Heterozygous Variants in FREM2 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Supernumerary Teeth, Oral Exostoses, and Odontomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Patients
2.3. Whole-Exome Sequencing, Mutation Analysis, and Bioinformatic Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. FREM2 Variants and Their Pathogenicities
4.2. FREM2 Variants, Probability of Being the Loss-of-Function Intolerant (pLI), and the Clinical Significance
4.3. The Absence of Rare Variants in Other Known Dental Anomaly-Related Genes
4.4. FREM2 Heterozygous Carriers with Phenotypes
4.5. FREM2, Tooth Development, and Supernumerary Tooth Formation
4.6. FREM2 Variants and Oral Exostoses
4.7. FREM2 Variant and Odontomas
4.8. Clinical Implication
4.9. Future Studies
5. Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anthonappa, R.P.; King, N.M.; Rabie, A.B. Aetiology of supernumerary teeth: A literature review. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2013, 14, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippi, R. Odontomas and supernumerary teeth: Is there a common origin? Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 1282–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajab, L.D.; Hamdan, M.A. Supernumerary teeth: Review of the literature and a survey of 152 cases. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2002, 12, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilpa, G.; Gokhale, N.; Mallineni, S.K.; Nuvvula, S. Prevalence of dental anomalies in deciduous dentition and its association with succedaneous dentition: A cross-sectional study of 4180 South Indian children. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2017, 35, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.J. Hypodontia and hyperdontia of permanent teeth in Hong Kong schoolchildren. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1987, 15, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Uehara, T.; Narita, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Nakabayashi, S.; Araki, M. Prevalence and distribution of anomalies of permanent dentition in 9584 Japanese high school students. Odontology 2016, 104, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.; Cai, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S. The epidemiology of supernumerary teeth and the associated molecular mechanism. Organogenesis 2017, 13, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niswander, J.D.; Sujaku, C. Congenital Anomalies of Teeth in Japanese Children. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1963, 21, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, W.Y.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Tsai, T.P. Clinical evaluation of the timing of mesiodens removal. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunotai, W.; Ananpornruedee, P.; Lubinsky, M.; Pruksametanan, A.; Kantaputra, P.N. Making extra teeth: Lessons from a TRPS1 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubinsky, M.; Kantaputra, P.N. Syndromes with supernumerary teeth. