Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phantom Study
2.2. Intra-Observer Correlation Coefficient of Radiomic Features in Bosniak Lesions
2.3. Classification Capacity of the Selected Features for Bosniak Cyst Prediction
3. Results
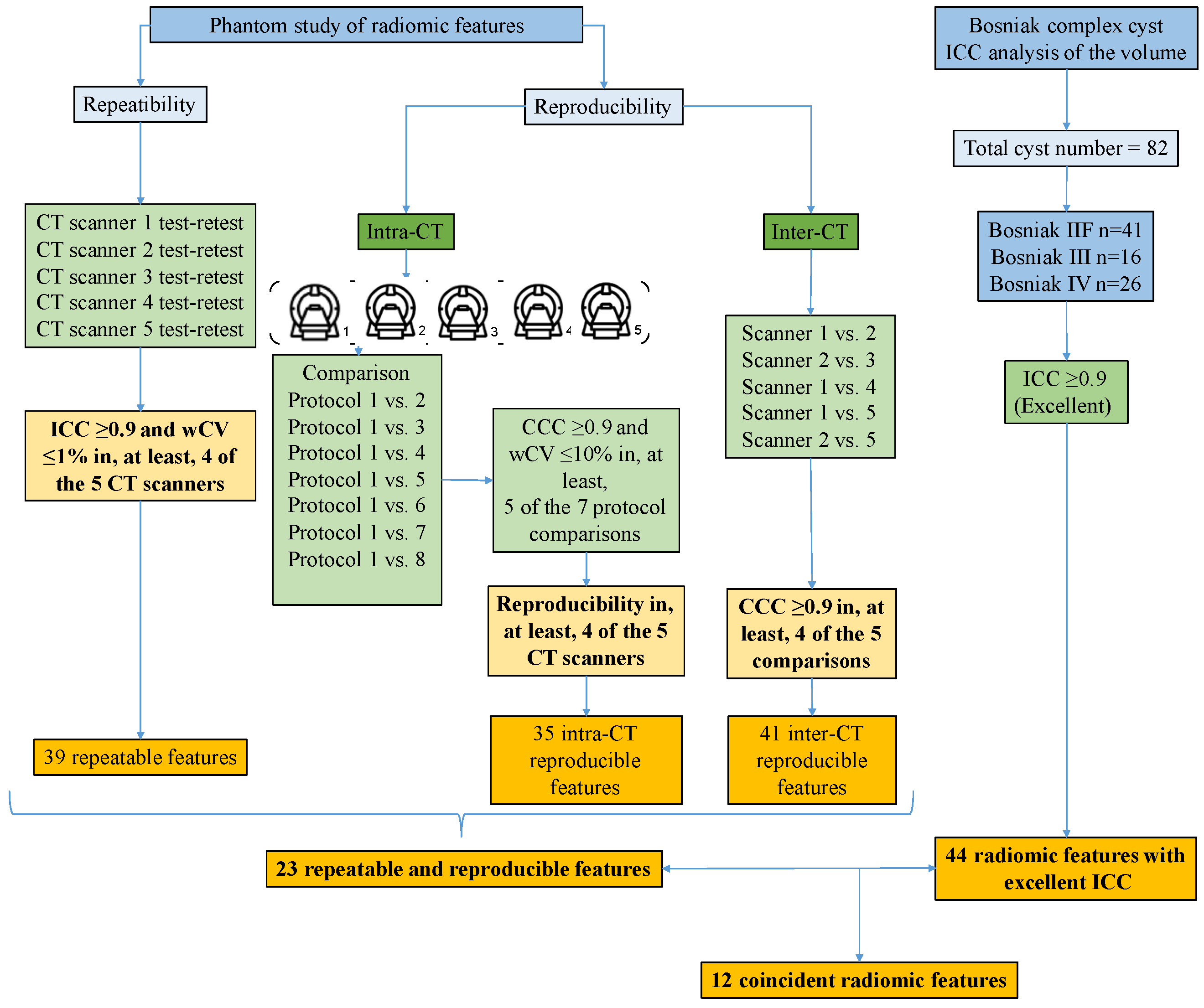
3.1. Phantom Study
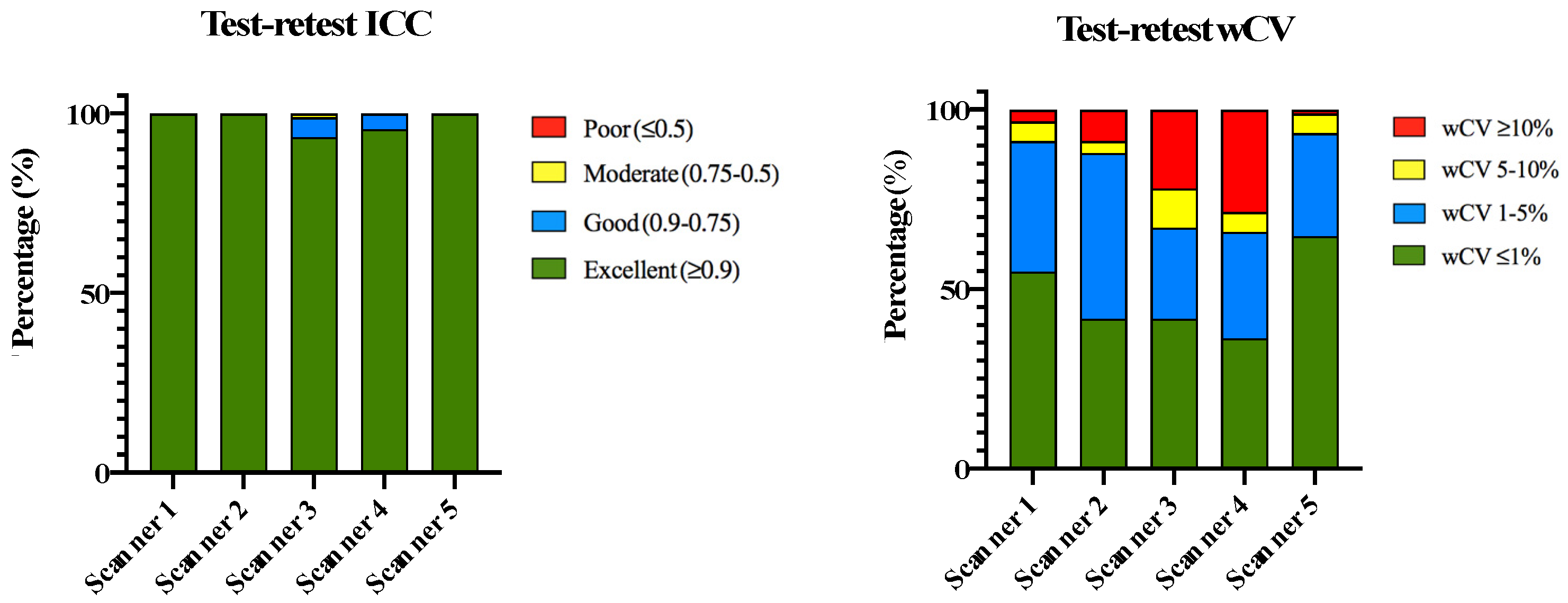
3.1.1. Phantom Repeatability
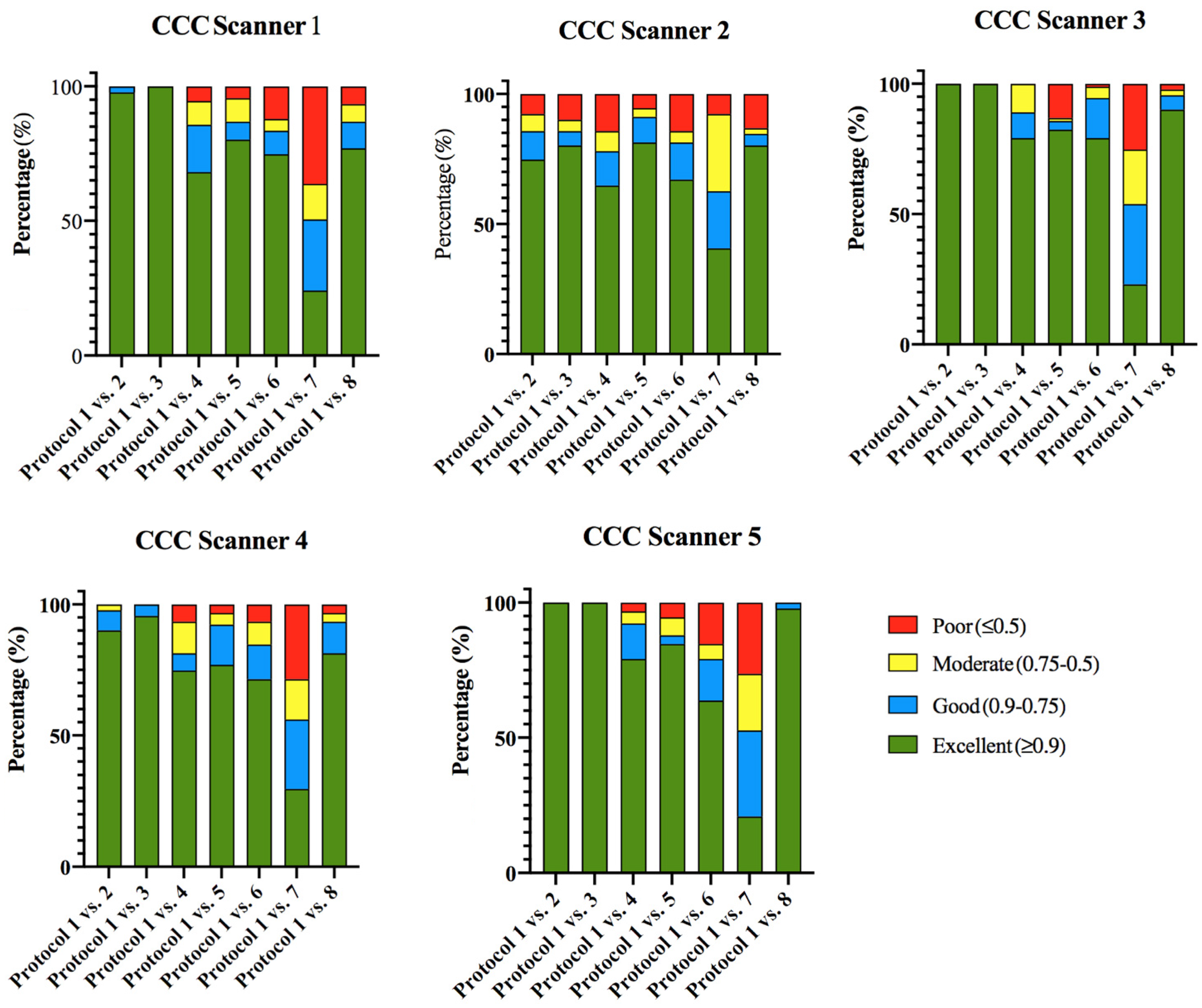
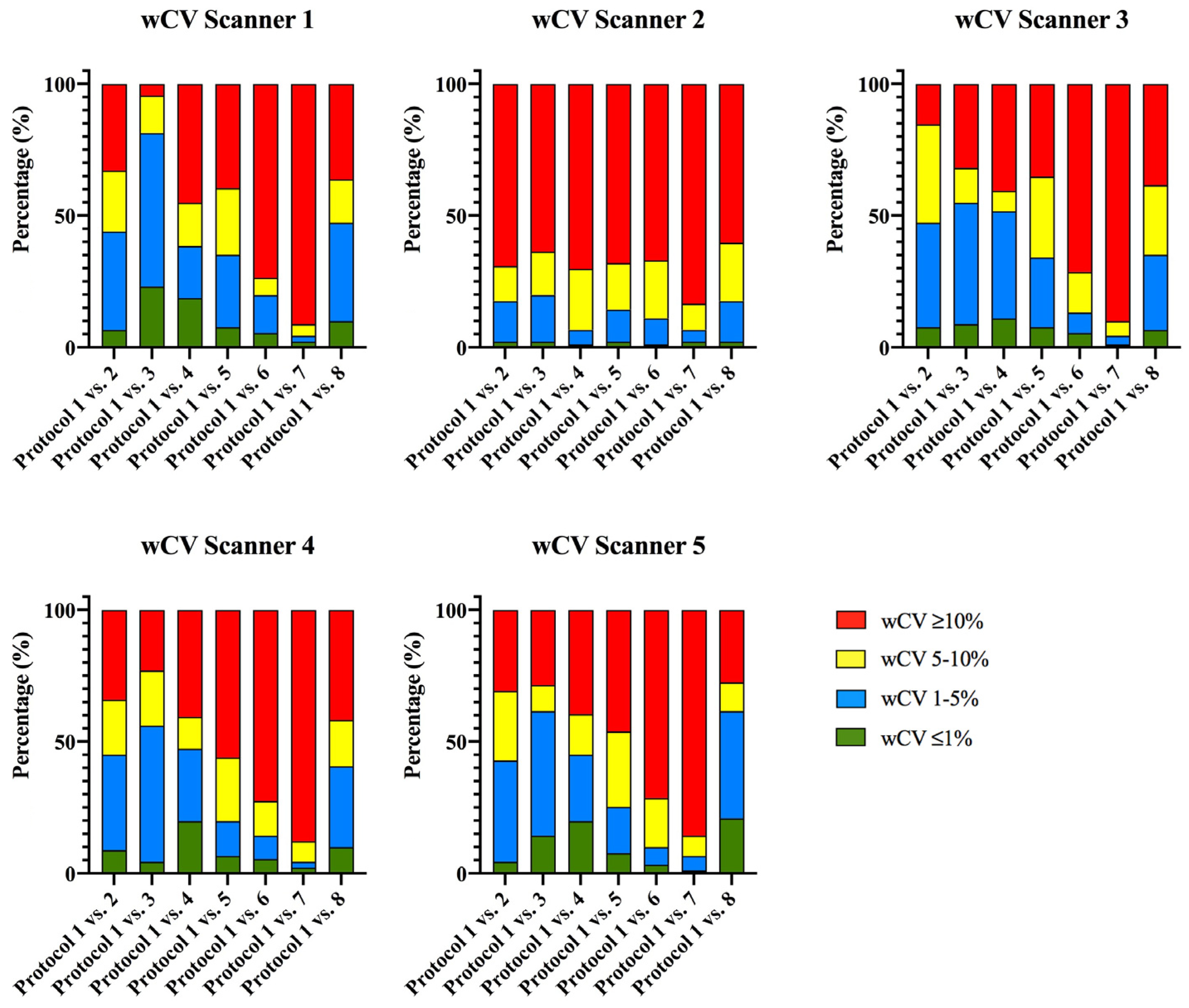
3.1.2. Phantom Intra-CT Reproducibility
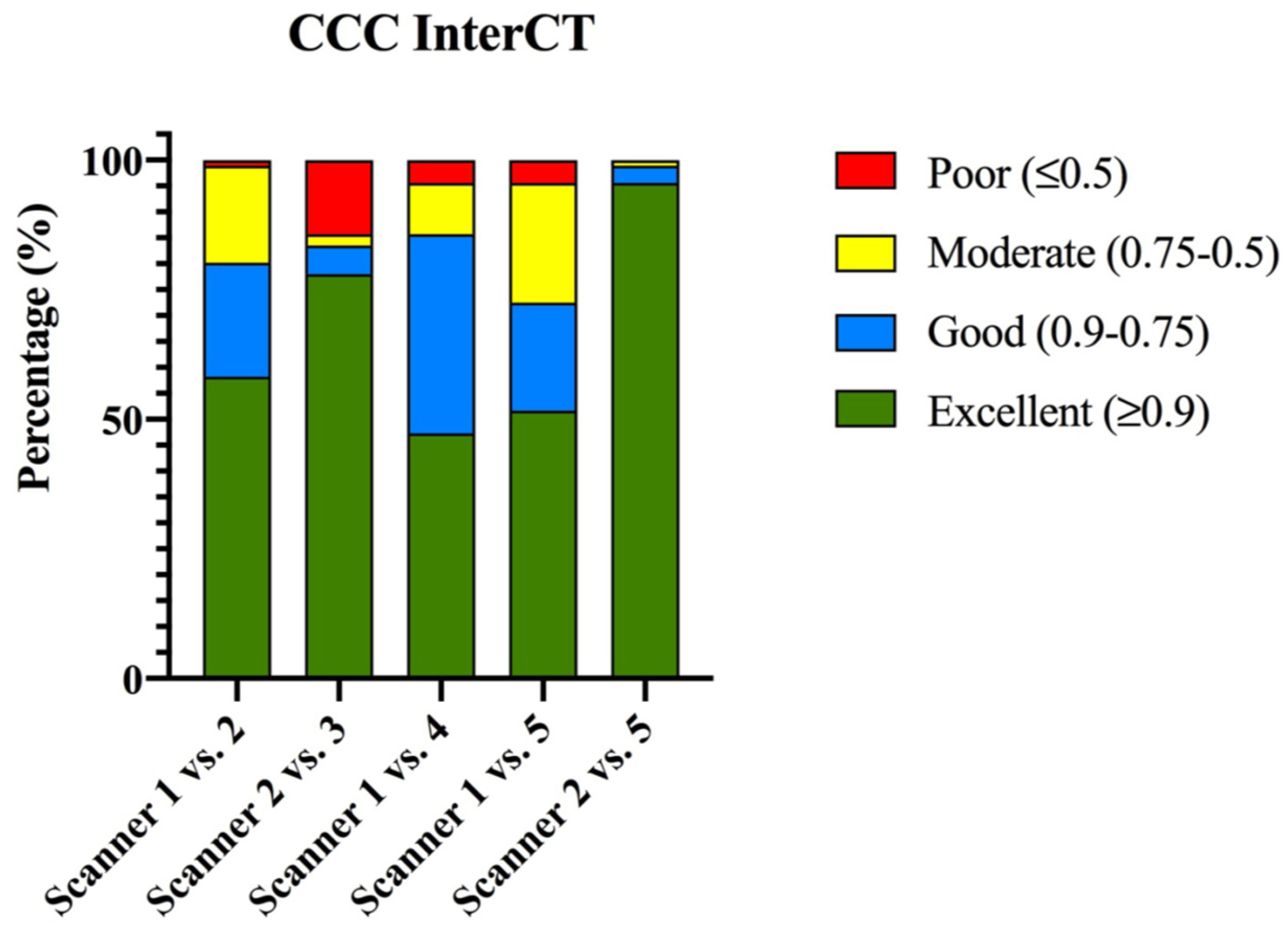
3.1.3. Phantom Inter-CT Reproducibility
3.2. Intra-Observer Correlation Coefficient of Radiomic Features in Bosniak Lesions
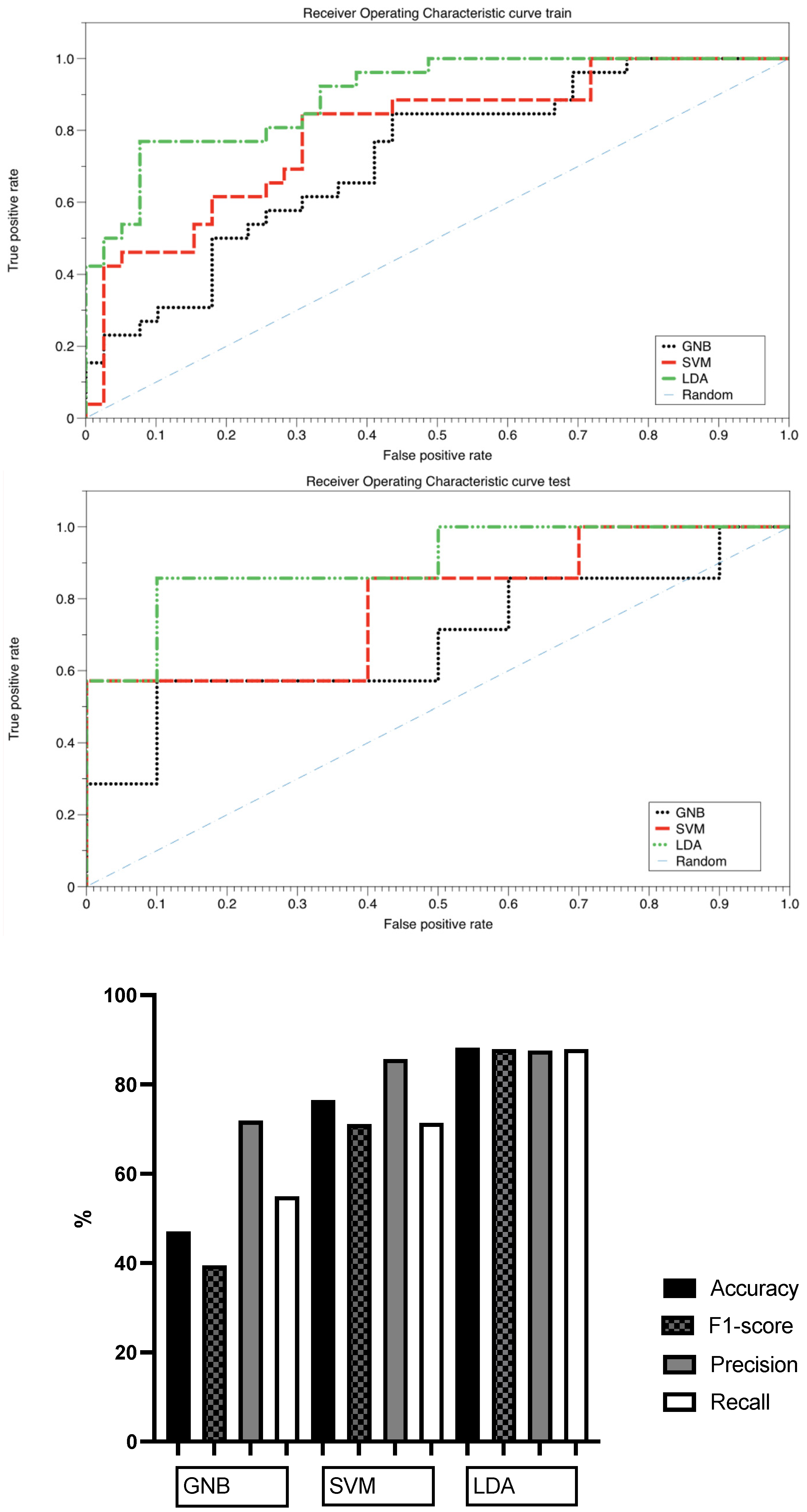
3.3. Classification Capacity of the Selected Features for Bosniak Cyst Prediction
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewski, M.R.; Gillies, R.J. The Biological Meaning of Radiomic Features. Radiology 2021, 298, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xing, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, J.; Pan, L.; Qiu, J.; Xing, W. CT-based radiomic model predicts high grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 103, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubner, M.G. Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence for Renal Mass Characterization. Radiol. Clin. 2020, 58, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Erdim, C.; Ates, E.; Kaya, O.K.; Kilickesmez, O. Radiomics of renal masses: Systematic review of reproduci-bility and validation strategies. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Scalera, J.; Khalid, M.; Touret, A.-S.; Bloch, B.N.; Li, B.; Qureshi, M.M.; Soto, J.A.; Anderson, S.W. Texture analysis as a radiomic marker for differentiating renal tumors. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosniak, M.A. The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology 1986, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosniak, M.A.; Rofsky, N.M. Problems in the detection and characterization of small renal masses. Radiology 1996, 198, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefik, E.; Bozkurt, I.H.; Adibelli, Z.H.; Aydin, M.E.; Celik, S.; Oguzdogan, G.Y.; Basmaci, I.; Gorgel, S.N.; Vardar, E.; Gunlusoy, B.; et al. The Histopathologic Correlation of Bosniak 3 Cyst Subclassification. Urology 2019, 129, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruthi, D.K.; Liu, Q.; Kirkpatrick, I.D.; Gelfond, J.; Drachenberg, D.E. Long-term surveillance of complex cystic renal masses and het-erogeneity of Bosniak 3 lesions. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, S.; Krishna, S.; Shanbhogue, A.P.; Flood, T.A.; Sadoughi, N.; Sathiadoss, P.; Schieda, N. Contemporary update on imaging of cystic renal masses with histo-pathological correlation and emphasis on patient management. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Schieda, N. Advances in Imaging of Cystic Renal Masses: Appraisal of Emerging Evidence from Bosniak Version 2019 to Use of Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Clin. Rad. 2022, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskin, N.; Qin, L.; Matalon, S.A.; Tirumani, S.H.; Alessandrino, F.; Silverman, S.G.; Shinagare, A.B. Stratification of cystic renal masses into benign and potentially malignant: Applying machine learning to the bosniak classification. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 46, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, J.; Lefebvre, T.L.; Savadjiev, P.; Bodard, S.; Gauvin, S.; Bhatnagar, S.R.; Forghani, R.; Hélénon, O.; Reinhold, C. Malignancy risk stratification of cystic renal lesions based on a contrast-enhanced CT-based machine learning model and a clinical decision algorithm. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 4116–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.H.; Tan, H.; Liao, F.T.; Zheng, Y.N.; Lv, F.J.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, M.Z. Stratification of malignant renal neoplasms from cystic renal lesions using deep learning and radiomics features based on a stacking ensemble CT machine learning algorithm. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1028577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.H.; Feng, J.J.; Lv, F.J.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, M.Z. Deep learning and radiomic feature-based blending ensemble classifier for malig-nancy risk prediction in cystic renal lesions. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursprung, S.; Beer, L.; Bruining, A.; Woitek, R.; Stewart, G.D.; Gallagher, F.A.; Sala, E. Radiomics of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in renal cell carcinoma—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Gillies, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 102, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azadikhah, A.; Varghese, B.A.; Lei, X.; Martin-King, C.; Cen, S.Y.; Duddalwar, V.A. Radiomics