Chest X-ray Interpretation: Detecting Devices and Device-Related Complications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classification of Medical Devices
3. Intravascular Devices
3.1. Central Vein Catheter (CVC)
3.2. Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
3.3. PORT, or Totally Implantable Vascular Access Device
3.4. Midline
3.5. Swan-Ganz Catheter
4. Airway Devices
4.1. Endotracheal Tubes
4.2. Tracheostomy Tubes
5. Cardiac Devices
5.1. Loop Recorder
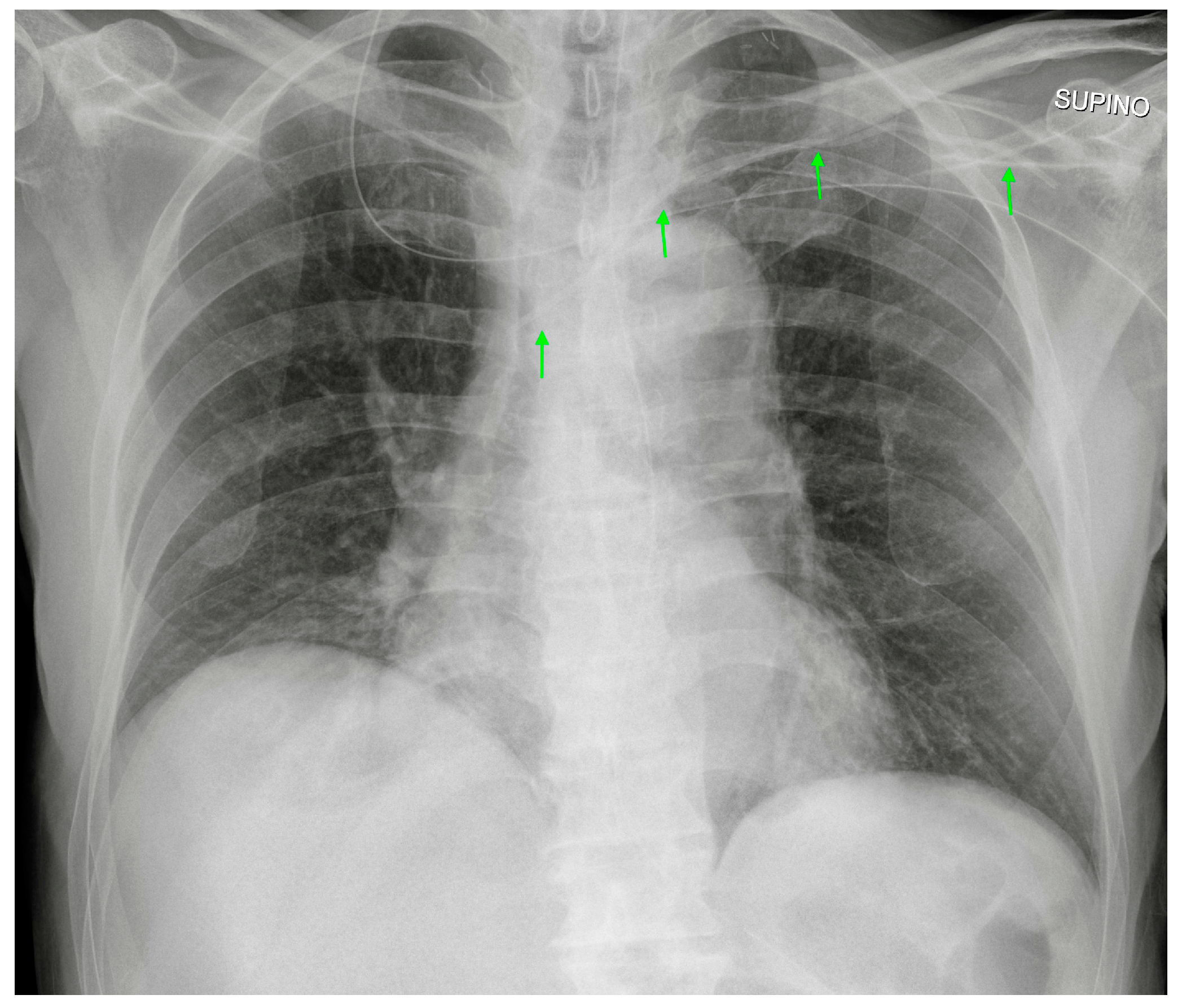
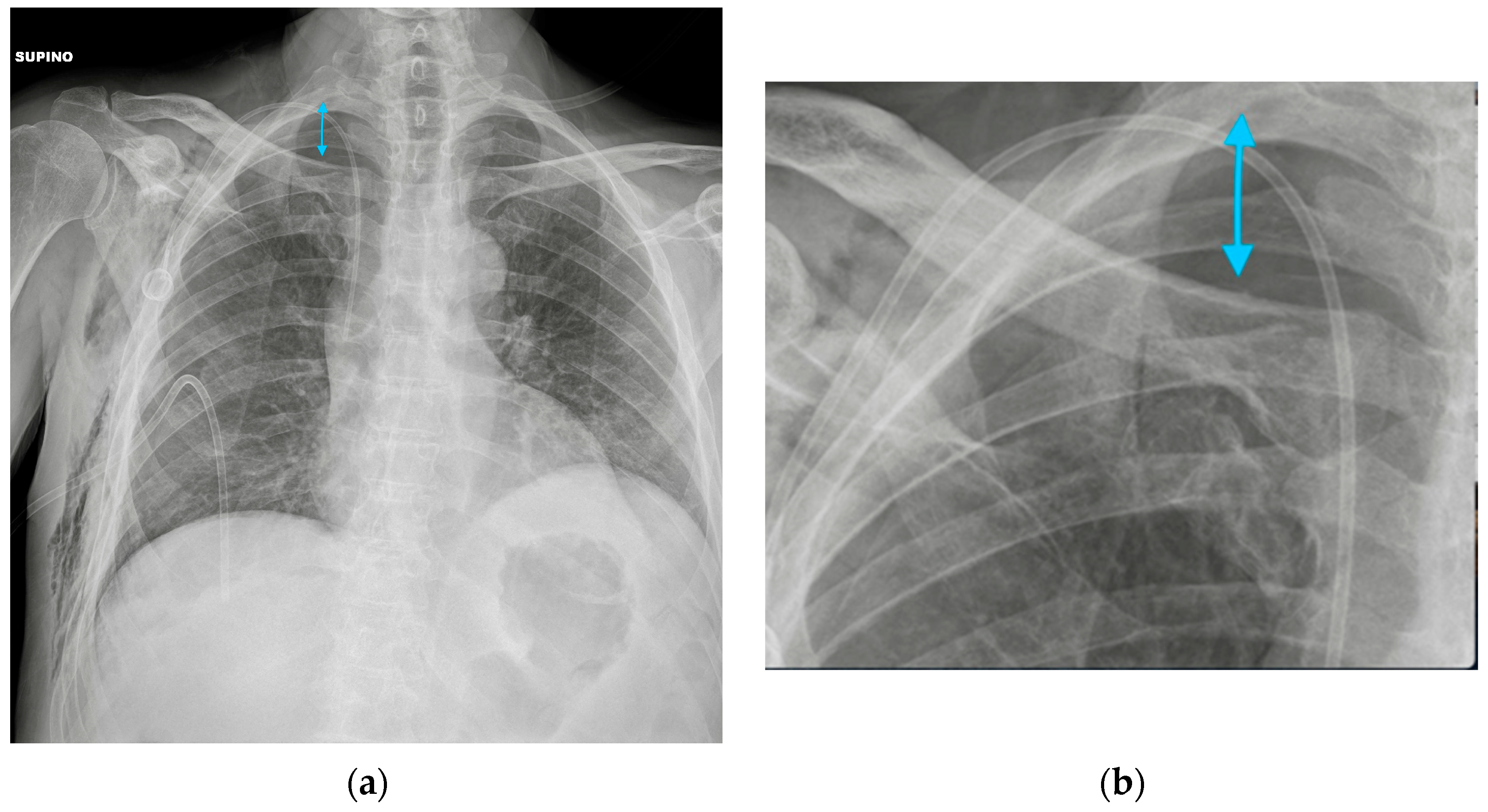
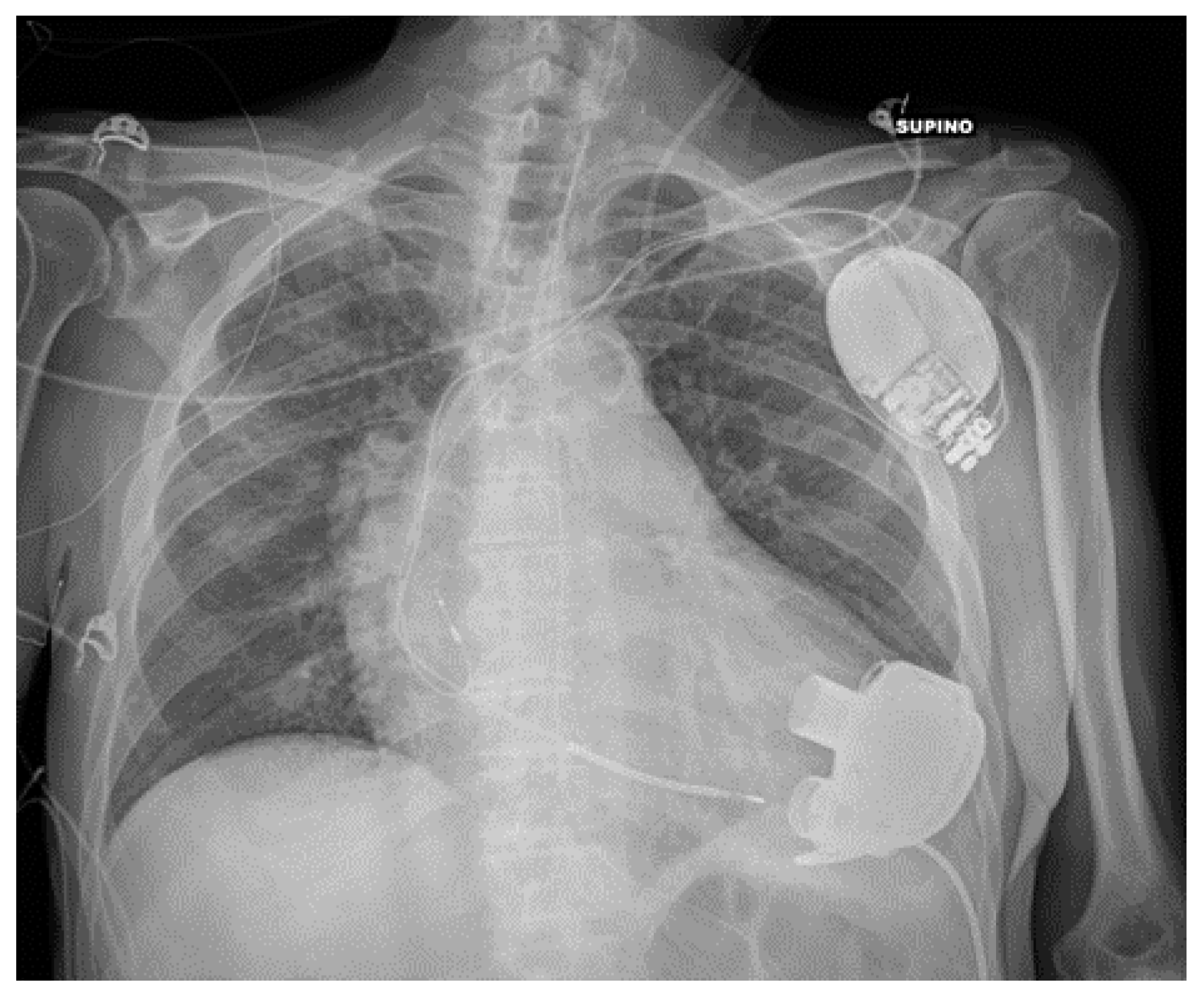
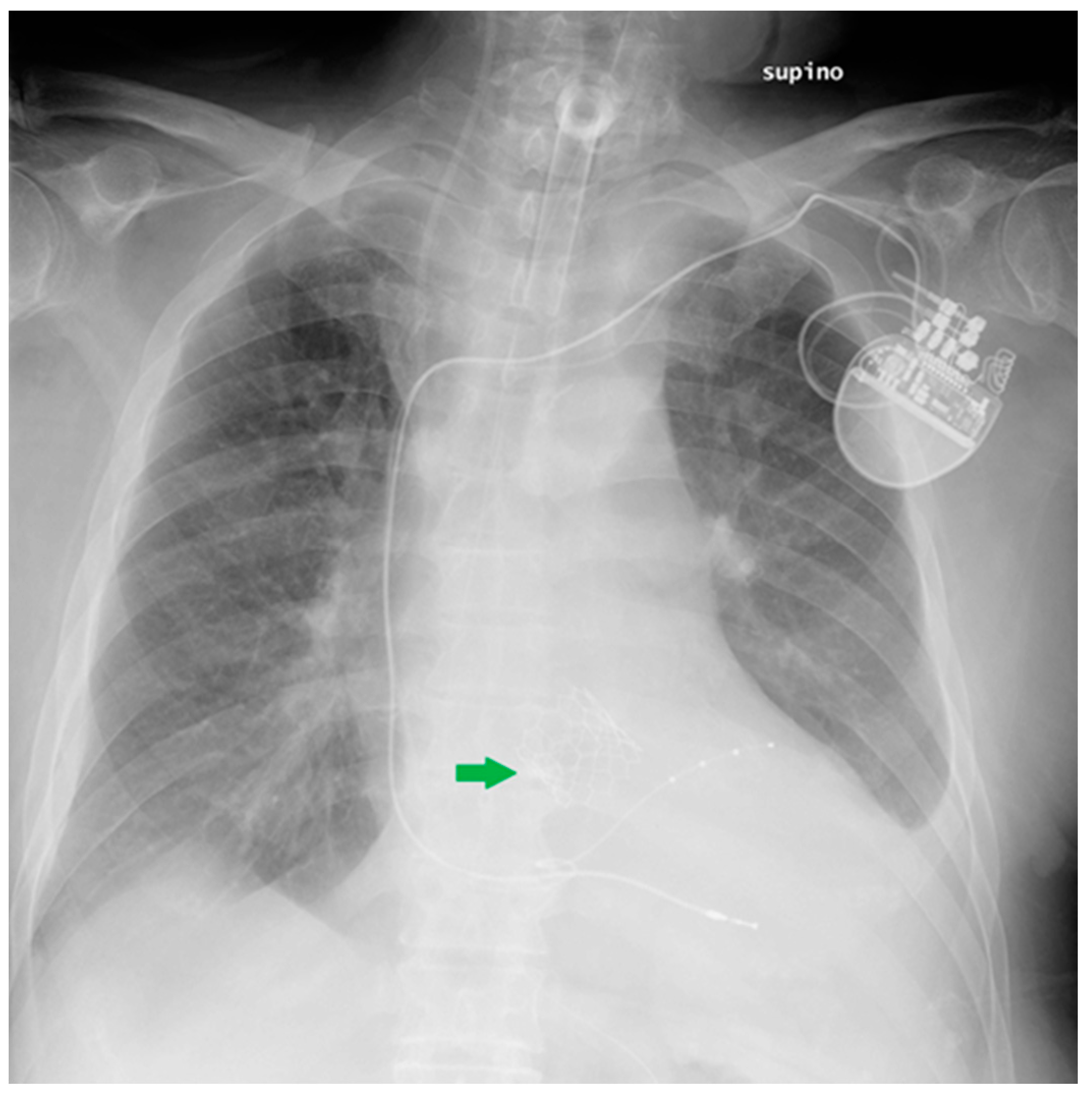
5.2. Pacemaker (PM) and Automatic Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (AICD)
5.3. Ventricular Assistance Devices (VADs)
5.4. Impella
5.5. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
5.6. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
5.7. Other Cardiac Devices
6. Gastro-Intestinal Devices
6.1. Nasogastric Tubes
6.2. Nasoenteric Tubes
7. Chest Tubes
8. Miscellaneous
8.1. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Shunts
8.2. Vagal Nerve Stimulator (VNS)
8.3. Other Devices
9. Deep-Learning-Based Algorithms for Chest Devices’ Detection on CXR: A Glimpse into the Future
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quaia, E.; Baratella, E.; Poillucci, G.; Kus, S.; Cioffi, V.; Cova, M.A. Digital Tomosynthesis as a Problem-Solving Imaging Technique to Confirm or Exclude Potential Thoracic Lesions Based on Chest X-ray Radiography. Acad. Radiol. 2013, 20, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T.B.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Tsau, P.H.; Berger, W.G.; Standen, J.R. Medical Devices of the Chest. Radiographics 2004, 24, 1725–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.P.; Alexander, T.; Patel, V.; Low, G. Chest radiographs of cardiac devices (Part 1): Lines, tubes, non-cardiac medical devices and materials. S. Afr. J. Radiol. 2019, 23, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissbach, A.; Gendler, Y.; Lakovsky, Y.; Kadmon, G.; Nahum, E.; Kaplan, E. Routine chest X-ray following ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein catheterization in critically ill children: A prospective observational Study. Pediatr. Anesthesia 2020, 30, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, C.