The Prognostic Effect of CDKN2A/2B Gene Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Independent Prognostic Significance in BFM-Based Protocols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Diagnosis; Morphologic, Molecular, and Cytogenetic Testing
2.3. Flow Cytometry (FC)
2.4. G-Banding, FISH, and RT-PCR
2.5. MLPA (Multiple-Ligation Probe Amplification)
2.6. Conventional Risk Stratification, Therapy Groups, and Treatment Protocol
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. FISH and MLPA Concordance in CDKN2A/2B Evaluation
3.2. The Incidence of CDKN2A/2B Deletions and Comparative Description of Clinical and Genetic Disease Features between the CDKN2A/2B Deleted and Non-Deleted Subgroup
3.3. Impact of CDKN2A/2B Deletions in Treatment Response and MRD Clearance
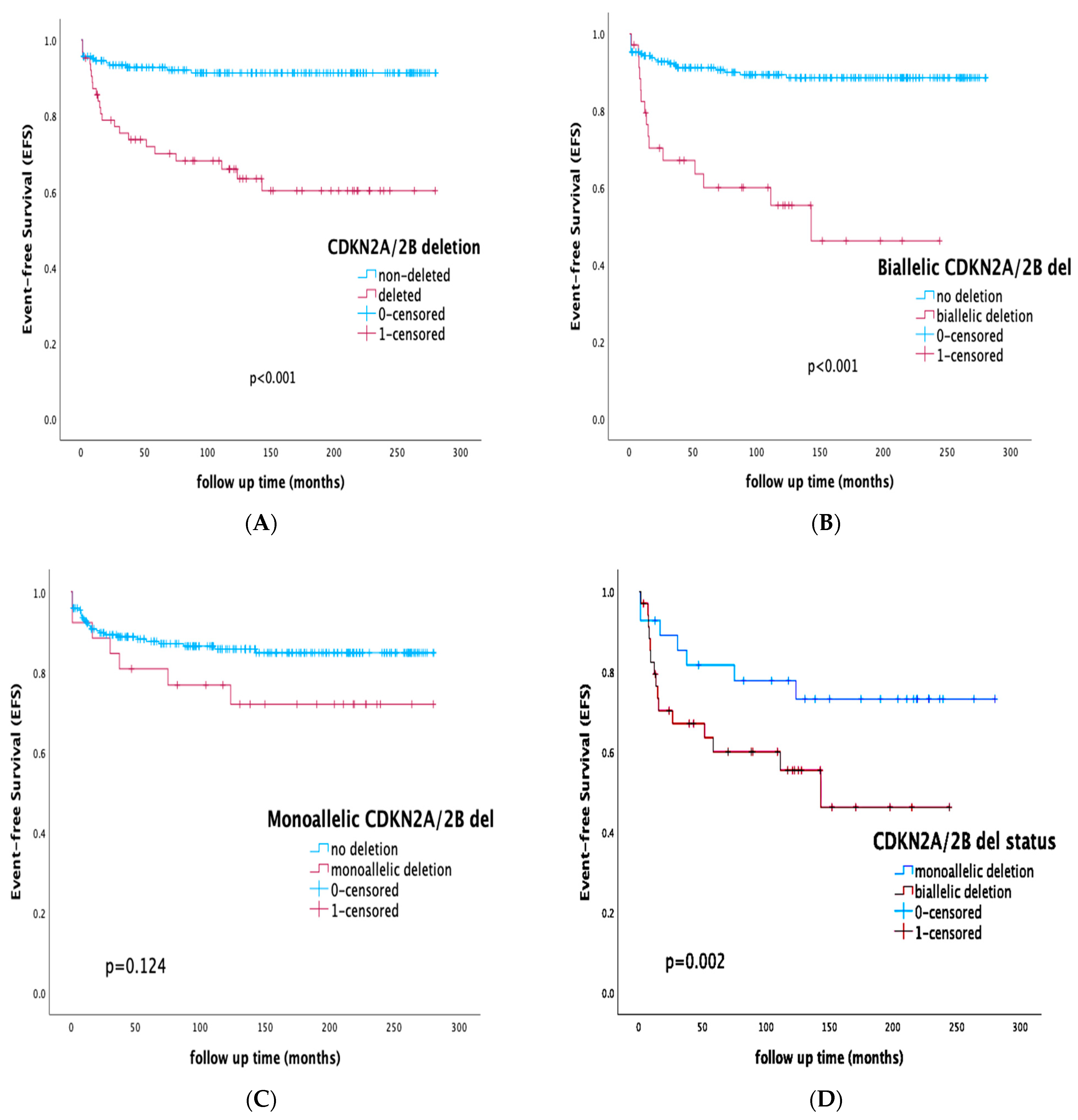
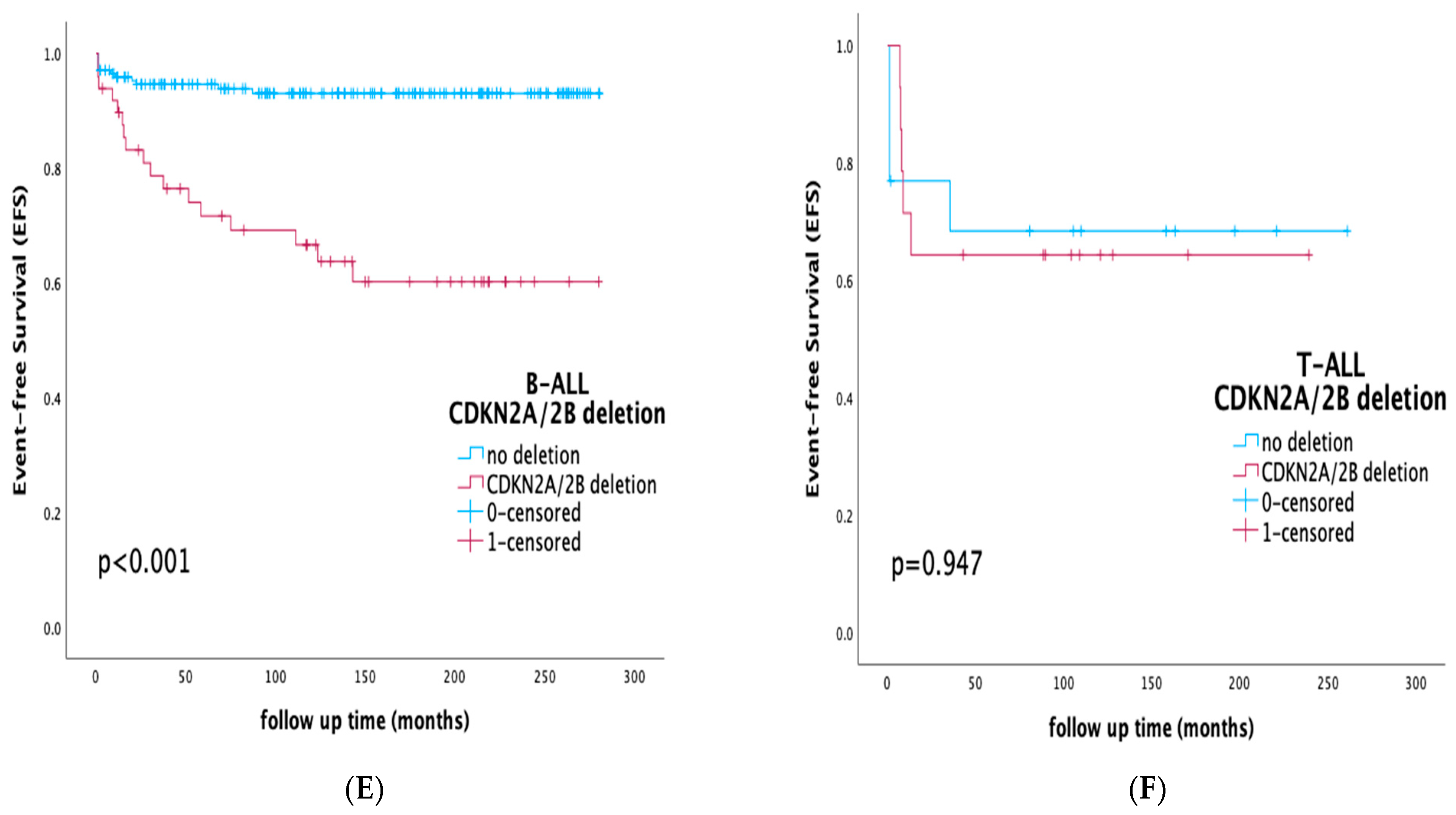
3.4. Prognostic Impact of CDKN2A/2B Deletions on Survival Rates and Outcome
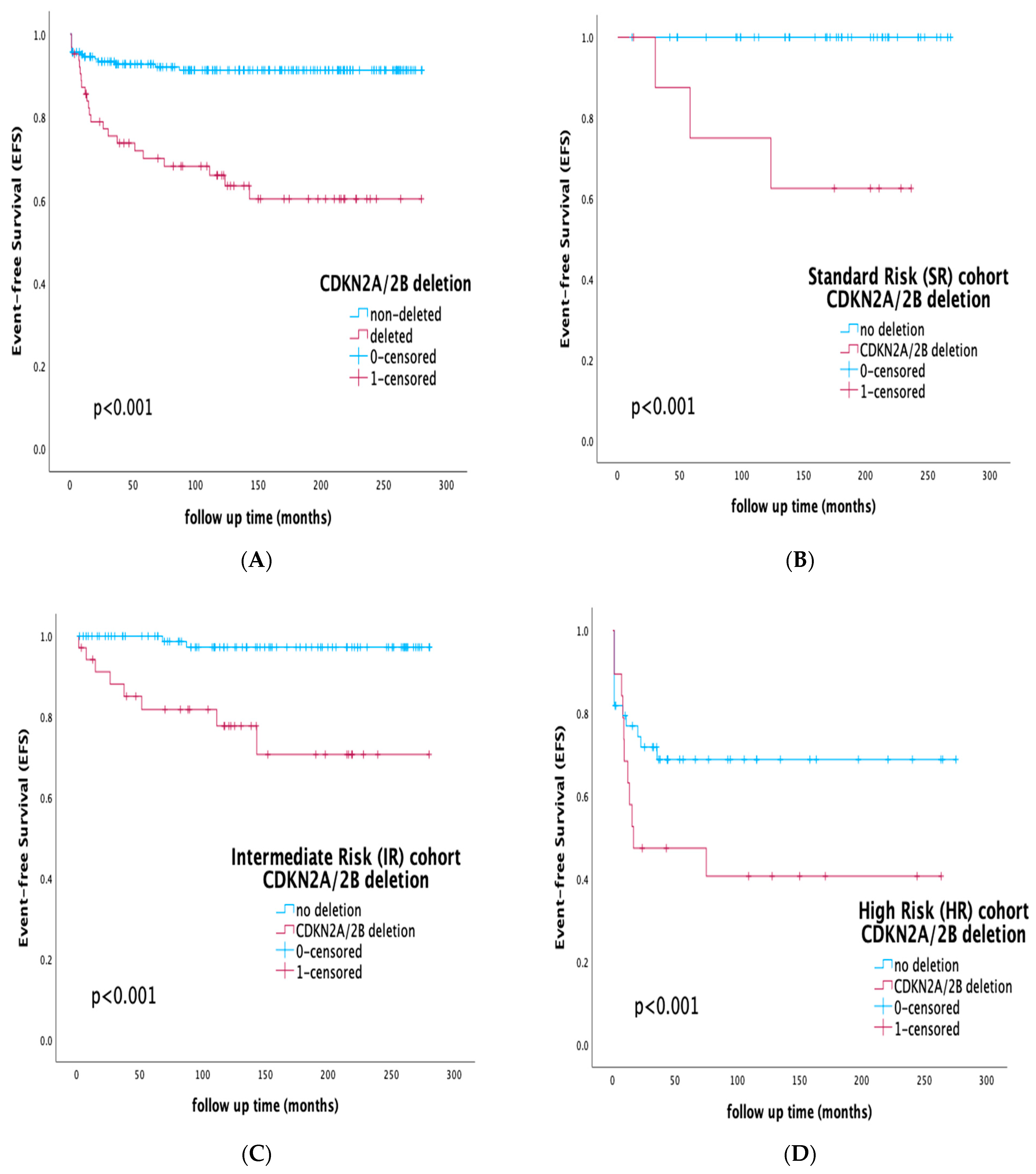
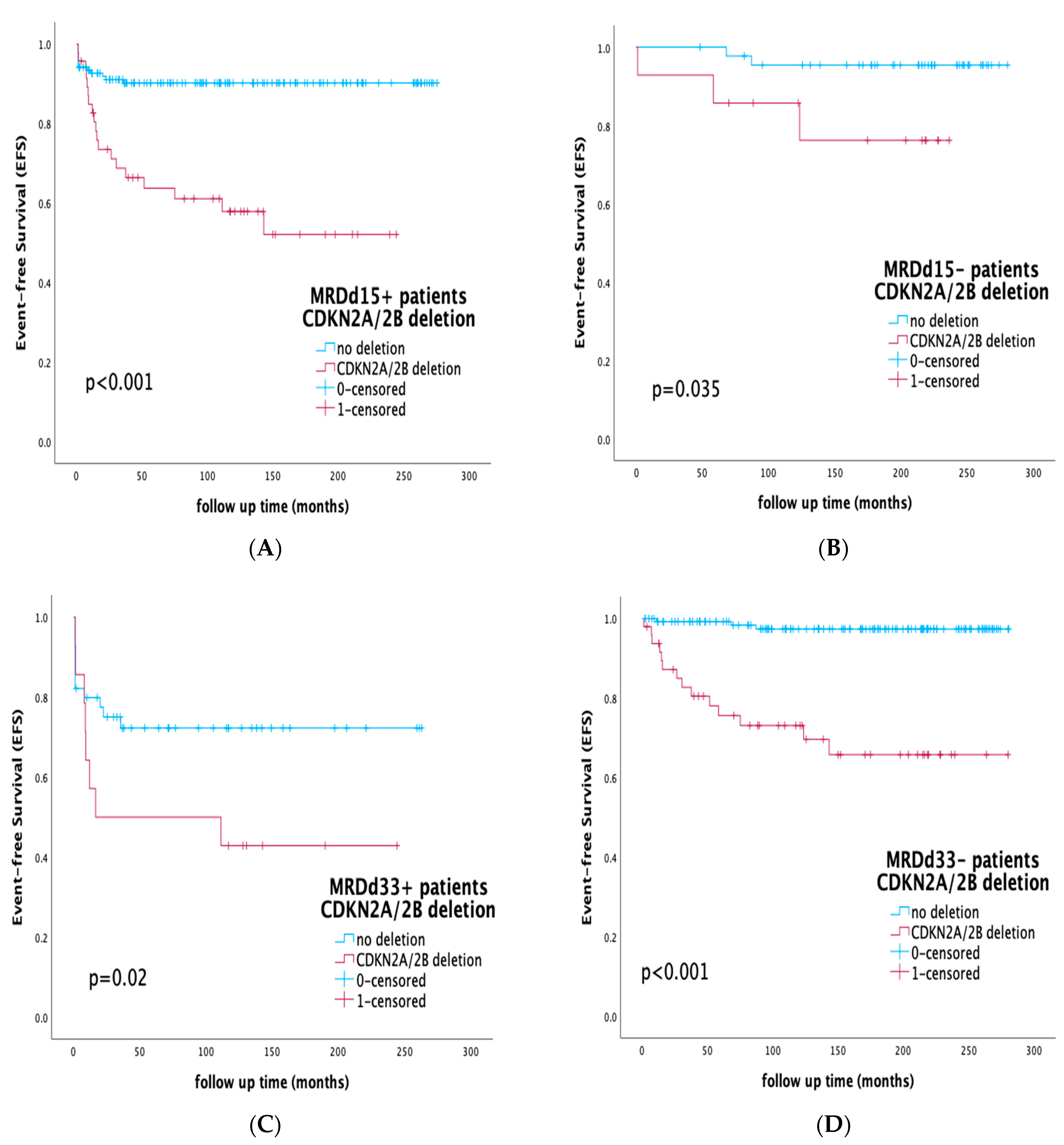
3.5. Prognostic Impact of CDKN2A/2B Deletions by Risk Stratification and Integration of MRD Status
3.6. Mutivariate Analysis and Correlation with Protocol Conventional Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pui, C.-H.; Yang, J.J.; Hunger, S.P.; Pieters, R.; Schrappe, M.; Biondi, A.; Vora, A.; Baruchel, A.; Silverman, L.B.; Schmiegelow, K.; et al. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Progress through collaboration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2938–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunger, S.P.; Mullighan, C.G. Redefining ALL classification: Toward detecting high-risk ALL and implementing precision medicine. Blood 2015, 125, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Paterakis, G.; Vasdekis, V.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Papadakis, V.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Polychronopoulou, S. Prognostic significance of flow cytometry MRD log reduction during induction treatment of childhood ALL. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 60, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.W.; Roberts, K.G.; Gu, Z.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Dai, Y.; Devidas, M.; Qu, C.; et al. The genomic landscape of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, I.; Mullighan, C.G. Genetic basis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V. New and emerging prognostic and predictive genetic biomarkers in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, R.P.; Schoenmakers, E.F.P.M.; Van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y.; Van Kessel, A.G.; Van Leeuwen, F.N.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M. High-resolution genomic profiling of childhood ALL reveals novel recurrent genetic lesions affecting pathways involved in lymphocyte differentiation and cell cycle progression. