Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases
Abstract
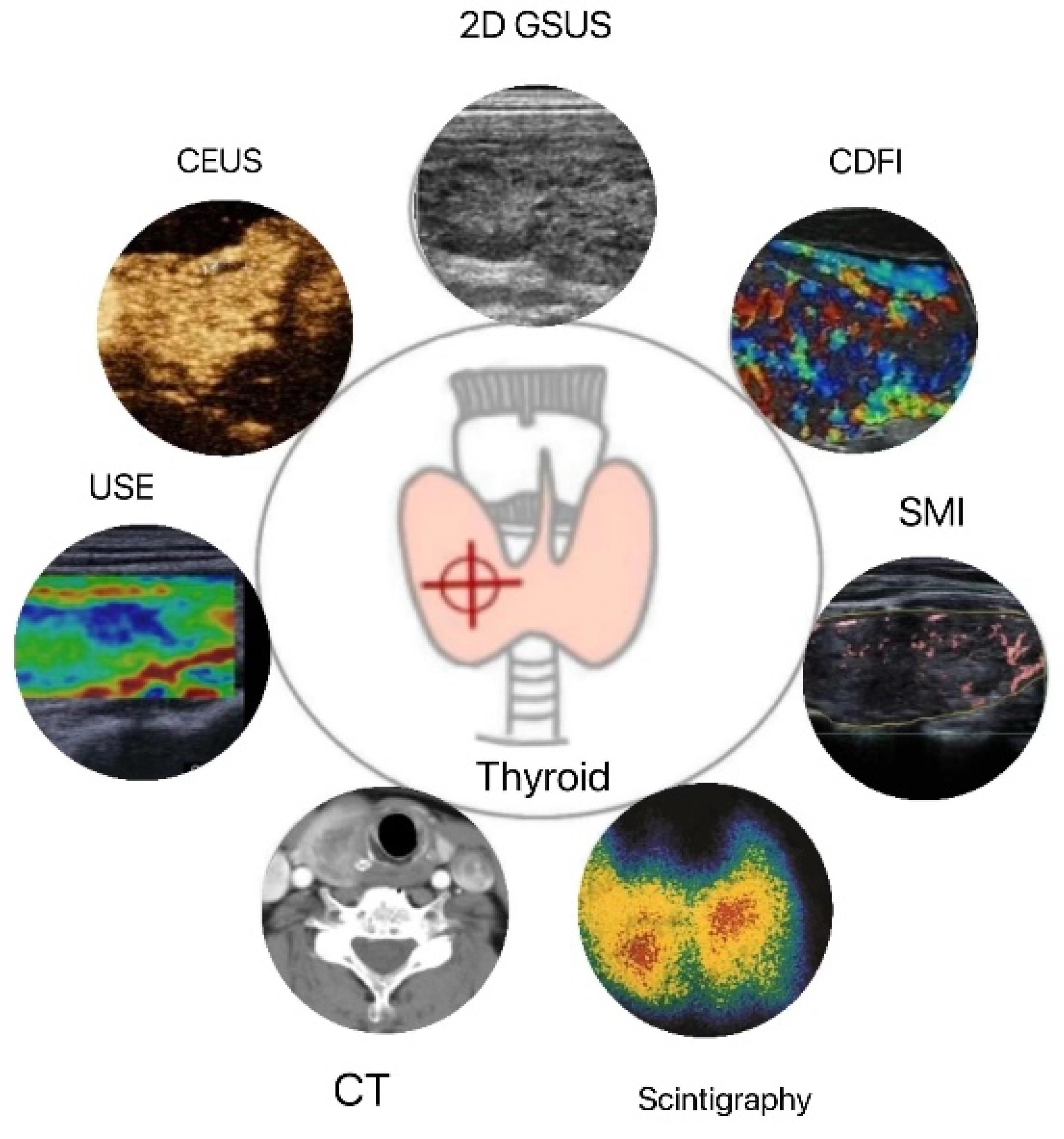
1. Introduction
2. Applications of Routine Technology for Quantitative Diagnosis by High-Frequency Ultrasound (HFUS)
2.1. Two-Dimensional Grayscale Ultrasound (2D GSUS)
2.2. Doppler Ultrasound
3. Application of New Technology for Quantitative Diagnosis by High-Frequency Ultrasound
3.1. Microvascular Ultrasound Imaging
3.2. Three-Dimensional Ultrasound (3D US)
3.3. Ultrasound Elastography (USE)
3.4. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
4. Applications of Other Quantitative Diagnostic Imaging Technology
4.1. Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
4.2. Thyroid Scintigraphy
4.3. Positron-Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, R.S. Autoimmune thyroid disease: Unlocking a complex puzzle. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Corrado, A.; Di Domenicantonio, A.; Fallahi, P. Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ragusa, F.; Elia, G.; Paparo, S.R.; Ruffilli, I.; Patrizio, A.; Giusti, C.; Gonnella, D.; Cristaudo, A.; et al. Graves’ disease: Epidemiology, genetic and environmental risk factors and viruses. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, F.; Fallahi, P.; Elia, G.; Gonnella, D.; Paparo, S.R.; Giusti, C.; Churilov, L.P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A. Hashimotos’ thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, J.; Jassil, N. Conversion of Hypothyroidism to Hyperthyroidism: A Rare Clinical Phenomenon. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 6, e279–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Aronow, W.S.; Patel, L.; Gandhi, K.; Desai, H. Hyperthyroidism. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, RA85–RA91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Feller, M.; Bauer, D.C.; Collet, T.-H.; da Costa, B.R.; Auer, R.; Peeters, R.P.; Brown, S.J.; Bremner, A.P.; O’Leary, P.C.; et al. Initial evaluation of thyroid dysfunction—Are simultaneous TSH and fT4 tests necessary? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, M.; Barr, R.; Bojunga, J.; Cantisani, V.; Chammas, M.C.; Cosgrove, D.O.; Cui, X.W.; Dong, Y.; Fenner, F.; Radzina, M.; et al. Thyroid Ultrasound: State of the Art Part 1—Thyroid Ultrasound reporting and Diffuse Thyroid Diseases. Med. Ultrason. 2017, 19, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, D.M.; Frates, M.C. Ultrasound of the Normal Thyroid with Technical Pearls and Pitfalls. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 58, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, L.F.; Patel, N.J.; Caserta, M.P.; Robbin, M.L. Thyroid Ultrasound: Diffuse and Nodular Disease. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 58, 1041–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.Y.; Kim, H.L.; Ha, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Han, M. Computer-aided diagnosis system for thyroid nodules on ultrasonography: Diagnostic performance and reproducibility based on the experience level of operators. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghervan, C. Thyroid and parathyroid ultrasound. Med. Ultrason. 2011, 13, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Słowińska-Klencka, D.; Wojtaszek-Nowicka, M.; Klencki, M.; Wysocka-Konieczna, K.; Popowicz, B. The Presence of Hypoechoic Micronodules in Patients with Hashimoto′s Thyroiditis Increases the Risk of an Alarming Cytological Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, R.; Di Bari, F.; Perelli, S.; Capodicasa, G.; Benvenga, S. Thyroid vascularization is an important ultrasonographic parameter in untreated Graves’ disease patients. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.; Middleton, W.D.; Teefey, S.A.; Reading, C.C.; Langer, J.E.; Desser, T.; Szabunio, M.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Cronan, J.J. Hashimoto Thyroiditis: Part 2, Sonographic Analysis of Benign and Malignant Nodules in Patients With Diffuse Hashimoto Thyroiditis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.; Middleton, W.D.; Teefey, S.A.; Reading, C.C.; Langer, J.E.; Desser, T.; Szabunio, M.M.