moderate | 7 (38.9%) | 3 (37.5%) | 4 (40.0%) | 1.0 | |
| ≥severe | 3 (16.7%) | 1 (12.5%) | 2 (20.0%) | 1.0 | |
| Intracranial calcification | 2 (11.1%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | 1.0 | |
| Cysts/pseudocysts in the brain | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.0 | |
| Microcephaly | 2 (11.1%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.2 | |
| Ascites | 9 (50.0%) | 2 (25.0%) | 7 (70.0%) | 0.2 | |
| Hepatomegaly | 10 (55.6%) | 2 (25.0%) | 8 (80.0%) | 0.054 | |
| Splenomegaly | 1 (5.6%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 1.0 | |
| Hyperechoic bowel | 4 (22.2%) | 1 (12.5%) | 3 (30.0%) | 0.6 | |
| Placentomegaly | 4 (22.2%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (40.0%) | 0.09 | |
| All n = 18 | cCMV with FGR n = 8 | cCMV without FGR n = 10 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal characteristics | ||||
| GW at birth | 35 (30–38) | 36 (31–36) | 34 (30–38) | 0.7 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2188 (1255–3216) | 1842 (1255–2192) | 2667 (1660–3216) | 0.006 |
| Cesarean delivery | 15 (83.3%) | 8 (100%) | 7 (70%) | 0.2 |
| Physical and imaging findings of newborns | ||||
| Ventriculomegaly | 15 (83.3%) | 6 (75.0%) | 9 (90.0%) | 0.6 |
| Intracranial calcification | 10 (55.6%) | 5 (62.5%) | 5 (50.0%) | 0.7 |
| Cysts/pseudocysts in the brain | 7 (38.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 6 (60.0%) | 0.07 |
| Microcephaly | 2 (11.1%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.2 |
| Ascites | 6 (33.3%) | 1 (12.5%) | 5 (50.0%) | 0.2 |
| Hepatomegaly | 10 (55.6%) | 5 (62.5%) | 5 (50.0%) | 0.7 |
| Splenomegaly | 4 (22.2%) | 3 (37.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.3 |
| Anemia | 3 (16.7%) | 2 (25.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.6 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 13 (72.2%) | 7 (87.5%) | 6 (60.0%) | 0.3 |
| Adverse outcomes in affected newborns | ||||
| Death | 2 (11.1%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1 (10.0%) | 1.0 |
| Bilateral hearing impairment | 5 (31.3% a) | 3 (42.9% b) | 2 (22.2% c) | 0.6 |
| Epilepsy | 2 (12.5% a) | 2 (28.6% b) | 0 (0% c) | 0.2 |
| Cerebral palsy | 4 (26.7% d) | 3 (42.9% b) | 1 (12.5% e) | 0.3 |
| Overall DQ < 70 | 4 (26.7% d) | 3 (42.9% b) | 1 (12.5% e) | 0.3 |
| Findings Associated with cCMV | Subjects | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Positive Predictive Value (%) | Negative Predictive Value (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ventriculomegaly | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 66.7 | 50.0 | 80.0 | 33.3 | 62.5 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 88.9 | 0 | 88.9 | 0 | 80.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 80.0 | 33.3 | 85.7 | 25.0 | 72.2 | |
| Intracranial calcification | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 20.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 42.9 | 50.0 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 20.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 55.6 | 60.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 20.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 | 55.6 | |
| Cysts/pseudocysts | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 0 | 100.0 | N/A | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 0 | 100.0 | N/A | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 0 | 100.0 | N/A | 66.7 | 66.7 | |
| Microcephaly | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 50.0 | 83.3 | 50.0 | 83.3 | 75.0 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | N/A | 100.0 | N/A | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 50.0 | 93.8 | 50.0 | 93.8 | 88.9 | |
| Ascites | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 100.0 | 85.7 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 87.5 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 100.0 | 60.0 | 71.4 | 100.0 | 80.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 100.0 | 75.0 | 66.7 | 100.0 | 83.3 | |
| Hepatomegaly | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 40.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 | 62.5 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 100.0 | 40.0 | 62.5 | 100.0 | 70.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 70.0 | 62.5 | 70.0 | 62.5 | 66.7 | |
| Splenomegaly | cCMV with FGR (n = 8) | 0 | 100.0 | N/A | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| cCMV without FGR (n = 10) | 0 | 88.9 | 0 | 88.9 | 80.0 | |
| All (n = 18) | 0 | 92.9 | 0 | 76.5 | 72.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanimura, K.; Uchida, A.; Uenaka, M.; Imafuku, H.; Tairaku, S.; Hashimura, H.; Ueno, Y.; Kido, T.; Fujioka, K. Fetal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Associated with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020306
Tanimura K, Uchida A, Uenaka M, Imafuku H, Tairaku S, Hashimura H, Ueno Y, Kido T, Fujioka K. Fetal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Associated with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020306
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanimura, Kenji, Akiko Uchida, Mizuki Uenaka, Hitomi Imafuku, Shinya Tairaku, Hiromi Hashimura, Yoshiko Ueno, Takumi Kido, and Kazumichi Fujioka. 2023. "Fetal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Associated with and without Fetal Growth Restriction" Diagnostics 13, no. 2: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020306
APA StyleTanimura, K., Uchida, A., Uenaka, M., Imafuku, H., Tairaku, S., Hashimura, H., Ueno, Y., Kido, T., & Fujioka, K. (2023). Fetal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Associated with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Diagnostics, 13(2), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020306