quality score in renal masses: A systematic assessment on current literature. Br. J. Rad. 2022, 95, 20211211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackin, D.; Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Fried, D.; Yang, J.; Taylor, B.; Rodriguez-Rivera, E.; Dodge, C.; Jones, A.K.; Court, L. Measuring CT scanner variability of radiomics features. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, R.; del Rosario Pastor-Juan, M.; Canales-Vazquez, J.; Castro-García, M.; Villas, M.V.; Masilla Legorburo, F.; Sabater, S. Radiomics of CT Features May Be Nonreproducible and Redundant: Influence of CT Acquisition Parameters. Radiology 2018, 288, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Reeves, A.P.; Huang, E.P.; Huang, E.P.; Wang, X.-F.; Buckler, A.; Kim, H.J.; Barnhart, H.X.; Jackson, E.; Giger, M.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers: A review of statistical methods for computer algorithm comparisons. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2015, 24, 68–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terada, N.; Arai, Y.; Kinukawa, N.; Yoshimura, K.; Terai, A. Risk factors for renal cysts. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, L.; Santinha, J.; Loução, N.; Figueiredo, M.; Botta, F.; Origgi, D.; Cremonesi, M.; Cassano, E.; Papanikolaou, N.; Lascialfari, A. A multicenter study on radiomic features from T2-weighted images of a customized MR pelvic phantom setting the basis for robust radiomic models in clinics. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 85, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornacon-Wood, I.; Mistry, H.; Ackermann, C.J.; Blackhall, F.; McPartlin, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Price, G.; O’Connor, J.P.B. Reliability and prognostic value of radiomic features are highly dependent on choice of feature extraction platform. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6241–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, L.D.; Abel, E.J.; Nystrom, J.; Stabo, N.J.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Lubner, M.G. Comparison of CT Texture Analysis Software Plat-forms in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Reproducibility of Numerical Values and Association With Histologic Subtype Across Platforms. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midya, A.; Chakraborty, J.; Gönen, M.; Do, R.K.; Simpson, A.L. Influence of CT acquisition and reconstruction parameters on radiomic feature reproducibility. J. Med. Imaging 2020, 5, 011020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B. Understanding Sources of Variation to Improve the Reproducibility of Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larue, R.T.; van Timmeren, J.E.; de Jong, E.E.; Feliciani, G.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Schreurs, W.M.J.; Sosef, M.N.; Raat, F.H.P.J.; Van Der Zande, F.H.R.; Das, M.; et al. Influence of gray level discretization on radiomic feature stability for different CT scanners, tube currents and slice thicknesses: A comprehensive phantom study. Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-Ul-Hassan, M.; Zhang, G.G.; Latifi, K.; Ullah, G.; Hunt, D.C.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Abdalah, M.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Goldgof, D.G.; Mackin, D.; et al. Intrinsic dependencies of CT radiomic features on voxel size and number of gray levels. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ligero, M.; Jordi-Ollero, O.; Bernatowicz, K.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.; Delgado-Muñoz, E.; Leiva, D.; Mast, R.; Suarez, C.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Calvo, N.; et al. Minimizing acquisition-related radiomics variability by image resampling and batch effect correction to allow for large-scale data analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, J.J.; Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Grekoski, V.; Tran, T.; Guruvadoo, K.; Iii, S.G.A.; Sensakovic, W.F. Harmonization of radiomic feature variability resulting from differences in CT image acquisition and reconstruction: Assessment in a cadaveric liver. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 205008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalendralis, P.; Traverso, A.; Shi, Z.; Zhovannik, I.; Monshouwer, R.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Klein, S.; Pfaehler, E.; Boellaard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Multicenter CT phantoms public dataset for radiomics reproducibility tests. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, S.G.; Pedrosa, I.; Ellis, J.H.; Hindman, N.M.; Schieda, N.; Smith, A.D.; Remer, E.M.; Shinagare, A.B.; Curci, N.E.; Raman, S.S.; et al. Bosniak Classification of Cystic Renal Masses, Version 2019: An Update Proposal and Needs Assessment. Radiology 2019, 292, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avanzo, M.; Wei, L.; Stancanello, J.; Vallières, M.; Rao, A.; Morin, O.; Mattonen, S.A.; El Naqa, I. Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, e185–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, A.M.; Tong, A.; Davenport, M.S.; Khalaf, A.M.; Mresh, R.; Rusinek, H.; Schieda, N.; Shinagare, A.B.; Smith, A.D.; Thornhill, R.; et al. Assessment of Renal Cell Carcinoma by Texture Analysis in Clinical Practice: A Six-Site, Six-Platform Analysis of Reliability. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Desrosiers, C.; Toews, M.; Abdulkarim, B. Predicting survival time of lung cancer patients using radiomic analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 104393–104407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ehmke, R.C.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zhao, B. Assessing Agreement between Radiomic Features Computed for Multiple CT Imaging Settings. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2021, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, L.; Costaridou, L.; Bidaut, L.; Michoux, N.; Lecouvet, F.E.; de Geus-Oei, L.-F.; Boellaard, R.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Caroli, A.; et al. Incorporating radiomics into clinical trials: Expert consensus on considerations for data-driven compared to biologically driven quantitative biomarkers. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6001–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| CT Scanner 1: Siemens Somaton X.cite | |||||
| Tube Voltage (kVp) | Tube Current (mA) | Slice Thickness (mm) | Field of View (mm) | Reconstruction Algorithm | |
| Protocol 1 | 120 | 60 | 1 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 2 | 100 | 90 | 1 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 3 | 140 | 40 | 1 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 4 | 120 | 430 | 1 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 5 | 120 | 60 | 0.5 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 6 | 120 | 60 | 2 | 600 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 7 | 120 | 60 | 1 | 250 | ADMIRE 3 |
| Protocol 8 | 120 | 60 | 1 | 600 | FBP |
| CT Scanner 2: GE LightSpeed VCT-1 | |||||
| Protocol 1 | 120 | 60 | 1.25 | 500 | ASIR 30% |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| CT Scanner 3: GE LightSpeed VCT-2 | |||||