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Mandel, S.J.; Cronan, J.J. Hashimoto Thyroiditis: Part 1, Sonographic Analysis of the Nodular Form of Hashimoto Thyroiditis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotti, G.; Sorvillo, F.; Iorio, S.; Carbone, A.; Romeo, A.; Piscopo, M.; Capuano, S.; Capuano, E.; Amato, G.; Carella, C. Grey-scale analysis allows a quantitative evaluation of thyroid echogenicity in the patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2003, 59, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.C.; Futterweit, W.; Gilbert, P. Micronodulation: Ultrasonographic sign of Hashimoto thyroiditis. J. Ultrasound Med. 1996, 15, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Chen, H.; Yao, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Lin, B.; Chen, X. Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasonography in Subacute Thyroiditis. Scanning 2022, 7, 7456622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.L.; Seeberger, U.; Hengstmann, J.H. Color Doppler sonography in hypothyroidism. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2003, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, D.; Yang, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J. The Adler grade by Doppler ultrasound is associated with clinical pathology of cervical cancer: Implication for clinical management. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralls, P.; Mayekawa, D.; Lee, K.; Colletti, P.; Radin, D.R.; Boswell, W.; Halls, J. Color-flow Doppler sonography in Graves disease: “thyroid inferno”. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 150, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, M.F.; Anil, C.; Cesur, M.; Başkal, N.; Erdoğan, G. Color Flow Doppler Sonography for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism. Thyroid 2007, 17, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaka, I.; Thomas, D.; Kaltsas, G. Value of the Left Inferior Thyroid Artery Peak Systolic Velocity in Diagnosing Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.A.; Choh, N.A.; Misgar, R.A.; Khan, S.H.; Shah, Z.A.; Rather, T.A.; Shehjar, F.; Laway, B.A. Comparison between peak systolic velocity of the inferior thyroid artery and technetium-99m pertechnetate thyroid uptake in differentiating Graves’ disease from thyroiditis. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2019, 63, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.A.R.R.; Marui, S.; Watanabe, T.; Lima, N.; Ozaki, C.O.; Cerri, G.G.; Chammas, M.C. Color Duplex Doppler US can Follow up the Response of Radioiodine in Graves’ Disease by Evaluating the Thyroid Volume and Peak Systolic Velocity. Ultraschall Med. 2019, 41, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurajoh, M.; Yamasaki, A.; Nagasaki, T.; Nagata, Y.; Yamada, S.; Imanishi, Y.; Emoto, M.; Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Shintani, A.; et al. Thyroid blood flow in inferior thyroid artery as predictor for increase in levothyroxine dosage during pregnancy in women with Hashimoto's thyroiditis—A retrospective study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Cohnen, M.; Fürst, G.; Mödder, U.; Feldkamp, J. Prediction of Relapse after Antithyroid Drug Therapy of Graves' Disease: Value of Color Doppler Sonography. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2004, 112, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Mo, X.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Clinical Applications of Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Superficial Tissues and Organs: A Systematic Review. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 28, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Karahan, A.Y.; Oncu, F.; Bakdik, S.; Durmaz, M.S.; Tolu, I. Diagnostic Performance of Superb Microvascular Imaging and Other Sonographic Modalities in the Assessment of Lateral Epicondylosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 37, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınçer, A.; Durmaz, M.S.; Kıraç, C.O.; Baldane, S.; Ateş, F.; Batur, A. Evaluation of parenchymal vascularity of the thyroid gland with vascularization index by color superb microvascular imaging in patients with Graves’ disease. J. Ultrason. 2021, 21, e41–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayramoglu, Z.; Kandemirli, S.G.; Sarı, Z.N.A.; Kardelen, A.D.; Poyrazoglu, S.; Bas, F.; Darendeliler, F.; Adaletli, I. Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Evaluation of Pediatric Graves Disease and Hashimoto Thyroiditis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Amino, N.; Morita, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Kubota, S.; Fukata, S.; Kamiyama, N.; Miyauchi, A. Quantitative measurement of thyroid blood flow for differentiation of painless thyroiditis from Graves’ disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Xu, H.; Zhan, X.; Li, L.; Song, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ge, L. Using 3-dimensional ultrasound islice technology for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 39, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakas, O.; Karakas, E.; Cullu, N.; Demir, Y.; Kucukyavas, Y.; Surucu, E.; Yener, S.; Igci, E. An evaluation of thyrotoxic autoimmune thyroiditis patients with triplex Doppler ultrasonography. Clin. Imaging 2013, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, S.C.; Hsieh, M.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, J.D.; Chen, C.C.; Hsu, W.H.; Jeng, L.B.; Chang, C.T.; Chen, R.H.; Wang, T.Y.; et al. The reproducibility of the virtual organ computer-aided analysis program for evaluating 3-dimensional power Doppler ultrasonography of diffuse thyroid disorders. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2009, 32, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophir, J.; Céspedes, I.; Ponnekanti, H.; Yazdi, Y.; Li, X. Elastography: A Quantitative Method for Imaging the Elasticity of Biological Tissues. Ultrason. Imaging 1991, 13, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyshchik, A.; Higashi, T.; Asato, R.; Tanaka, S.; Ito, J.; Mai, J.J.; Pellot-Barakat, C.; Insana, M.F.; Brill, A.B.; Saga, T.; et al. Thyroid Gland Tumor Diagnosis at US Elastography. Radiology 2005, 237, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.; Barr, R.; Bojunga, J.; Cantisani, V.; Chammas, M.C.; Dighe, M.; Vinayak, S.; Xu, J.-M.; Dietrich, C.F. WFUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography: Part 4. Thyroid. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-K.; Xu, H.-X. Ultrasound elastography of the thyroid: Principles and current status. Ultrasonography 2019, 38, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Cui, G.; Fu, F. Assessment of Diffuse Thyroid Disease by Strain Ratio in Ultrasound Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 2884–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeha, C.; Paul, C.; Borlea, A.; Borcan, F.; Fofiu, R.; Dehelean, C.; Stoian, D. The Value of Strain Elastography in Predicting Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporea, I.; Sirli, R.; Bota, S.; Vlad, M.; Popescu, A.; Zosin, I. ARFI elastography for the evaluation of diffuse thyroid gland pathology: Preliminary results. World J. Radiol. 2012, 4, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporea, I.; Vlad, M.; Bota, S.; Sirli, R.L.; Popescu, A.; Danila, M.; Sendroiu, M.; Zosin, I. Thyroid Stiffness Assessment by Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography (ARFI). Ultraschall der Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2011, 32, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Kim, E.-K.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, K.H.; Son, E.J.; Moon, H.J.; Kwak, J.Y. Diagnostic Role of Conventional Ultrasonography and Shearwave Elastography in Asymptomatic Patients with Diffuse Thyroid Disease: Initial Experience with 57 Patients. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazem, M.; Al Jabr, I.K.; AlYahya, A.A.; Hassanein, A.G.; Algahlan, H.A.E. Reliability of shear wave elastography in the evaluation of diffuse thyroid diseases in children and adolescents. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 143, 109942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P.S.; Cantisani, V.; Dietrich, C.F.; Gilja, O.H.; Saftoiu, A.; Bartels, E.; Bertolotto, M.; Calliada, F.; Clevert, D.-A.; Cosgrove, D.; et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations for the Clinical Practice of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in Non-Hepatic Applications: Update 2017 (Long Version). Ultraschall der Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2018, 39, e2–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Lai, X.-J.; Zhu, S.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y. Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound of thyroid nodules coexisting with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2015, 37, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Sun, M.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J.; Cheng, J.N.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, B. Values of the Quantitative Parameters of Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Benign and Malignant Nodules. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2020, 42, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Kang, J.K.; Pham, T.D.; Batchuluun, G.; Park, K.R. Ultrasound Image-Based Diagnosis of Malignant Thyroid Nodule Using Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2020, 20, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, J.C.; Soderlund, K.A.; Glastonbury, C.M. Imaging of Head and Neck Cancer With CT, MRI, and US. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, J.; Velhonoja, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Happonen, T.; Nyman, M.; Irjala, H.; Soukka, T.; Mattila, K.; Hirvonen, J. Emergency neck MRI: Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy in cases of neck infection. Acta Radiol. 2020, 62, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Choo, H.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Lim, H.K.; Ryu, J.H. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography for differentiating diffuse thyroid disease from normal thyroid parenchyma: A multicenter study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, M.; Murata, Y.; Ishida, R.; Ohashi, I.; Hirata, Y.; Shibuya, H. MR imaging of the thyroid: Correlation between apparent diffusion coefficient and thyroid gland scintigraphy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003, 17, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.H.; Morris, J.C. The Sodium-Iodide Symporter. Curr. Drug Targets Immune Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2004, 4, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, L.; Avram, A.M.; Iakovou, I.; Kwak, J.; Lawson, S.A.; Lulaj, E.; Luster, M.; Piccardo, A.; Schmidt, M.; Tulchinsky, M.; et al. EANM practice guideline/SNMMI procedure standard for RAIU and thyroid scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 46, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okosieme, O.E.; Chan, D.; Price, S.A.; Lazarus, J.; Premawardhana, L. The utility of radioiodine uptake and thyroid scintigraphy in the diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, G.; Tonacchera, M.; Grosso, M.; Orsolini, F.; Vitti, P.; Strauss, H.W. The Role of Nuclear Medicine in the Clinical Management of Benign Thyroid Disorders, Part 1: Hyperthyroidism. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 62, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänscheid, H.; Canzi, C.; Eschner, W.; Flux, G.; Luster, M.; Strigari, L.; Lassmann, M. EANM Dosimetry Committee Series on Standard Operational Procedures for Pre-Therapeutic Dosimetry II. Dosimetry prior to radioiodine therapy of benign thyroid diseases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 40, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohammed, H.I.; Mansour, S.; Alhulwah, A.H.; Mayhoub, F.H.; Arafah, A.M. Scintigraphy has the potential to replace thyroid stimulating hormone and ultrasonography in hyperthyroidism diagnosis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1722–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Suzuki, R.; Kasai, T.; Onose, H.; Komiya, K.; Goto, H.; Takeno, K.; Ishii, S.; Sato, J.; Honda, A.; et al. Cutoff value of thyroid uptake of 99mTc-pertechnetate to discriminate between Graves’ disease and painless thyroiditis: A single center retrospective study. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidokoro-Kunii, Y.; Emoto, N.; Cho, K.; Oikawa, S. Analysis of the Factors Associated with Tc-99m Pertechnetate Uptake in Thyrotoxicosis and Graves' Disease. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2006, 73, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Xin, Y.; Wen, Q.; Bail, L.; Guan, F.; Bin, J. 99mTc-pertechnetate thyroid scintigraphy predicts clinical outcomes in personalized radioiodine treatment for Graves' disease. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen Mol. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 37, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, D.; Treglia, G.; Giovanella, L.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. Detection of thyroiditis on PET/CT imaging: A systematic review. Hormones 2020, 19, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambara, N.; Liu, S.Y.W.; Lo, X.; Ying, M. Comparative Analysis of Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Computer-Assisted Subjective Assessment in Thyroid Ultrasound. Life 2021, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.J.; Baek, J.H. Applications of machine learning and deep learning to thyroid imaging: Where do we stand? Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Technology | Quantitative Methods | Value | Ref. |
| 2D GSUS | Volume | 10–15 mL, female, normal | [12] |
| 12–18 mL, male, normal | |||
| Grayscales (GWE) | 71.9 ± 3.1 GWE, HT * | [17] | |
| 61.9 ± 8.3 GWE, normal | |||
| CDFI | Adler’s semi-quantitative evaluation | Grade I–IV | [21] |
| PSV-ITA | 61.65 cm/s, HT * & GD * | [24,25] | |
| 30 cm/s, GD * & thyroiditis | |||
| 90.06 ± 44.13 cm/s, before I131 | [26] | ||
| 32.95 ± 16.36 cm/s, 6 months later | |||
| PSV-ITA & VFR | 139 cm/s, 195 mL/min, relapse patients | [28] | |
| 71 cm/s, 67 mL/min, remission patients | |||
| SMI | Vascularization index | 12 (2.3–32.1), GD * | [31,32] |
| 5.04 (1.1–10.8), normal | |||
| 17.35, pediatric GD * & HT * | |||
| ADF | ADF-TBF | >4%, GD * & thyroiditis | [33] |
| 3D US | STA/CCA-TDU | STA-PSV, STA-EDV, PSVR, EDVR | [35,36] |
| 3D US and VOCAL | Vascularization index | ||
| USE | Strain elastic ultrasound | Strain ratio (SR) | [41,42] |
| 1.64, CAT * | |||
| ARFI-VTI/VTQ | TS 2.36 m/s, DTD * | [43] | |
| SWE | Shear wave velocity 2.53 m/s | [44,45] | |
| Young’s modulus 27.6 kPa | |||
| CEUS | CEUS | Identification of nodules or tumors | [46] |
| CT | Mean CT values | 103 HU, non-enhanced CT * | [53] |
| 205 HU, contrast-enhanced CT * | |||
| MRI | ADC values | 1.82 × 10–3 mm2/s, GD * | [54] |
| Thyroid Scintigraphy | Tc-99m uptake | 0.97–40.1%, GD * | [61] |
| 0.15–0.8%, HT * | |||
| <0.5%, subacute thyroiditis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Zhao, J. Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040700
Huang J, Zhao J. Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(4):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040700
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jing, and Jiaqi Zhao. 2023. "Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases" Diagnostics 13, no. 4: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040700
APA StyleHuang, J., & Zhao, J. (2023). Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases. Diagnostics, 13(4), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040700