-A. Malposition of Central Venous Catheter. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratella, E.; Marrocchio, C.; Bozzato, A.M.; Roman-Pognuz, E.; Cova, M.A. Chest X-ray in intensive care unit patients: What there is to know about thoracic devices. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldan, C.J.; Paniagua, L. Central Venous Catheter Intravascular Malpositioning: Causes, Prevention, Diagnosis, and Correction. West. J. Emerg. 2015, 16, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayer, G.; Rozenman, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Apter, S.; Simansky, D.A.; Yellin, A.; Itzchak, Y. CT diagnosis of malpositioned chest tubes. Br. J. Radiol. 2000, 73, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, K.; Huang, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Gu, Z.; Fu, G.; Hu, M.; et al. Detection of peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) in chest X-ray images: A multi-task deep learning model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 197, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-F.; Ko, P.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Kao, T.-C.; Yu, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hsieh, H.-C. Analysis of chest X-ray plain film images of intravenous ports inserted via the superior vena cava. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.S.; Desai, N.K.; Kalra, A.; Gajera, M.; Cavanaugh, S.K.; Brampton, W.; Young, D.; Harvey, S.; Rowan, K. Pulmonary artery catheters for adult patients in intensive care. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2018, CD003408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudziński, P.N.; Henzel, J.; Dzielińska, Z.; Lubiszewska, B.; Michałowska, I.; Szymański, P.; Pracoń, R.; Hryniewiecki, T.; Demkow, M. Pulmonary artery rupture as a complication of Swan-Ganz catheter application. Diagnosis and endovascular treatment: A single centre’s experience. Adv. Interv. Cardiol. 2016, 12, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kang, J.-M. Plain endotracheal tube insertion carries greater risk for malpositioning than does reinforced endotracheal tube insertion in females. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2013, 65, S23–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, G.; Lazaridis, G.; Baka, S.; Mpoukovinas, I.; Karavasilis, V.; Lampaki, S.; Kioumis, I.; Pitsiou, G.; Papaiwannou, A.; Karavergou, A.; et al. Barotrauma and pneumothorax. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, S38–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jougon, J.; Cantini, O.; Delcambre, F.; Minniti, A.; Velly, J. Esophageal perforation: Life threatening complication of endotracheal intubation. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2001, 20, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M.; Reed, J.C.; Choplin, R.H. Radiographic detection of esophageal malpositioning of endotracheal tubes. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1990, 154, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Young, P. Over-inflation of the tracheal tube cuff: A case for routine monitoring. Crit. Care 2002, 6, P37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striebel, H.W.; Pinkwart, L.U.; Karavias, T. Trachealruptur durch zu stark geblockte Tubusmanschette. Der Anaesthesist 1995, 44, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.C.B.; Leitman, B.S.; de Groot, P.M.; Vlahos, I.; Naidich, D.P. Chest Radiography in the ICU: Part 1, Evaluation of Airway, Enteric, and Pleural Tubes. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, I.; Sousa, M.J.; Antunes, N.; Silva, V.; Roque, C.; Pinheiro-Vieira, A.; Lagarto, V.; Hipólito-Reis, A.; Luz, A.; Torres, S. Efficacy and Safety Of Implantable Loop Recorder: Experience Of A Center. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2016, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnie, A.A.; Hasnie, A.A.; Assaly, R.A. The Case of the Migrating Loop Recorder. JACC Case Rep. 2019, 1, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.L.; Volokhina, Y.V.; Fisher, K.L. Radiography of Cardiac Conduction Devices: A Comprehensive Review. Radiographics 2011, 31, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakia, S.; Moore, R.; Ambur, V.; Toyoda, Y. Current status of the implantable LVAD. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.G.; Thomas, J.D.; Freed, B.H.; Rich, J.D.; Sauer, A.J. Echocardiography and Continuous-Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigakis, C.J.G.; Mathai, S.K.; Suby-Long, T.D.; Restauri, N.L.; Ocazionez, D.; Bang, T.J.; Restrepo, C.S.; Sachs, P.B.; Vargas, D. Radiographic Review of Current Therapeutic and Monitoring Devices in the Chest. Radiographics 2018, 38, 1027–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.N.; Hsia, T.