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.; Gángó, A.; Benard-Slagter, A.; Egyed, B.; Haltrich, I.; Hegyi, L.; de Groot, K.; Kiraly, P.A.; Krizsan, S.; Kajtar, B.; et al. Comprehensive profiling of disease-relevant copy number aberrations for advanced clinical diagnostics of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Kelaidi, C.; Dworzak, M.N.; Polychronopoulou, S. Adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic and acute myeloid leukemia. MEMO-Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2018, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Boeree, A.; de Haas, V.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; Boer, M.L.D. Copy number alterations in B-cell development genes, drug resistance, and clinical outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Enshaei, A.; Bartram, J.; Hancock, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Hough, R.; Samarasinghe, S.; Schwab, C.; Vora, A.; Wade, R.; et al. Genotype specific minimal residual disease interpretation improves stratification in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanulla, M.; Dagdan, E.; Zaliova, M.; Möricke, A.; Palmi, C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Eckert, C.; Te Kronnie, G.; Bourquin, J.P.; Bornhauser, B.; et al. IKZF1(plus) defines a new minimal residual disease-dependent very-poor prognostic profile in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Enshaei, A.; Schwab, C.; Wade, R.; Chilton, L.; Elliott, A.; Richardson, S.; Hancock, J.; Kinsey, S.E.; Mitchell, C.D.; et al. A novel integrated cytogenetic and genomic classification refines risk stratification in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Florentin, L.; Papadakis, V.; Paterakis, G.; Tzanoudaki, M.; Bouzarelou, D.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Polychronopoulou, S. Copy number alteration profile provides additional prognostic value for acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients treated on BFM protocols. Cancers 2021, 13, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Kumar, L.; Kamal, V.K.; Kumar, R. Gene copy number alteration profile and its clinical correlation in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Kuang, P.; Liu, T. Prognostic significance of CDKN2A/B deletions in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco Salas, P.; Fernandez, L.; Vela, M.; Bueno, D.; Gonzalez, B.; Valentin, J.; Lapunzina, P.; Perez-Martinez, A. The role of CDKN2A/B deletions in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 33, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, W.