Ultrasonographic Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Its Clinical Application in the Management of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diaphragm Function Assessment
3. Clinical Application of Diaphragm Ultrasound
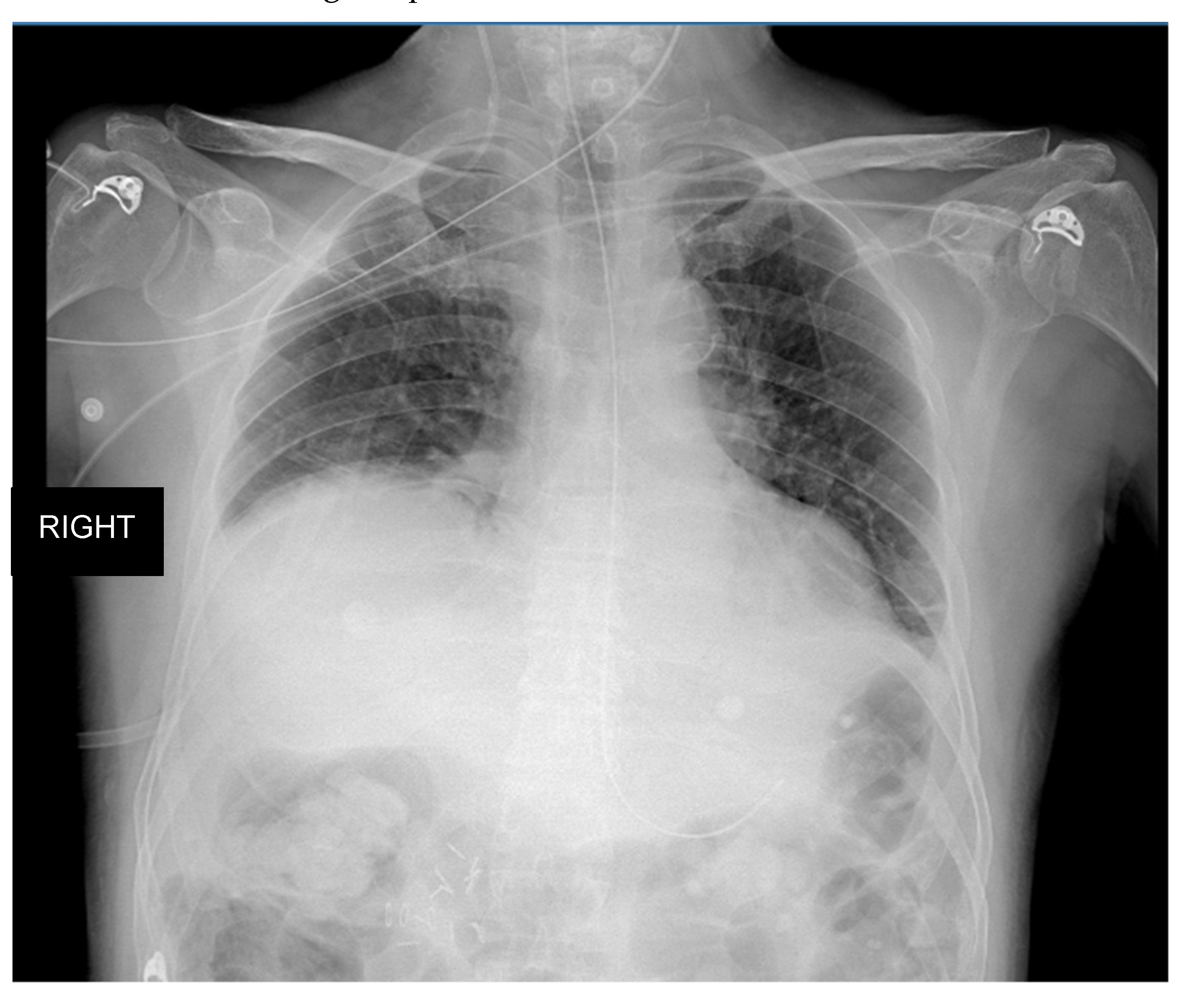
3.1. Clinical Case One
3.2. Clinical Case Two
3.3. Case Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franco, L.; Tobin, M.J. Disorders of the Respiratory Muscles. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 10–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, M.J.; Laghi, F.; Jubran, A. Ventilatory Failure, Ventilator Support, and Ventilator Weaning. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 2871–2921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nason, L.K.; Walker, C.M.; McNeeley, M.F.; Burivong, W.; Fligner, C.L.; Godwin, J.D. Imaging of the Diaphragm: Anatomy and Function. Radiographics 2012, 32, E51–E70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rie, T. Dynamic Chest Radiography: Flat-Panel Detector (Fpd) Based Functional X-Ray Imaging. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2016, 9, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, H.; Laghi, F. Role of Diaphragm Ultrasound When Niv Fails in Copd Exacerbations. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 1600–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wei, J.; Huang, H.; Gaebler, C.P.; Yuan, A.; Deasy, J.O. Automatic Assessment of Average Diaphragm Motion Trajectory from 4dct Images through Machine Learning. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2015, 1, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takazakura, R.; Takahashi, M.; Nitta, N.; Murata, K. Diaphragmatic Motion in the Sitting and Supine Positions: Healthy Subject Study Using a Vertically Open Magnetic Resonance System. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 19, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.E.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Lisboa, L.G.; Linné, L.M.S.; de Souza Tavares, M.G.; Yamaguti, W.P.; Paulin, E. Validity and Reliability of Fluoroscopy for Digital Radiography: A New Way to Evaluate Diaphragmatic Mobility. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarwal, A.; Walker, F.O.; Cartwright, M.S. Neuromuscular Ultrasound for Evaluation of the Diaphragm. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, G.; Mazziotti, S.; Blandino, A.; Granata, F.; Gaeta, M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Diaphragm: From Normal to Pathologic Findings. