Cerebellar Abscess Secondary to Cholesteatomatous Otomastoiditis—An Old Enemy in New Times
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Report
2.1. Patient Information and Clinical Findings
2.2. Diagnostic Assessment
2.2.1. Laboratory Studies
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)—leukocitosis of 10,300/µL (4000–10,000/µL)
- Neutrophilia—7250/µL (1100–7000/µL)
- Erytrocite sedimentation rate—79 (0–10/mm/1 h)
- Serum C-protein reactive (CRP)—4.8 (0–1.0/mg/dL)
- Fibrinogen—522 (150–400/mg/dL)
- HIV test—negative
- Blood cultures in fever, cultures from the ear—negative.
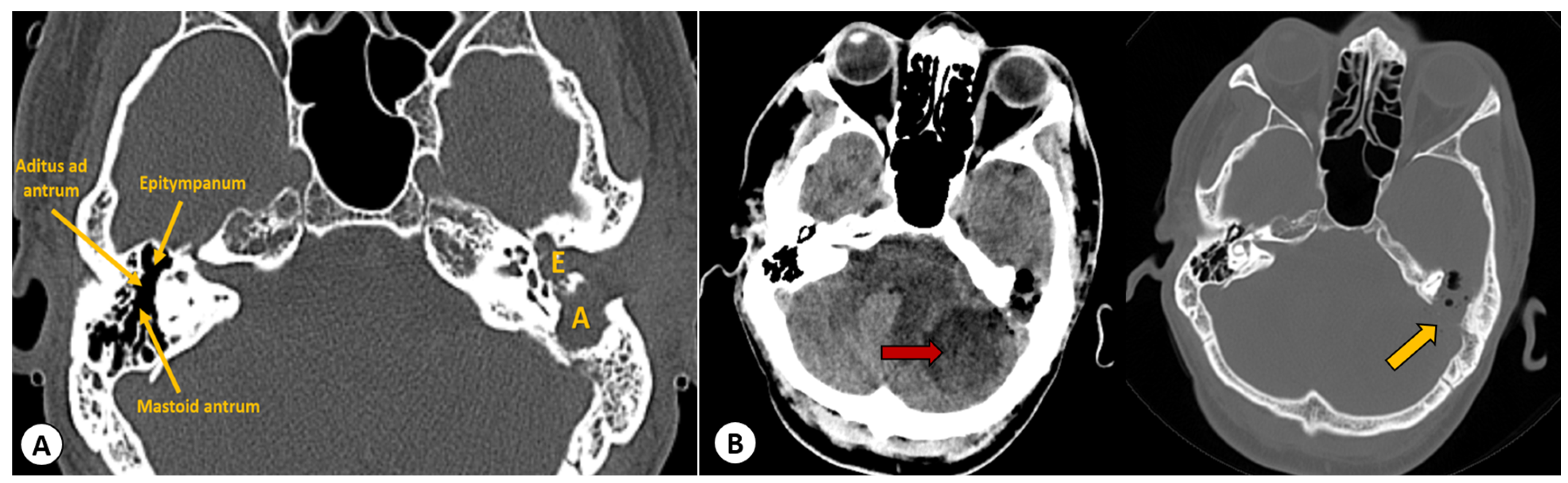
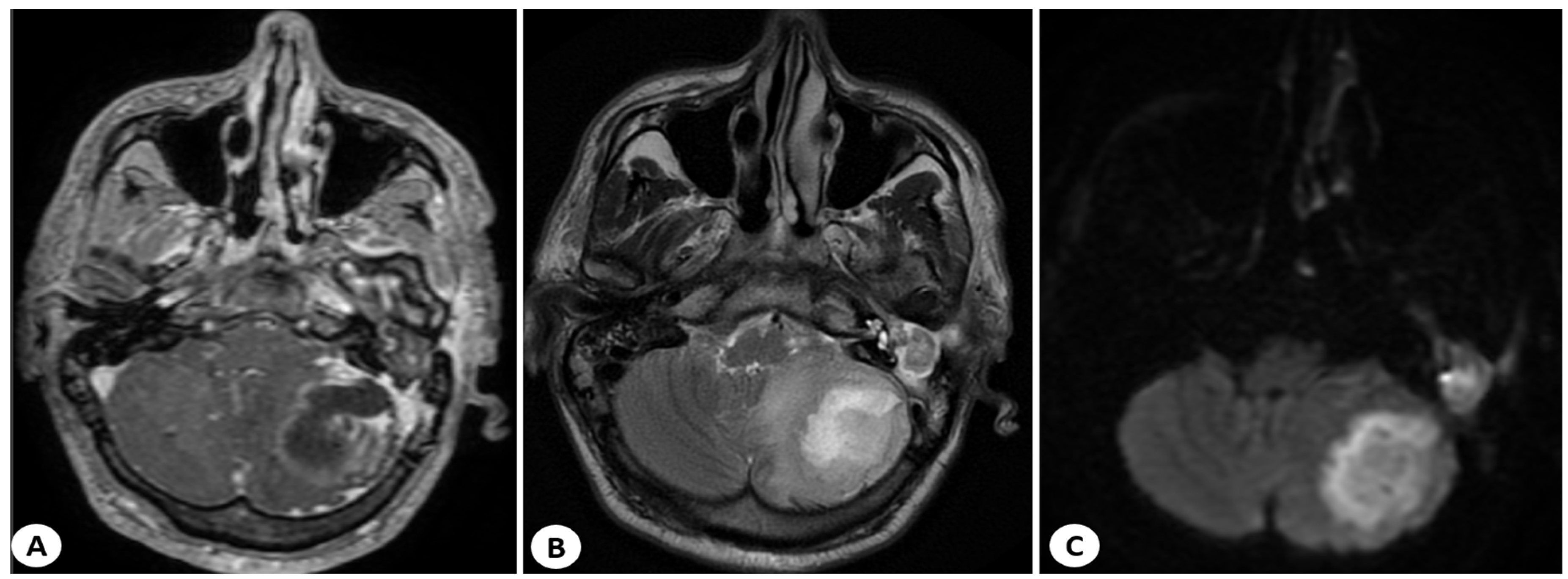
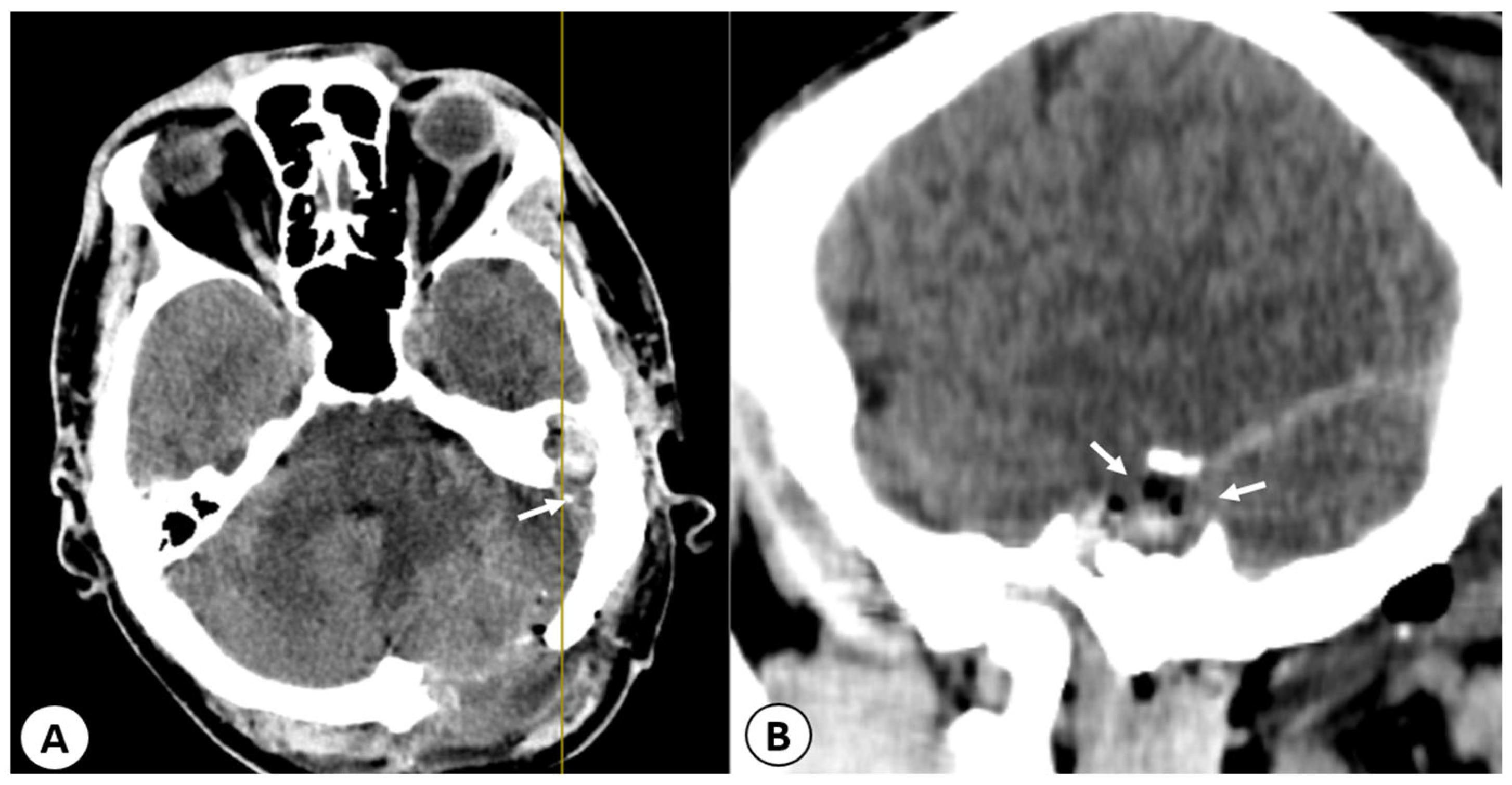
2.2.2. Imaging Studies
2.3. Therapeutic Intervention
3. Discussion
3.1. Anatomical Pathways for the Spread of Infection to the Intracranial Space
3.2. Microbial Etiology
3.3. Signs and Symptoms
3.4. Laboratory Studies
3.5. Imaging Studies
3.6. Medical Treatment
3.7. Surgical Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verhoeff, M.; van der Veen, E.L.; Rovers, M.M.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Schilder, A.G.M. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A Review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluestone, C.D. Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1998, 42, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.J.; do Han, K.; Park, K.H.; Cho, C.H.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Rate of Chronic Otitis Media Operations and Cholesteatoma Surgeries in South Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study (2006–2018). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.U.; Ashraf, M.F.; Qureshi, M.A.; Shehryar, M.; Tareen, H.K.; Ashraf, M.A. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media Leading to Cerebellar Brain Abscess, Still a Problem in 21st Century: A Case Report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 80, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.; Wilkinson, E.; Wagner, R. Management of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media and Otosclerosis in Developing Countries. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 51, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Burden of Illness and Management Options. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/42941/9241591587.pdf?isAl&sequence=1 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Alho, O.P.; Jokinen, K.; Laitakari, K.; Palokangas, J. Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media and Cholesteatoma. Vanishing Diseases among Western Populations? Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1997, 22, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakzouk, S.M.; Hajjaj, M.F. Epidemiology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media among Saudi Children—A Comparative Study of Two Decades. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 62, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, V.B.; Chavan, V.R.; Borade, V.R.; Kotnis, D.P.; Jaiswal, S.J. Intracranial Complications of Otitis Media: In Retrospect. Indian. