End-to-End Automatic Classification of Retinal Vessel Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Improved U-Net
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A model based on GAN and improved U-Net is proposed for the automatic end-to-end classification of fundus arteriovenous vessels. The introduction of ASPP and attention modules can also improve the classification capability of the model. The classification results of the proposed model are highly competitive.
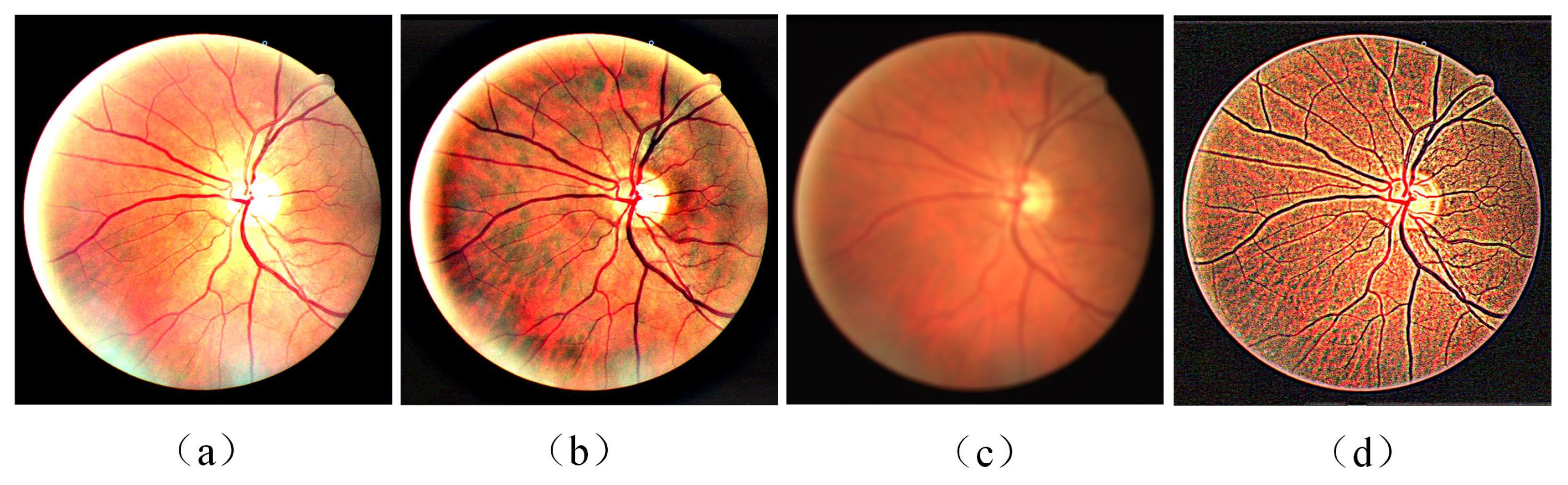
- A local contrast enhancement method was used to preprocess the input images. Through preprocessing, the problems of low overall brightness and poor contrast between blood vessels and background of the original fundus image data were solved. The effectiveness of this method was verified by ablation experiments.
- The proposed method allows simultaneous classification of vessel crossings in fundus images in addition to the classification of arterioles, which is innovative in the study of fundus vascular classification.
