Optimal Parameter Configuration of a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput, Label-Free Circulating Tumor Cell Separation and Enrichment Based on Inertial Focusing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Working Principle
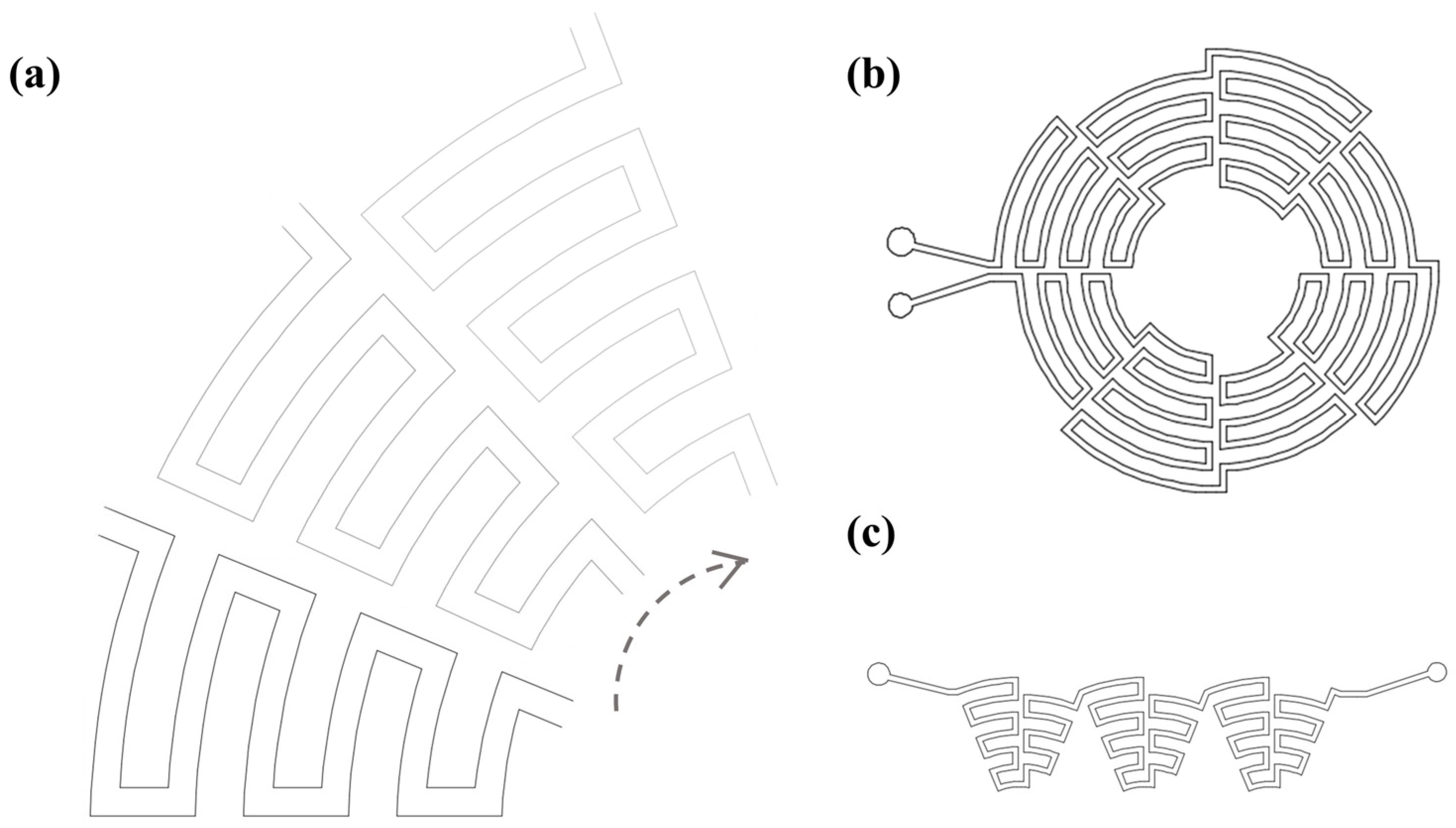
2.2. Chip Fabrication
2.3. Preparation of Polystyrene Particle Samples
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Fluorescence Staining
2.6. Blood Sample Preparation
2.7. Chip Characterization
3. Results
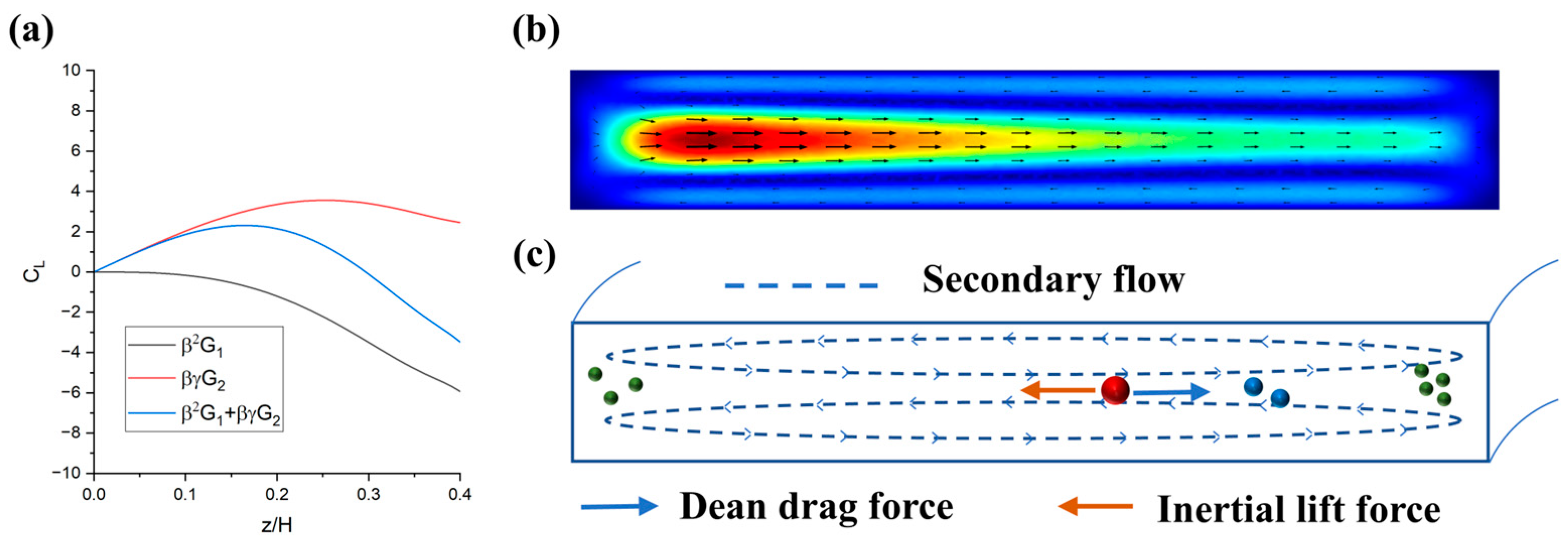
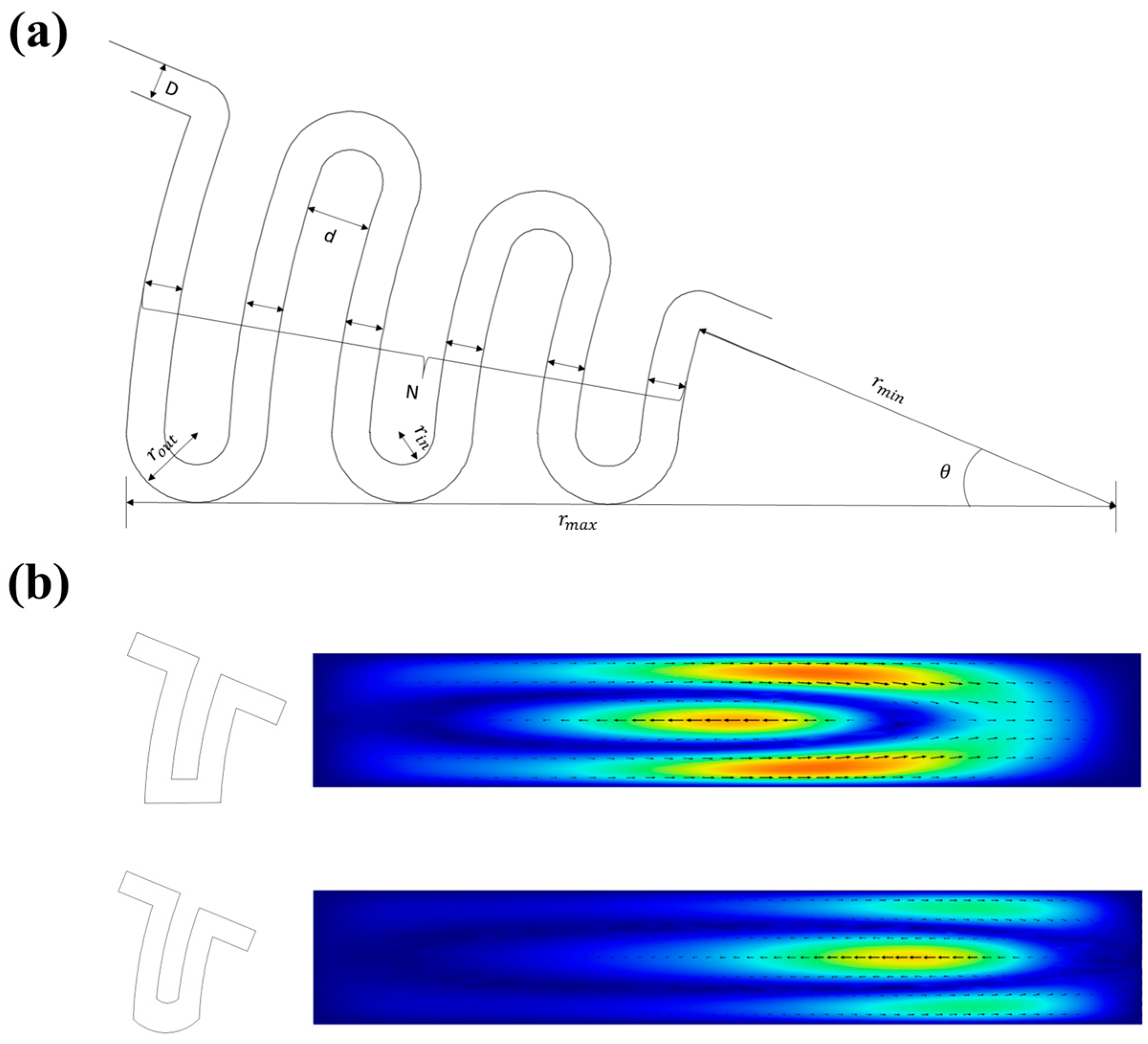
3.1. The Design of the Inertial Focusing Structure
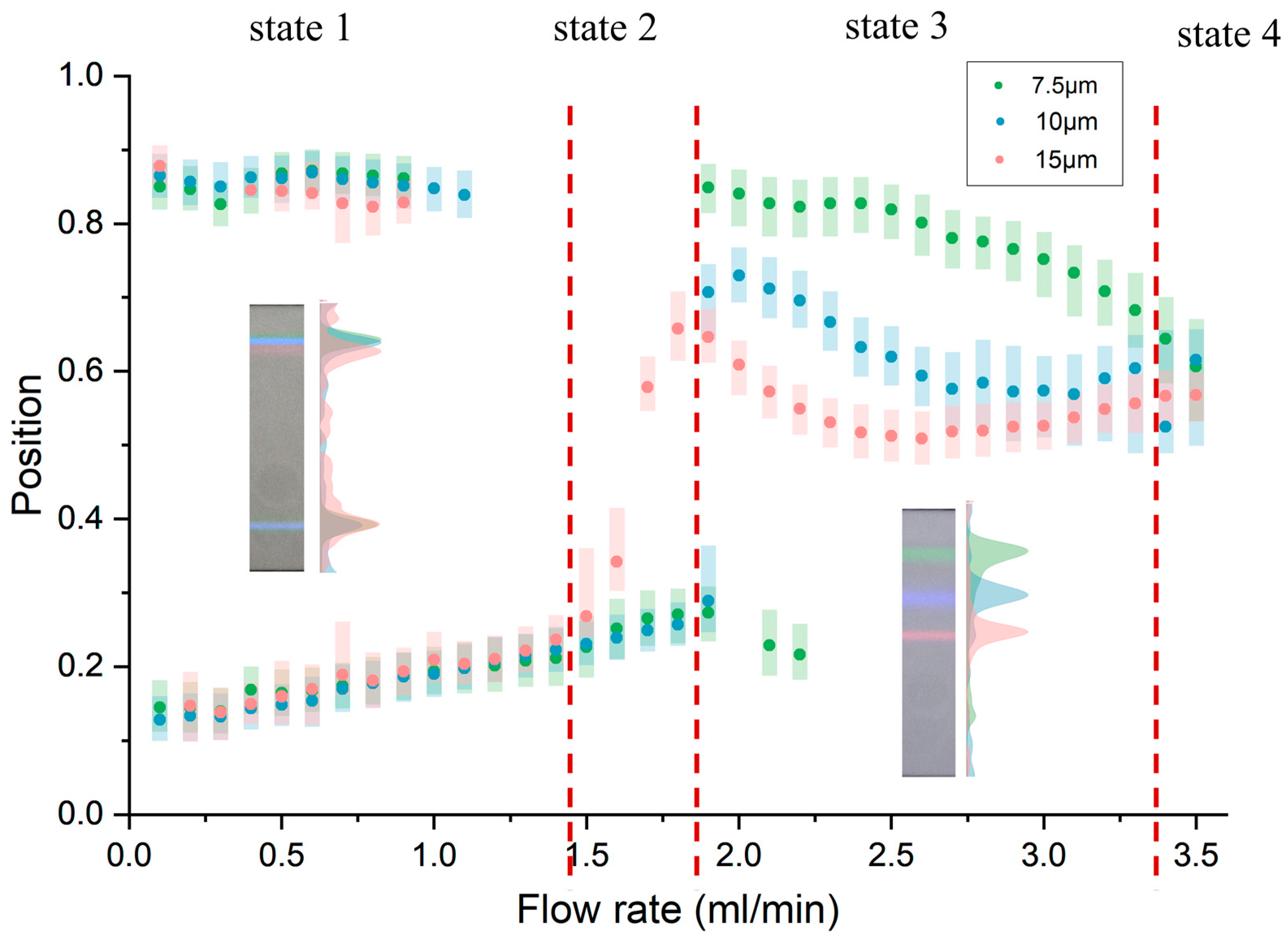
3.2. Particle Focusing Performance
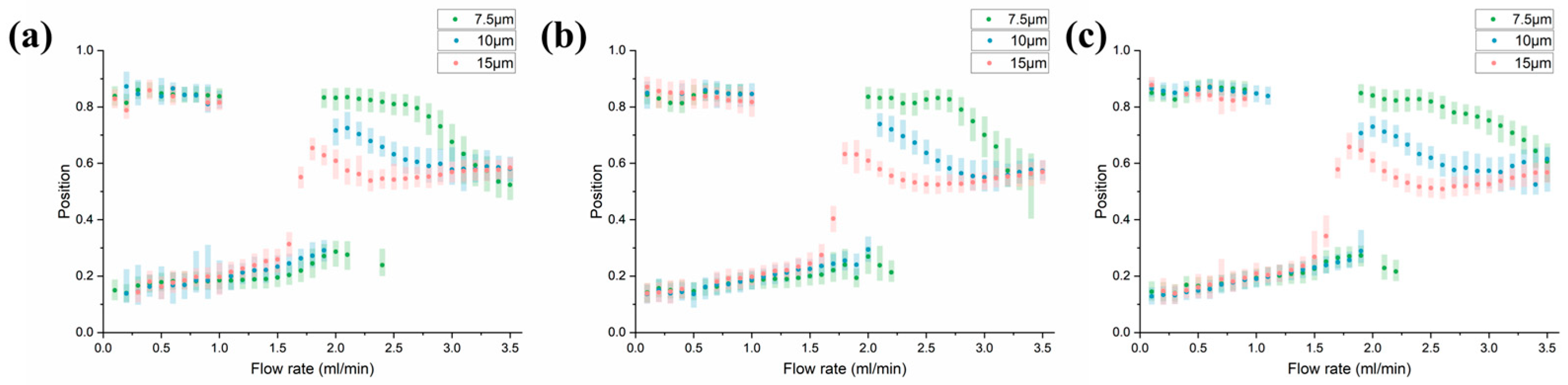
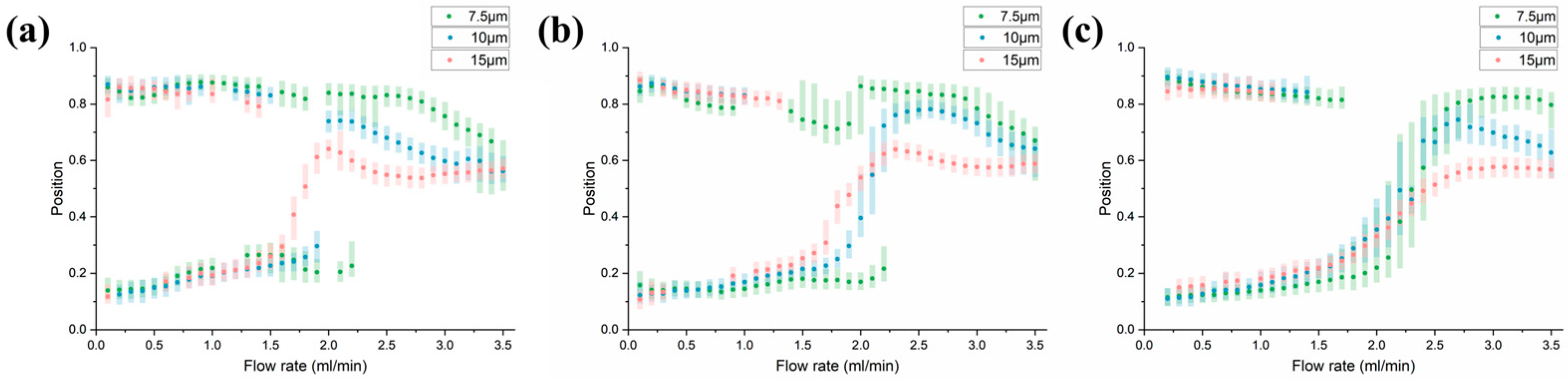
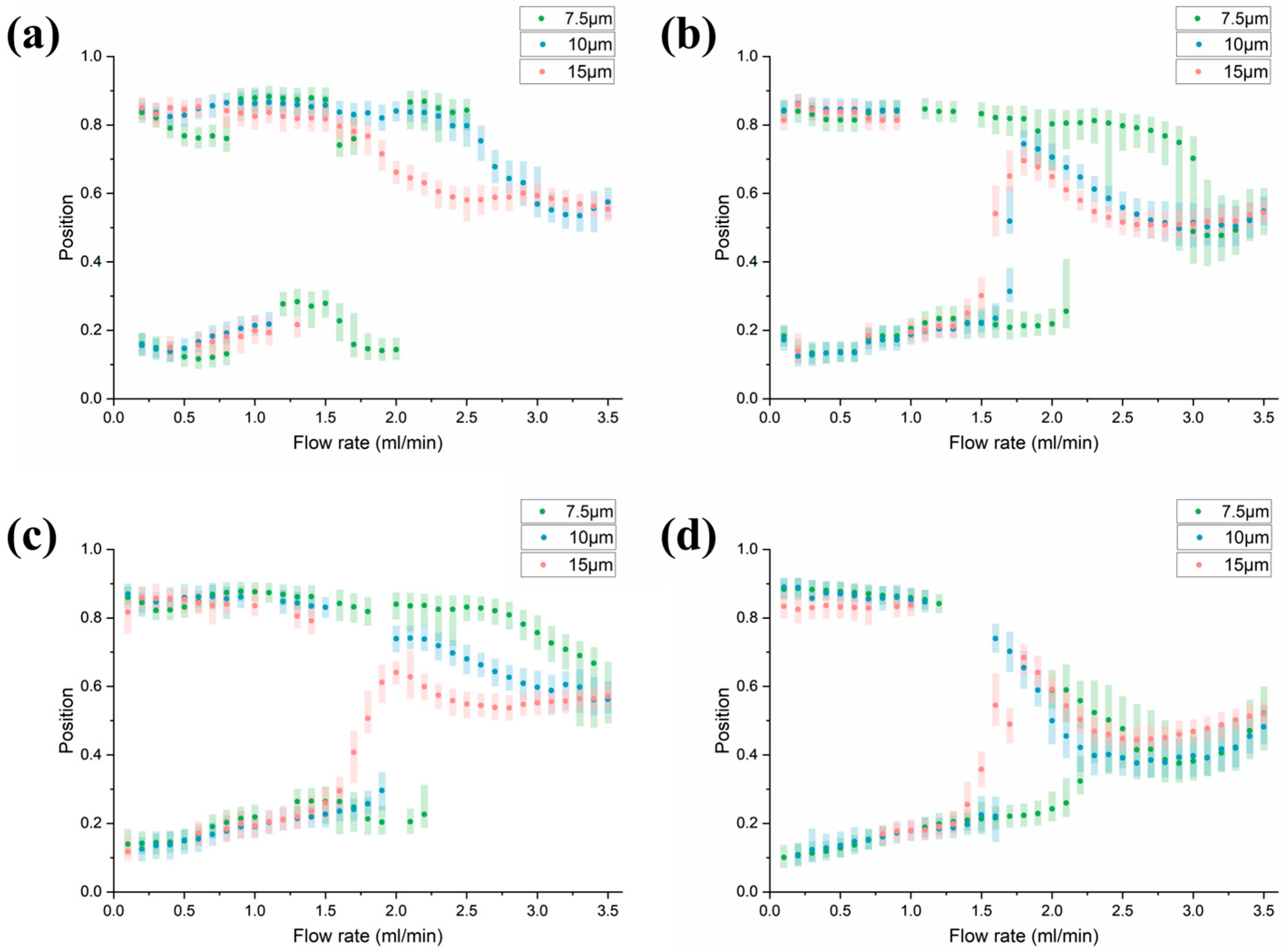
3.3. Parametric Analysis
3.4. Performance Testing of the Inertial Focusing Chip
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.Y.; Oskarsson, T.; Acharyya, S.; Nguyen, D.X.; Zhang, X.H.F.; Norton, L.; Massague, J. Tumor Self-Seeding by Circulating Cancer Cells. Cell 2009, 139, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, T.R. A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after death. Aust. Med. J. 1869, 14, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, A.H.K.; Chow, C.; To, K.F. Latest development of liquid biopsy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1645–S1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.K.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.B.; Chang, H.; Yu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J. Liquid Biopsy Applications in the Clinic. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riethdorf, S.; Müller, V.; Zhang, L.; Rau, T.; Loibl, S.; Komor, M.; Roller, M.; Huober, J.; Fehm, T.; Schrader, I.; et al. Detection and HER2 Expression of Circulating Tumor Cells: Prospective Monitoring in Breast Cancer Patients Treated in the Neoadjuvant GeparQuattro Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2634–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating Tumor Cells Predict Survival Benefit from Treatment in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Benali, N.L. Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future directions. Cancer Lett. 2007, 253, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.P.; Thendral, V.; Uthappa, U.T.; Lee, K.-H.; Kigga, M.; Altalhi, T.; Kurkuri, M.D.; Kant, K. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Platform for Physical and Immunological Detection and Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biosensors 2022, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahinia, A.; Zhang, W.; Badea, I. Recent Developments in Inertial and Centrifugal Microfluidic Systems along with the Involved Forces for Cancer Cell Separation: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, L.; Garcia, J.; Barthelemy, D.; Laurenceau, E.; Payen, L.; Le Roy, D.; Deman, A.-L. MagPure chip: An immunomagnetic-based microfluidic device for high purification of circulating tumor cells from liquid biopsies. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 4151–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusyk, A.; Polyak, K. Tumor heterogeneity: Causes and consequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2010, 1805, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.M.; Yu, M.; Nakamura, Z.; Ciciliano, J.; Ulman, M.; Kotz, K.; Stott, S.L.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Toner, M. Biopolymer System for Cell Recovery from Microfluidic Cell Capture Devices. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3682–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Cai, L.; Chang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Sun, J. Label-free isolation of rare tumor cells from untreated whole blood by interfacial viscoelastic microfluidics. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3436–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xu, J.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Xue, N.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; et al. A novel microfluidic device integrating focus-separation speed reduction design and trap arrays for high-throughput capture of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 4094–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H. Capturing and Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells with Wave Microfluidic Chip. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 190, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, W. A high-throughput liquid biopsy for rapid rare cell separation from large-volume samples. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zong, S.; Yun, B.; Cui, Y. Combining Multiplex SERS Nanovectors and Multivariate Analysis for In Situ Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cell Phenotype Using a Microfluidic Chip. Small 2018, 14, 1704433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-H.; Lim, M.; Park, J.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, H.C.; Jung, S.; Kim, B.C.; et al. FAST: Size-Selective, Clog-Free Isolation of Rare Cancer Cells from Whole Blood at a Liquid–Liquid Interface. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, A.F.; Aceto, N.; Kojic, N.; Donaldson, M.C.; Zeinali, M.; Hamza, B.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Miyamoto, D.T.; et al. A microfluidic device for label-free, physical capture of circulating tumor cell clusters. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Yang, L.; et al. Highly Sensitive Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Biomimetic Multivalent Aptamer Nanoclimber Functionalized Microfluidic Chip. Small 2020, 16, 2000949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edd, J.F.; Mishra, A.; Dubash, T.D.; Herrera, S.; Mohammad, R.; Williams, E.K.; Hong, X.; Mutlu, B.R.; Walsh, J.R.; de Carvalho, F.M.; et al. Microfluidic concentration and separation of circulating tumor cell clusters from large blood volumes. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrinucci, D.; Bethel, K.; Lazar, D.; Fisher, J.; Huynh, E.; Clark, P.; Bruce, R.; Nieva, J.; Kuhn, P. Cytomorphology of Circulating Colorectal Tumor Cells: A Small Case Series. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 861341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Jin, C.; Guo, Q.; Ang, R.R.; Duffy, S.P.; Matthews, K.; Azad, A.; Abdi, H.; Todenhöfer, T.; Bazov, J.; et al. Continuous Flow Deformability-Based Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Microfluidic Ratchets. Small 2016, 12, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pødenphant, M.; Ashley, N.; Koprowska, K.; Mir, K.U.; Zalkovskij, M.; Bilenberg, B.; Bodmer, W.; Kristensen, A.; Marie, R. Separation of cancer cells from white blood cells by pinched flow fractionation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4598–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Lee, J.; Ra, M.; Gwon, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Yoo, K.-C.; Sul, O.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, W.-Y.; et al. Continuous Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Whole Blood Using a Slanted Weir Microfluidic Device. Cancers 2019, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakova, M.S.S.; Menyailo, M.E.E.; Schegoleva, A.A.A.; Bokova, U.A.A.; Larionova, I.V.V.; Denisov, E.V.V. Technologies for Viable Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, L.; Le Roy, D.; Deman, A.-L. Microfluidic-Based Technologies for CTC Isolation: A Review of 10 Years of Intense Efforts towards Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SegrÉ, G.; Silberberg, A. Radial Particle Displacements in Poiseuille Flow of Suspensions. Nature 1961, 189, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.P.; Leal, L.G. Inertial migration of rigid spheres in two-dimensional