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2020, 10, 31966931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallbridge, P.; Steinfort, D.; Tay, T.R.; Irving, L.; Hew, M. Diagnostic Chest Ultrasound for Acute Respiratory Failure. Respir. Med. 2018, 141, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bobbia, X.; Clement, A.; Claret, P.G.; Bastide, S.; Alonso, S.; Wagner, P.; Tison, T.; Muller, L.; de La Coussaye, J.E. Diaphragmatic Excursion Measurement in Emergency Patients with Acute Dyspnea: Toward a New Diagnostic Tool? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchioni, A.; Castaniere, I.; Tonelli, R.; Fantini, R.; Fontana, M.; Tabbì, L.; Viani, A.; Giaroni, F.; Ruggieri, V.; Cerri, S. Ultrasound-Assessed Diaphragmatic Impairment Is a Predictor of Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Undergoing Noninvasive Ventilation. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antenora, F.; Fantini, R.; Iattoni, A.; Castaniere, I.; Sdanganelli, A.; Livrieri, F.; Tonelli, R.; Zona, S.; Monelli, M.; Clini, E.M.; et al. Prevalence and Outcomes of Diaphragmatic Dysfunction Assessed by Ultrasound Technology During Acute Exacerbation of Copd: A Pilot Study. Respirology 2017, 22, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamis, D.; Soilemezi, E.; Tsagourias, M.; Akoumianaki, E.; Dimassi, S.; Boroli, F.; Richard, J.C.; Brochard, L. Sonographic Evaluation of the Diaphragm in Critically Ill Patients. Technique and Clinical Applications. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goligher, E.C.; Laghi, F.; Detsky, M.E.; Farias, P.; Murray, A.; Brace, D.; Brochard, L.J.; Sebastien-Bolz, S.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Kavanagh, B.P. Measuring Diaphragm Thickness with Ultrasound in Mechanically Ventilated Patients: Feasibility, Reproducibility and Validity. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Sferrazza Papa, G.F.; Artigas, A.; Bouhemad, B.; Grgic, A.; Heunks, L.; Markstaller, K.; Pellegrino, G.M.; Pisani, L.; Rigau, D.; et al. Ers Statement on Chest Imaging in Acute Respiratory Failure. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, D.K.; Gandevia, S.C.; Gorman, R.B.; Southon, F.C. Dynamic Changes in the Zone of Apposition and Diaphragm Length During Maximal Respiratory Efforts. Thorax 1994, 49, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troyer, A.D.; Wilson, T.A. Action of the Diaphragm on the Rib Cage. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenyon, C.M.; Cala, S.J.; Yan, S.; Aliverti, A.; Scano, G.; Duranti, R.; Pedotti, A.; Macklem, P.T. Rib Cage Mechanics during Quiet Breathing and Exercise in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laghi, F.A., Jr.; Saad, M.; Shaikh, H. Ultrasound and Non-Ultrasound Imaging Techniques in the Assessment of Diaphragmatic Dysfunction. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, J.L.; Nahormek, P.A.; Yost, W.T.; Rochester, D.P. Diaphragmatic Thickness-Lung Volume Relationship in Vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaksma, M.E.; Smit, J.M.; Boussuges, A.; Demoule, A.; Dres, M.; Ferrari, G.; Formenti, P.; Goligher, E.C.; Heunks, L.; Lim, E.H.T.; et al. Expert Consensus on Diaphragm Ultrasonography in the Critically Ill (Exodus): A Delphi Consensus Statement on the Measurement of Diaphragm Ultrasound-Derived Parameters in a Critical Care Setting. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussuges, A.; Gole, Y.; Blanc, P. Diaphragmatic Motion Studied by M-Mode Ultrasonography: Methods, Reproducibility, and Normal Values. Chest 2009, 135, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, J.; Dowlen, H.; Cartwright, M.; Sarwal, A. Neuromuscular Ultrasound for Evaluation of the Normal and Abnormal Diaphragm (P05. 084); AAN Enterprises: Faridabad, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boussuges, A.; Finance, J.; Chaumet, G.; Bregeon, F. Diaphragmatic Motion Recorded by M-Mode Ultrasonography: Limits of Normality. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, A.J.; Harper, C.J.; Ghahfarokhi, L.S.; Strommen, J.A.; Watson, J.C.; Sorenson, E.J. Two-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging of the Diaphragm: Quantitative Values in Normal Subjects. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, J.; De Bruin, P.F.; Pride, N.B. In Vivo Assessment of Diaphragm Contraction by Ultrasound in Normal Subjects. Thorax 1995, 50, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirompanich, P.; Romsaiyut, S. Use of Diaphragm Thickening Fraction Combined with Rapid Shallow Breathing Index for Predicting Success of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilator in Medical Patients. J. Intensive Care 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turton, P.; ALAidarous, S.; Welters, I. A Narrative Review of Diaphragm Ultrasound to Predict Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation: Where Are We and Where Are We Heading? Ultrasound J. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Digala, L.P.; Govindarajan, R. Thickening Fraction as a Measure of Ultrasonographic Diaphragm Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2020, 5, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Singh, R.K.; Baronia, A.K.; Poddar, B.; Azim, A.; Gurjar, M. Diaphragm Thickening Fraction to Predict Weaning-a Prospective Exploratory Study. J. Intensive Care 2017, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoodpoor, A.; Fouladi, S.; Ramouz, A.; Shadvar, K.; Ostadi, Z.; Soleimanpour, H. Diaphragm Ultrasound to Predict Weaning Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2022, 54, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, F.; Vetrugno, L.; Orso, D.; Bove, T.; Schreiber, A.; Boero, E.; Santori, G.; Isirdi, A.; Barbieri, G.; Forfori, F. Diaphragmatic Thickening Fraction as a Potential Predictor of Response to Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Ventilation in Covid-19 Pneumonia: A Single-Center Pilot Study. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 284, 103585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrugno, L.; Orso, D.; Corradi, F.; Zani, G.; Spadaro, S.; Meroi, F.; D’Andrea, N.; Bove, T.; Cammarota, G.; De Robertis, E.; et al. Diaphragm Ultrasound Evaluation During Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation in Covid-19 Patients: A Pragmatic, Cross-Section, Multicenter Study. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammarota, G.; Sguazzotti, I.; Zanoni, M.; Messina, A.; Colombo, D.; Vignazia, G.L.; Vetrugno, L.; Garofalo, E.; Bruni, A.; Navalesi, P.; et al. Diaphragmatic Ultrasound Assessment in Subjects with Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure Admitted to the Emergency Department. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbrello, M.; Formenti, P.; Longhi, D.; Galimberti, A.; Piva, I.; Pezzi, A.; Mistraletti, G.; Marini, J.J.; Iapichino, G. Diaphragm Ultrasound as Indicator of Respiratory Effort in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Assisted Mechanical Ventilation: A Pilot Clinical Study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haaksma, M.; Tuinman, P.R.; Heunks, L. Ultrasound to Assess Diaphragmatic Function in the Critically Ill-a Critical Perspective. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulard, T.; Bachasson, D.; Fossé, Q.; Niérat, M.-C.; Hogrel, J.-Y.; Demoule, A.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Dres, M. Poor Correlation between Diaphragm Thickening Fraction and Transdiaphragmatic Pressure in Mechanically Ventilated Patients and Healthy Subjects. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiesshoefer, J.; Herkenrath, S.; Henke, C.; Langenbruch, L.; Schneppe, M.; Randerath, W.; Young, P.; Brix, T.; Boentert, M. Evaluation of Respiratory Muscle Strength and Diaphragm Ultrasound: Normative Values, Theoretical Considerations, and Practical Recommendations. Respiration 2020, 99, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussuges, A.; Rives, S.; Finance, J.; Bregeon, F. Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function by Ultrasonography: Current Approach and Perspectives. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 2408–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magder, S.; Malhotra, A.; Hibbert, K.A.; Hardin, C.C. Cardiopulmonary Monitoring: Basic Physiology, Tools, and Bedside Management for the Critically Ill; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, E.; Bruni, A.; Pelaia, C.; Landoni, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Antonelli, M.; Conti, G.; Biasucci, D.G.; Mercurio, G.; Cortegiani, A. Comparisons of Two Diaphragm Ultrasound-Teaching Programs: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Educational Study. Ultrasound J. 2019, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouby, J.-J.; Arbelot, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, J.; An, Y.; Chunyao, W.; Bin, D.; Barbas, C.S.V.; Neto, F.L.D.; et al. Training for Lung Ultrasound Score Measurement in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerolle, N.; Guerot, E.; Dimassi, S.; Zegdi, R.; Faisy, C.; Fagon, J.Y.; Diehl, J.L. Ultrasonographic Diagnostic Criterion for Severe Diaphragmatic Dysfunction after Cardiac Surgery. Chest 2009, 135, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, S.; Fuld, J.P.; Carter, R.; McEntegart, M.; MacFarlane, N.G. Diaphragm Ultrasonography as an Alternative to Whole-Body Plethysmography in Pulmonary Function Testing. J. Ultrasound Med. 2006, 25, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dres, M.; Goligher, E.C.; Heunks, L.M.A.; Brochard, L.J. Critical Illness-Associated Diaphragm Weakness. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palkar, A.; Narasimhan, M.; Greenberg, H.; Singh, K.; Koenig, S.; Mayo, P.; Gottesman, E. Diaphragm Excursion-Time Index: A New Parameter Using Ultrasonography to Predict Extubation Outcome. Chest 2018, 153, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yan, W. Application of Bedside Ultrasound in Predicting the Outcome of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation in Elderly Patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Ye, C.; Hu, W.; Gong, S. Diaphragmatic Ultrasonography-Based Rapid Shallow Breathing Index for Predicting Weaning Outcome during a Pressure Support Ventilation Spontaneous Breathing Trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.-W.