Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management
Abstract
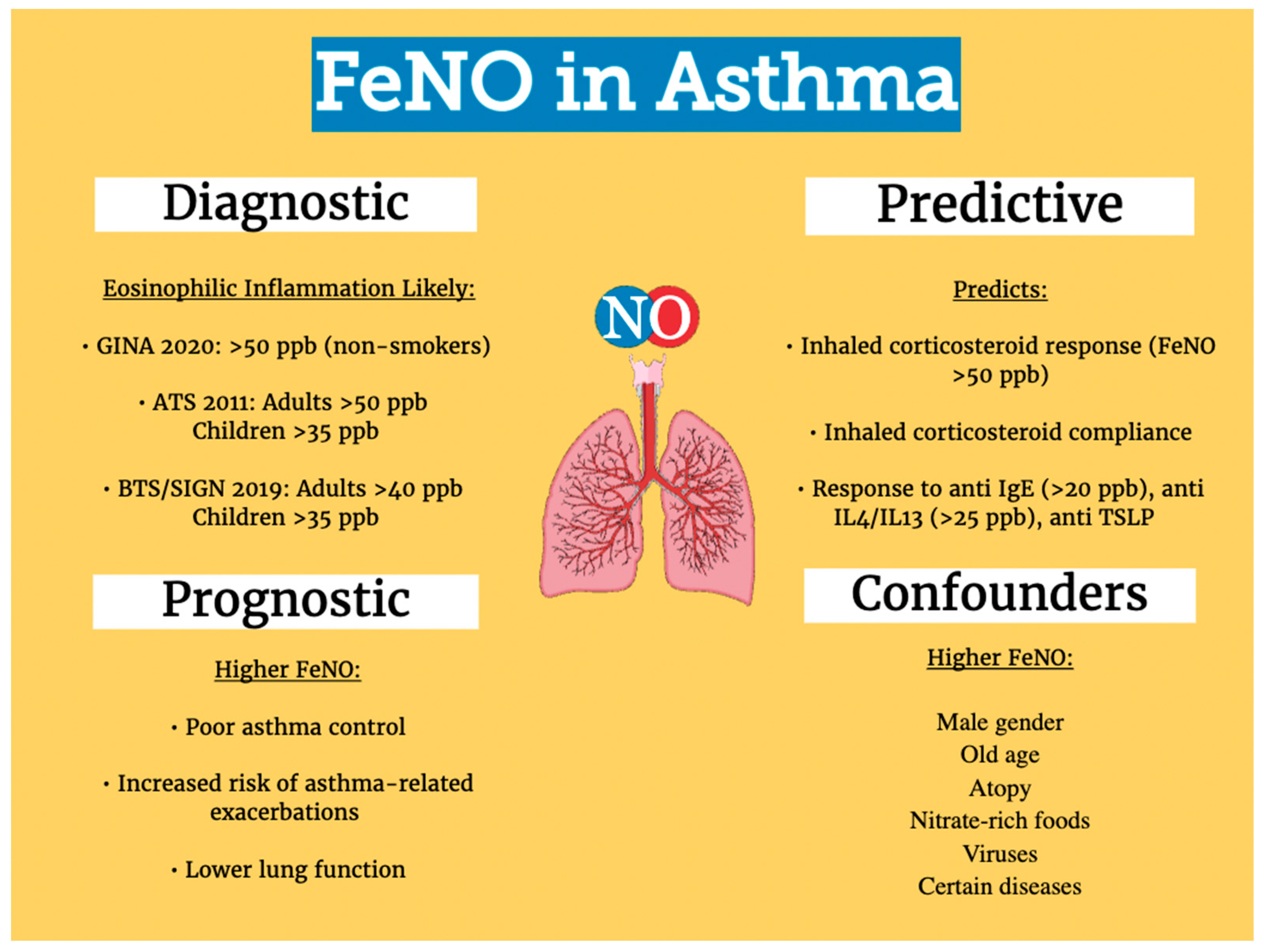
:1. Introduction
2. Role of Nitric Oxide in Type 2 Inflammation
3. FeNO as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Asthma
4. FeNO as a Biomarker of Predicting Asthma Control, Exacerbation and Lung Function Decline
5. FeNO as a Biomarker to Guide Inhaled Corticosteroids Therapy
6. FeNO as a Predictive and Pharmacodynamic Biomarker in Targeted Biologic Therapy
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soriano, J.B.; Alemu Abajobir, A.; Hassen Abate, K.; GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilemann, L.; Gindner, L.; Meyer, F.J.; Laux, G.; Szecsenyi, J.; Schneider, A. Diagnostic value of peak flow variability in patients with suspected diagnosis of bronchial asthma in general practice. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2009, 134, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Mansur, A.H.; Brightling, C.E. Clinical utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in severe asthma management. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, A.H.; De Nijs, S.B.; Lutter, R.; Sousa, A.R.; Weersink, E.J.M.; Bel, E.H.; Sterk, P.J. External validation of blood eosinophils, FE(NO) and serum periostin as surrogates for sputum eosinophils in asthma. Thorax 2015, 70, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schleich, F.N.; Manise, M.; Sele, J.; Henket, M.; Seidel, L.; Louis, R. Distribution of sputum cellular phenotype in a large asthma cohort: Predicting factors for eosinophilic vs neutrophilic inflammation. BMC Pulm. Med. 2013, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, M.A.; Shaw, D.E.; Green, R.H.; Brightling, C.E.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Pavord, I.D. The use of exhaled nitric oxide concentration to identify eosinophilic airway inflammation: An observational study in adults with asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Armstrong, S.; Efthimiadis, A.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Hargreave, F.E. Nitric oxide in exhaled breath is poorly correlated to sputum eosinophils in patients with prednisone-dependent asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevorgyan, A.; Fokkens, W.J. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) measurement in asthma and rhinitis. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2013, 22, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dweik, R.A.; Boggs, P.B.; Erzurum, S.C.; Irvin, C.G.; Leigh, M.W.; Lundberg, J.O.; Olin, A.; Plummer, A.L.; Taylor, D.R. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: Interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FeNO) for clinical applications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Sorbello, V.; Ciprandi, G. A pathophysiological approach for FeNO: A biomarker for asthma. Allergol. Immunopathol. (Madr.) 2015, 43, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffler, E.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Favero, E.; Guida, G.; Maniscalco, M.; Motta, A.; Paoletti, G.; Rolla, G.; Baraldi, E.; Pezzella, V.; et al. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) in the management of asthma: A position paper of the Italian Respiratory Society (SIP/IRS) and Italian Society of Allery, Asthma and Clinical Immunology (SIAAIC). Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2020, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maarsingh, H.; Zaagsma, J.; Meurs, H. Arginase: A key enzyme in the pathophysiology of allergic asthma opening novel therapeutic perspectives. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosova, M.; Mokra, D.; Pepucha, L.; Plevkova, J.; Buday, T.; Sterusky, M.; Bencova, A. Physiology of nitric oxide in the respiratory system. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Gil, J.M.; Fernandez-Nieto, M.; Acevedo, N. Understanding the Cellular Sources of the Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) and Its Role as a Biomarker of Type 2 Inflammation in Asthma. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5753524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, E.D.; Hurd, S.S.; Barnes, P.J.; Bousquet, J.; Drazen, J.M.; FitzGerald, M.; Gibson, P.; Ohta, K.; O’Byrne, P.; Pedersen, S.E.; et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 143–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Methacholine and Exercise Challenge Testing—1999: This official statement of the American Thoracic Society was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 309–329. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulrik, C.S.; Lange, P.; Hilberg, O. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide as a determinant for the clinical course of asthma: A systematic review. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 8, 1891725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.; Knight, D.; Burgess, S.; Franklin, P.; Horak, F.; Legg, J.; Moeller, A.; Stick, S. Epithelial inducible nitric oxide synthase activity is the major determinant of nitric oxide concentration in exhaled breath. Thorax 2004, 59, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karrasch, S.; Linde, K.; Rücker, G.; Sommer, H.; Karsch-Völk, M.; Kleijnen, J.; Jörres, R.A.; Schneider, A. Accuracy of FE NO for diagnosing asthma: A systematic review. Thorax 2017, 72, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, G.; Schleich, F.; Guillaume, M.; Kirkove, D.; Zahrei, H.N.; Donneau, A.F.; Henket, M.; Paulus, V.; Guissard, F.; Louis, R.; et al. Development and validation of a predictive model combining patient-reported outcome measures, spirometry and exhaled nitric oxide fraction for asthma diagnosis. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00451-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, I.A.; Bocsan, I.C.; Vesa, S.; Miron, N.; Nedelea, I.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Deleanu, D. Could FeNO Predict Asthma in Patients with House Dust Mites Allergic Rhinitis? Medicina (Kaunas) 2020, 56, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnenburg, M.W. The Role of FeNO in Predicting Asthma. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, R.L.M.; Rabahi, M.F.; Oliveira-e-Sá, T.S.; Magalhães-da-Silveira, F.J.; Mello, F.C.Q.; Gozal, D. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements and Screening of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in a Sleep-Laboratory Setting: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lung 2019, 197, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Gonio, F.; Kelly, C.; Meah, S.; Barnes, P.J. Reproducibility of exhaled nitric oxide measurements in healthy and asthmatic adults and children. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Expert Panel Working Group of the National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute (NHLBI) administered and coordinated National Asthma Education Prevention Program Coordinating Committee (NAEPPCC); Cloutier, M.M.; Baptist, A.P.; Blake, K.V.; Brooks, E.G.; Bryant-Stephens, T.; DiMango, E.; Dixon, A.E.; Elward, K.S.; Hartert, T.; et al. 2020 focused updates to the asthma management guidelines: A report from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1217–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, R.; Satia, I.; Ojanguren, I.; Schleich, F.; Bonini, M.; Tonia, T.; Rigau, D.; Ten Brinke, A.; Buhl, R.; Loukides, S.; et al. European Respiratory Society Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Asthma in Adults. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 210158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2020. International Guideline. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/gina-2020-full-report_-final-_wms/ (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Pignatti, P.; Visca, D.; Loukides, S.; Märtson, A.G.; Alffenaar, J.W.C.; Migliori, G.B.; Spanevello, A. A snapshot of exhaled nitric oxide and asthma characteristics: Experience from high to low income countries. Pulmonology 2022, 28, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, S.; Takahashi, K.; Ng Kee Kwong, F.; Xie, J.; Hoda, U.; Sun, K.; Elyasigomari, V.; Agapow, P.; Loza, M.; Baribaud, F.; et al. “T2-high” in severe asthma related to blood eosinophil, exhaled nitric oxide and serum periostin. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, A.; Hirano, T.; Yamaji, Y.; Ito, K.; Oishi, K.; Edakuni, N.; Kawano, R.; Matsunaga, K. Determinants of Incomplete Asthma Control in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, C.; Idzko, M.; Škrgat, S.; Koch, A.; Milger, K.; Schulz, C.; Zehetmayer, S.; Hamelmann, E.; Buhl, R.; Korn, S. Fraction of exhaled nitric oxide is associated with disease burden in the German Asthma Net severe asthma cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, A.H.; Srivastava, S.; Sahal, A. Disconnect of type 2 biomarkers in severe asthma; dominated by FeNO as a predictor of exacerbations and periostin as predictor of reduced lung function. Respir. Med. 2018, 143, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffler, E.; Pizzimenti, S.; Badiu, I.; Guida, G.; Ricciardolo, F.L.; Bucca, C.; Rolla, G. Nasal nitric oxide is a marker of poor asthma control. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 026009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Saito, J.; Fukuhara, A.; Uematsu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Togawa, R.; Sato, Y.; Nikaido, T.; Wang, X.; Tanino, Y.; et al. The clinical role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in asthma control. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, S.; Pijnenburg, M.; de Jongste, J.C.; Pike, K.C.; Roberts, G.; Petsky, H.; Chang, A.B.; Fritsch, M.; Frischer, T.; Szefler, S.; et al. Change in FEV1 and Feno Measurements as Predictors of Future Asthma Outcomes in Children. Chest 2019, 155, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Davis, B.; Alvarez-Puebla, M.J.; Nguyen, D.; Levin, L.; Olaguibel, J.M. Is exhaled nitric oxide a useful adjunctive test for assessing asthma? J. Asthma 2009, 46, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.K.; Raj, D.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide for Identification of Uncontrolled Asthma in Children. Indian Pediatr. 2016, 53, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pianosi, P.; Keogh, K.; Zaiem, F.; Alsawas, M.; Alahdab, F.; Almasri, J.; Mohammed, K.; Larrea-Mantilla, L.; Farah, W.; et al. The Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2017.