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 57, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Arora, N.; Meher, R.; Passey, J.C.; Bansal, R. Intracranial Complications of CSOM in Pediatric Patients: A Persisting Problem in Developing Countries. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 100, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; Gupta, S.; Prakash, A.; Garg, A.; Dixit, R. HRCT Imaging of Acquired Cholesteatoma: A Pictorial Review. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nager, F.R. Cholesteatoma of the Middle Ear—Its Etiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1925, 34, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadé, J.; Konak, S.; Hinchcliffe, R. Cholesteatoma and Mastoid Surgery: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 22–27 March 1981; Kugler Publications: Tel-Aviv, Israel, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- De Aquino, J.E.A.P.; Cruz Filho, N.A.; de Aquino, J.N.P. Epidemiology of Middle Ear and Mastoid Cholesteatomas: Study of 1146 Cases. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 77, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, J.; Berco, E.; Buyanover, D. Ossicular Damage in Chronic Middle Ear Inflammation. In Cholesteatoma and Mastoid Surgery; Sade, J., Ed.; Kugler Publication: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sade, J.; Berco, E.; Halevy, A. Bone Resorption in Chronic Otitis Media with and without Cholesteatoma. In Cholesteatoma; McCabe, B.S., Sade, J., Abramson, M., Eds.; Aesculapius: Birmingham, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, I. Microbiology and Treatment of Brain Abscess. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 38, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, D.A.; Browning, G.G. Risks of Developing an Otogenic Intracranial Abscess. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1990, 104, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H.; Park, M.K.; Lee, J.D.; Hwang, S.C. Otogenic Brain Abscess Presenting with Gait Ataxia. Korean J. Audiol. 2012, 16, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Suri, A.; Mahapatra, A.K. Primary Excision of Pediatric Posterior Fossa Abscesses—Towards Zero Mortality? A Series of Nine Cases and Review. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2003, 38, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucu, A.I.; Costea, C.F.; Perciaccante, A.; Carauleanu, A.; Turliuc, S.; Costachescu, B.; Poeata, I.; Turliuc, M.D. The History of Arachne Through Historic Descriptions of Meningiomas with Hyperostosis: From Prehistory to the Present. World Neurosurg. 2019, 128, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melkundi, S.; Melkundi, R.S. Otogenic Brain Abscess and Its Management with Review of Literature. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2017, 3, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrascu, R.E.; Cucu, A.I.; Costea, C.F.; Cosman, M.; Blaj, L.A.; Hristea, A. Brain Tuberculosis: An Odyssey through Time to Understand This Pathology. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.D.; Russell, J.A. Cerebellar Abscess. A Review of 47 Cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1975, 38, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macewen, W. Pyogenic Infective Diseases of the Brain and Spinal Cord; Maclehose: Glasgow, UK, 1893. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, D.S.; Clark, K. A Current Review of Brain Abscess. Am. J. Med. 1973, 54, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennybacker, J. Cerebellar abscess. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1948, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolosi, A.; Hauser, W.A.; Musicco, M.; Kurland, L.T. Incidence and Prognosis of Brain Abscess in a Defined Population: Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1935–1981. Neuroepidemiology 1991, 10, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Chang, W.-N.; Lui, C.-C. Strategies for the Management of Bacterial Brain Abscess. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 13, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangsanarak, J.; Fooanant, S.; Ruckphaopunt, K.; Navacharoen, N.; Teotrakul, S. Extracranial and Intracranial Complications of Suppurative Otitis Media. Report of 102 Cases. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1993, 107, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feraco, P.; Donner, D.; Gagliardo, C.; Leonardi, I.; Piccinini, S.; Del Poggio, A.; Franciosi, R.; Petralia, B.; van den Hauwe, L. Cerebral Abscesses Imaging: A Practical Approach. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 27, e11–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; Bharadwaj, R.; Chowdhary, A.; Kaundinya, D.V.; Palande, D.A. Current Epidemiology of Intracranial Abscesses: A Prospective 5 Year Study. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Coutinho, J.M.; van de Beek, D. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Brain Abscess: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathisen, G.E.; Johnson, J.P. Brain Abscess. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 763–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludman, H. Complications of Suppurative Otitis Media. In Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology (Otology); Booth, I.B., Ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Aduda, D.S.O.; Macharia, I.M.; Mugwe, P.; Oburra, H.; Farragher, B.; Brabin, B.; Mackenzie, I. Bacteriology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) in Children in Garissa District, Kenya: A Point Prevalence Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Taous, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Ekramuddaula, A.F.M.; Islam, M.S. Comparative Study of Tubotympanic and Atticoantral Variety of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Bangladesh J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 16, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laza, C.O. Bilateral Succesive Otogenic Cerebellar Abscesses—Case Report. Glob. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 6, 555697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.J.; Kozin, E.D.; Barshak, M.B.; Reinshagen, K.; Knoll, R.M.; Abdullah, K.G.; Welling, D.B.; Jung, D.H. Otogenic Brain Abscesses: A Systematic Review. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giant Brain Abscess in A Pediatric Patient with Congenital Heart Disease: A Case Report|Setia Utama|Journal of Health Science and Medical Research. Available online: https://www.jhsmr.org/index.php/jhsmr/article/view/872 (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Sugianto, P.; Sutantoyo, F.F. Skipped Multilevel Lesion as an Atypical Tuberculous Spondylitis Mimicking Spinal Metastasis: A Case Report. Neurol. Asia 2021, 26, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzyński, M.; Wróbel, B.; Zawisza, E.; Kopala, W. A case of otogenic cerebellar abscess. Pol. Merkur. Lek. 2002, 13, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, E.; Castellote, A.; Piqueras, J.; Mauleon, S.; Creixell, S.; Pumarola, F.; Figueras, C.; Carreño, J.-C.; Lucaya, J. Imaging of Complications of Acute Mastoiditis in Children. Radiographics 2003, 23, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, R.H.; Enzmann, D.R. Clinical Stages of Human Brain Abscesses on Serial CT Scans after Contrast Infusion. Computerized Tomographic, Neuropathological, and Clinical Correlations. J. Neurosurg. 1983, 59, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzmann, D.R.; Britt, R.H.; Placone, R. Staging of Human Brain Abscess by Computed Tomography. Radiology 1983, 146, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Khosla, V.K. Current Concepts in the Management of Pyogenic Brain Abscess. Neurol. India 2000, 48, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, M.; Kagawa, M.; Izawa, M.; Takakura, K. Current Treatment Strategies and Factors Influencing Outcome in Patients with Bacterial Brain Abscess. Acta Neurochir. 1998, 140, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osenbach, R.K.; Loftus, C.M. Diagnosis and Management of Brain Abscess. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 1992, 3, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, R.K.; Rajshekhar, V. Management of Brain Abscess: An Overview. Neurosurg. Focus. 2008, 24, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radiansyah, R.S.; Sugianto, P.; Cecilia, C. Complete Resolution of Otogenic Cerebellar Abscess with Conservative Approach: Two Case Reports. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 79, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, H.B. Factors in Mortality of Cerebellar Abscesses. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1968, 31, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, M.L.; Mampalam, T.J.; Pons, V.G. Controversies in the Management of Brain Abscesses. Clin. Neurosurg. 1986, 33, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.; Wood, M.W.; Murphey, F. Experience with 88 Consecutive Cases of Brain Abscess. J. Neurosurg. 1973, 38, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, P.; Graybill, J.R.; Charache, P. Penetration of Brain Abscess by Systemically Administered Antibiotics. J. Neurosurg. 