Combined Rotating Ultra-High-Resolution Spectral Domain OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging for In Vivo Corneal Optical Biopsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Scheimpflug Imaging
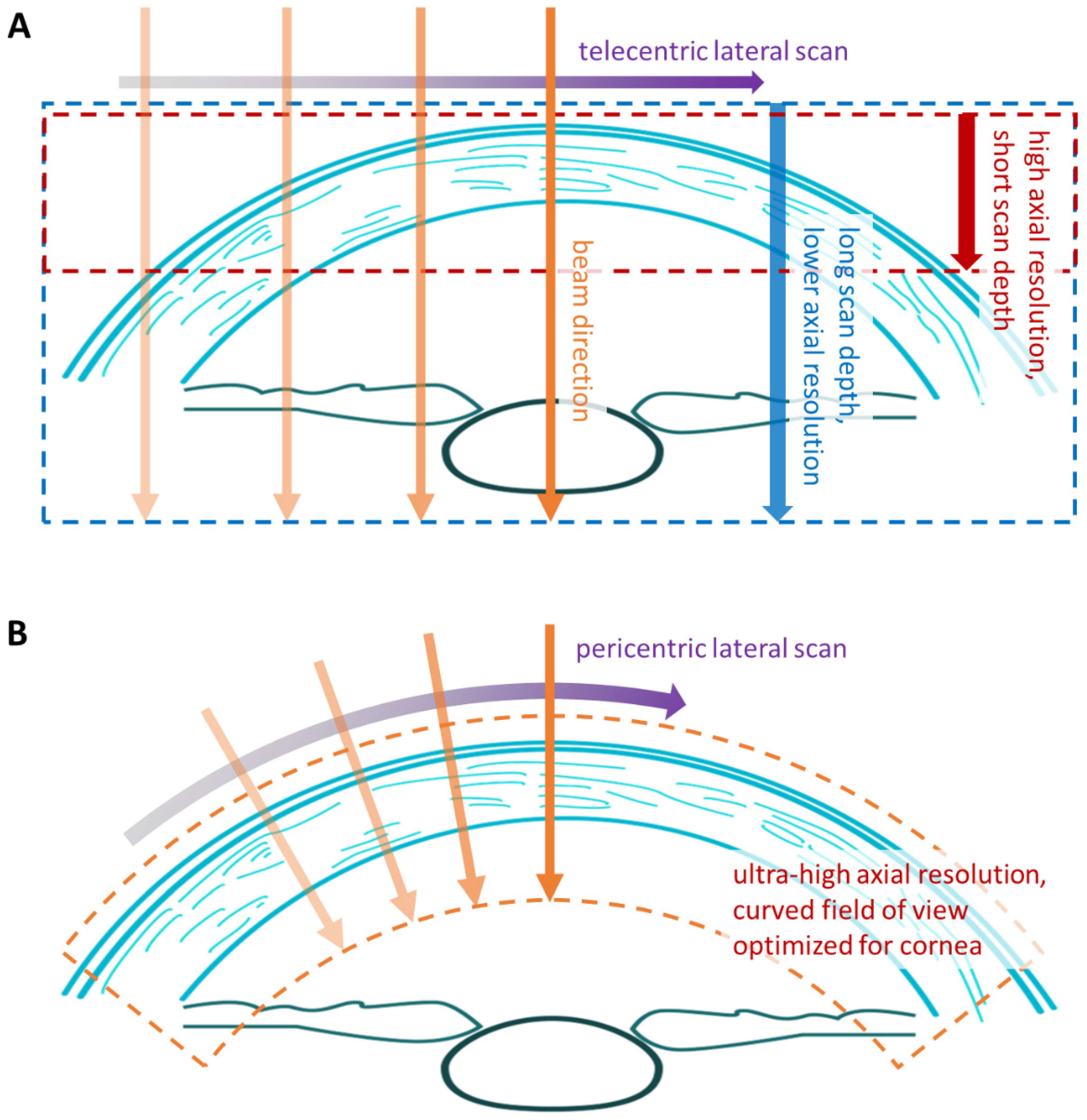
1.2. Optical Coherence Tomography