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantaputra, P.; Miletich, I.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Suzuki, E.Y.; Praphanphoj, V.; Shivdasani, R.; Wuelling, M.; Vortkamp, A.; Napierala, D.; Sharpe, P.T. Tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome with supernumerary teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Coury, S.A.; Tan, W.H. Impaired dentin mineralization, supernumerary teeth, hypoplastic mandibular condyles with long condylar necks, and a TRPS1 mutation. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 116, 104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Jotikasthira, D.; Carlson, B.; Wongmaneerung, T.; Quarto, N.; Khankasikum, T.; Powcharoen, W.; Intachai, W.; Tripuwabhrut, K. TRPS1 mutation associated with trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 with 15 supernumerary teeth, hypoplastic mandibular condyles with slender condylar necks and unique hair morphology. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Song, J.S.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, J.H. Genetic analysis of non-syndromic familial multiple supernumerary premolars. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Gan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. Identification of a novel missense mutation in non-syndromic familial multiple supernumerary teeth. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 143, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colak, H.; Uzgur, R.; Tan, E.; Hamidi, M.M.; Turkal, M.; Colak, T. Investigation of prevalence and characteristics of mesiodens in a non-syndromic 11256 dental outpatients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 2684–2689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazanci, F.; Celikoglu, M.; Miloglu, O.; Yildirim, H.; Ceylan, I. The frequency and characteristics of mesiodens in a Turkish patient population. Eur. J. Dent. 2011, 5, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, S. Mesiodens: A clinical and radiographic study in children. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2011, 29, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Fan, J. Molecular genetics of supernumerary tooth formation. Genesis 2011, 49, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantaputra, P.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Chintakanon, K.; Intachai, W.; Pradermdutsadeeporn, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Tongsima, S.; Ngamphiw, C.; Olsen, B.; Tucker, A.S.; et al. Mutations in LRP6 highlight the role of WNT signaling in oral exostoses and dental anomalies. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 142, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaputra, P.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Kottege, N.; Anthonappa, R.P.; Kaewgahya, M.; Tongsima, S.; Ngamphiw, C.; Cairns, J.R.K.; Predes, D.; He, X. DKK1 is a strong candidate for mesiodens and taurodontism. Clin. Genet. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.; Tripuwabhrut, K.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Hatsadaloi, A.; Porntrakoolsaree, N.; Kaewgaya, M.; Olsen, B.; Tongsima, S.; Ngamphiw, C.; et al. Mutations in the WLS are associated with dental anomalies, torus palatinus, and torus mandibularis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Guven, Y.; Tripuwabhrut, K.; Adisornkanj, P.; Hatsadaloi, A.; Kaewgahya, M.; Olsen, B.; Ngamphiw, C.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Tongsima, S.; et al. Mutations in LRP5 and BMP4 are associated with mesiodens, tooth agenesis, root malformation, and oral exostoses. Clin. Genet. 2022, 102, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Jatooratthawichot, P.; Adisornkanj, P.; Kitsadayurach, P.; Kaewgahya, M.; Olsen, B.; Ohazama, A.; Ngamphiw, C.; Tongsima, S.; Cox, T.C.; et al. Rare Variants in LRP4 are Associated with Mesiodens, Root Maldevelopment, and Oral Exostoses in Humans. Biology 2023, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyozumi, D.; Takeichi, M.; Nakano, I.; Sato, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Sekiguchi, K. Basement membrane assembly of the integrin α8β1 ligand nephronectin requires Fraser syndrome-associated proteins. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Wangtiraumnuay, N.; Ngamphiw, C.; Olsen, B.; Intachai, W.; Tucker, A.S.; Tongsima, S. Cryptophthalmos, dental anomalies, oral vestibule defect, and a novel FREM2 mutation. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 67, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, F.; Kayserili, H.; Midro, A.; de Silva, D.; Basnayake, S.; Güven, Y.; Borys, J.; Schanze, D.; Stellzig-Eisenhauer, A.; Bloch-Zupan, A.; et al. Characteristic dental pattern with hypodontia and short roots in Fraser syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2020, 182, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chu, E.Y.; Watt, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gallant, N.M.; Andl, T.; Yang, S.H.; Lu, M.M.; Piccolo, S.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling directs multiple stages of tooth morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2008, 313, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, Z.L.; Berg, J.J.; Mostafavi, H.; Sella, G.; Przeworski, M. Measuring intolerance to mutation in human genetics. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Hutsadaloi, A.; Kaewgahya, M.; Intachai, W.; German, R.; Koparal, M.; Leethanakul, C.; Tolun, A.; Cairns, J.R.K. WNT10B mutations associated with isolated dental anomalies. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Colin, E.; Goudenège, D.; Bonneau, D. A snapshot of some pLI score pitfalls. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, C.; Yoshizaki, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Saito, K.; Yamada, A.; Han, X.; Funada, K.; Fukumoto, E.; Haruyama, N.; Iwamoto, T.; et al. Nephronectin plays critical roles in Sox2 expression and proliferation in dental epithelial stem cells via EGF-like repeat domains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelberman, D.; de Castro, S.C.; Huang, S.; Crolla, J.A.; Palmer, R.; Gregory, J.W.; Taylor, D.; Cavallo, L.; Faienza, M.F.; Fischetto, R.; et al. SOX2 plays a critical role in the pituitary, forebrain, and eye during human embryonic development. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chacon-Camacho, O.F.; Fuerte-Flores, B.I.; Ricardez-Marcial, E.F.; Zenteno, J.C. SOX2 anophthalmia syndrome and dental anomalies. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2015, 167A, 2830–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakura, C.; Kitanaka, S.; Kato, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Hamamoto, Y.; Katsushima, Y.; Kimura, T.; Hayasaka, K. Supernumerary impacted teeth in a patient with SOX2 anophthalmia syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152A, 2355–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedano, H.O.; Gorlin, R.J. Familial occurrence of mesiodens. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1969, 27, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M.T.; Barry, H.J.; Blake, M. Supernumerary teeth—An overview of classification, diagnosis and management. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 1999, 65, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butera, A.; Maiorani, C.; Morandini, A.; Simonini, M.; Morittu, S.; Barbieri, S.; Bruni, A.; Sinesi, A.; Ricci, M.; Trombini, J.; et al. Assessment of Genetical, Pre, Peri and Post Natal Risk Factors of Deciduous Molar Hypomineralization (DMH), Hypomineralized Second Primary Molar (HSPM) and Molar Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH): A Narrative Review. Children 2021, 8, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

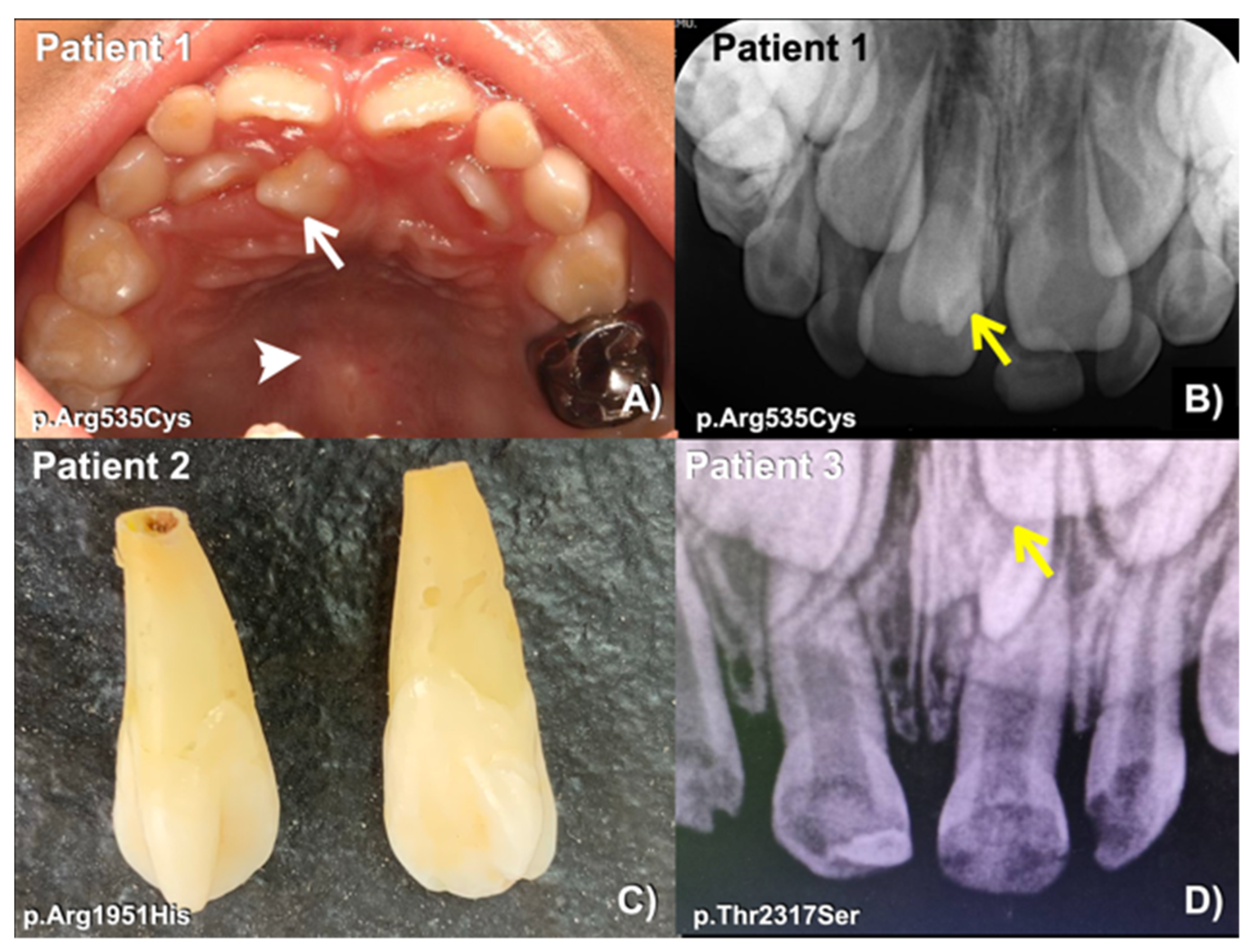
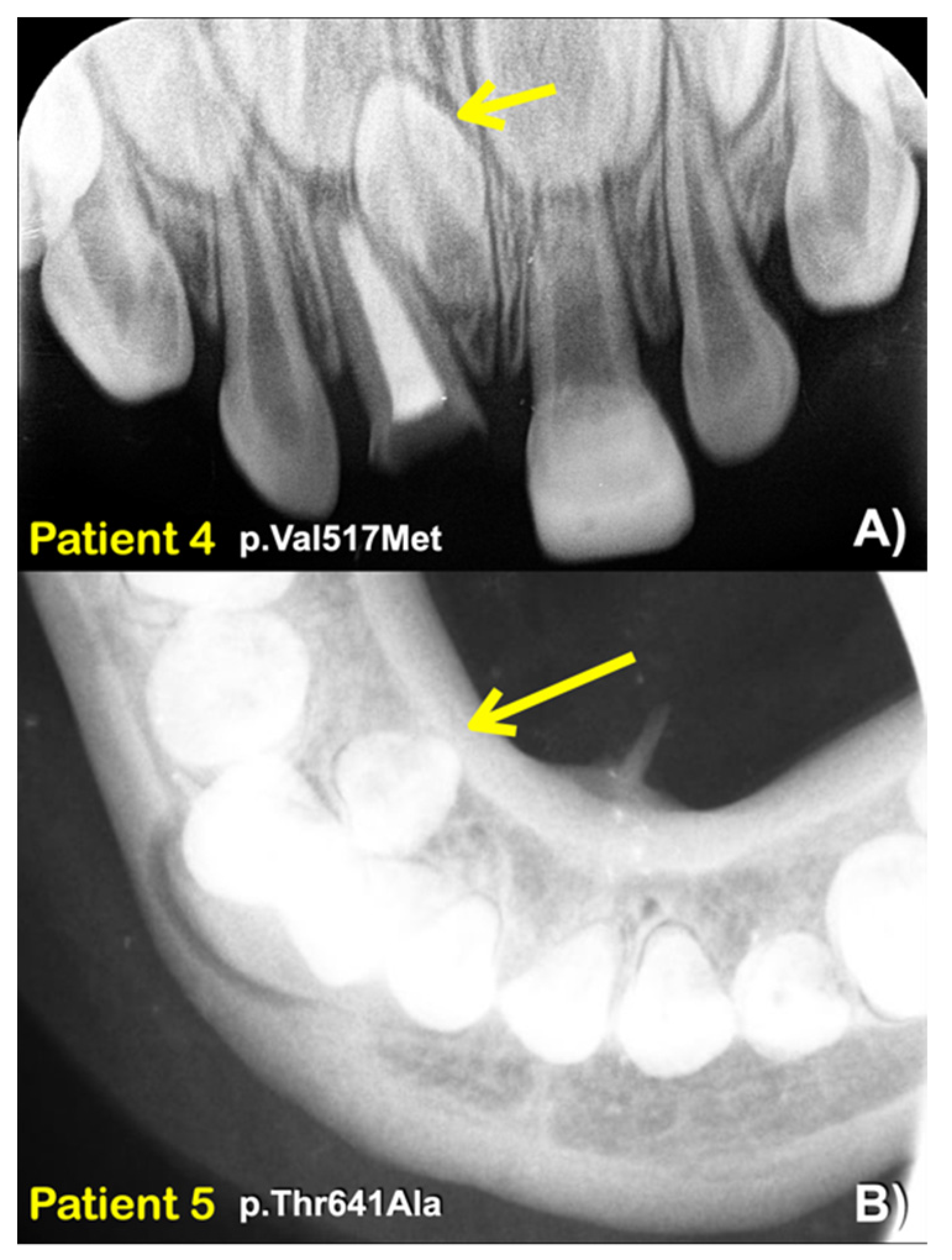

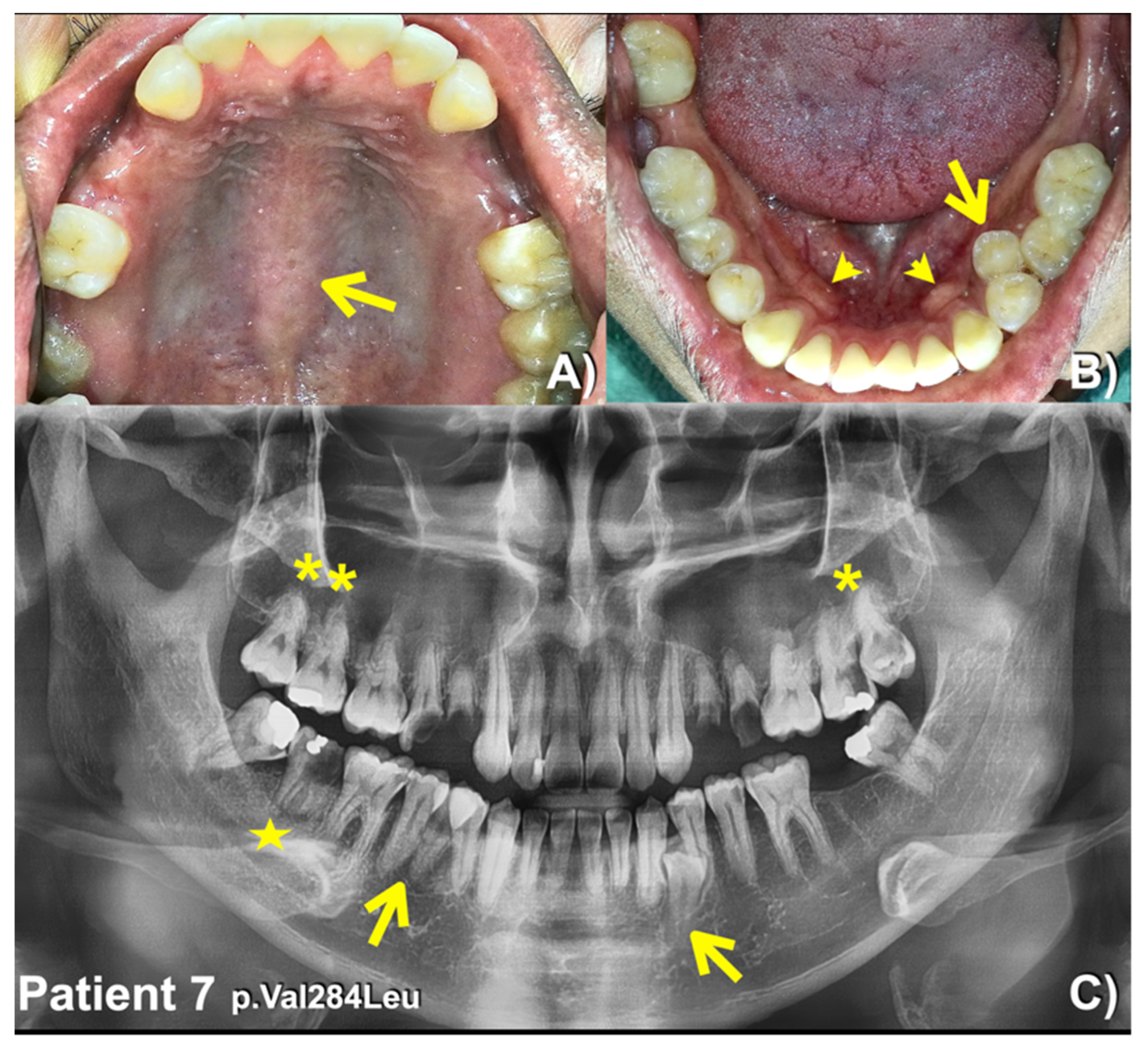


| Patients | Phenotypes | FREM2 Variant NM_207361.6; NP_997244.4 | Mutation Predictions/Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Female) | Mesiodens and torus palatinus | c.1603C>T; p.Arg535Cys rs201457616; chr13-39263084-C-T gnomAD Global = 0.0001712 gnomAD South Asian = 0.000 gnomAD East Asian = 0.002164; dbSNP T = 0.0039 In-house EXOME bank 4/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 4/2184 (T:0.0018315 or 0.18%) | MutationTaster: disease causing (0.99999999580175) PolyPhen-2: Possibly damaging (0.994) SIFT: Damaging (0.001) CADD: VUS (25.4) DANN: Uncertain (0.9992) |
| 2 (Male) | Mesiodens (double) | c.5852G>A; p.Arg1951His rs201806885; chr13-39358778-G-A gnomAD Global = 0.000003982 gnomAD South Asian = 0.000 gnomAD East Asian = 0.00005448 dbSNP A = 0.000 In-house EXOME bank 1/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 0% | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.99712280816916) PolyPhen-2: Possibly damaging (0.873) SIFT: TOLERATED (0.068) CADD: Moderate benign (19.18) DANN: Uncertain (0.9985) |