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.C. Comparison of Clinical Utility between Diaphragm Excursion and Thickening Change Using Ultrasonography to Predict Extubation Success. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.J.; Roy, S.; Iktidar, M.A.; Padma, F.K.; Nipun, K.I.; Chowdhury, S.; Nath, R.K.; Rashid, H.-O. Diaphragm Ultrasound as a Better Predictor of Successful Extubation from Mechanical Ventilation Than Rapid Shallow Breathing Index. Acute Crit. Care 2022, 37, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, R.; Nivedita, K.; Karthik, K.; Venkatraman, R. Role of Diaphragm Ultrasound in Weaning Mechanically Ventilated Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2022, 66, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Neindre, A.; Philippart, F.; Luperto, M.; Wormser, J.; Morel-Sapene, J.; Aho, S.L.; Mongodi, S.; Mojoli, F.; Bouhemad, B. Diagnostic Accuracy of Diaphragm Ultrasound to Predict Weaning Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 117, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; Dimassi, S.; Vargas, F.; Lyazidi, A.; Thille, A.W.; Brochard, L. Diaphragm Ultrasonography to Estimate the Work of Breathing during Non-Invasive Ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbrello, M.; Formenti, P.; Lusardi, A.C.; Guanziroli, M.; Caccioppola, A.; Coppola, S.; Chiumello, D. Oesophageal Pressure and Respiratory Muscle Ultrasonographic Measurements Indicate Inspiratory Effort During Pressure Support Ventilation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, e148–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Calfee, C.S.; Paul, D.W.; Janz, D.R.; May, A.K.; Zhuo, H.; Bernard, G.R.; Matthay, M.A.; Ware, L.B.; Kangelaris, K.N. One-Year Mortality and Predictors of Death among Hospital Survivors of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulou, I.; Daganou, M.; Dafni, U.; Karakatsani, A.; Khoury, M.; Geroulanos, S.; Jordanoglou, J. Phrenic Nerve Dysfunction after Cardiac Operations: Electrophysiologic Evaluation of Risk Factors. Chest 1998, 113, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Kato, H.; Tsujimoto, S.; Kitamura, R. Diabetes Mellitus, Internal Thoracic Artery Grafting, and Risk of an Elevated Hemidiaphragm after Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1994, 8, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Suh, H.J.; Hong, S.B.; Koh, Y.; Lim, C.M. Diaphragm Dysfunction Assessed by Ultrasonography: Influence on Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2627–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.; Moury, P.H.; Mahul, M.; de Jong, A.; Galia, F.; Prades, A.; Albaladejo, P.; Chanques, G.; Molinari, N.; Jaber, S. Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Icu-Acquired Weakness and Its Impact on Extubation Failure. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moury, P.H.; Cuisinier, A.; Durand, M.; Bosson, J.L.; Chavanon, O.; Payen, J.F.; Jaber, S.; Albaladejo, P. Diaphragm Thickening in Cardiac Surgery: A Perioperative Prospective Ultrasound Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, M.; Zhao, S.; Tan, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, W.; Pan, M.; et al. Quantification of Diaphragmatic Dynamic Dysfunction in Septic Patients by Bedside Ultrasound. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.; Nguyen, T.; Taylor, N.; Friscia, M.E.; Budak, M.T.; Rothenberg, P.; Zhu, J.; Sachdeva, R.; Sonnad, S.; Kaiser, L.R. Rapid Disuse Atrophy of Diaphragm Fibers in Mechanically Ventilated Humans. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilakopoulos, T.; Petrof, B.J. Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demoule, A.; Jung, B.; Prodanovic, H.; Molinari, N.; Chanques, G.; Coirault, C.; Matecki, S.; Duguet, A.; Similowski, T.; Jaber, S. Diaphragm Dysfunction on Admission to the Intensive Care Unit. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Prognostic Impact—A Prospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formenti, P.; Coppola, S.; Umbrello, M.; Froio, S.; Caccioppola, A.; De Giorgis, V.; Galanti, V.; Lusardi, A.C.; Ferrari, E.; Noè, D. Time Course of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis and Muscular Ultrasound in Critically Ill Patients. J. Crit. Care 2022, 68, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formenti, P.; De Giorgis, V.; Coppola, S.; Pozzi, T.; Chiodaroli, E.; Dres, M.; Marini, J.J.; Chiumello, D. The Possible Predictive Value of Muscle Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of ICUAW in Long-Term Critically Ill Patients. J. Crit. Care 2022, 71, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, F.; Shaikh, H.; Radovanovic, D. Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. In Civetta, Taylor, and Kirby’s Handbook of Critical Care, 5th ed.; Gabrielli, A., Layon, A.J., Yu, M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al Tayar, A.S.; Abdelshafey, E.E. Diaphragm Electromyography Versus Ultrasonography in the Prediction of Mechanical Ventilation Liberation Outcome. Respir. Care 2022, 67, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Cai, S.; Hu, B.; Li, J. Comparison of Assessment of Diaphragm Function Using Speckle Tracking between Patients with Successful and Failed Weaning: A Multicentre, Observational, Pilot Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayan-Ramirez, G.; Decramer, M. Mechanisms of Striated Muscle Dysfunction During Acute Exacerbations of Copd. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dube, B.P.; Dres, M. Diaphragm Dysfunction: Diagnostic Approaches and Management Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Lim, C.M. Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction: Diagnosis and Role of Pharmacological Agents. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
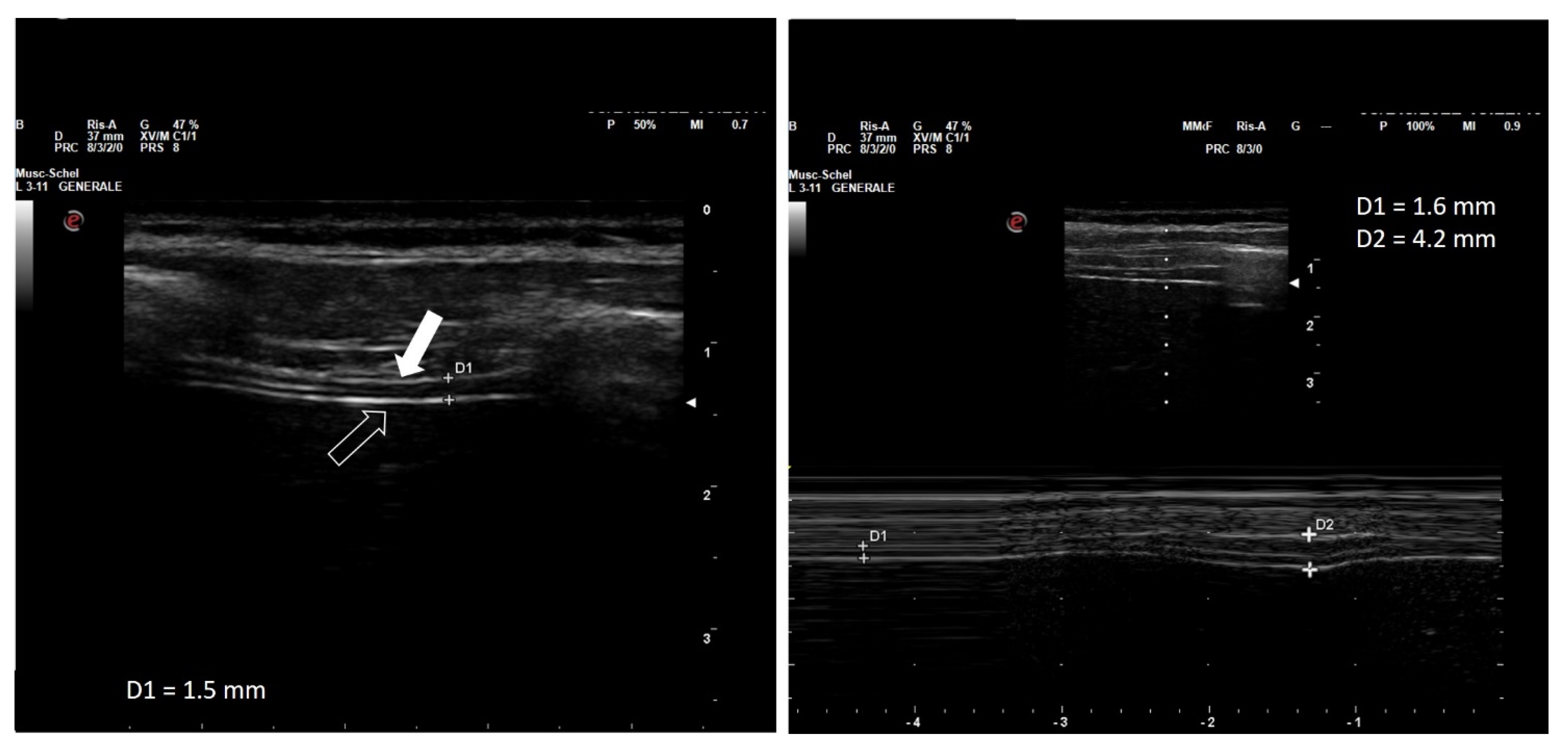
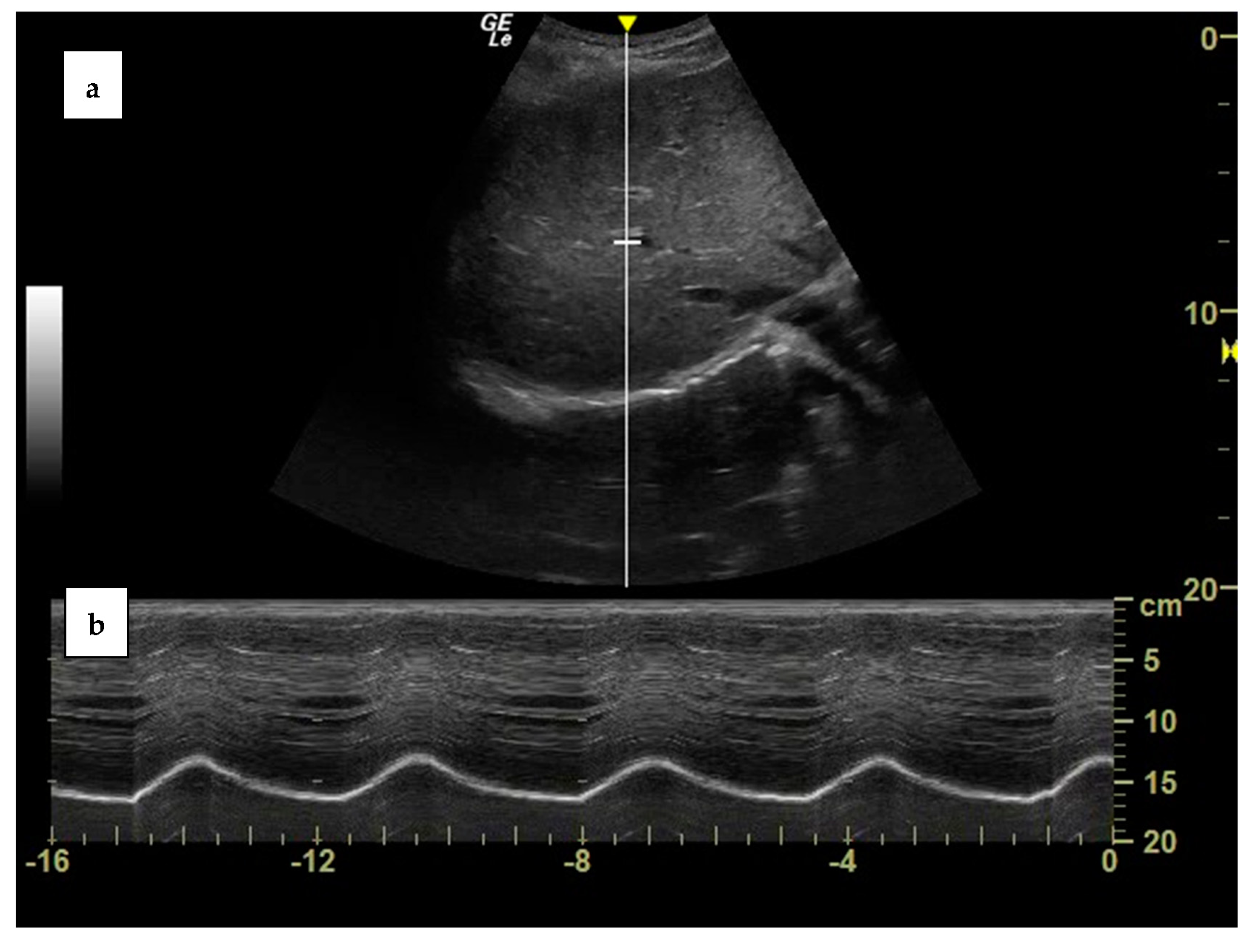
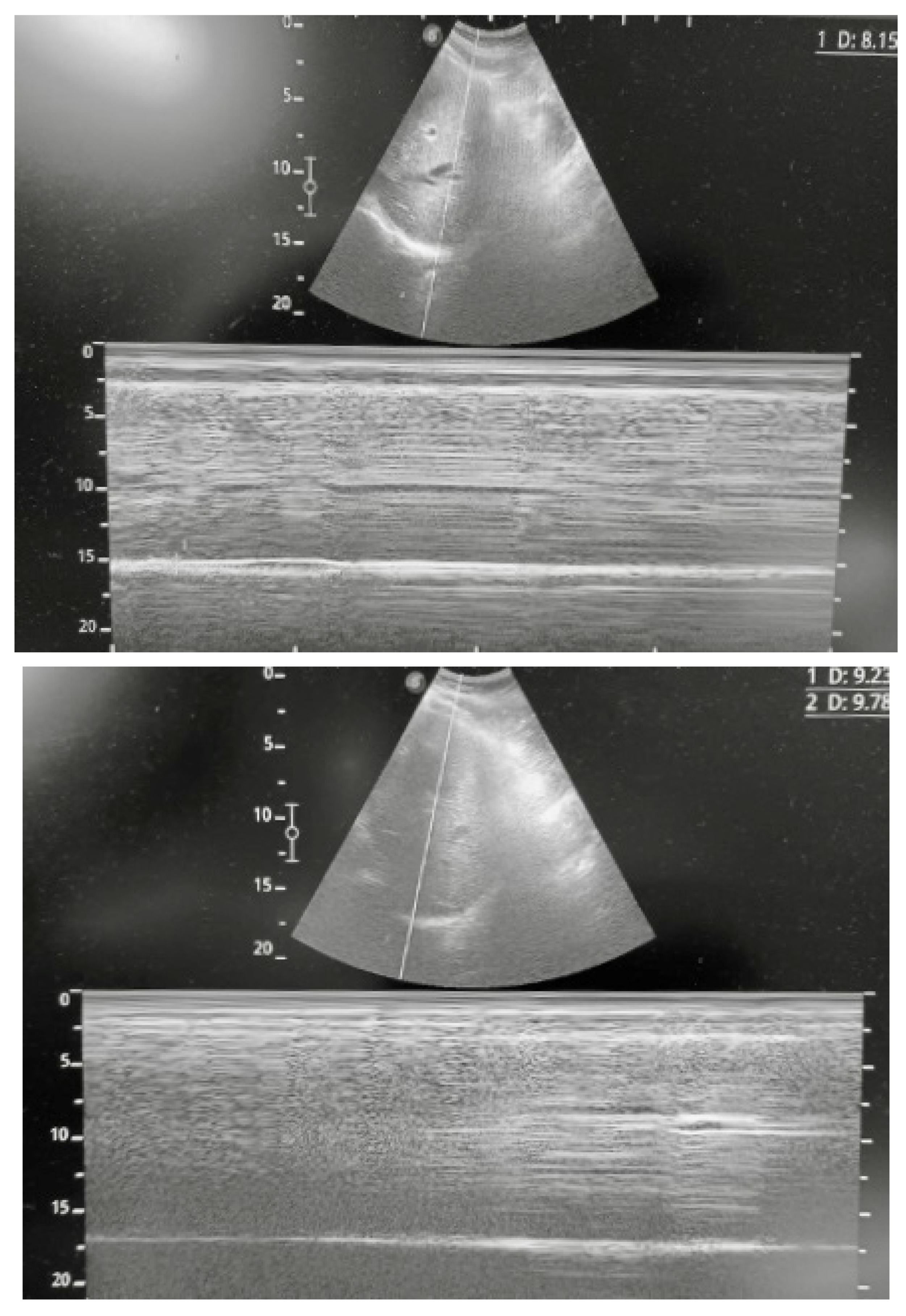
| Measurement | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| End-expiratory thickness of the right hemidiaphragm | 3.3 mm (0.17 mm–5.3 mm) |
| Thickening fraction during resting breathing | 20% (5–50%) |
| Maximum diaphragmatic thickening fraction | 80% (20–180%) |
| Diaphragmatic excursion during resting breathing | 1.7 cm (1.0–2.5 cm) |
| Diaphragmatic excursion during a maneuver of inspiratory capacity | 6.5 cm (3.6–9.2 cm) |
| Risk Factors for Diaphragmatic Dysfunction |
|---|
| Acquired Conditions |
|
| Pre-Existent Conditions |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, M.; Pini, S.; Danzo, F.; Mandurino Mirizzi, F.; Arena, C.; Tursi, F.; Radovanovic, D.; Santus, P. Ultrasonographic Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Its Clinical Application in the Management of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030411
Saad M, Pini S, Danzo F, Mandurino Mirizzi F, Arena C, Tursi F, Radovanovic D, Santus P. Ultrasonographic Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Its Clinical Application in the Management of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030411
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, Marina, Stefano Pini, Fiammetta Danzo, Francesca Mandurino Mirizzi, Carmine Arena, Francesco Tursi, Dejan Radovanovic, and Pierachille Santus. 2023. "Ultrasonographic Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Its Clinical Application in the Management of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030411
APA StyleSaad, M., Pini, S., Danzo, F., Mandurino Mirizzi, F., Arena, C., Tursi, F., Radovanovic, D., & Santus, P. (2023). Ultrasonographic Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Its Clinical Application in the Management of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. Diagnostics, 13(3), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030411