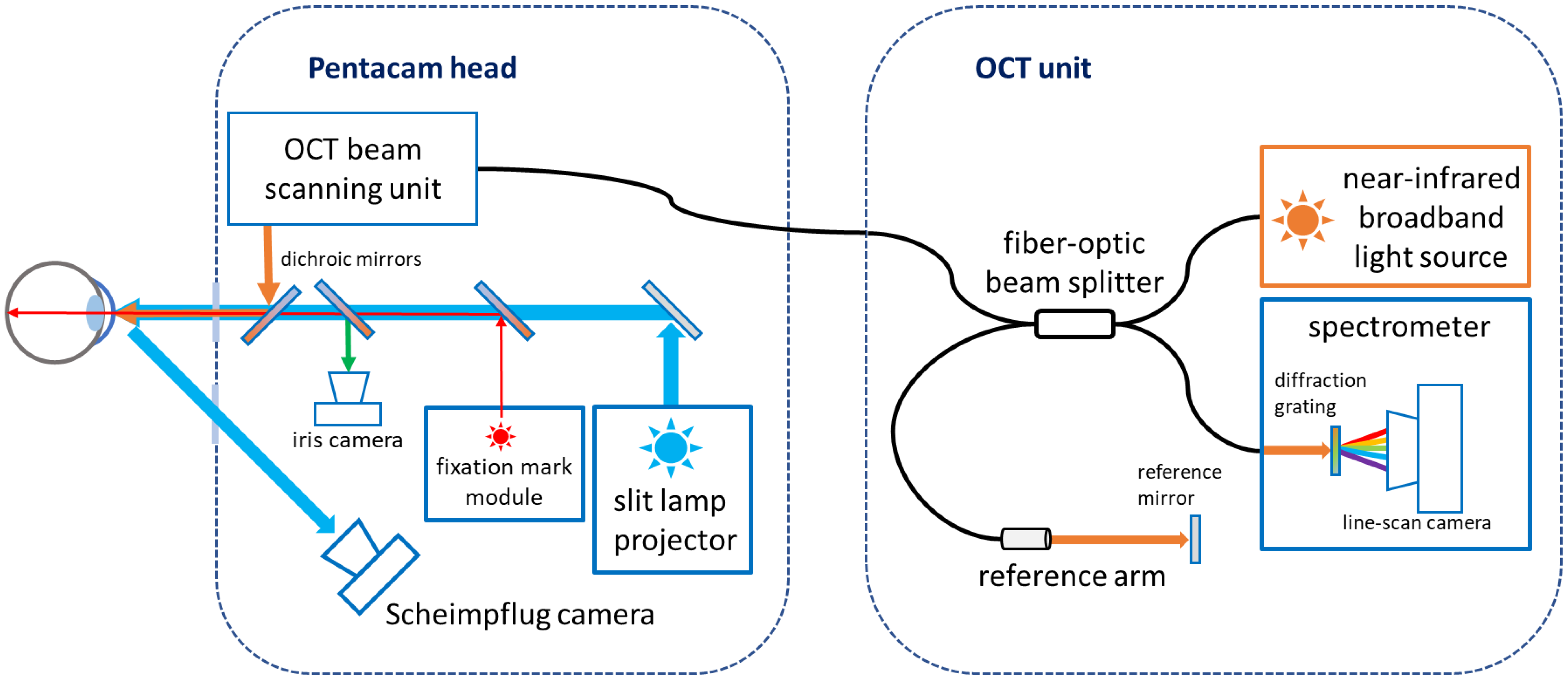
1.3. The Pentacam® Cornea OCT
2. Materials and Methods