| 3 (Male) | Mesiodens (double; one unerupted and one inverted) | c.6949A>T; p.Thr2317Ser chr13-39430286-A-T Not reported in gnomAD and dbSNP In-house EXOME bank 3/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 1/2184 (T:0.00045788 or 0.04%) | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.999998598060573) PolyPhen-2: Benign (0.118) SIFT: Tolerated (0.285) CADD: VUS (22.4) DANN: Uncertain (0.9904) |
| 4 (Female) | Mesiodens (single unerupted inverted) | c.1549G>A; p.Val517Met rs566143955; chr13-39263030-G-A gnomAD Global = 0.00002012 gnomAD South Asian = 0.000 gnomAD East Asian = 0.0002730 dbSNP A = 0.000 In-house EXOME bank 1/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 0% | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.999999999751131) PolyPhen-2: Possibly damaging (1.000) SIFT: Damaging (0) CADD: Pathogenic (26.3) DANN: Uncertain (0.9991) |
| 5 (Female) | Two supernumerary mandibular premolars | c.1921A>G; p.Thr641Ala rs116802472; chr13-39263402-A-G gnomAD Global = 0.00002829 gnomAD South Asian = 0.000 gnomAD East Asian = 0.0003510; dbSNP G = 0.000; In-house EXOME bank 3/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 2/244 = 0.819672% Allele freq in T-Rex = 5/2184 (G:0.00228938 or 0.22%) | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.999961580268265) PolyPhen-2: POSSIBLY Damaging (0.474) SIFT: Damaging (0.008) CADD: Benign (22.1) DANN: Uncertain (0.9889) |
| 6 (Male) | Mesiodens, agenesis of 18 and 28, and taurodontism of 27 | ||
| 7 (Male) | Supernumerary mandibular premolars, unseparated roots of molars, torus palatinus, and torus mandibularis | c.850G>C; p.Val284Leu rs770004356; chr13-39262331-G-C gnomAD Global = 0.0002231 gnomAD South Asian = 0.000 gnomAD East Asian = 0.003158; dbSNP C = 0.000 In-house EXOME bank 3/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 4/2184 (G:0.0018315 or 0.18%) | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.999963783102466) PolyPhen-2: Benign (0.108) SIFT: Tolerated (0.17) CADD: VUS (23.8) DANN: Uncertain (0.9953) |
| 8 (Female) | Multiple supernumerary teeth and multiple odontomas | c.8498A>G; p.Asn2833Ser (NOVEL) chr13-39450473-A-G Not reported in gnomAD and dbSNP In-house EXOME bank 2/1016 Allele freq in extra tooth cohort 1/244 = 0.409836% Allele freq in T-Rex = 0% | MutationTaster: Disease causing (0.999943878525573) PolyPhen-2: Benign (0.002) SIFT: Tolerated (0.269) CADD: Moderate benign (17.14) DANN: Uncertain (0.9802) |
| Patients/ FREM2 Variants | Patient 1 p.Arg535Cys rs201457616 | Patient 2 p.Arg1951His rs201806885 | Patient 3 p.Thr2317Ser | Patient 4 p.Val517Met rs566143955 | Patient 5 p.Thr641Ala rs116802472 | Patient 6 p.Val284Leu rs770004356 | Patient 6 p.Asn2833Ser |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequencies in the study group (n = 122 persons or 244 alleles) | N = 1 (0.409836%) | N = 1 (0.409836%) | N = 1 (0.409836%) | N = 1 (0.409836%) | N = 2 (0.819672%) | N = 1 (0.409836%) | N = 1 (0.409836%) |
