Increased Risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exposure (Gout)
2.2. Outcome (Definition of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)
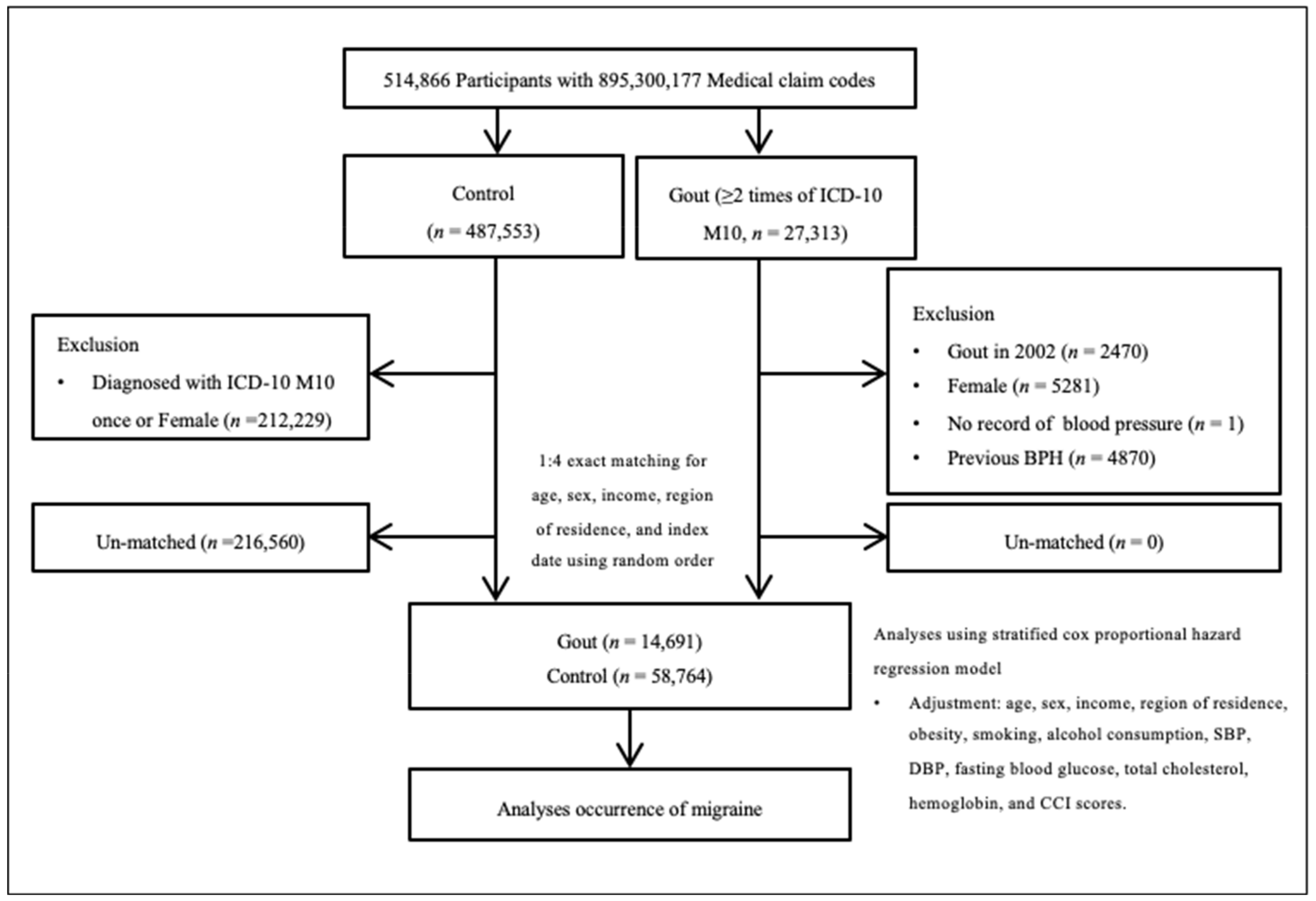
2.3. Participant Selection
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Priest, R.; Garzotto, M.; Kaufman, J. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Brief Overview of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 15, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, A.; Neal, D. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Lancet 2003, 361, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Pandya, B.J.; Choi, H.K. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3136–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, H.J.; Kim, S.A.; Nam, J.W.; Choi, B.Y.; Moon, H.S. Community-based research on the benign prostatic hyperplasia prevalence rate in Korean rural area. Korean J. Urol. 2015, 56, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miernik, A.; Gratzke, C. Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2020, 117, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, F.; Creta, M.; Trama, F.; Esposito, F.; Crocetto, F.; Aveta, A.; Mangiapia, F.; Imbimbo, C.; Capece, M.; La Rocca, R.; et al. Tamsulosin plus a new complementary and alternative medicine in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: Results from a retrospective comparative study. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2020, 92, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, S.D.; Del Giudice, F.; Chung, B.I.; Manfredi, C.; De Sio, M.; Damiano, R.; Cherullo, E.E.; De Nunzio, C.; Cacciamani, G.E.; Cindolo, L.; et al. Robotic assisted simple prostatectomy versus other treatment modalities for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of over 6500 cases. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023, 26, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plochocki, A.; King, B. Medical Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2022, 49, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Yang, L.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Yan, S.-Y.; Luo, L.-S.; Chen, P.; Zeng, X.-T. Causal relationship between obesity, lifestyle factors and risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarsten, J.; Högstedt, B.; Holthuis, N.; Mellström, D. Components of the metabolic syndrome—Risk factors for the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 1998, 1, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K. Gout. Lancet 2016, 388, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Kwak, S.G.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.-K.; Choe, J.-Y.; Park, S.-H. Prevalence and incidence of gout in Korea: Data from the national health claims database 2007–2015. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-M.; Pasaribu, N.; Lee, S.-S.; Tsai, W.-C.; Li, C.-Y.; Lin, G.-T.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Tung, Y.