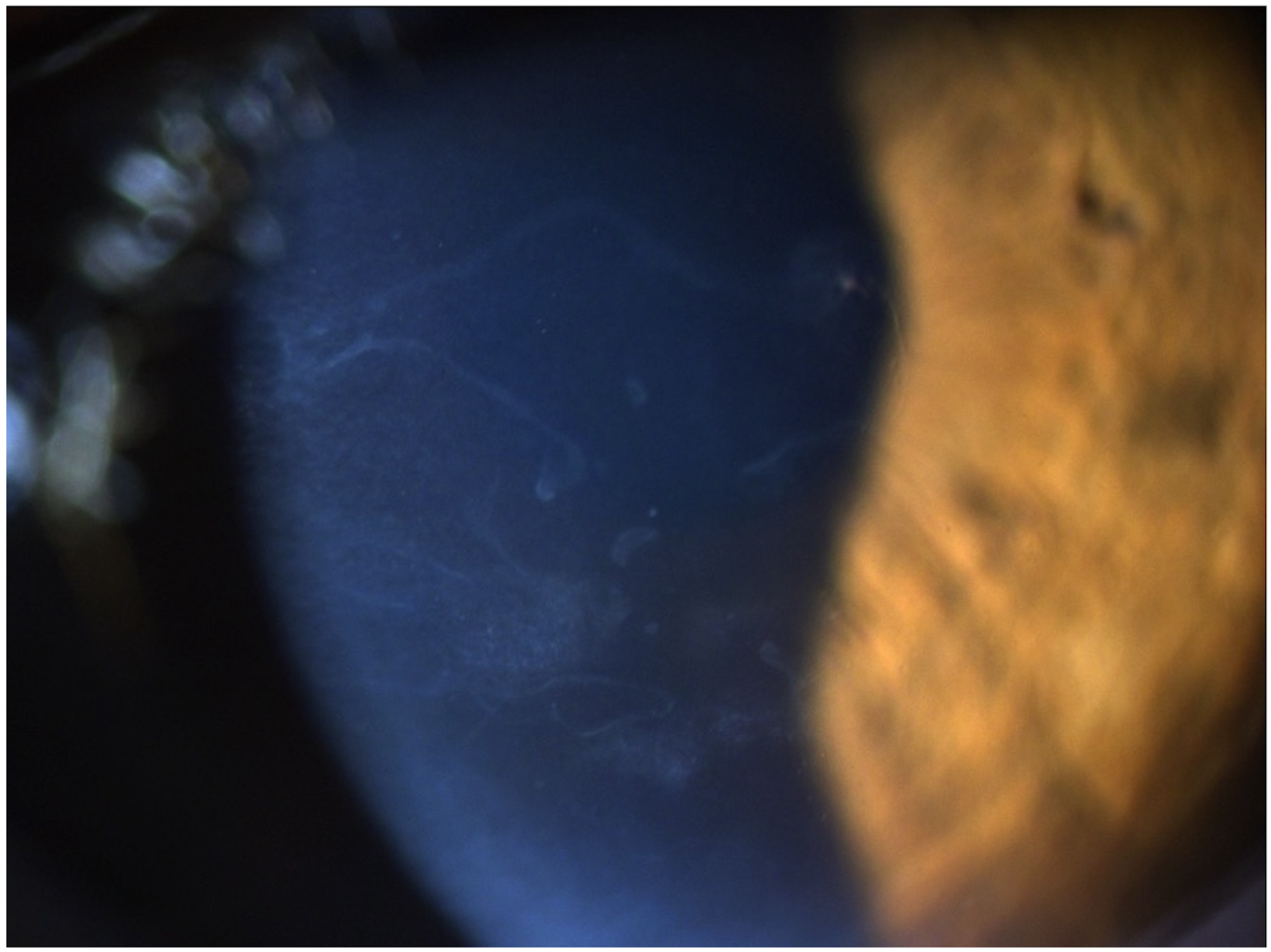
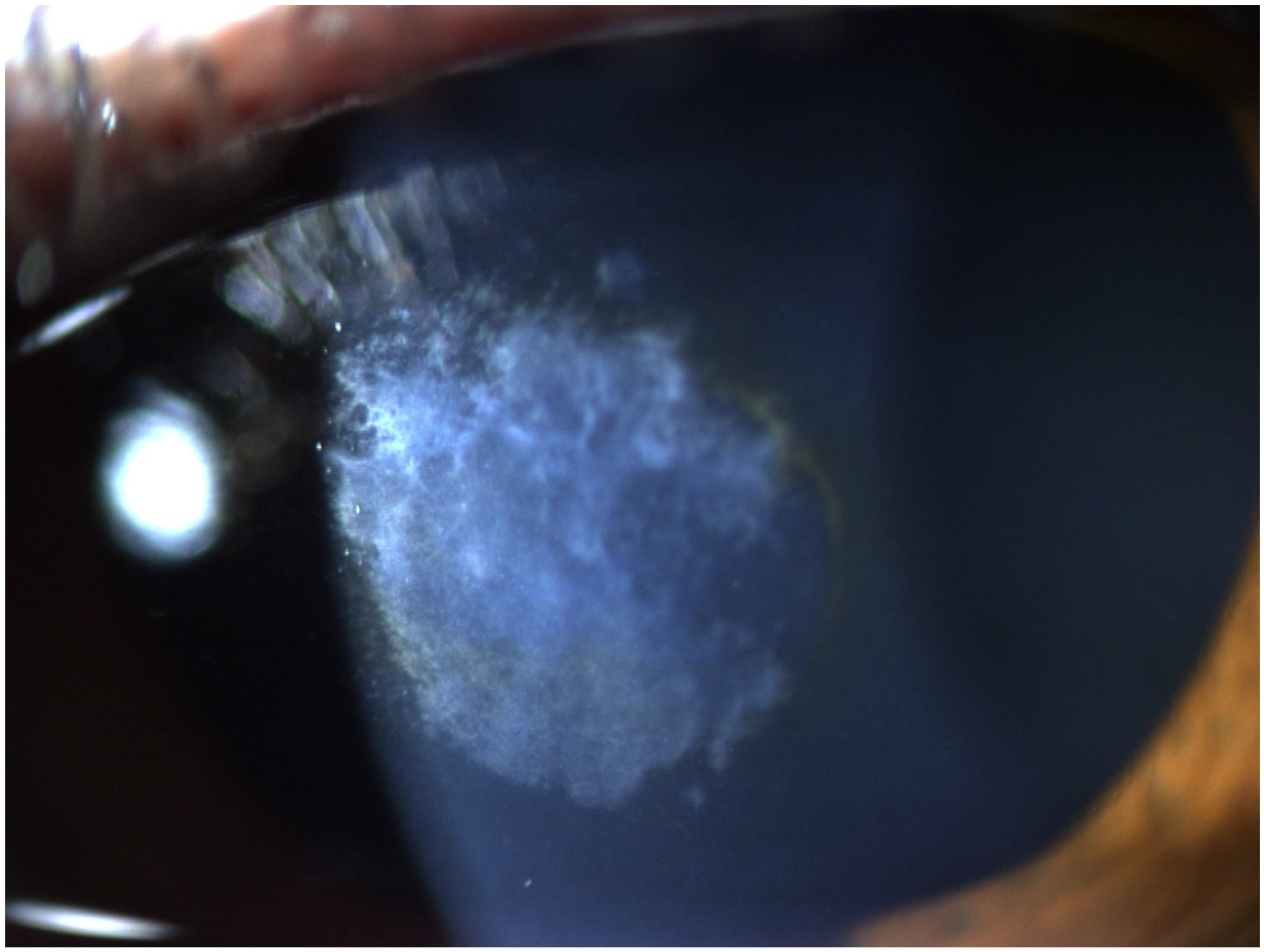