- Price, D.B.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Pavord, I.D.; Roche, N.; Halpin, D.M.G.; Bjermer, L.; Usmani, O.S.; Brusselle, G.; Ming, S.W.Y.; Rastogi, S. Association of elevated fractional exhaled nitric oxide concentration and blood eosinophil count with severe asthma exacerbations. Clin. Transl. Allerg. 2019, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Wenzel, S.E.; Casale, T.B.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Rice, M.S.; Daizadeh, N.; Deniz, Y.; Patel, N.; Harel, S.; Rowe, P.J.; et al. Baseline FeNO as a prognostic biomarker for subsequent severe asthma exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma receiving placebo in the LIBERTY ASTHMA QUEST study: A post-hoc analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, C.; Silva, D.; Severo, M.; Rufo, J.; Paciência, I.; Madureira, J.; Padrão, P.; Moreira, P.; Delgado, L.; Oliveira Fernandes, E.; et al. Spirometry-adjusted fraction of exhaled nitric oxide increases accuracy for assessment of asthma control in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Eom, S.Y.; Hahn, Y.S. Combined use of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and bronchodilator response in predicting future loss of asthma control among children with atopic asthma. Respirology 2017, 22, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumou, H.; Westerhof, G.A.; de Nijs, S.B.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bel, E.H. Predictors of accelerated decline in lung function in adult-onset asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K.; Hirano, T.; Oka, A.; Ito, K.; Edakuni, N. Persistently high exhaled nitric oxide and loss of lung function in controlled asthma. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, E.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.I.; Jung, Y.H.; Park, G.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, J. The association of lung function, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and exhaled nitric oxide differs between atopic and non-atopic asthma in children. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogensen, I.; Alving, K.; Jacinto, T.; Fonseca, J.; Janson, C.; Malinovschi, A. Simultaneously elevated FeNO and blood eosinophils relate to asthma morbidity in asthmatics from NHANES 2007-12. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.B.; Buhl, R.; Chan, A.; Freeman, D.; Gardener, E.; Godley, C.; Gruffydd-Jones, K.; McGarvey, L.; Ohta, K.; Ryan, D.; et al. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide as a predictor of response to inhaled corticosteroids in patients with non-specific respiratory symptoms and insignificant bronchodilator reversibility: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hahn, P.Y.; Morgenthaler, T.Y.; Lim, K.G. Use of exhaled nitric oxide in predicting response to inhaled corticosteroids for chronic cough. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, N.A.; Massanari, M.; Jain, N. Measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in real-world clinical practice alters asthma treatment decisions. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 414–418.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamási, L.; Bohács, A.; Bikov, A.; Andorka, C.; Rigó Jr, J.; Losonczy, G.; Horváth, I. Exhaled nitric oxide in pregnant healthy and asthmatic women. J. Asthma 2009, 46, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, H.; Murphy, V.E.; Taylor, D.R.; Hensley, M.J.; McCaffery, K.; Giles, W.; Clifton, V.L.; Gibson, P.G. Management of asthma in pregnancy guided by measurement of fraction of exhaled nitric oxide: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morten, M.; Collison, A.; Murphy, V.E.; Barker, D.; Oldmeadow, C.; Attia, J.; Meredith, J.; Powell, H.; Robinson, P.D.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Managing Asthma in Pregnancy (MAP) trial: FENO levels and childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1765–1772.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loewenthal, L.; Menzies-Gow, A. FeNO in Asthma. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 43, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholl, D.M.; Stevenson, M.; McGarvey, L.P.; Heaney, L.G. The utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide suppression in the identification of nonadherence in difficult asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaney, L.G.; Busby, J.; Bradding, P.; Chaudhuri, R.; Mansur, A.H.; Niven, R.; Pavord, I.D.; Lindsay, J.T.; Costello, R.W. Remotely monitored therapy and nitric oxide suppression identifies nonadherence in severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Oke, J.; Fleming-Nouri, A.; Brewin, J.; Roberts, N.; Harada, N.; Atsuta, R.; Takahashi, K.; Mori, K.; et al. Using fractional exhaled nitric oxide to guide step-down treatment decisions in patients with asthma: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.J.; Massanari, M.; Lee, T.A.; Brooks, E. A Review of the Utility and Cost Effectiveness of Monitoring Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management. Manag. Care 2018, 27, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Darbà, J.; Ascanio, M.; Syk, J.; Alving, K. Economic Evaluation of the Use of FeNO for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Patients in Primary Care in Sweden. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2021, 13, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Lee, F.E.; Lee, G.B. Understanding Asthma Phenotypes, Endotypes, and Mechanisms of Disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custovic, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Saglani, S. Considering biomarkers in asthma disease severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrish, M.; Hanania, N.A. Choosing and switching biological agents in severe asthma. Respirology 2022, 27, 926–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, N.A.; Alpan, O.; Hamilos, D.L.; Condemi, J.J.; Reyes-Rivera, I.; Zhu, J.; Rosen, K.E.; Eisner, M.D.; Wong, D.A.; Busse, W. Omalizumab in severe allergic asthma inadequately controlled with standard therapy: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011, 154, 573–582, Erratum in Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanania, N.A.; Wenzel, S.; Rosén, K.; Hsieh, H.J.; Mosesova, S.; Choy, D.F.; Lal, P.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Busse, W. Exploring the effects of omalizumab in allergic asthma: An analysis of biomarkers in the EXTRA study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, D.; Busse, W.; Trzaskoma, B.; Omachi, T.A.; Rosén, K.; Chipps, B.E.; Luskin, A.T.; Solari, P.G. A randomized multicenter study evaluating Xolair persistence of response after long-term therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 162–169.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casale, T.B.; Luskin, A.T.; Busse, W.; Zeiger, R.S.; Trzaskoma, B.; Yang, M.; Griffin, N.M.; Chipps, B.E. Omalizumab Effectiveness by Biomarker Status in Patients with Asthma: Evidence from PROSPERO, A Prospective Real-World Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 156–164.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, H.G.; Liu, M.C.; Pavord, I.D.; Brusselle, G.G.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chetta, A.; Humbert, M.; Katz, L.E.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1198–1207, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corren, J.; Weinstein, S.; Janka, L.; Zangrilli, J.; Garin, M. Phase 3 Study of Reslizumab in Patients With Poorly Controlled Asthma: Effects Across a Broad Range of Eosinophil Counts. Chest 2016, 150, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleecker, E.R.; Wechsler, M.E.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wu, Y.; Hirsch, I.; Goldman, M.; Newbold, P.; Zangrilli, J.G. Baseline patient factors impact on the clinical efficacy of benralizumab for severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.P.; Kavanagh, J.; d’Ancona, G.; Roxas, C.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Fernandes, M.; Kent, B.D.; Dhariwal, J.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. The relationship between Feno and effectiveness of mepolizumab and benralizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2093–2096.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonell, R.P.; Lee, F.E.; Levy, J.M.; Kuruvilla, M. Exhaled nitric oxide measurements are not influenced by anti-eosinophil therapy in patients with asthma: A retrospective analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Busse, W.W.; Ford, L.; Sher, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, N.A.; Korenblat, P.; Chapman, K.R.; Bateman, E.D.; Kopecky, P.; Paggiaro, P.; Yokoyama, A.; Olsson, J.; Gray, S.; Holweg, C.T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of lebrikizumab in patients with uncontrolled asthma (LAVOLTA I and LAVOLTA II): Replicate, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Sjöbring, U.; Péterffy, A.; Wessman, P.; Bowen, K.; Piper, E.; Colice, G.; Brightling, C.E. Tralokinumab for severe, uncontrolled asthma (STRATOS 1 and STRATOS 2): Two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, C.T. The Efficacy and Safety of Antiinterleukin 13, a Monoclonal Antibody, in Adult Patients With Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianigiani, T.; Alderighi, L.; Meocci, M.; Messina, M.; Perea, B.; Luzzi, S.; Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Refini, R.M.; Bargagli, E.; et al. Exploring the Interaction between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Biologic Treatment in Severe Asthma: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murugesan, N.; Saxena, D.; Dileep, A.; Adrish, M.; Hanania, N.A. Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081428
Murugesan N, Saxena D, Dileep A, Adrish M, Hanania NA. Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(8):1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081428
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurugesan, Neveda, Damini Saxena, Arundhati Dileep, Muhammad Adrish, and Nicola A. Hanania. 2023. "Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management" Diagnostics 13, no. 8: 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081428
APA StyleMurugesan, N., Saxena, D., Dileep, A., Adrish, M., & Hanania, N. A. (2023). Update on the Role of FeNO in Asthma Management. Diagnostics, 13(8), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13081428