1973, 38, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampalam, T.J.; Rosenblum, M.L. Trends in the Management of Bacterial Brain Abscesses: A Review of 102 Cases over 17 Years. Neurosurgery 1988, 23, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, U.S.; Gajendran, R.; Joseph, M.J. Pyogenic Brain Abscess Managed by Repeated Elective Aspiration. Neurol. India 1999, 47, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Trimis, G.; Mostrou, G.; Lourida, A.; Prodromou, F.; Syriopoulou, V.; Theodoridou, M. Petrositis and Cerebellar Abscess Complicating Chronic Otitis Media. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2003, 39, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatova, T.S.; Rasulova, A.K. Otogenic cerebellar abscesses (in the light of 10-year observation materials at the ENT clinic at the Tashkent institute of continuing education of physicians). Vestn. Otorinolaringol. 2000, 4, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzoidis, K.S.; Vranos, G.; Exarchakos, G.; Argyropoulou, M.I.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Skevas, A. Subdural Empyema and Cerebellar Abscess Due to Chronic Otitis Media. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2004, 58, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, T.D.; Bhayani, R.; Goel, A.; Karapurkar, A.P. Bilateral Otogenic Cerebellar Abscesses. J. Postgrad. Med. 1993, 39, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, K.; He, T.; Sun, Y. Potential Otogenic Complications Caused by Cholesteatoma of the Contralateral Ear in Patients with Otogenic Abscess Secondary to Middle Ear Cholesteatoma of One Ear: A Case Report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 10220–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyfter, W.; Kruk-Zagajewska, A.; Borucki, L.; Bartochowska, A. Evolution in Management of Otogenic Brain Abscess. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laulajainen Hongisto, A.; Aarnisalo, A.A.; Lempinen, L.; Saat, R.; Markkola, A.; Leskinen, K.; Blomstedt, G.; Jero, J. Otogenic Intracranial Abscesses, Our Experience Over the Last Four Decades. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2017, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.J.; Manning, K.P.; Shaw, M.D. Brain Abscess Secondary to Otitis Media. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1984, 98, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, J. Intracranial Complications of Chronic Otitis Media. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathoo, N.; Nadvi, S.S.; Narotam, P.K.; van Dellen, J.R. Brain Abscess: Management and Outcome Analysis of a Computed Tomography Era Experience with 973 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2011, 75, 716–726; discussion 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.N.; Sukumar, R.; Hazarika, P.; Rao, A.D.; Mukulchand; Raja, A. Otogenic Brain Abscess in Childhood. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1991, 22, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadol, J.R. Osseus Approaches to the Temporal Bone. In Surgery of the Ear and Temporal Bone; Nadol, J.B., Jr., Schuknecht, H.F., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nadol, J.R., Jr. Chronic Otitis Media. In Surgery of the Ear and Temporal Bone; Nadol, J.B., Jr., Schuknecht, H.F., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasoba, T.; Kaga, K. Surgical Treatment for the Cavity Problem after Open Method Surgery. Otol. Jpn. 2000, 10, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, D.J.; Jenkins, H.A.; Horowitz, B.L.; Coker, N.J. Management of Petrous Apex Lesions. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1989, 115, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morwani, K.P.; Jayashankar, N. Single Stage, Transmastoid Approach for Otogenic Intracranial Abscess. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2009, 123, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takasaka, T. Petrosal Cholesteatoma: Report of Five Cases. Otol. Jpn. 1992, 2, 634–641. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, S.; Beasley, N.; Swift, A.C. Changing Trends in Intracranial Abscesses Secondary to Ear and Sinus Disease. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2009, 123, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Targeted System | Findings |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| No significant findings related to case |
| Tubotympanic (Safe Type) | Atticoantral (Unsafe Type) | |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge | Profuse, mucoid | Scanty, purulent, foul-smelling |
| Perforation | Central | Attic or marginal |
| Granulations | Uncommon | Common |
| Cholesteatoma | Absent | Present |
| Complications | Rare | Common |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cucu, A.I.; Patrascu, R.E.; Cosman, M.; Costea, C.F.; Vonica, P.; Blaj, L.A.; Hartie, V.; Istrate, A.C.; Prutianu, I.; Boisteanu, O.; et al. Cerebellar Abscess Secondary to Cholesteatomatous Otomastoiditis—An Old Enemy in New Times. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233566
Cucu AI, Patrascu RE, Cosman M, Costea CF, Vonica P, Blaj LA, Hartie V, Istrate AC, Prutianu I, Boisteanu O, et al. Cerebellar Abscess Secondary to Cholesteatomatous Otomastoiditis—An Old Enemy in New Times. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(23):3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233566
Chicago/Turabian StyleCucu, Andrei Ionut, Raluca Elena Patrascu, Mihaela Cosman, Claudia Florida Costea, Patricia Vonica, Laurentiu Andrei Blaj, Vlad Hartie, Ana Cristina Istrate, Iulian Prutianu, Otilia Boisteanu, and et al. 2023. "Cerebellar Abscess Secondary to Cholesteatomatous Otomastoiditis—An Old Enemy in New Times" Diagnostics 13, no. 23: 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233566
APA StyleCucu, A. I., Patrascu, R. E., Cosman, M., Costea, C. F., Vonica, P., Blaj, L. A., Hartie, V., Istrate, A. C., Prutianu, I., Boisteanu, O., Patrascanu, E., & Hristea, A. (2023). Cerebellar Abscess Secondary to Cholesteatomatous Otomastoiditis—An Old Enemy in New Times. Diagnostics, 13(23), 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233566