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X. Childhood Acute B-Lineage Lymphoblastic Leukemia With CDKN2A/B Deletion Is a Distinct Entity With Adverse Genetic Features and Poor Clinical Outcomes. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 878098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulong, S.; Moorman, A.V.; Irving, J.A.E.; Strefford, J.C.; Konn, Z.J.; Case, M.C.; Minto, L.; Barber, K.E.; Parker, H.; Wright, S.L.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of the CDKN2A gene in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals genomic deletion, copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and association with specific cytogenetic subgroups. Blood 2009, 113, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Bakhshi, S.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Kabra, M.; Shukla, R.; Seth. R. Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A/B gene deletions are markers of poor prognosis in Indian children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasian, S.K.; Loh, M.L.; Hunger, S.P. Philadelphia chromosome-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Chopra, A.; Kamal, V.K. Molecular genetic profile in BCR-ABL1 negative pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia can further refine outcome prediction in addition to that by end-induction minimal residual disease detection. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 59, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf Einsiedel, H.; Taube, T.; Hartmann, R.; Eckert, C.; Seifert, G.; Wellmann, S.; Henze, G.; Seeger, K. Prognostic value of p16(INK4a) gene deletions in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 4002–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kees, U.R.; Burton, P.R.; Lu, C.; Baker, D.L. Homozygous deletion of the p16/MTS1 gene in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome. Blood 1997, 89, 4161–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, T.L.; Watt, P.M.; Kumar, R.; Burton, P.R.; Reaman, G.H.; Sather, H.N.; Baker, D.L.; Kees, U.R. Hemizygous p16(INK4A) deletion in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia predicts independent risk of relapse. Blood 2001, 97, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, J.H.; Fournier, M.; Nelken, B.; Mazingue, F.; Lai, J.-L.; Bauters, F.; Fenaux, P.; Quesnel, B. p16(INK4a) immunocytochemical analysis is an independent prognostic factor in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 2620–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero Moreno, T.M.; Gustafsson, G.; Garwicz, S.; Grander, D.; Jonmundsson, G.K.; Frost, B.-M.; Makipernaa, A.; Rasool, O.; Savolainen, E.