-C.; Tu, H.-P. Risk of incident benign prostatic hyperplasia in patients with gout: A retrospective cohort study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukko, V.; Kaipia, A.; Talala, K.; Taari, K.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Auvinen, A.; Murtola, T.J. Allopurinol and risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia in a Finnish population-based cohort. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Yoo, D.M.; Chang, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G. Hearing Impairment Increases Economic Inequality. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 14, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific Perespective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.-M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and Validating the Charlson Comorbidity Index and Score for Risk Adjustment in Hospital Discharge Abstracts Using Data From 6 Countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Presicce, F.; Tubaro, A. Inflammatory mediators in the development and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkop, F.; Singh, G.; Rodrigues, E.; Gold, E.; Bahn, A. Uric acid: A modulator of prostate cells and activin sensitivity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 414, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Ryu, S.; Ahn, J.K. Higher Levels of Serum Uric Acid Have a Significant Association with Lower Incidence of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Healthy Korean Men. Metabolites 2022, 12, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Gosling, A.L.; Gaffo, A.; Abhishek, A. Gout. Lancet 2021, 397, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, A.K.; Martinon, F. Inflammation in gout: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.; Zeng, T.; Liao, Y.; Min, J.; Zhang, N.; Peng, M.; Kong, W.; Chen, L.-L. Identification of Inflammation-Related Biomarker Pro-ADM for Male Patients with Gout by Comprehensive Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 798719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madersbacher, S.; Sampson, N.; Culig, Z. Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Benign Prostatic Enlargement: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2019, 65, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, G.L.; Marks, J.M.; Ricke, W.A. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: What Is the Role and Significance of Inflammation? Curr. Urol. Rep. 2019, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-K.; Hung, K.-C.; Liao, C.-C.; Pan, L.-F.; Hung, C.-L.; Yang, D.-H. The Association between Serum Testosterone and Hyperuricemia in Males. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, E.A.; Kawachi, I.; Rimm, E.B.