-Y.; Schievano, S.; Bozkurt, S. Complications in children with ventricular assist devices: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 27, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Sidebotham, D. Postoperative care and complications after ventricular assist device implantation. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2012, 26, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, J.J.; Kaki, A. The Impella Device: Historical Background, Clinical Applications and Future Directions. Int. J. Angiol. 2018, 28, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, Y.; Bauer, S.; Immohr, M.B.; Mehdiani, A.; Rellecke, P.; Westenfeld, R.; Aubin, H.; Boeken, U.; Lichtenberg, A.; Akhyari, P. Outcome of Patients Supported by Large Impella Systems After Re-implantation Due to Continued or Recurrent Need of Temporary Mechanical Circulatory Support. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D.; Massey, H.T.; Bhatt, S.; Dogra, V. Imaging of Mechanical Cardiac Assist Devices. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2011, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Dave, S.; Goerlich, C.E.; Kaczorowski, D.J. Hybrid and parallel extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuits. JTCVS Tech. 2021, 8, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.W.; Cullen, J.; Kornhauser, M.S.; Wolfson, P.J. Thoracic complications of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Findings on chest radiographs and sonograms. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 158, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Types of ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation|ECLS. Available online: https://www.elso.org/ecmo-resources/types-of-ecmo.aspx (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Beck, L.; Burg, M.C.; Heindel, W.; Schülke, C. Extrakorporale Membranoxygenierung bei Erwachsenen–Varianten, Komplikationen unter Therapie und die Rolle der radiologischen Diagnostik. Rofo 2016, 189, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnacle, A.M.; Smith, L.C.; Hiorns, M.P. The Role of Imaging during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Pediatric Respiratory Failure. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidegran, M.K.; Ringertz, H.G.; Frenckner, B.; Lindén, V.B. Chest and abdominal CT during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Clinical benefits in diagnosis and treatment1. Acad. Radiol. 2005, 12, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, D.B.; Pezzollo, J.P.; Lam, D.K.; Epstein, R.H. Tracheopulmonary Complications of a Malpositioned Nasogastric Tube. Anesthesia Prog. 2020, 67, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Manara, A.R. X-ray checks of NG tube position: A case for guided tube placement. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verpoorte, R. Alkaloids. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Worsfold, P., Townshend, A., Poole, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 56–61. ISBN 9780123693976. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, S.; Behera, B.K.; Sahoo, A.K. Internal jaw thrust for nasogastric tube insertion. Indian J. Anaesth. 2018, 62, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiorah, S.C.S.; Moldovan, K.; Doberstein, C. Intracranial insertion of a nasogastric tube following septoplasty: Case report and literature review. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2020, 22, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M. Chest Tube Drainage of the Pleural Space: A Concise Review for Pulmonologists. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2018, 81, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mosa, A.F.H.; Ishaq, M.; Ahmed, M.H.M. Unusual Malposition of a Chest Tube, Intrathoracic but Extrapleural. Case Rep. Radiol. 2018, 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtaka, K.; Hase, R.; Chiba, R.; Miyasaka, M.; Sato, S.; Shoji, Y.; Ichimura, T.; Senmaru, N.; Kaga, K.; Matsui, Y. Noninvasive management for iatrogenic splenic injury caused by chest tube insertion: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2016, 4, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serji, B.; MirAli, H.; Chablou, M.; Kamaoui, I.; El Harroudi, T. Liver injury secondary to chest tube placement: A case report of conservative management and review of literature. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 6, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesieme, E.B.; Dongo, A.; Ezemba, N.; Irekpita, E.; Jebbin, N.; Kesieme, C. Tube Thoracostomy: Complications and Its Management. Pulm. Med. 2011, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, S.; Baumann, H.J.; Regelsberger, J.; Kehler, U.; Gliemroth, J.; Koziej, B.; Klose, H.; Meyer, A. Pulmonary hypertension after ventriculoatrial shunt implantation. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, E.J.; Goo, J.M.; Yoon, S.H.; Beck, K.S.; Seo, J.B.; Choi, B.W.; Chung, M.J.; Park, C.M.; Jin, K.N.; Lee, S.M. Use of Artificial Intelligence-Based Software as Medical Devices for Chest Radiography: A Position Paper from the Korean Society of Thoracic Radiology. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pehrson, L.M.; Lauridsen, C.A.; Tøttrup, L.; Fraccaro, M.; Elliott, D.; Zając, H.D.; Darkner, S.; Carlsen, J.F.; Nielsen, M.B. The Added Effect of Artificial Intelligence on Physicians’ Performance in Detecting Thoracic Pathologies on CT and Chest X-ray: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kalra, M.K.; Nitiwarangkul, C.; Patti, J.A.; Homayounieh, F.; Padole, A.; Rao, P.; Putha, P.; Muse, V.V.; Sharma, A.; et al. Deep learning in chest radiography: Detection of findings and presence of change. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmici, G.; Cè, M.; Caloro, E.; Khenkina, N.; Della Pepa, G.; Ascenti, V.; Martinenghi, C.; Papa, S.; Oliva, G.; Cellina, M. Chest X-ray in Emergency Radiology: What Artificial Intelligence Applications Are Available? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Mansouri, M.; Tajmir, S.; Lev, M.H.; Do, S. A Deep-Learning System for Fully-Automated Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Tip Detection. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 31, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.J.; Henderson, R.D.E.; Yi, X.; Babyn, P. Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Analysis of X-ray Images. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2020, 72, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, V.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.T.; Wong, K.C.L.; Sharma, A.; Syeda-Mahmood, T. Automated Detection and Type Classifica-tion of Central Venous Catheters in Chest X-Rays. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019; Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Amer, R.; Greenspan, H. Endotracheal Tube Detection and Segmentation in Chest Radiographs Using Synthetic Data. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019; Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 784–792. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Adams, S.J.; Henderson, R.D.E.; Babyn, P. Computer-aided Assessment of Catheters and Tubes on Radiographs: How Good Is Artificial Intelligence for Assessment? Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