-R.; Schmiegelow, K.; et al. Deletion of the Ink4-locus (the p16ink4a, p14ARF and p15ink4b genes) predicts relapse in children with ALL treated according to the Nordic protocols NOPHO-86 and NOPHO-92. Leukemia 2002, 16, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiravan, M.; Singh, M.; Bhatia, P.; Trehan, A.; Varma, N.; Sachdeva, M.S.; Bansal, D.; Jain, R.; Naseem, S. Deletion of CDKN2A/B is Associated with Inferior Relapse Free Survival in Pediatric B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Pastorczak, A.; Fendler, W.; Madzio, J.; Tomasik, B.; Taha, J.; Bielska, M.; Sedek, L.; Szczepanski, T.; Matysiak, M.; et al. Biallelic Loss of CDKN2A is Associated with Poor Response to Treatment in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Tsakiridou, A.A.; Androutsos, G.; Paterakis, G.S.; Athanassiadou, F. p16 inactivation associated with aggressive clinical course and fatal outcome in TEL/AML1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2005, 27, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirebeau, D.; Acquaviva, C.; Suciu, S.; Bertin, R.; Dastugue, N.; Robert, A.; Boutard, P.; Méchinaud, F.; Plouvier, E.; Otten, J.; et al. The prognostic significance of CDKN2A, CDKN2B and MTAP inactivation in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. Results of the EORTC studies 58881 and 58951. Haematologica 2006, 91, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Yim, S.-H.; Cho, N.-S.; Kang, S.-H.; Ko, D.-H.; Oh, B.; Kim, T.Y.; Min, H.J.; She, C.J.; Kang, H.J.; et al. Homozygous Deletion of CDKN2A (P16, P14) and CDKN2B (P15) Genes is a Poor Prognostic Factor in Adult But Not in Childhood B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Comparative Deletion and Hypermethylation Study. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2009, 195, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zutven, L.J.; van Drunen, E.; de Bont, J.M.; Wattel, M.M.; Boer, M.L.D.; Pieters, R.; Hagemeijer, A.; Slater, R.M.; Beverloo. H.B. CDKN2 deletions have no prognostic value in childhood precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworzak, M.N.; Buldini, B.; Gaipa, G.; Ratei, R.; Hrusak, O.; Luria, D.; Rosenthal, E.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Sartor, M.; Schumich, A.; et al. AIEOP-BFM Consensus Guidelines 2016 for Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C.J.; Jones, L.R.; Morrison, H.; Ryan, S.L.; Yigittop, H.; Schouten, J.P.; Harrison, C.J. Evaluation of multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification as a method for the detection of copy number abnormalities in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 49, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konialis, C.; Savola, S.; Karapanou, S.; Markaki, A.; Karabela, M.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Ampatzidou, M.; Voulgarelis, M.; Viniou, N.-A.; Variami, E.; et al. Routine application of a novel MLPA-based first-line screening test uncovers clinically relevant copy number aberrations in haematological malignancies undetectable by conventional cytogenetics. Hematology 2014, 19, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M.; Reiter, A. Trial ALL-BFM 95. Treatment protocol ALL-BFM 95 for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A cooperative multicenter trial of the German Society for Pediatric Hematology and Oncology. Blood 2008, 111, 4477–4489. [Google Scholar]