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E. Physical activity and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, A.E.; Liu, T.T.; Pascal, L.E.; Bauer, S.R.; DeFranco, D.B.; Ricke, W.A. Aging-Related Mitochondrial Dysfunction is Associated with Fibrosis in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, glad222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, S.D.; Crauso, F.; Aveta, A.; Cilio, S.; Barone, B.; Napolitano, L.; Scarpato, A.; Mirto, B.F.; Serino, F.; Del Giudice, F.; et al. A Novel Low-Cost Uroflowmetry for Patient Telemonitoring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.K.; Shinn, S.H.; Kim, K.S.; Moon, H.S. Changes in Prevalence and Treatment Pattern of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Korea. Int. Neurourol. J. 2021, 25, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Lai, J.-N.; Lin, C.-L.; Loh, C.-H.; Huang, H.-K.; Huang, L.-K. Association of alpha-1-adrenergic antagonist use with the risk of gout development in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients: A population-based cohort study. Fam. Pr. 2022, 39, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gout | Control | Standardized Difference | |
| Age (years old) (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 40–44 | 497 (3.38) | 1988 (3.38) | |
| 45–49 | 1660 (11.30) | 6640 (11.30) | |
| 50–54 | 2654 (18.07) | 10,616 (18.07) | |
| 55–59 | 3136 (21.35) | 12,544 (21.35) | |
| 60–64 | 2440 (16.61) | 9760 (16.61) | |
| 65–69 | 1910 (13.00) | 7640 (13.00) | |
| 70–74 | 1288 (8.77) | 5152 (8.77) | |
| 75–79 | 752 (5.12) | 3008 (5.12) | |
| 80–84 | 280 (1.91) | 1120 (1.91) | |
| 85+ | 74 (0.50) | 296 (0.50) | |
| Sex (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Male | 14,691 (100.0) | 58,764 (100.0) | |
| Income (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 1901 (12.94) | 7604 (12.94) | |
| 2 | 1807 (12.30) | 7228 (12.30) | |
| 3 | 2245 (15.28) | 8980 (15.28) | |
| 4 | 3127 (21.29) | 12,508 (21.29) | |
| 5 (highest) | 5611 (38.19) | 22,444 (38.19) | |
| Region of residence (n, %) | 0.00 | ||
| Urban | 6268 (42.67) | 25,072 (42.67) | |
| Rural | 8423 (57.33) | 33,692 (57.33) | |
| Obesity † (n, %) | 0.33 | ||
| Underweight | 173 (1.18) | 1508 (2.57) | |
| Normal | 3395 (23.11) | 20,146 (34.28) | |
| Overweight | 4067 (27.68) | 16,689 (28.40) | |
| Obese I | 6442 (43.85) | 19,123 (32.54) | |
| Obese II | 614 (4.18) | 1298 (2.21) | |
| Smoking status (n, %) | 0.03 | ||
| Nonsmoker | 6226 (42.38) | 24,436 (41.58) | |
| Past smoker | 2460 (16.74) | 9126 (15.53) | |
| Current smoker | 6005 (40.88) | 25,202 (42.89) | |
| Alcohol consumption (n, %) | 0.14 | ||
| <1 time a week | 6931 (47.18) | 31,880 (54.25) | |
| ≥1 time a week | 7760 (52.82) | 26,884 (45.75) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.20 | ||
| <120 mmHg | 3779 (24.22) | 14,711 (25.43) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 7850 (50.32) | 29,617 (51.19) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 3972 (25.46) | 13,526 (23.38) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (n, %) | 0.19 | ||