2. Related Work
- (A)
- Traditional Machine Learning Based Methods
- (B)
- Deep Learning Methods
3. Experimental Materials and Preprocessing
3.1. Dataset
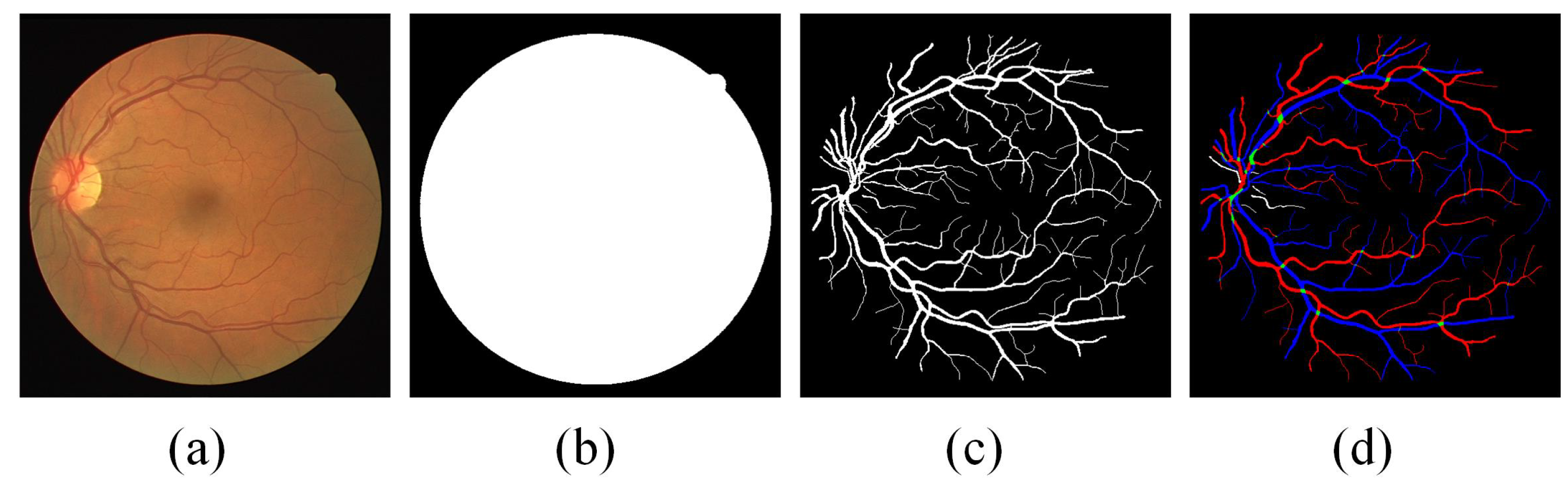
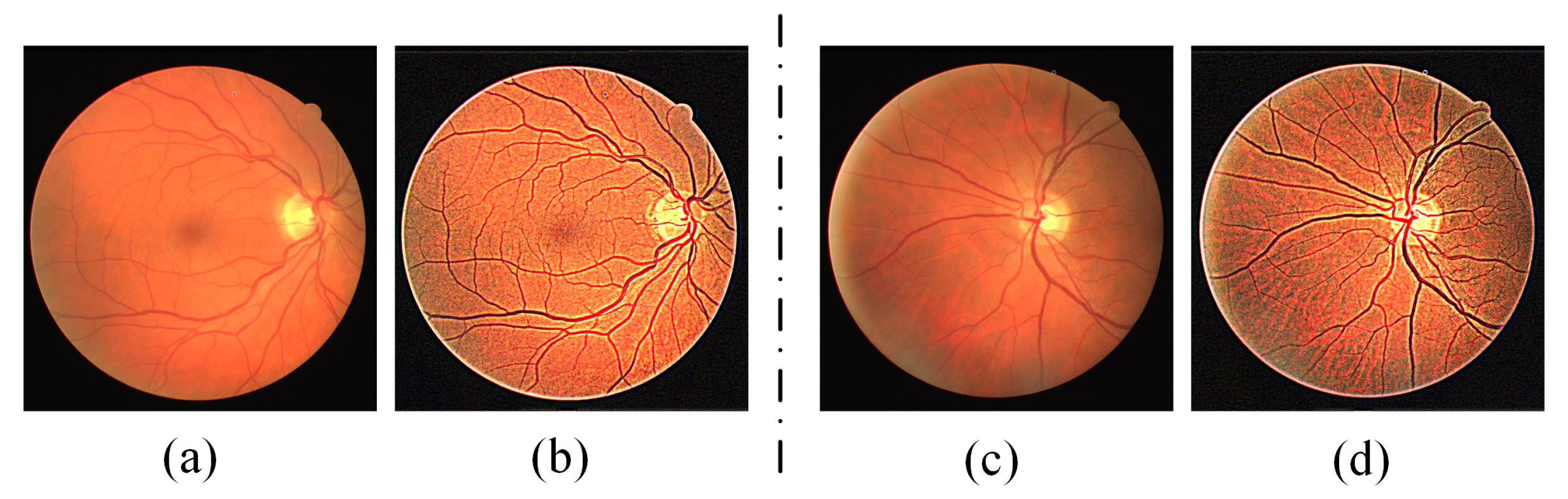
3.2. Preprocessing
4. Methods
4.1. Method Architecture Overview
4.2. Network Structure

4.2.1. ASPP Module

4.2.2. Attention Module

5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Evaluation Metrics
5.2. Implementation Details
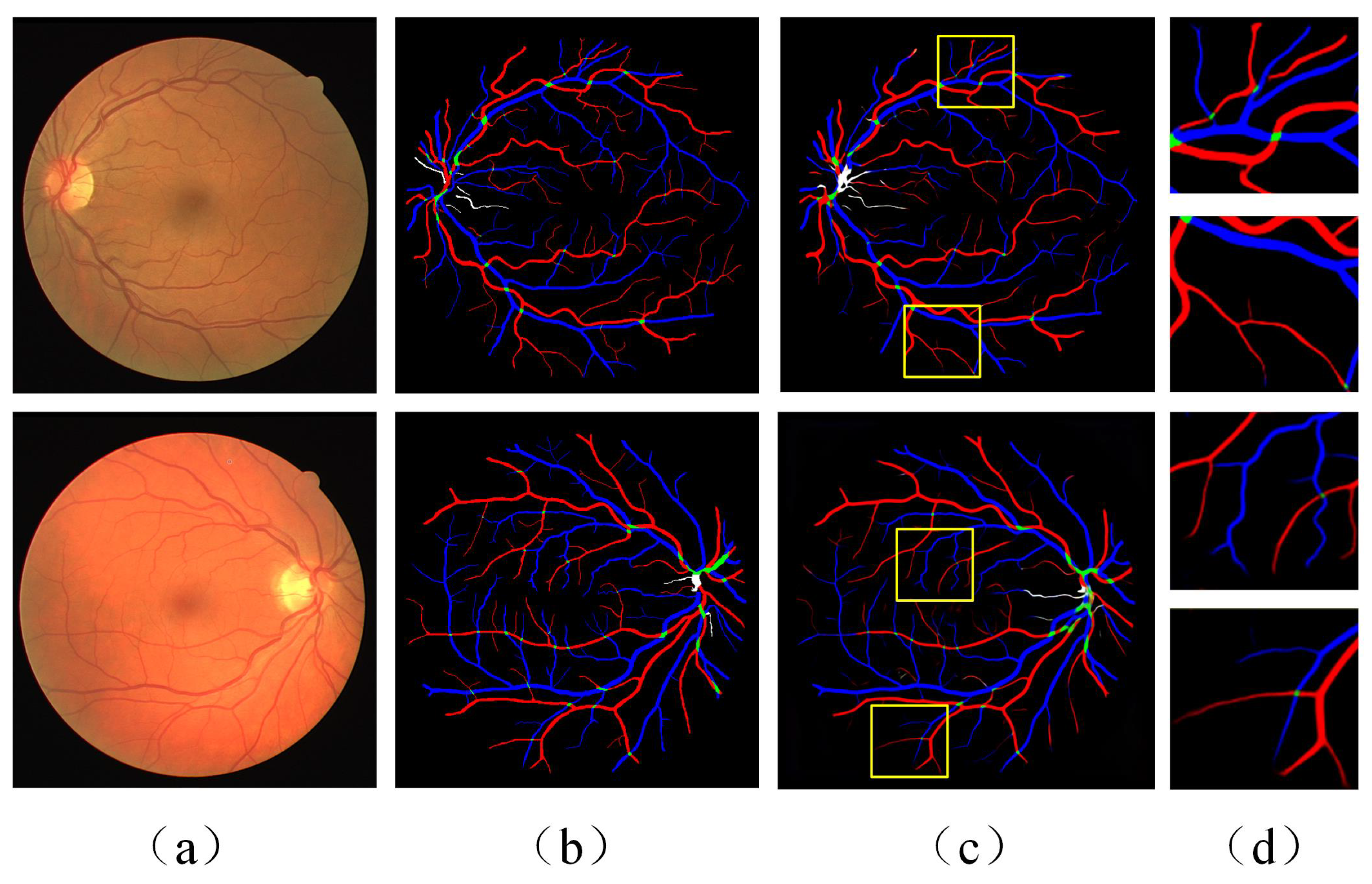
5.3. Classification Results
5.4. Ablation Study
5.5. Discussion
5.6. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Report on Vision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, H.A.; Broman, A.T. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Liang, W. Clinical observation of fundus photography screening for primary glaucoma in community patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. China Pract. Med. 2020, 15, 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- David, S.A.; Mahesh, C.; Kumar, V.D.; Polat, K.; Alhudhaif, A.; Nour, M. Retinal Blood Vessels and Optic Disc Segmentation Using U-Net. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8030954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, B.S.; Adabifirouzjaei, F.; Lando, L.; Yarmohammadi, A.; Long, C.P.; Mas, C.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Sarraf, D.; Demaria, A.N.; Envelope, M.F.; et al. Retinal Ischemic Perivascular Lesions, a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2022, 6, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Comparison of different methods in early screening for diabetic retinopathy. China Contin. Med. Educ. 2020, 12, 152–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, C.Y.; Mok, V.; Foster, P.J.; Trucco, E.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liang, C. Relationship of Gensini score with retinal vessel diameter and arteriovenous ratio in senile CHD. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, E.J.; Chung, P.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Song, S.J. Relationship of retinal vascular caliber variation with intracranial arterial stenosis. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 108, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciecholewski, M.; Kassjański, M. Computational Methods for Liver Vessel Segmentation in Medical Imaging: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xue, L.; Lin, J.; Yu, L. Retinal vessel segmentation method based on matched filtering and automatic threshold. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2017, 1, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.; Verma, S.; Kavita; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Masud, M.; Baz, M. Curvelet Transform Based on Edge Preserving Filter for Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 2459–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, D.A.; Natarajan, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Retinal vessel segmentation using multifractal characterization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 94, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Tan, S.; Lin, J.; Bu, W. PCAT-UNet: UNet-like network fused convolution and transformer for retinal vessel segmentation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookiah, M.R.K.; Hogg, S.; MacGillivray, T.J.; Prathiba, V.; Pradeepa, R.; Mohan, V.; Anjana, R.M.; Doney, A.S.; Palmer, C.N.; Trucco, E. A review of machine learning methods for retinal blood vessel segmentation and artery/vein classification. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 68, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chuah, J.H.; Ali, R.; Wang, Y. Retinal vessel segmentation using deep learning: A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 111985–112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Kim, J.K.; Ryu, I.H.; Yoo, T.K. Application of generative adversarial networks (GAN) for ophthalmology image domains: A survey. Eye Vis. 2022, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, S.; De Momi, E.; El Hadji, S.; Mattos, L.S. Blood vessel segmentation algorithms—Review of methods, datasets and evaluation metrics. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 158, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulsahib, A.A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Rasheed, H.H.; Mostafa, S.A.; Maashi, M.S. Comprehensive review of retinal blood vessel segmentation and classification techniques: Intelligent solutions for green computing in medical images, current challenges, open issues, and knowledge gaps in fundus medical images. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2021, 10, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathananthavathi, V.; Indumathi, G. BAT optimization based Retinal artery vein classification. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 2821–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinidhi, C.L.; Aparna, P.; Rajan, J. Automated method for retinal artery/vein separation via graph search metaheuristic approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtbozorg, B.; Mendonca, A.M.; Campilho, A. An Automatic Graph-Based Approach for Artery/Vein Classification in Retinal Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, S.; Cancela, B.; Barreira, N.; Penedo, M.G.; Rodríguez-Blanco, M.; Pena Seijo, M.; de Tuero, G.; Barceló, M.A.; Saez, M. Improving retinal artery and vein classification by means of a minimal path approach. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2013, 24, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welikala, R.A.; Foster, P.J.; Whincup, P.H.