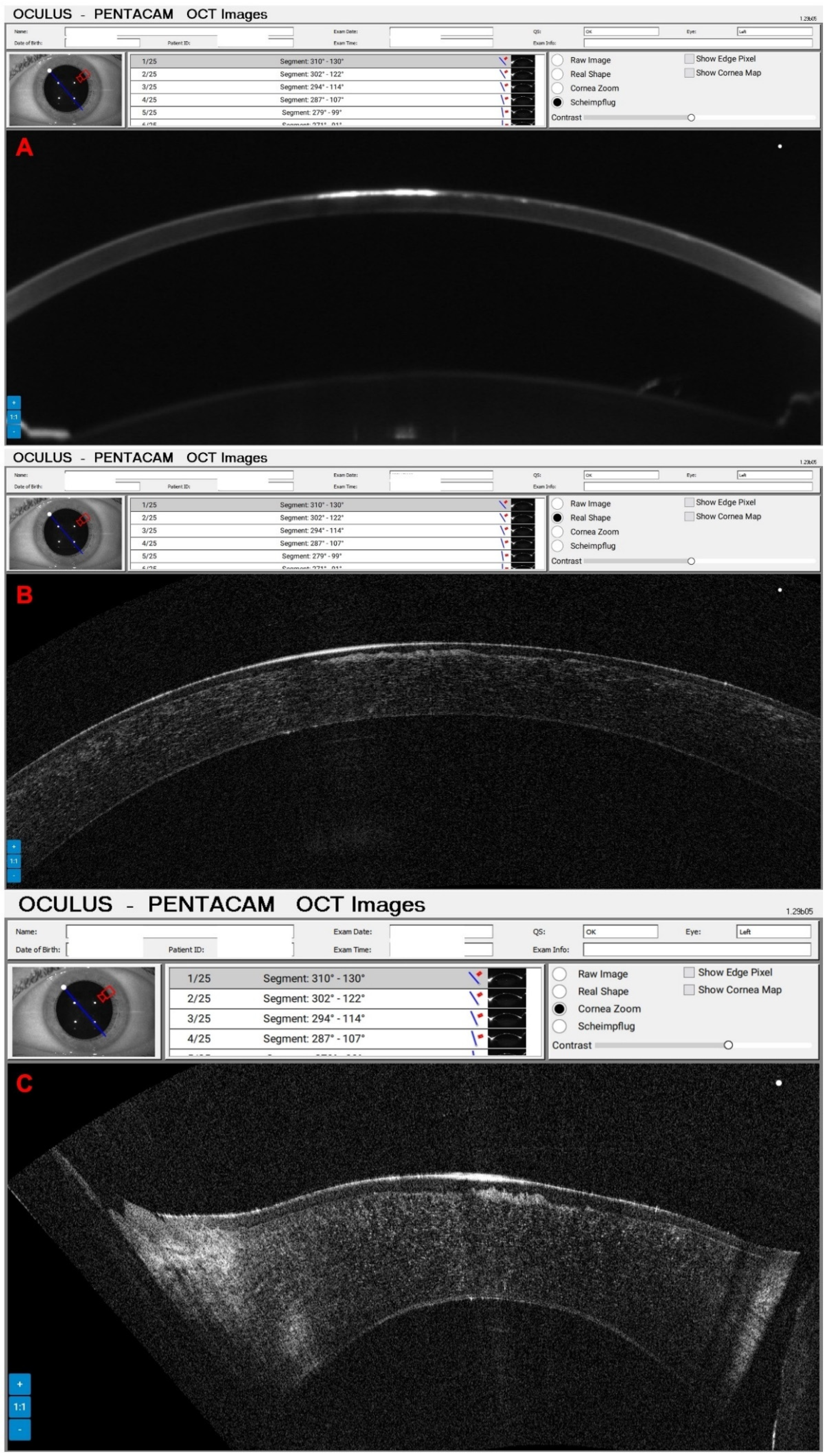
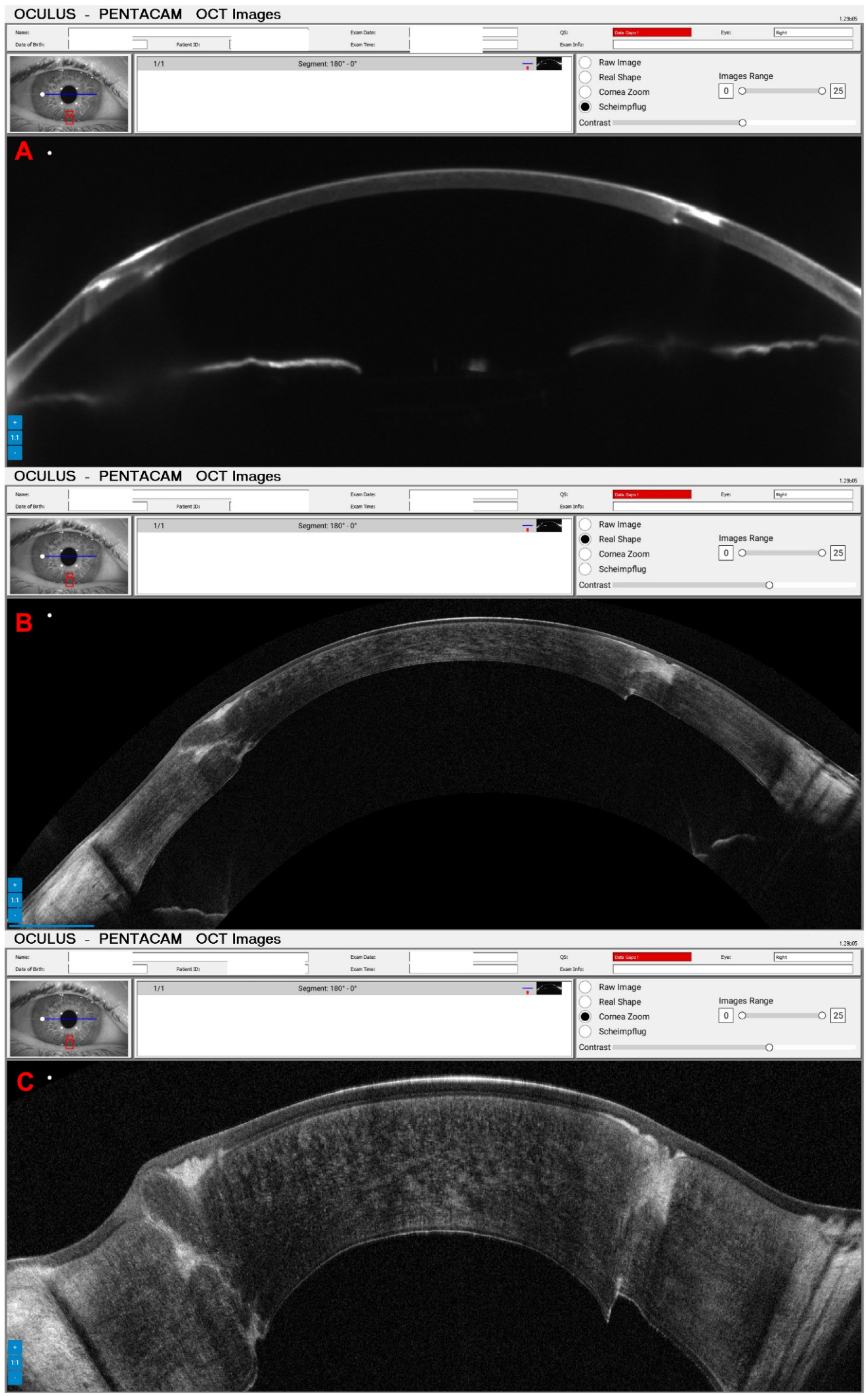