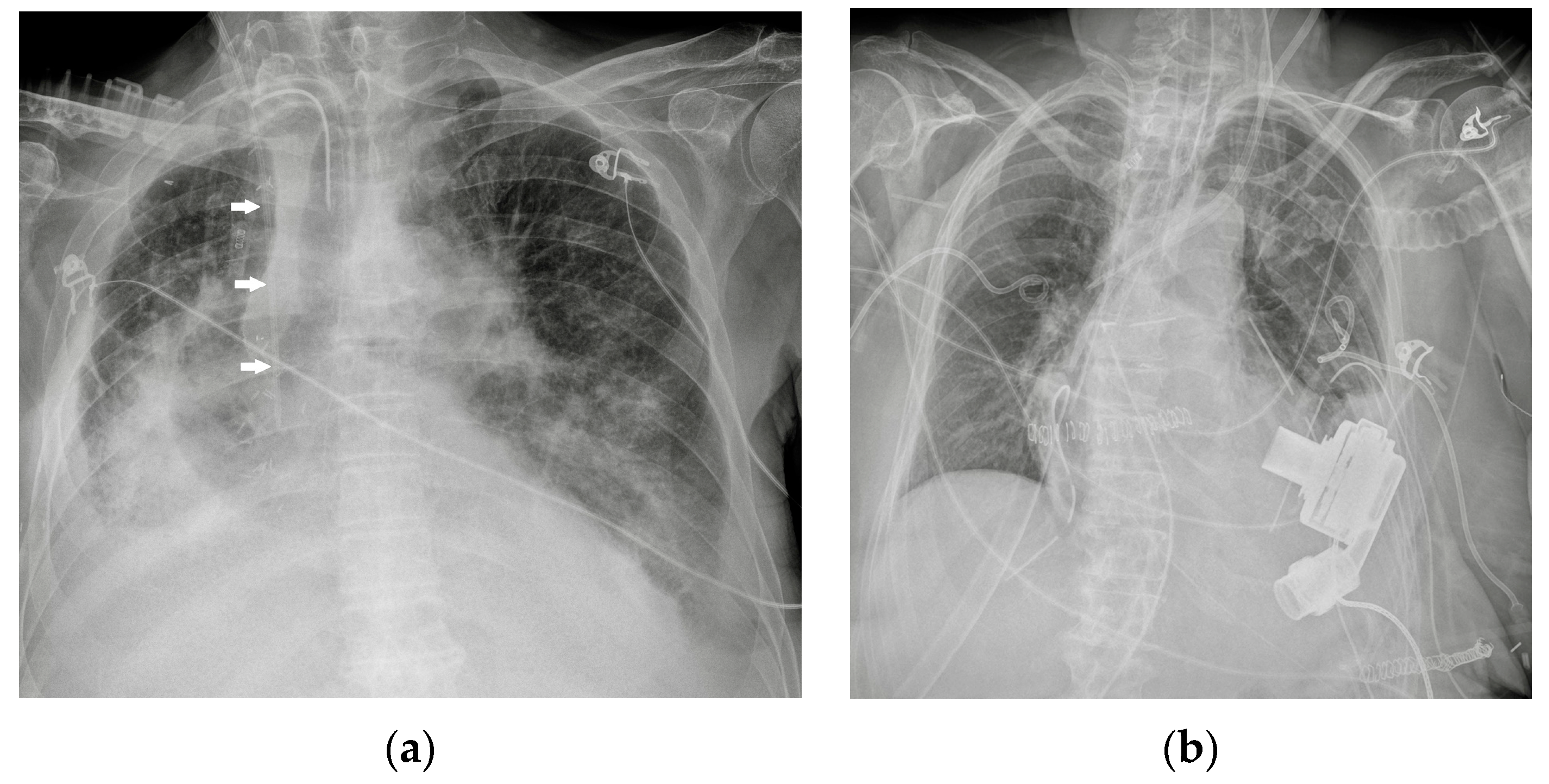
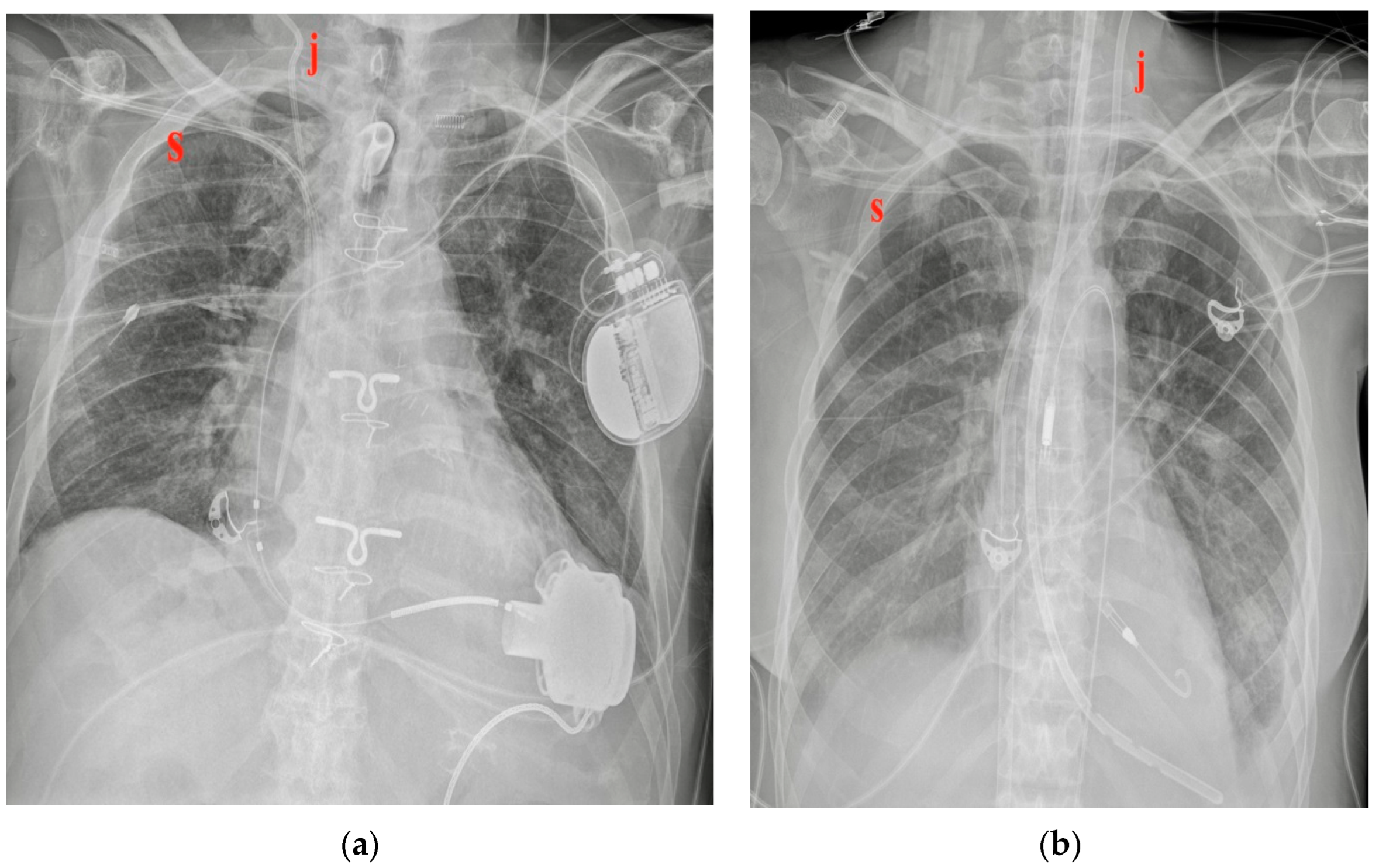

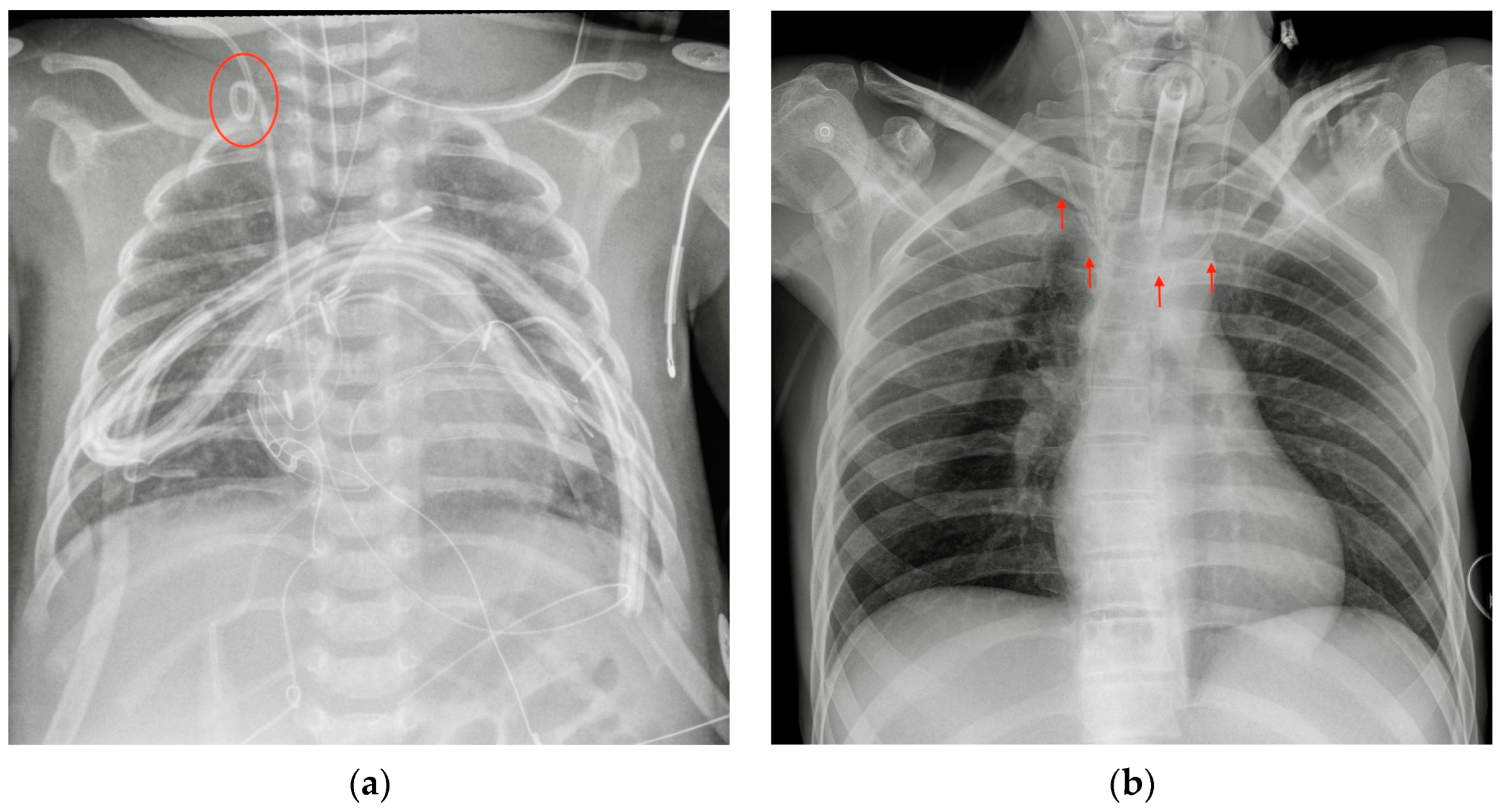
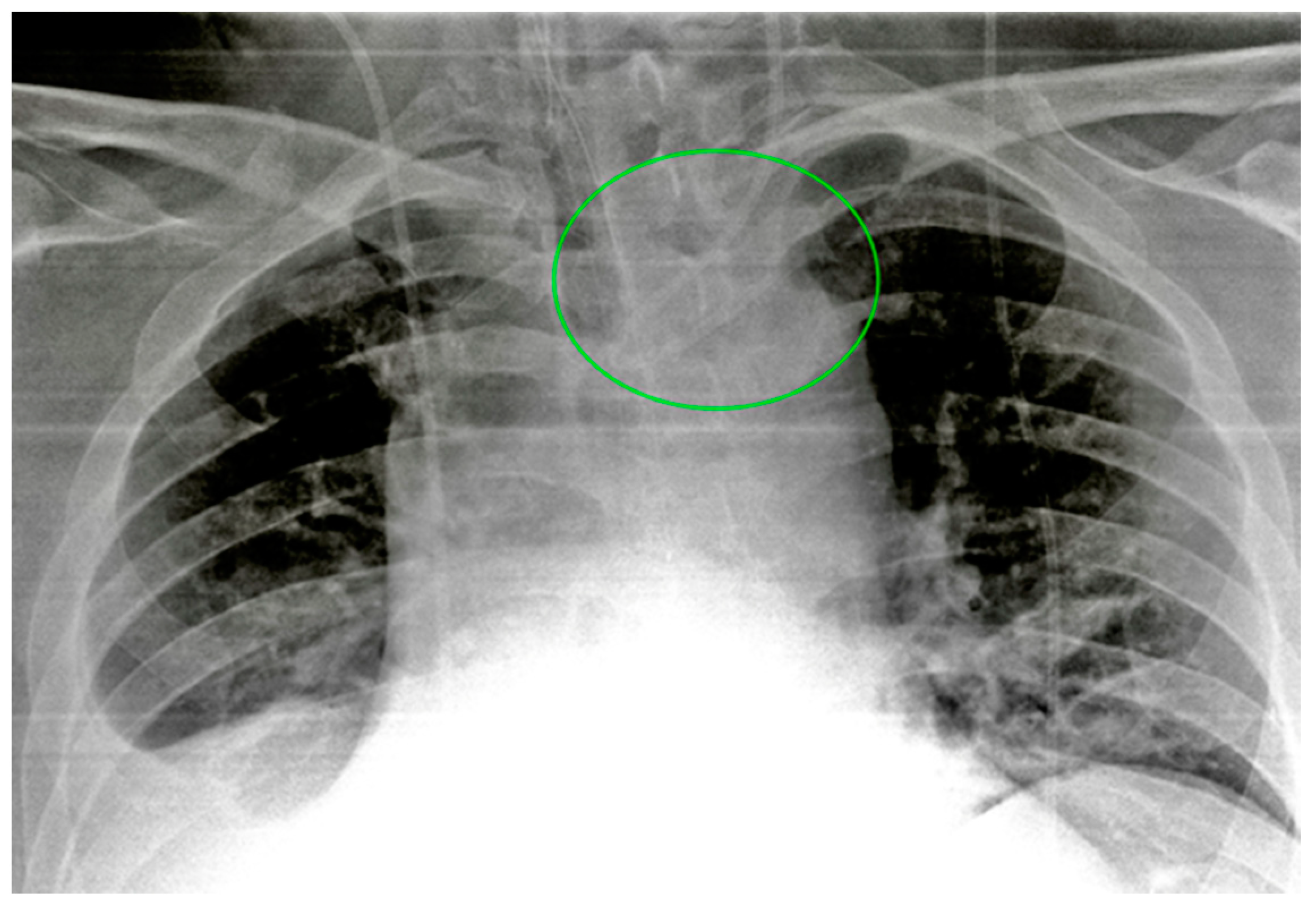










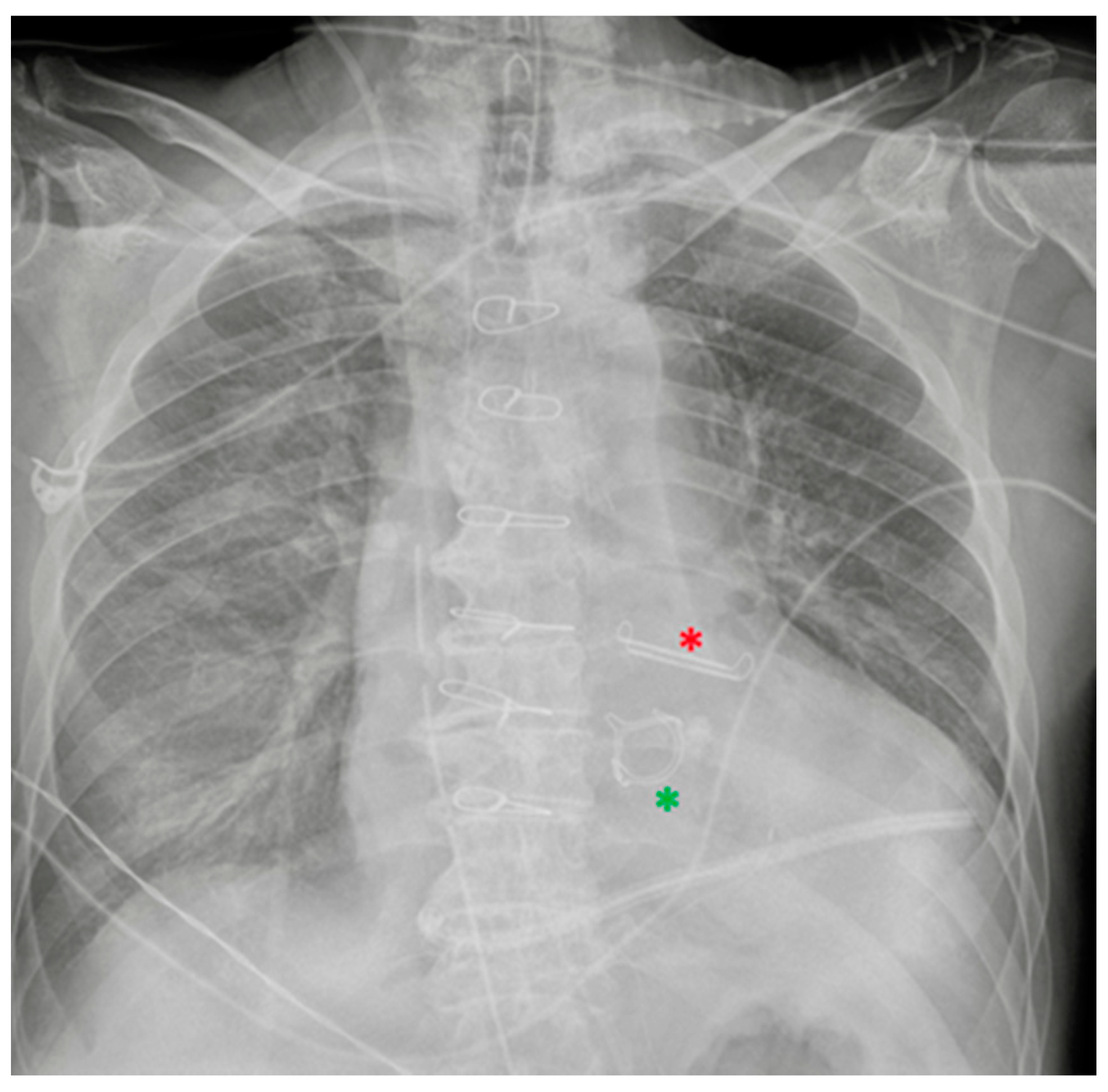








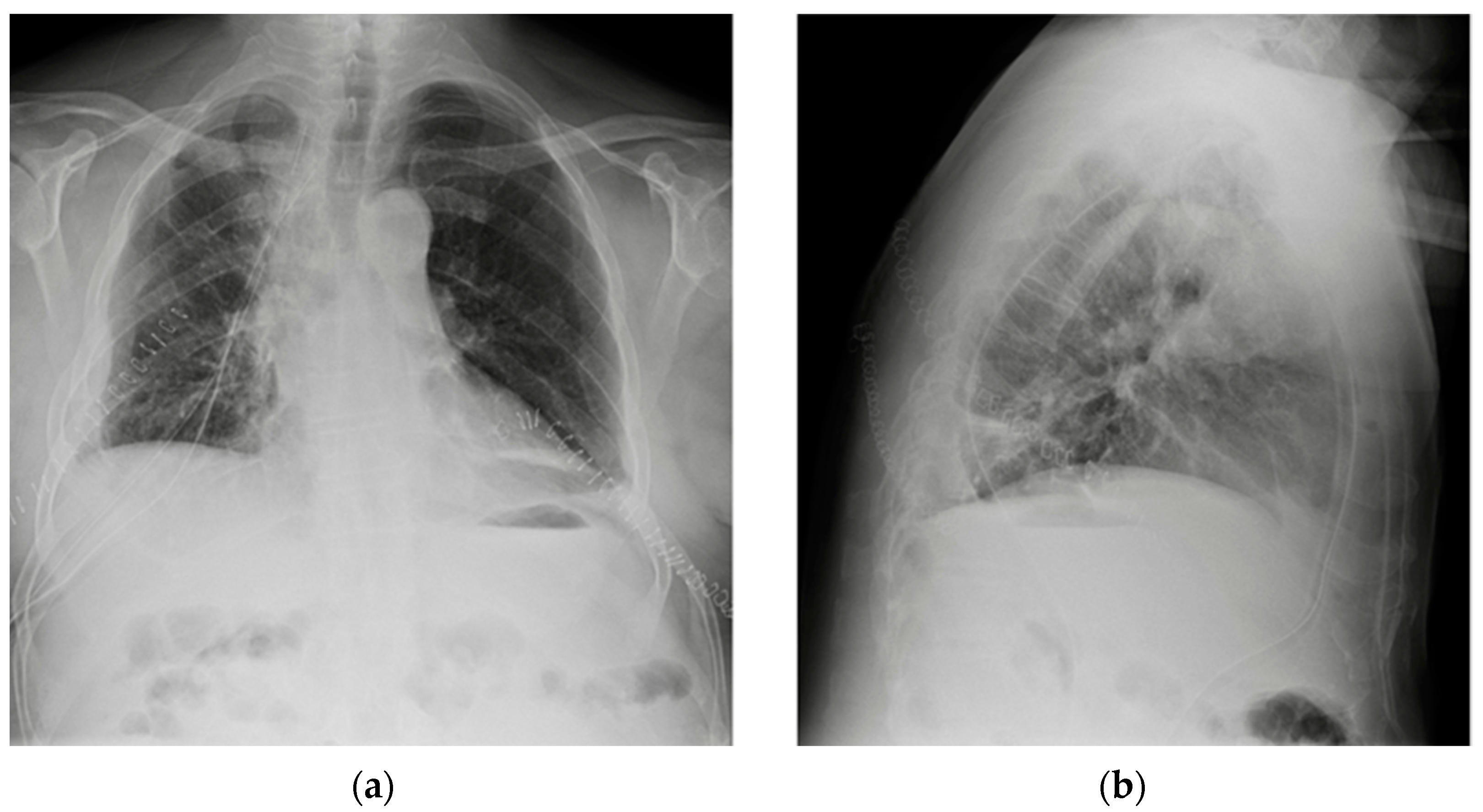







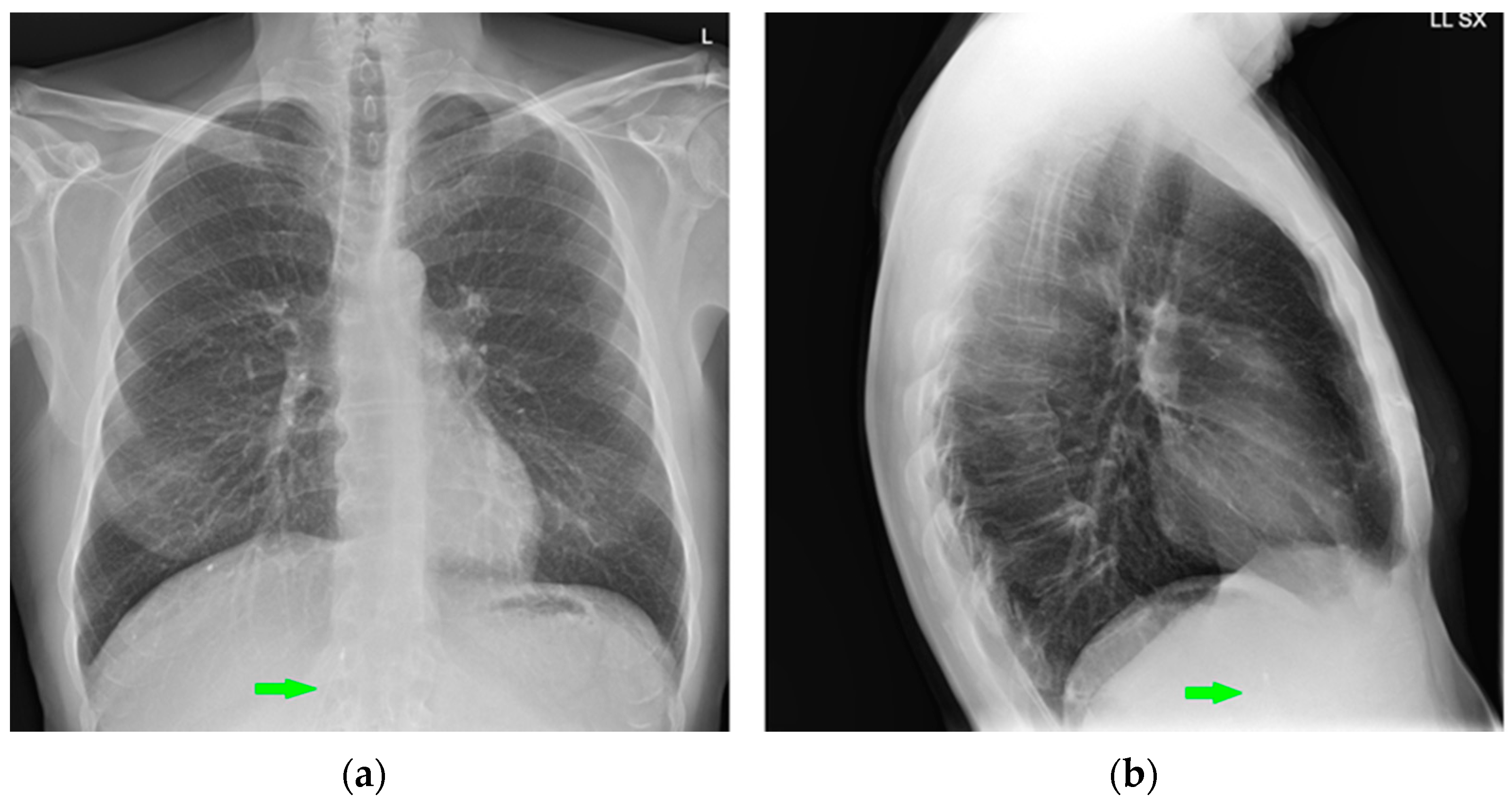


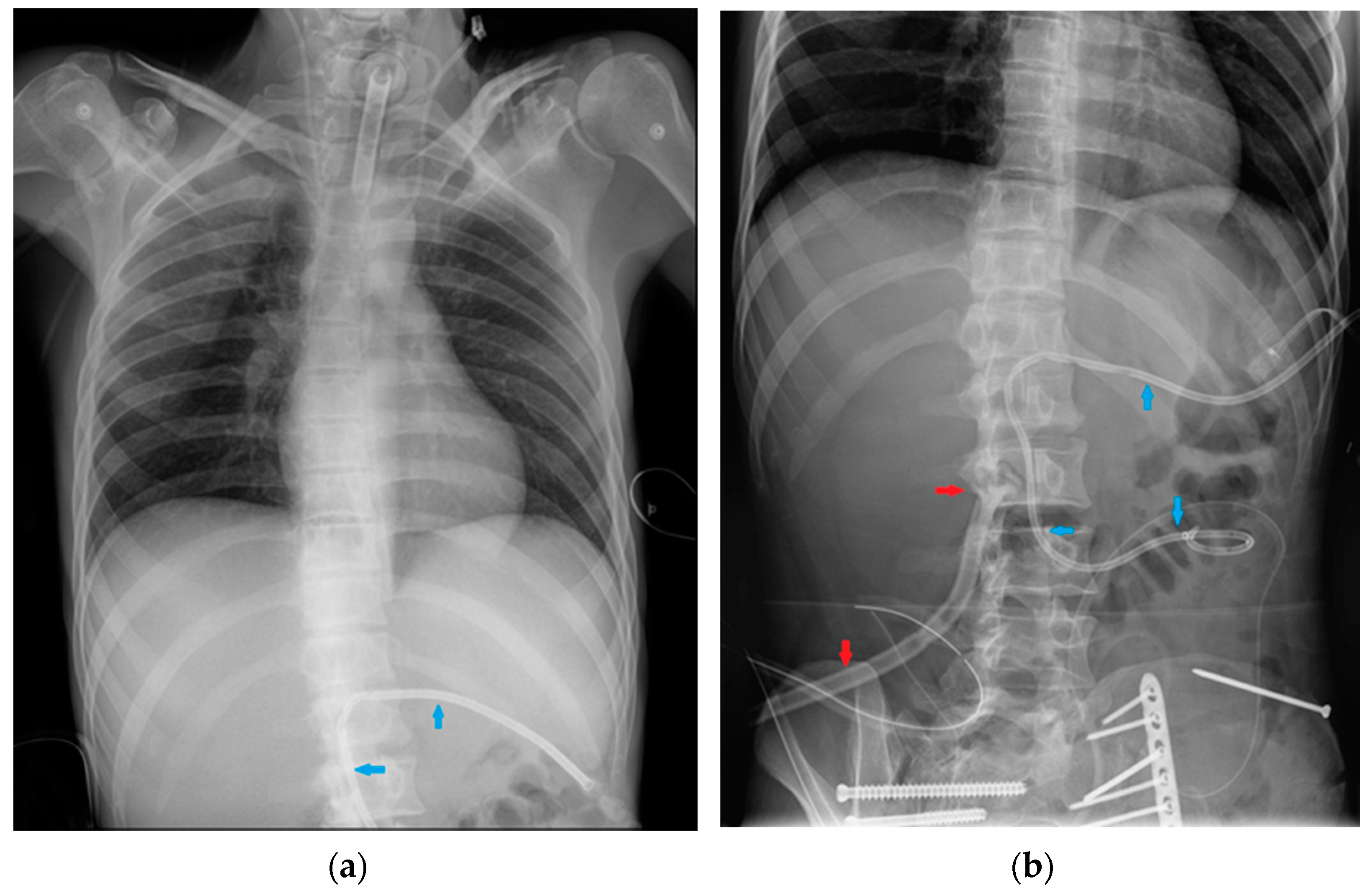
| Device Classification | |
|---|---|
| Intravascular devices | Central vein catheter |
| Peripherally inserted central catheter | |
| Port Swan-Ganz catheter | |
| Airway devices | Endotracheal tubes |
| Tracheostomy tubes | |
| Cardiac devices | Loop recorder |
| Pacemaker and automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator Ventricular assistance devices | |
| Impella | |
| Intra-aortic balloon pump Other cardiac devices | |
| Gastro-intestinal devices | Nasogastric tubes |
| Nasoenteric tubes | |
| Chest tubes | |
| Miscellaneous | |
| Device | Most Frequent CXR-Detectable Anomalies and Complications |
|---|---|
| CVC | Malposition (looping, IVC tip positioning, wrong thoracic vein cannulation) |
| Pneumothorax | |
| Vascular perforation (less frequent) | |
| PICC | Misposition |
| Pneumothorax/hemothorax (infrequent) | |
| PORT | Pneumothorax |
| Midline | Misposition |
| Swan-Ganz catheter | Malposition (looping, knotting) |
| RA or pulmonary artery wall perforation (diagnosis mostly clinical- or echocardiography-based) |
| Device | CXR-Detectable Mispositions | Complications |
|---|---|---|
| ETT | Laryngeal tip positioning | Cord trauma |
| Bronchus cannulation | Contralateral atelectasis, ipsilateral overinflation (risk of barotrauma, pneumothorax) | |
| Oesophageal intubation | Non-improving respiratory function, esophageal perforation | |
| Balloon overinflation | Throat pain, tissue ischemia, tracheal perforation, fistulae formation | |
| Tracheostomy tube | Subcutaneous emphysema Hematoma Pneumomediastinum Tracheal stenosis (late complication) |
| Device | Most Frequent CXR-Detectable Anomalies and Complications |
|---|---|