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Strachan, D.P.; Barman, S.A. Automated arteriole and venule classification using deep learning for retinal images from the UK Biobank cohort. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Su, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Retinal Vascular Network Topology Reconstruction and Artery/Vein Classification via Dominant Set Clustering. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Deng, Q.; Li, H. The Arteriovenous Classification in Retinal Images by U-net and Tracking Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Beijing, China, 10–12 July 2020; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Binh, N.T.; Hien, N.M.; Tin, D.T. Improving U-Net architecture and graph cuts optimization to classify arterioles and venules in retina fundus images. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 4015–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, J.; Hervella, Á.S.; Novo, J.; Rouco, J. Simultaneous segmentation and classification of the retinal arteries and veins from color fundus images. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 118, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdran, A.; Meyer, M.; Costa, P.; MendonÇa; Campilho, A. Uncertainty-aware artery/vein classification on retinal images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Garvin, M.K. Automated construction of arterial and venous trees in retinal images. J. Med. Imaging 2015, 2, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staal, J.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; Van Ginneken, B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, P.M.; Fitch, R.C. Real-time adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1981, PAMI-3, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imageshop. Available online: https://www.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/p/3324282.html (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Gu, Z.; Hao, H.; Qi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Frangi, A.; Liu, J. CS-Net: Channel and spatial attention network for curvilinear structure segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, R.; Lv, P.; Gao, B.; Li, C.; Tian, Z.; Tan, T.; Xu, F. Simultaneous arteriole and venule segmentation with domain-specific loss function on a new public database. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 3153–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Gao, Y.; Guo, S.; Xu, X.; Li, T.; Wang, K. AVNet: A retinal artery/vein classification network with category-attention weighted fusion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 195, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Yu, S.; Ma, K.