| Frequencies in normal Thai population (T-Rex) (n = 2184 alleles) | N = 4 (0.18315%) | 0% | 0% | 0% | N = 5 (0.228938%) | N = 4 (0.18315%) | 0% |
| Frequencies in global population gnomAD | 0.01712% | 0.0003982% | Not reported or 0% | 0.0002012% | 0.002829% | 0.02231% | Not reported or 0% |
| Frequencies in South Asian population gnomAD | 0% | 0% | Not reported or 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Not reported or 0% |
| Frequencies in East Asian population gnomAD | 0.2164% | 0.005448% | Not reported or 0% | 0% | 0.03510% | 0.3158% | Not reported or 0% |
| Tooth-Related Genes | Patient 1 3212 Mesiodens | Patient 2 095 Mesiodens (Double) | Patient 3 2952 Mesiodens (Double) | Patient 4 3346 Mesiodens | Patient 5 2775 Supernumerary Premolars | Patient 6 3036 Mesiodens and Tooth Agenesis, and Taurodontism | Patient 7 3099 Supernumerary Premolars, Oral tori, Root Maldevelopment | Patient 8 3262 Multiple Supernumerary Teeth and Multiple Odontomas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WNT10A | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| WNT10B | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| PAX9 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| AXIN2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| MSX1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | MSX1 Variant NM_002448.3:c.461C>T NP_002439.2:p.Pro154Leu rs545651715 chr4:g.4862087C>T MAF = 0.00003574 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| LRP4 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| LRP5 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| LRP6 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| WLS | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | WLS Variant NM_001002292.3:c.130A>T NP_001002292.3:p.Met44Leu chr1:g.68659881T>A rs368633951 MAF: 0.00003891 | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| DKK1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| BMP4 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| GREM2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| TFAP2B | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| TSPEAR | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| EDA | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| EDAR | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | |
| EDARADD | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| PITX2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| EVC | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| EVC2 | EVC2 Variant NM_001166136.2:c.33dup NP_001159608.1:p.Lys12Ter chr4:g.5699332dup No rs number Not reported in gnomAD | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| COL1A2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| ANTXR1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| FGF10 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| SMOC2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| KREMEN1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| KDF1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| ATF1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| DUSP10 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| CASC8 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| RUNX2 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| TRPS1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| C2CD3 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| NHS | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| MID1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| CREBBP | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| EP300 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| BCOR | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| WNT5A | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| DVL1 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| DVL3 | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| IL11RA | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found | Not found |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kantaputra, P.N.; Tripuwabhrut, K.; Anthonappa, R.P.; Chintakanon, K.; Ngamphiw, C.; Adisornkanj, P.; Porntrakulseree, N.; Olsen, B.; Intachai, W.; Hennekam, R.C.; et al. Heterozygous Variants in FREM2 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Supernumerary Teeth, Oral Exostoses, and Odontomas. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13071214
Kantaputra PN, Tripuwabhrut K, Anthonappa RP, Chintakanon K, Ngamphiw C, Adisornkanj P, Porntrakulseree N, Olsen B, Intachai W, Hennekam RC, et al. Heterozygous Variants in FREM2 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Supernumerary Teeth, Oral Exostoses, and Odontomas. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(7):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13071214
Chicago/Turabian StyleKantaputra, Piranit Nik, Kanich Tripuwabhrut, Robert P. Anthonappa, Kanoknart Chintakanon, Chumpol Ngamphiw, Ploy Adisornkanj, Nop Porntrakulseree, Bjorn Olsen, Worrachet Intachai, Raoul C. Hennekam, and et al. 2023. "Heterozygous Variants in FREM2 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Supernumerary Teeth, Oral Exostoses, and Odontomas" Diagnostics 13, no. 7: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13071214
APA StyleKantaputra, P. N., Tripuwabhrut, K., Anthonappa, R. P., Chintakanon, K., Ngamphiw, C., Adisornkanj, P., Porntrakulseree, N., Olsen, B., Intachai, W., Hennekam, R. C., Vieira, A. R., & Tongsima, S. (2023). Heterozygous Variants in FREM2 Are Associated with Mesiodens, Supernumerary Teeth, Oral Exostoses, and Odontomas. Diagnostics, 13(7), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13071214