| Protocol 1 | 120 | 60 | 1.25 | 500 | ASIR 30% |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| CT Scanner 4: Siemens Somaton Drive | |||||
| Protocol 1 | 120 | 60 | 1 | 500 | ADMIRE 3 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| CT Scanner 5: Philips Ingenuity | |||||
| Protocol 1 | 120 | 60 | 1 | 500 | iDose 4 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Benign Cysts (n = 49) | Malignant Cysts (n = 33) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Women (n = 28) | 16 (32.7%) | 12 (36.4%) | 0.728 |
| Men (n = 51) | 33 (67.3%) | 21 (63.6%) | ||
| Mean age (years) | 67.39 ± 13.47 | 67.33 ± 11.39 | 0.985 | |
| Cyst location | Left kidney (n = 45) | 26 (53.1%) | 19 (57.6%) | 0.687 |
| Right kidney (n = 37) | 23 (46.9%) | 14 (42.4%) | ||
| Maximum diameter (mm) | 33 (12–235) | 40 (5–76) | 0.653 | |
| Anatomopathological result | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (n = 20) | |||
| Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (n = 5) | ||||
| Papillary type I (n = 3) | ||||
| Papillary type II (n = 3) | ||||
| Multilocular cyst renal neoplasm of low malignant potential (n = 2) | ||||
| Test–Retest Repeatability Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | Scanner 1 | Scanner 2 | Scanner 3 | Scanner 4 | Scanner 5 |
| Excellent (≥0.9) | 100% (91/91) | 100% (91/91) | 93.4% (85/91) | 95.6% (87/91) | 100% (91/91) |
| Good (0.9–0.75) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) | 5.5% (5/91) | 4.4% (4/91) | 0% (0/91) |
| Moderate (0.75–0.5) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) | 1.1% (1/91) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) |
| Poor (≤0.5) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) | 0% (0/91) |
| wCV | Scanner 1 | Scanner 2 | Scanner 3 | Scanner 4 | Scanner 5 |
| ≤1% | 54.9% (50/91) | 41.8% (38/91) | 41.8% (38/91) | 36.2% (33/91) | 64.8% (59/91) |
| 1–5% | 36.3% (33/91) | 46.1% (42/91) | 25.3% (23/91) | 29.7% (27/91) | 28.6% (26/91) |
| 5–10% | 5.5% (5/91) | 3.3% (3/91) | 10.9% (10/91) | 5.5% (5/91) | 5.5% (5/91) |
| ≤10% | 3.3% (3/91) | 8.8% (8/91) | 22% (20/91) | 28.6% (26/91) | 1.1% (1/91) |
| Intra-CT Reproducibility Analysis | |||||
| Scanner 1 | Scanner 2 | Scanner 3 | Scanner 4 | Scanner 5 | |
| CCC ≥ 0.9 and wCV ≤ 10% in, at least, 5 of the 7 protocol comparisons | 48.4% (44/91) | 26.4% (24/91) | 46.2% (42/91) | 42.9% (39/91) | 44% (40/91) |
| Inter-CT Reproducibility Analysis | |||||
| CCC | Scanner 1 vs. 2 | Scanner 2 vs. 3 | Scanner 1 vs. 4 | Scanner 1 vs. 5 | Scanner 2 vs. 5 |