- Möricke, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Henze, G.; Schrauder, A.; Gadner, H.; Ludwig, W.D.; Ritter, J.; Harbott, J.; Mann, G.; et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia 2010, 24, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALL IC 2009 Trial of the I-BFM Study Group. 2009. Available online: https://bfminternational.wordpress.com/clinical-trials/ongoing-trials/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Papadakis, V.; Panagiotou, J.P.; Polychronopoulou-Androulakaki, S.; Mikraki, V.; Paecharidou, A.; Tsitsikas, C.; Vrachnou, E.; Paterakis, G.; Mavrou, A.; Sambani, C.; et al. Results of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment in Greek patients using a BFM-based protocol. HAEMA 2003, 6, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Panagiotou, J.P.; Paterakis, G.; Papadakis, V.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Parcharidou, A.; Papargyri, S.; Rigatou, E.; Avgerinou, G.; Tsitsikas, K.; et al. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: 12 years of experience, using a Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster approach, in a Greek center. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 56, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Paterakis, G.; Pavlidis, D.; Tsitsikas, K.; Kostopoulos, I.V.; Papadakis, V.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Polychronopoulou, S. ETV6/RUNX1-positive childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): The spectrum of clonal heterogeneity and its impact on prognosis. Cancer Genet. 2018, 224–225, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usvasalo, A.; Savola, S.; Räty, R.; Vettenranta, K.; Harila-Saari, A.; Koistinen, P.; Savolainen, E.-R.; Elonen, E.; Saarinen-Pihkala, U.M.; Knuutila, S. CDKN2A Deletions in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of Adolescents and Young Adults—An Array CGH Study. Leukemia Res. 2008, 32, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrman, K.; Castor, A.; Behrendtz, M.; Forestier, E.; Olsson, L.; Ehinger, M.; Biloglav, A.; Fioretos, T.; Paulsson, K.; Johansson, B. Deep sequencing and SNP array analyses of pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveal NOTCH1 mutations in minor subclones and a high incidence of uniparental isodisomies affecting CDKN2A. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, R.B.; Morash, B.A.; Riddell, C.; Wang, H.; Fernandez, C.V.; Yhap, M.; Berman, J.N. Using MS-MLPA as an efficient screening tool for detecting 9p21 abnormalities in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Lou, Y.; Mai, W.; et al. CDKN2A deletions are associated with poor outcomes in 101 adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Park, J.; Kwon, A.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, G.D.; Han, E.; Jekarl, D.W.; Chae, H.; Han, K.; et al. CDKN2B downregulation and other genetic characteristics in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. Prognostic relevance of genetic variations in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoblastic lymphoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 2485–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Ali, M.S.; Singh, J.; Arora, M.; Verma, D.; Pandey, A.K.; Benjamin, M.; Bakhshi, S.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Sharma, A.; et al. Prognostic utility of key copy number alterations in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Easton, J.; Shao, Y.; Maciaszek, J.; Wang, Z.; Wilkinson, M.R.; McCastlain, K.; Edmonson, M.; Pounds, S.B.; Shi, L.; et al. The genomic landscape of pediatric and young adult T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsellou, E.; Troungos, C.; Moschovi, M.; Athanasiadou-Piperopoulou, F.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Kosmidis, H.; Kalmanti, M.; Hatzakis, A.; Dessypris, N.; Kalofoutis, A.; et al. Hypermethylation of CpG islands in the promoter region of the p15INK4B gene in childhood acute leukaemia. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Singh, J.; Arora, M.; Ali, M.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Benjamin, M.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Qamar, I.; Chopra, A. Copy Number Alterations in CDKN2A/2B and MTAP Genes Are Associated with Low MEF2C Expression in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cureus 2022, 14, e32151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomer-Lahiguera, S.; Pisecker, M.; König, M.; Nebral, K.; Pickl, W.F.; Kauer, M.O.; Haas, O.A.; Ullmann, R.; Attarbaschi, A.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. MEF2C-dysregulated pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with CDKN1B deletions and a poor response to glucocorticoid therapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conter, V.; Bartram, C.R.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Schrauder, A.; Panzer-Grümayer, R.; Möricke, A.; Aricò, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; De Rossi, G.; et al. Molecular response to treatment redefines all prognostic factors in children and adolescents with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results in 3184 patients of the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 study. Blood 2010, 115, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; Beach, D.; Shapiro, G.I. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Schoenwaelder, N.; Sender, S.; Junghanss, C.; Maletzki, C. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors in Hematological Malignancies—Current Understanding, (Pre)Clinical Application and Promising Approaches. Cancers 2021, 13, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bride, K.L.; Hu, H.; Tikhonova, A.; Fuller, T.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Shraim, R.; Li, M.M.; Carroll, W.L.; Raetz, E.A.; Aifantis, I.; et al. Rational Drug Combinations With CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 107, 1746–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (N = 247) | Patients with CDKN2A/2B Deletions (N = 63) | Patients without CDKN2A/2B Deletions (N = 184) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Gender | ||||
| 151 (61.1) | 40 (63.5) | 110 (59.8) | |
| 96 (38.9) | 23 (36.5) | 74 (40.2) | 0.92 |
| Age | ||||
| 5.0 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 0.04 |
| Immunophenotype | ||||
| 220 (89.1) | 49 (77.8) | 171 (92.9) | |
| 27 (10.9) | 14 (22.2) | 13 (7.1) | <0.001 |
| White-Blood-Cell Count | ||||
| 12.21 | 22.15 | 9.33 | <0.001 |
| CNS Infiltration | ||||
| 38 (15.4) | 12 (19.0) | 26 (14.1) | 0.37 |
| Genetics | ||||
| 50 (20.2) | 10 (15.9) | 40 (21.7) | 0.32 |
| 12 (4.8) | 1 (1.6) | 11 (6.0) | 0.03 |
| 5 (2.0) | 3 (4.8) | 2 (1.1) | 0.04 |
| 10 (4.0) | 3 (4.8) | 7 (3.8) | 0.97 |
| 3 (0.8) | 1 (1.6) | 2 (1.1) | 0.78 |
| 61 (24.7) | 10 (15.9) | 51 (27.7) | 0.06 |
| 2 (0.8) | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.1) | 0.90 |
| 13 (13.7) * | 2 (6.9) ** | 11 (16.7) *** | 0.02 |
| 1 (1.0) * | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) *** | 0.31 |
| 8 (8.4) * | 4 (13.8) ** | 4 (6.1) *** | 0.04 |
| Treatment Protocol | ||||
| 119 (48.2) | 31 (49.2) | 88 (47.8) | 0.95 |
| 128 (51.8) | 32 (50.8) | 96 (52.2) | 0.65 |
| Protocol Risk Group | ||||
| 54 (21.9) | 9 (14.3) | 45 (24.5) | 0.03 |
| 130 (52.6) | 35 (55.6) | 95 (51.6) | 0.08 |
| 63 (25.5) | 19 (30.1) | 44 (23.9) | 0.09 |
| Therapy Risk Group | ||||
| 7 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 7 (3.8) | 0.04 |
| 167 (67.6) | 43 (68.3) | 124 (67.4) | 0.09 |
| 73 (29.6) | 20 (31.7) | 53 (28.8) | 0.06 |
| FC-MRD status | ||||
| 185 (74.9) | 47 (74.6) | 138 (75.0) | 0.84 |
| 59 (23.9) | 14 (22.2) | 45 (24.4) | 0.94 |
| Complete Remission (EOI-CR #) | ||||
| 230 (93.1) | 61 (96.8) | 167 (90.8) | 0.08 |
| 17 (6.9) | 2 (3.2) | 17 (9.2) | 0.06 |
| (A) | ||||||
| SE | Wald | Sig. p-Value | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95.0% CI for HR | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| CDKN2A/2B deletion | 0.354 | 21.641 | <0.001 | 5.199 | 2.596 | 10.412 |