| <80 mmHg | 5905 (37.85) | 23,356 (40.37) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 5985 (38.36) | 22,464 (38.83) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 3711 (23.79) | 12,034 (20.80) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (n, %) | 0.03 | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 9336 (59.84) | 31,992 (55.30) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 4680 (30.00) | 18,955 (32.76) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 1585 (10.16) | 6907 (11.94) | |
| Total cholesterol (n, %) | 0.11 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 8654 (55.47) | 32,689 (56.50) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 5070 (32.50) | 18,369 (31.75) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 1877 (12.03) | 6796 (11.75) | |
| CCI score (n, %) | 0.09 | ||
| 0 | 8533 (54.70) | 36,099 (62.40) | |
| 1 | 2649 (16.98) | 8539 (14.76) | |
| ≥2 | 4419 (28.33) | 13,216 (22.84) | |
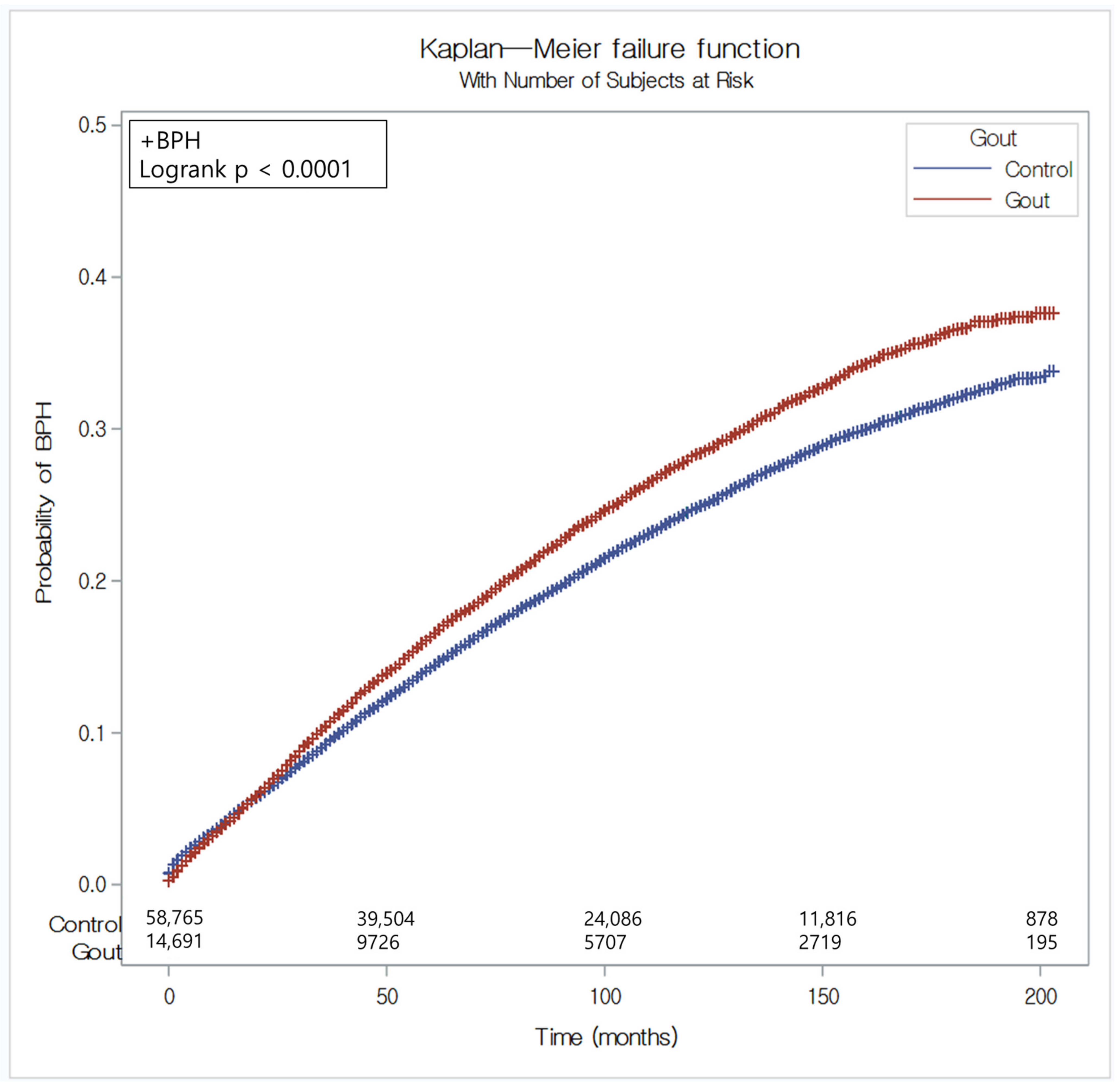
| Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (n, %) | 3438 (23.40) | 12,163 (20.70) | 0.07 |
| N of Event/ N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | Hazard Ratios for Migraine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude † | p Value | Adjusted †,‡ | p-Value | |||||
| Total Participants | ||||||||
| Gout | 3438/14,691 (23.40) | 98,582 | 34.90 | 5.00 (3.72–6.16) | 1.15 (1.11–1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.13 (1.09–1.18) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 12,163/58,764 (20.70) | 406,328 | 29.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age < 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 1862/7947 (23.43) | 64,773 | 28.70 | 5.00 (3.68–6.37) | 1.21 (1.15–1.27) | <0.001 * | 1.19 (1.13–1.25) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6378/31,788 (20.06) | 268,877 | 23.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Age ≥ 60 years old | ||||||||
| Gout | 1575/6744 (23.35) | 33,809 | 46.70 | 4.60 (2.03–6.96) | 1.10 (1.04–1.16) | 0.001 * | 1.07 (1.01–1.13) | 0.016 * |
| Control | 5785/26,976 (21.44) | 137,451 | 42.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| Gout | 3438/14,691 (23.40) | 98,582 | 34.90 | 5.00 (3.72–6.16) | 1.15 (1.11–1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.13 (1.09–1.18) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 12,163/58,764 (20.70) | 406,328 | 29.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low-income group | ||||||||
| Gout | 1336/5953 (22.44) | 38,036 | 35.10 | 6.40 (4.50–8.37) | 1.22 (1.14–1.29) | <0.001 * | 1.19 (1.12–1.27) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 4538/23,812 (19.06) | 158,159 | 28.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High-income group | ||||||||