unidirectional flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 65, 365–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.; Edd, J.F.; Humphry, K.J.; Stone, H.A.; Toner, M. Particle Segregation and Dynamics in Confined Flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 094503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, G. Machine learning assisted fast prediction of inertial lift in microchannels. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matas, J.; Morris, J.; Guazzelli, E. Lateral Forces on a Sphere. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.-Rev. IFP 2004, 59, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.; Irimia, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18892–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Jana, J.A.; Kaehr, A.; Purcell, E.; Opdycke, T.; Paoletti, C.; Cooling, L.; Thamm, D.H.; Hayes, D.F.; Nagrath, S. Inertial focusing of circulating tumor cells in whole blood at high flow rates using the microfluidic CTCKey™ device for CTC enrichment. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.; Fallahi, H.; Dai, Y.; Yadav, S.; Hettiarachchi, S.; McNamee, A.; An, H.; Xiang, N.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Zhang, J. Tuning particle inertial separation in sinusoidal channels by embedding periodic obstacle microstructures. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2789–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi Bazaz, S.; Mihandust, A.; Salomon, R.; Joushani, H.A.N.; Li, W.; Amiri, H.A.; Mirakhorli, F.; Zhand, S.; Shrestha, J.; Miansari, M.; et al. Zigzag microchannel for rigid inertial separation and enrichment (Z-RISE) of cells and particles. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 4093–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.W.; Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Li, Z.R.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.-T.; Han, J.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Lim, C.T. Isolation and retrieval of circulating tumor cells using centrifugal forces. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, H.M.; Leong, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Kong, F.; Upadya, M.; Dalan, R.; Tay, C.Y.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S.; Hou, H.W. Direct isolation of circulating extracellular vesicles from blood for vascular risk profiling in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2511–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, N.; Ni, Z. High-throughput concentration of rare malignant tumor cells from large-volume effusions by multistage inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Shin, J.H.; Bae, C.Y.; Choi, S.; Park, J.-K. Label-Free Cancer Cell Separation from Human Whole Blood Using Inertial Microfluidics at Low Shear Stress. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6213–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Rivera-Báez, L.; Fouladdel, S.; Yoon, H.J.; Guthrie, S.; Wieger, J.; Deol, Y.; Keller, E.; Sahai, V.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Syst. 2017, 5, 295–304.e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafeie, M.; Zhang, J.; Asadnia, M.; Li, W.; Warkiani, M.E. Multiplexing slanted spiral microchannels for ultra-fast blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Ma, Y.; Lu, C.; Cai, Z.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G. Optimal Parameter Configuration of a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput, Label-Free Circulating Tumor Cell Separation and Enrichment Based on Inertial Focusing. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233556
Sun X, Ma Y, Lu C, Cai Z, Han J, Wang Z, Yang G. Optimal Parameter Configuration of a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput, Label-Free Circulating Tumor Cell Separation and Enrichment Based on Inertial Focusing. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(23):3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233556
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xiaoyi, Yuqi Ma, Chunyang Lu, Ziwei Cai, Jintao Han, Zhigang Wang, and Gen Yang. 2023. "Optimal Parameter Configuration of a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput, Label-Free Circulating Tumor Cell Separation and Enrichment Based on Inertial Focusing" Diagnostics 13, no. 23: 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233556
APA StyleSun, X., Ma, Y., Lu, C., Cai, Z., Han, J., Wang, Z., & Yang, G. (2023). Optimal Parameter Configuration of a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput, Label-Free Circulating Tumor Cell Separation and Enrichment Based on Inertial Focusing. Diagnostics, 13(23), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233556