| Excellent (≥0.9) | 58.2% (58/91) | 78.1% (71/91) | 47.2% (43/91) | 51.6% (47/91) | 95.6% (87/91) |
| Good (0.9–0.75) | 22% (20/91) | 5.5% (5/91) | 38.5% (35/91) | 20.9% (19/91) | 3.3% (3/91) |
| Moderate (0.75–0.5) | 18.7% (17/91) | 2.2% (2/91) | 9.9% (9/91) | 23.1% (21/91) | 1.1% (1/91) |
| Poor (≤0.5) | 1.1% (1/91) | 14.2% (13/91) | 4.4% (4/91) | 4.4% (4/91) | 0% (0/91) |
| Repeatable and Reproducible Features from the Phantom Study | Features with ICC ≥ 0.9 from Bosniak Cyst Studies | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First order | 10th percentile 90th percentile Energy Entropy Mean absolute deviation Mean Median Root mean square Total energy | First order | 10th percentile (ICC = 0.95) |
| 90th percentile (ICC = 0.97) | |||
| Interquartile range (ICC = 0.92) | |||
| Kurtosis (ICC = 0.92) | |||
| Mean (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Median (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Robust mean absolute deviation (ICC = 0.91) | |||
| Root mean square (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Uniformity (ICC = 0.90) | |||
| Major axis length (ICC = 0.92) | |||
| Minor axis length (ICC = 0.97) | |||
| Least axis length (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Maximum 2D diameter (x-z plane) (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Maximum 2D diameter (y-z plane) (ICC = 0.90) | |||
| Maximum 3D diameter (ICC = 0.91) | |||
| Area (ICC = 092) | |||
| Voxel volume (ICC = 0.99) | |||
| GLCM | Difference average Difference entropy Joint entropy Inverse difference moment normalized Inverse difference Inverse difference normalized Sum entropy | GLCM | Contrast (ICC = 0.94) |
| Cluster prominence (ICC = 0.93) | |||
| Cluster tendency (ICC = 0.91) | |||
| Correlation (ICC = 0.90) | |||
| Joint energy (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| Imc1 (ICC = 0.92) | |||
| Imc1 (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| Maximum probability (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Sum squares (ICC = 0.91) | |||
| Difference average (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| Difference entropy (ICC = 0.93) | |||
| Joint entropy (ICC = 0.90) | |||
| Inverse difference moment (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| Inverse difference (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| Inverse variance (ICC = 0.94) | |||