| Gout | 2102/8738 (24.06) | 60,546 | 34.70 | 4.00 (2.42–5.57) | 1.12 (1.07–1.12) | <0.001 * | 1.10 (1.04–1.15) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 7625/34,952 (21.82) | 248,169 | 30.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 1546/6268 (24.66) | 42,536 | 36.30 | 4.60 (2.73–6.56) | 1.14 (1.07–1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.12 (1.06–1.18) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 5532/25,072 (22.06) | 174,491 | 31.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| Gout | 1892/8423 (22.46) | 56,046 | 33.80 | 5.20 (3.57–6.74) | 1.17 (1.11–1.23) | <0.001 * | 1.15 (1.09–1.21) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6631/33,692 (19.68) | 231,837 | 28.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Underweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 33/173 (19.08) | 913 | 36.10 | 7.00 (−4.72–18.78) | 1.20 (0.83–1.72) | 0.333 | 1.16 (0.81–1.68) | 0.420 |
| Control | 259/1508 (17.18) | 8896 | 29.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Normal weight | ||||||||
| Gout | 746/3395 (21.97) | 21,936 | 34.00 | 5.10 (2.71–7.60) | 1.16 (1.07–1.25) | <0.001 * | 1.13 (1.05–1.23) | 0.002 * |
| Control | 4014/20,146 (19.92) | 139,116 | 28.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Overweight | ||||||||
| Gout | 942/4067 (23.16) | 27,398 | 34.40 | 3.70 (1.33–5.99) | 1.11 (1.03–1.19) | 0.005 * | 1.08 (1.01–1.16) | 0.035 * |
| Control | 3584/16,689 (21.48) | 116,657 | 30.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Obese | ||||||||
| Gout | 1717/7056 (24.33) | 48,335 | 35.50 | 5.10 (3.29–6.96) | 1.16 (1.10–1.23) | <0.001 * | 1.15 (1.09–1.22) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 4306/20,421 (21.09) | 141,659 | 30.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Nonsmoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 1640/6226 (26.34) | 41,741 | 39.30 | 5.80 (3.81–7.80) | 1.29 (1.18 to 1.41) | <0.001 * | 1.29 (1.20 to 1.38) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 5592/24,436 (22.88) | 167,011 | 33.50 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Past and current smoker | ||||||||
| Gout | 1798/8465 (21.24) | 56,841 | 31.60 | 4.10 (2.64–5.71) | 1.17 (1.04 to 1.32) | 0.011 * | 1.19 (1.08 to 1.32) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6571/34,328 (19.14) | 239,317 | 27.50 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption < 1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 1642/6931 (23.69) | 46,053 | 35.70 | 3.80 (1.93–5.56) | 1.31 (1.20 to 1.43) | <0.001 * | 1.26 (1.18 to 1.35) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6970/31,880 (21.86) | 218,420 | 31.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alcohol consumption ≥ 1 time a week | ||||||||
| Gout | 1796/7760 (23.14) | 52,529 | 34.20 | 6.60 (4.91–8.20) | 1.22 (1.07 to 1.38) | 0.002 * | 1.23 (1.11 to 1.38) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 5193/26,884 (19.32) | 187,908 | 27.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP < 120 mmHg and DBP < 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 2102/9496 (22.14) | 60,258 | 34.90 | 5.00 (3.40–6.48) | 1.15 (1.10–1.21) | <0.001 * | 1.05 (1.00–1.10) | 0.050 |
| Control | 8497/42,344 (20.07) | 283,778 | 29.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| SBP ≥ 120 mmHg or DBP ≥ 80 mmHg | ||||||||