| Loop recorder | Migration (anecdotical) |
| PM and AICD | Leads misposition/breakage |
| Twiddler’s syndrome | |
| VADs | Hemopericardium, hemothorax |
| Impella | Dislocation |
| IABP | Misposition |
| ECMO | Misposition |
| Device | Most Frequent CXR-Detectable Anomalies and Complications |
|---|---|
| Nasogastric tubes | Proximal (oesophagus)/distal (duodenum) * misposition Coiling/kinking Insertion into the respiratory tree → aspiration pneumonia Gastric wall perforation Intracranial insertion (rare) * |
| Nasoenteric tubes | Comparable to NG tubes |
| Device | Most Frequent CXR-Detectable Anomalies and Complications |
|---|---|
| Chest tubes | Kinking Extrapleural/intrafissural/intraparenchymal/misposition Mediastinum juxtaposition Diaphragmatic trespassing Mediastinal invasion (uncommon) |
| Device | Most Frequent CXR-Detectable Anomalies and Complications |
|---|---|
| CSF shunts | Breakages Disconnection/migration of the distal catheter Pneumothorax Subcutaneous emphysema Pulmonary hypertension (VA shunts only) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gambato, M.; Scotti, N.; Borsari, G.; Zambon Bertoja, J.; Gabrieli, J.-D.; De Cassai, A.; Cester, G.; Navalesi, P.; Quaia, E.; Causin, F. Chest X-ray Interpretation: Detecting Devices and Device-Related Complications. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040599
Gambato M, Scotti N, Borsari G, Zambon Bertoja J, Gabrieli J-D, De Cassai A, Cester G, Navalesi P, Quaia E, Causin F. Chest X-ray Interpretation: Detecting Devices and Device-Related Complications. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(4):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040599
Chicago/Turabian StyleGambato, Marco, Nicola Scotti, Giacomo Borsari, Jacopo Zambon Bertoja, Joseph-Domenico Gabrieli, Alessandro De Cassai, Giacomo Cester, Paolo Navalesi, Emilio Quaia, and Francesco Causin. 2023. "Chest X-ray Interpretation: Detecting Devices and Device-Related Complications" Diagnostics 13, no. 4: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040599
APA StyleGambato, M., Scotti, N., Borsari, G., Zambon Bertoja, J., Gabrieli, J.-D., De Cassai, A., Cester, G., Navalesi, P., Quaia, E., & Causin, F. (2023). Chest X-ray Interpretation: Detecting Devices and Device-Related Complications. Diagnostics, 13(4), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040599