| BCR/ABL1+ | 0.656 | 0.003 | 0.958 | 0.966 | 0.267 | 3.493 |
| KMT2A+ | 0.637 | 0.140 | 0.708 | 1.269 | 0.364 | 4.421 |
| Τ vs. B ALL | 0.416 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.443 | 2.258 |
| MRDd15 positivity | 0.564 | 0.046 | 0.830 | 0.886 | 0.293 | 2.678 |
| MRDd33 positivity | 0.405 | 5.118 | 0.024 | 2.501 | 1.130 | 5.535 |
| Therapy risk group | 0.453 | 8.867 | 0.003 | 3.851 | 1.585 | 9.353 |
| (B) | ||||||
| SE | Wald | Sig. p-Value | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95.0% CI for HR | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| CDKN2A/2B deletion | 0.355 | 25.260 | <0.001 | 5.958 | 2.970 | 11.949 |
| BCR/ABL1+ | 0.688 | 0.161 | 0.688 | 0.759 | 0.197 | 2.920 |
| KMT2A+ | 0.645 | 0.064 | 0.800 | 1.177 | 0.332 | 4.170 |
| Τ vs. B ALL | 0.430 | 0.054 | 0.817 | 0.905 | 0.389 | 2.104 |
| MRDd15 positivity | 0.570 | 0.001 | 0.979 | 1.015 | 0.332 | 3.102 |
| MRDd33 positivity | 0.407 | 3.355 | 0.067 | 2.106 | 0.949 | 4.674 |
| Therapy risk group | 0.485 | 12.755 | <0.001 | 5.657 | 2.186 | 14.640 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ampatzidou, M.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Paisiou, A.; Paterakis, G.; Tzanoudaki, M.; Papadakis, V.; Florentin, L.; Polychronopoulou, S. The Prognostic Effect of CDKN2A/2B Gene Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Independent Prognostic Significance in BFM-Based Protocols. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091589
Ampatzidou M, Papadhimitriou SI, Paisiou A, Paterakis G, Tzanoudaki M, Papadakis V, Florentin L, Polychronopoulou S. The Prognostic Effect of CDKN2A/2B Gene Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Independent Prognostic Significance in BFM-Based Protocols. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(9):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091589
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmpatzidou, Mirella, Stefanos I. Papadhimitriou, Anna Paisiou, Georgios Paterakis, Marianna Tzanoudaki, Vassilios Papadakis, Lina Florentin, and Sophia Polychronopoulou. 2023. "The Prognostic Effect of CDKN2A/2B Gene Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Independent Prognostic Significance in BFM-Based Protocols" Diagnostics 13, no. 9: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091589
APA StyleAmpatzidou, M., Papadhimitriou, S. I., Paisiou, A., Paterakis, G., Tzanoudaki, M., Papadakis, V., Florentin, L., & Polychronopoulou, S. (2023). The Prognostic Effect of CDKN2A/2B Gene Deletions in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Independent Prognostic Significance in BFM-Based Protocols. Diagnostics, 13(9), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091589