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Zheng, Y. Multi-task neural networks with spatial activation for retinal vessel segmentation and artery/vein classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, R.; Allingham, M.J.; Mettu, P.S.; Cousins, S.W.; Tomasi, C.; Farsiu, S. Retinal artery-vein classification via topology estimation. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2015, 34, 2518–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Ding, W.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Cao, R. An improved arteriovenous classification method for the early diagnostics of various diseases in retinal image. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 141, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Tan, T.; ter Haar Romeny, B.M. Retinal artery/vein classification using genetic-search feature selection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilakkiya, M.; Devi, S.S. Detection of Arteriovenous Nicking in Retinal Fundus Images for Screening Hypertensive Retinopathy. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343263226_Detection_of_Arteriovenous_Nicking_in_Retinal_Fundus_Images_For_Screening_Hypertensive_Retinopathy (accessed on 12 March 2023).



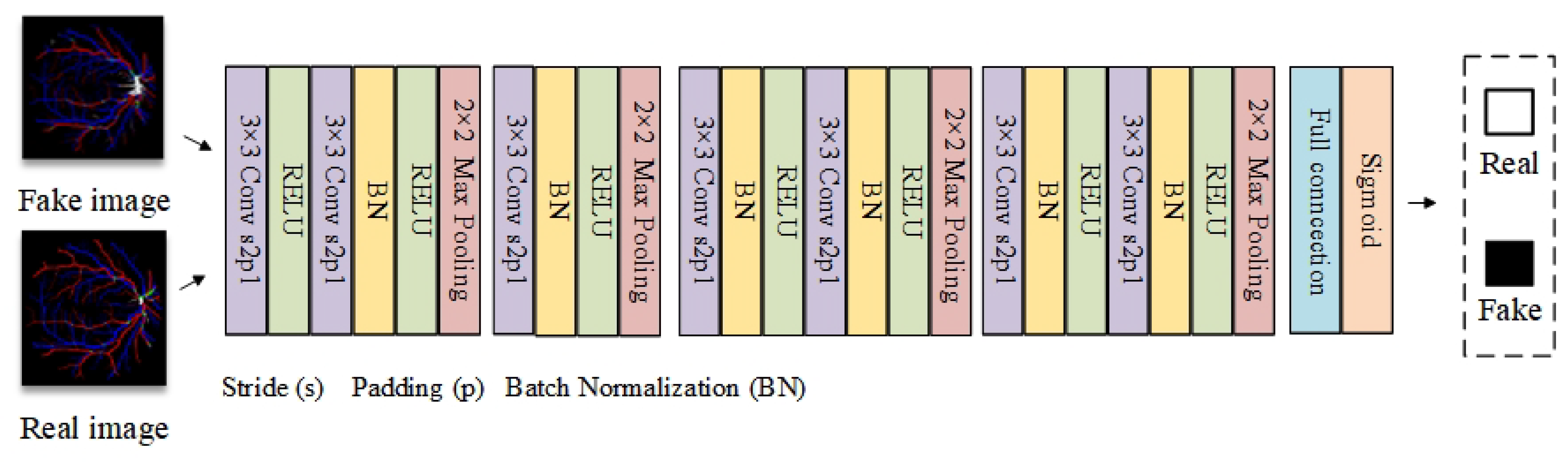
| Method | Category | Pros and Cons | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Manual features | The extracted vascular features can be explained, but feature processing requires more professional knowledge of fundus vascular medicine and images | [23,24,25,26] |
| Graph-based methods | The interpretable features can be extracted automatically, and the vascular segments are classified. However, accurate segmentation at the pixel level is not achieved | [27,28] | |
| Deep learning | Segmentation first and then classification | The accuracy of classification is good, but the vascular classification task is divided into multiple subtasks, and the errors in the vascular segmentation subtask will be directly transmitted to the vascular classification subtask | [18,29,30] |
| End-to-end classification | Automatic blood vessel segmentation and pixel-level classification are implemented synchronously, but the amount of related research is insufficient | [31,32] |
| Forecast Classification Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Category | A (Artery) | V (Vein) | U (Uncertain Vessel) | B (Background) |
| A (Artery) | TA | FVa | FUa | FBa |
| V (Vein) | FAv | TV | FUv | FBv |
| U (Uncertain vessel) | FAu | FVu | TU | FBu |
| B (Background) | FAb | FVb | FUb | TB |
| Formula | Index | Result | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Sens | 91.78% | The ability to classify arteries |
| (2) | Spec | 97.25% | The ability to classify veins |
| (3) | Acc | 96.86% | The ability to comprehensively classify the arteries and veins |