| Gout | 1336/5195 (25.72) | 38,324 | 34.90 | 5.00 (2.92–6.97) | 1.16 (1.09–1.24) | <0.001 * | 1.01 (0.94–1.07) | 0.876 |
| Control | 3666/16,420 (22.33) | 122,550 | 29.90 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose < 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 1988/8084 (24.59) | 57,414 | 34.60 | 4.40 (2.81–6.02) | 1.14 (1.08–1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.04 (0.99–1.09) | 0.166 |
| Control | 7348/33,244 (22.10) | 243,229 | 30.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Fasting blood glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 1450/6607 (21.95) | 41,168 | 35.20 | 5.70 (3.81–7.59) | 1.18 (1.12–1.25) | <0.001 * | 1.02 (0.96–1.08) | 0.567 |
| Control | 4815/25,520 (18.87) | 163,099 | 29.50 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 1779/7761 (22.92) | 49,680 | 35.80 | 5.20 (3.51–6.96) | 1.16 (1.10–1.22) | <0.001 * | 1.01 (0.96–1.07) | 0.663 |
| Control | 6875/33,582 (20.47) | 224,898 | 30.60 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL | ||||||||
| Gout | 1659/6930 (23.94) | 48,902 | 33.90 | 4.80 (3.04–6.51) | 1.16 (1.09–1.22) | <0.001 * | 1.05 (0.99–1.11) | 0.114 |
| Control | 5288/25,182 (21.00) | 181,430 | 29.10 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI scores = 0 | ||||||||
| Gout | 1682/8225 (20.45) | 56,651 | 29.70 | 3.50 (2.04–5.01) | 1.14 (1.07–1.20) | <0.001 * | 1.12 (1.06–1.18) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 6851/36,407 (18.82) | 261,857 | 26.20 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI scores = 1 | ||||||||
| Gout | 620/2410 (25.73) | 16,241 | 38.20 | 4.50 (1.24–7.70) | 1.17 (1.11–1.23) | <0.001 * | 1.15 (1.09–1.21) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 2029/8778 (23.11) | 60,200 | 33.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CCI scores ≥ 2 | ||||||||
| Gout | 1136/4056 (28.01) | 25,690 | 44.20 | 5.20 (2.46–8.06) | 1.13 (1.06–1.21) | <0.001 * | 0.98 (0.91–1.05) | 0.485 |
| Control | 3283/13,579 (24.18) | 84,271 | 39.00 | 1 | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, W.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Kwon, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.Y. Increased Risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010055
Bang WJ, Choi HG, Kang HS, Kwon MJ, Kim JH, Kim J-H, Kim SY. Increased Risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Woo Jin, Hyo Geun Choi, Ho Suk Kang, Mi Jung Kwon, Ji Hee Kim, Joo-Hee Kim, and So Young Kim. 2024. "Increased Risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort" Diagnostics 14, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010055
APA StyleBang, W. J., Choi, H. G., Kang, H. S., Kwon, M. J., Kim, J. H., Kim, J.-H., & Kim, S. Y. (2024). Increased Risk of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) in Patients with Gout: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Diagnostics, 14(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010055