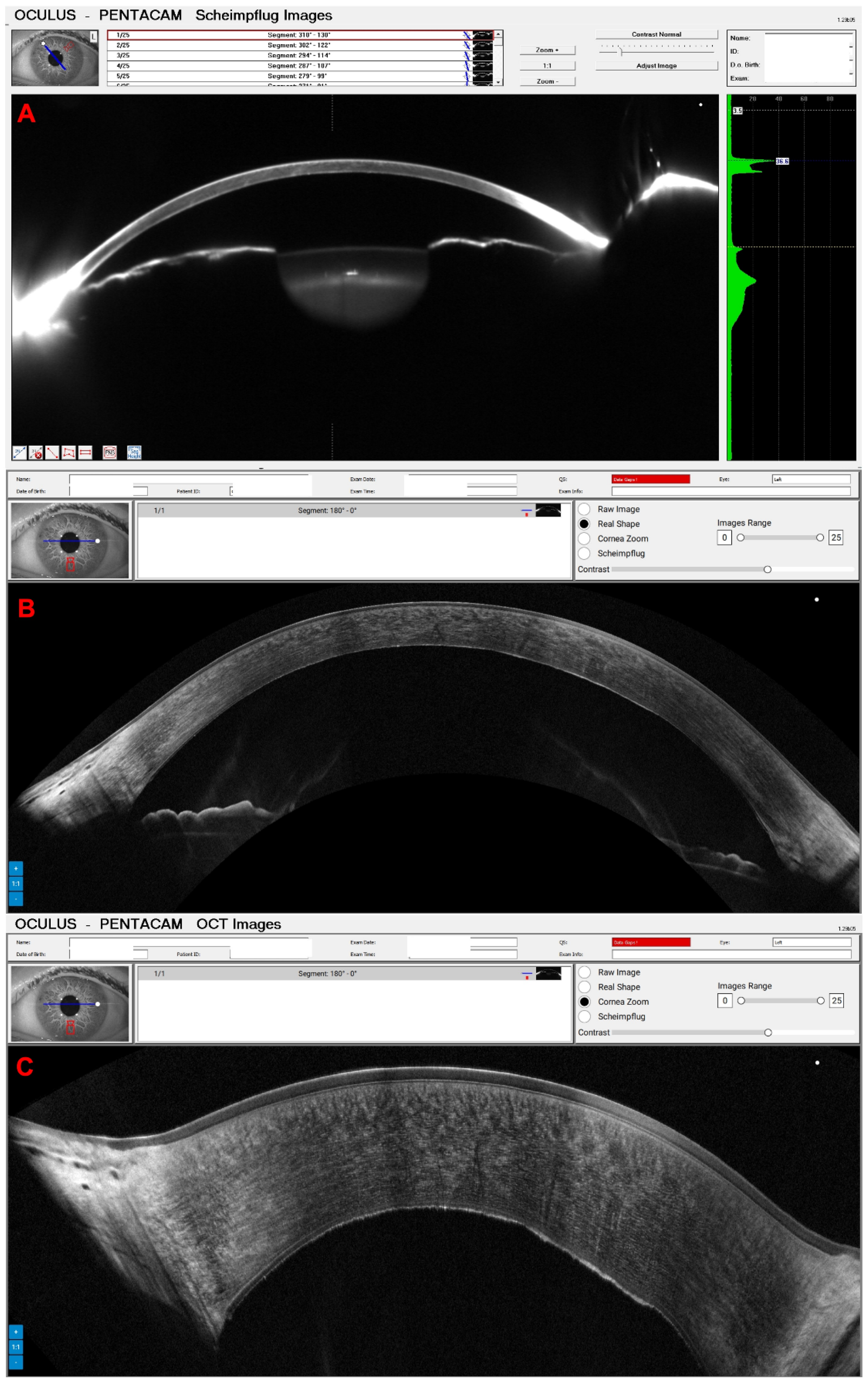
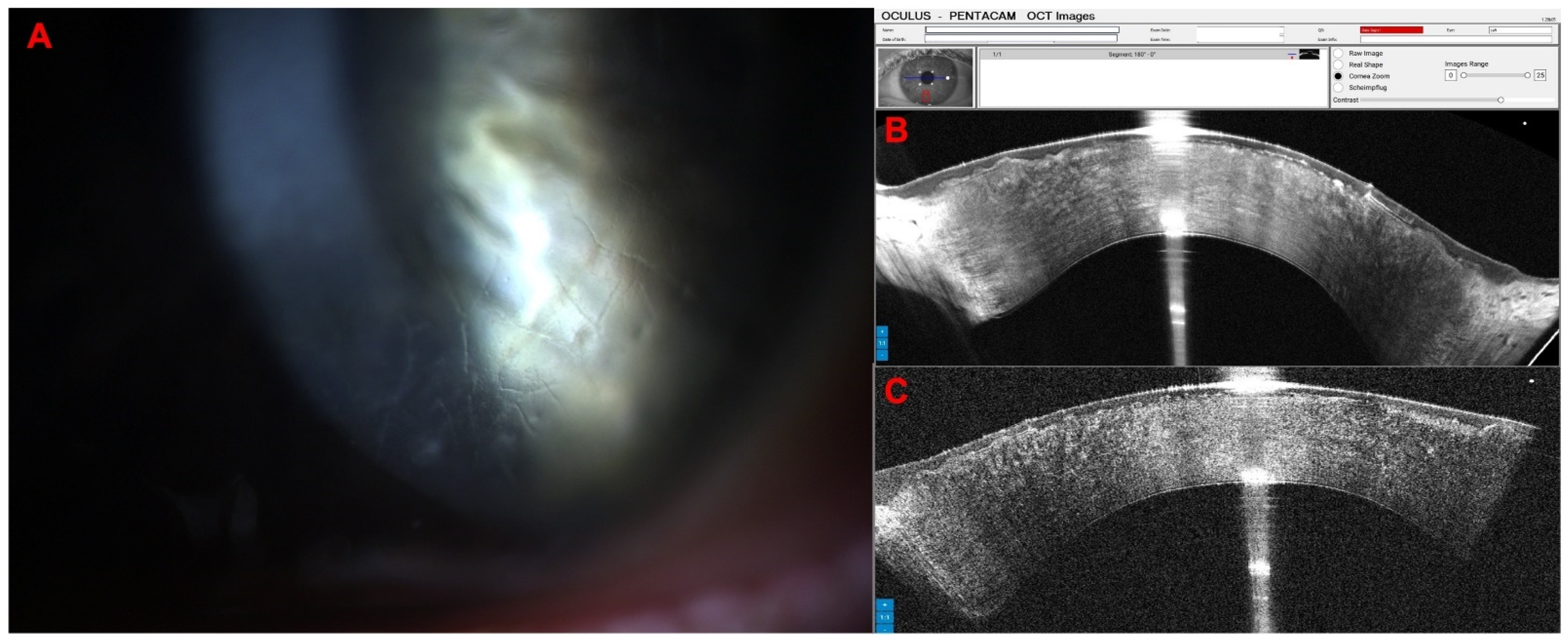
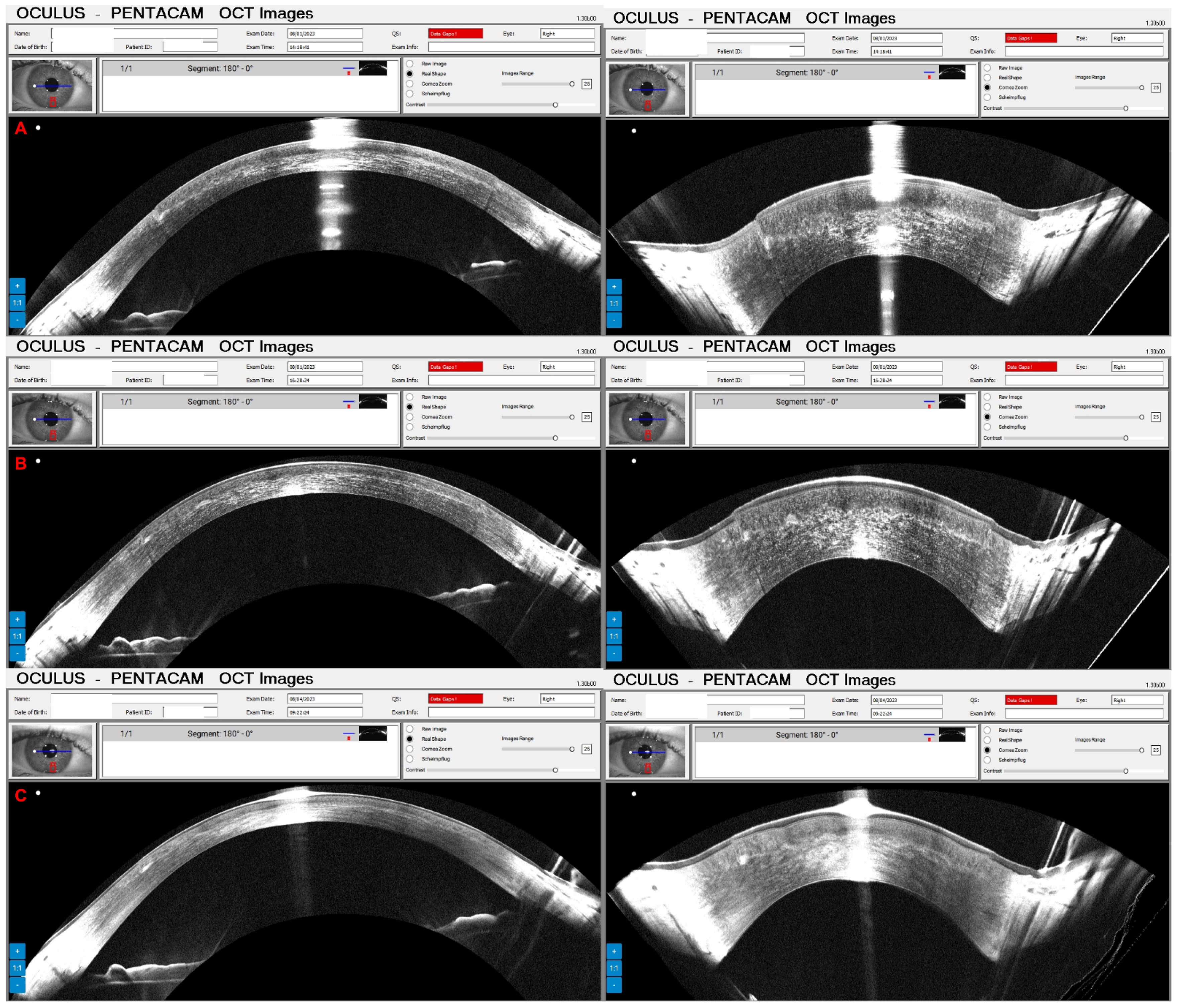