| (4) | Acc_U | 63.23% | The ability to classify uncertain vessels (including A-V crossing) |
| (5) | Acc_All | 96.87% | The ability to accurately classify the whole fundus image |
| (6) | Acc_B | 98.88% | The ability to classify non-vascular regions |
| Methods | Acc | Sens | Spec | Datasets | A-V Crossing | Years | End to End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu et al. [44] | 92.30% | 90.00% | 90.00% | RITE | No | 2017 | No |
| Dashtbozorg et al. [25] | 87.40% | 73.00% | 84.00% | DRIVE | No | 2014 | No |
| Kang et al. [41] | 90.81% | 88.63% | 92.97% | RITE | No | 2020 | No |
| Huang et al. [45] | 72.00% | 70.90% | 73.80% | DRIVE | No | 2018 | No |
| Galdran et al. [32] | 89.00% | 89.00% | 90.00% | RITE | Yes | 2019 | Yes |
| Morano et al. [31] | 96.05% | 78.07% | 98.67% | RITE | No | 2021 | Yes |
| This work | 96.86% | 91.78% | 97.25% | RITE | Yes | 2023 | Yes |
| Methods | Vessel Classification | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | RS | ASPPM | AttM | Pre | Acc | Sens | Spec | Acc_U |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | 91.13% | 72.67% | 92.33% | 52.08% |
| Yes | Yes | No | No | No | 94.77% | 79.90% | 96.61% | 54.31% |
| Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 94.23% | 88.41% | 95.35% | 58.98% |
| Yes | No | No | Yes | No | 95.69% | 87.33% | 96.91% | 57.11% |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | 96.04% | 89.26% | 97.87% | 59.86% |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 96.86% | 91.78% | 97.25% | 61.23% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Shen, Z.; Sang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Hao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M. End-to-End Automatic Classification of Retinal Vessel Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Improved U-Net. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061148
Zhang J, Yang K, Shen Z, Sang S, Yuan Z, Hao R, Zhang Q, Cai M. End-to-End Automatic Classification of Retinal Vessel Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Improved U-Net. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(6):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061148
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jieni, Kun Yang, Zhufu Shen, Shengbo Sang, Zhongyun Yuan, Runfang Hao, Qi Zhang, and Meiling Cai. 2023. "End-to-End Automatic Classification of Retinal Vessel Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Improved U-Net" Diagnostics 13, no. 6: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061148
APA StyleZhang, J., Yang, K., Shen, Z., Sang, S., Yuan, Z., Hao, R., Zhang, Q., & Cai, M. (2023). End-to-End Automatic Classification of Retinal Vessel Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Improved U-Net. Diagnostics, 13(6), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061148