| GLRLM | Run entropy Run length non uniformity Run length non uniformity normalized Run percentage Short run emphasis | GLRLM | Gray-level non-uniformity (ICC = 0.99) |
| Long-run emphasis (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Run length non-uniformity (ICC = 0.99) | |||
| Run length non-uniformity normalized (ICC = 0.90) | |||
| Run variance (ICC = 0.96) | |||
| Short-run emphasis (ICC = 0.91) | |||
| GLSZM | Zone entropy | GLSZM | Large area low gray-level emphasis (ICC = 0.95) Zone variance (ICC = 0.98) |
| GLDM | Dependence entropy | GLDM | Dependence non-uniformity (ICC = 0.99) Dependence variance (ICC = 0.96) Gray-level non-uniformity (ICC = 0.99) Large dependence emphasis (ICC = 0.94) |
| Model | Accuracy | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian Naïve Bayes (GNB) | 0.471 | 0.395 | 0.719 | 0.550 | 0.69 |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 0.765 | 0.717 | 0.857 | 0.714 | 0.79 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) | 0.882 | 0.879 | 0.876 | 0.879 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aymerich, M.; Riveira-Martín, M.; García-Baizán, A.; González-Pena, M.; Sebastià, C.; López-Medina, A.; Mesa-Álvarez, A.; Tardágila de la Fuente, G.; Méndez-Castrillón, M.; Berbel-Rodríguez, A.; et al. Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081384
Aymerich M, Riveira-Martín M, García-Baizán A, González-Pena M, Sebastià C, López-Medina A, Mesa-Álvarez A, Tardágila de la Fuente G, Méndez-Castrillón M, Berbel-Rodríguez A, et al. Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(8):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081384
Chicago/Turabian StyleAymerich, María, Mercedes Riveira-Martín, Alejandra García-Baizán, Mariña González-Pena, Carmen Sebastià, Antonio López-Medina, Alicia Mesa-Álvarez, Gonzalo Tardágila de la Fuente, Marta Méndez-Castrillón, Andrea Berbel-Rodríguez, and et al. 2023. "Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection" Diagnostics 13, no. 8: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081384
APA StyleAymerich, M., Riveira-Martín, M., García-Baizán, A., González-Pena, M., Sebastià, C., López-Medina, A., Mesa-Álvarez, A., Tardágila de la Fuente, G., Méndez-Castrillón, M., Berbel-Rodríguez, A., Matos-Ugas, A. C., Berenguer, R., Sabater, S., & Otero-García, M. (2023). Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection. Diagnostics, 13(8), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081384