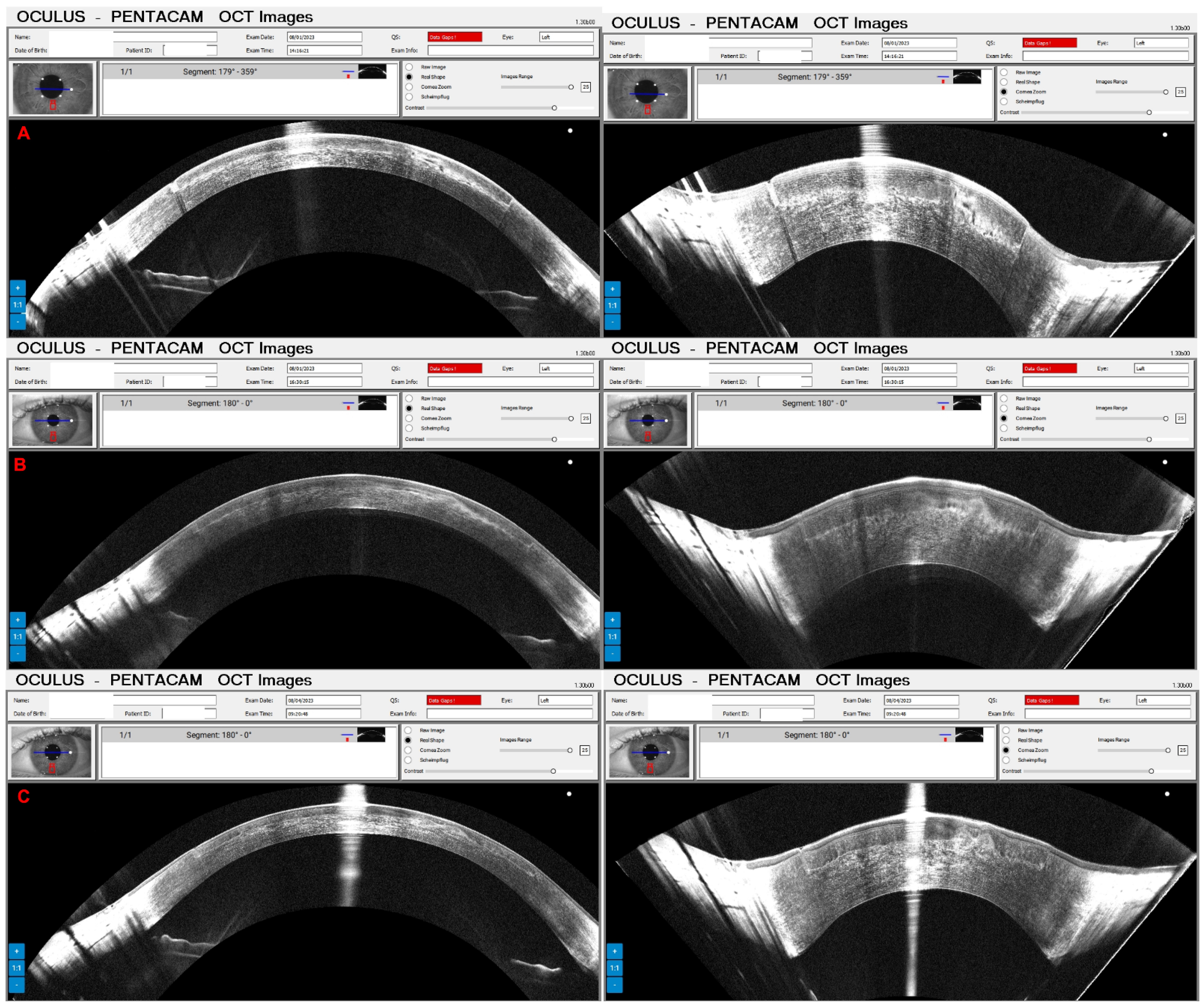
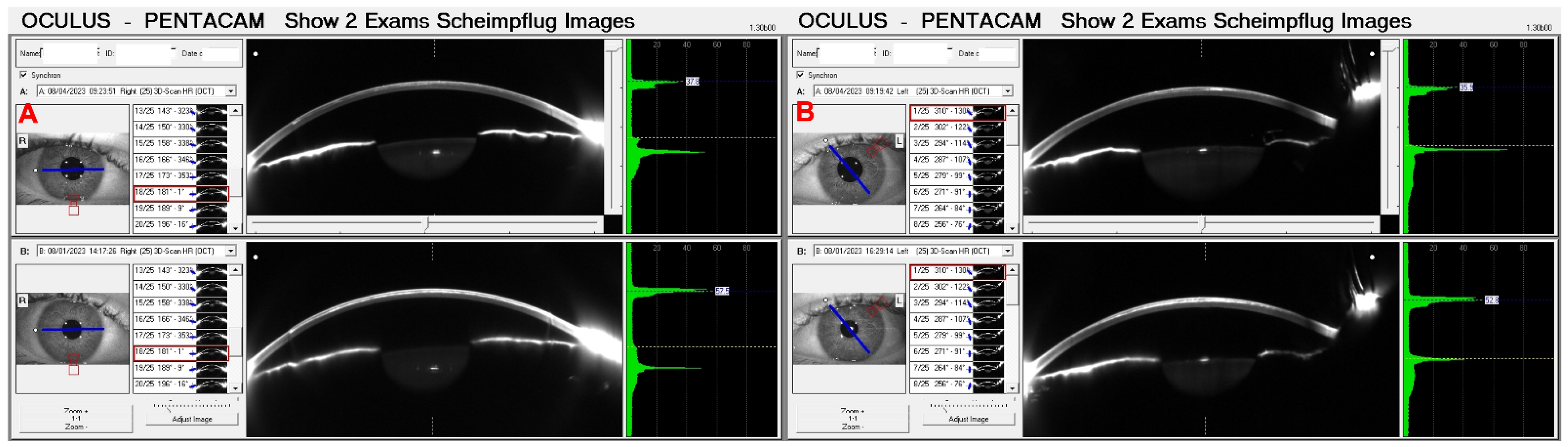
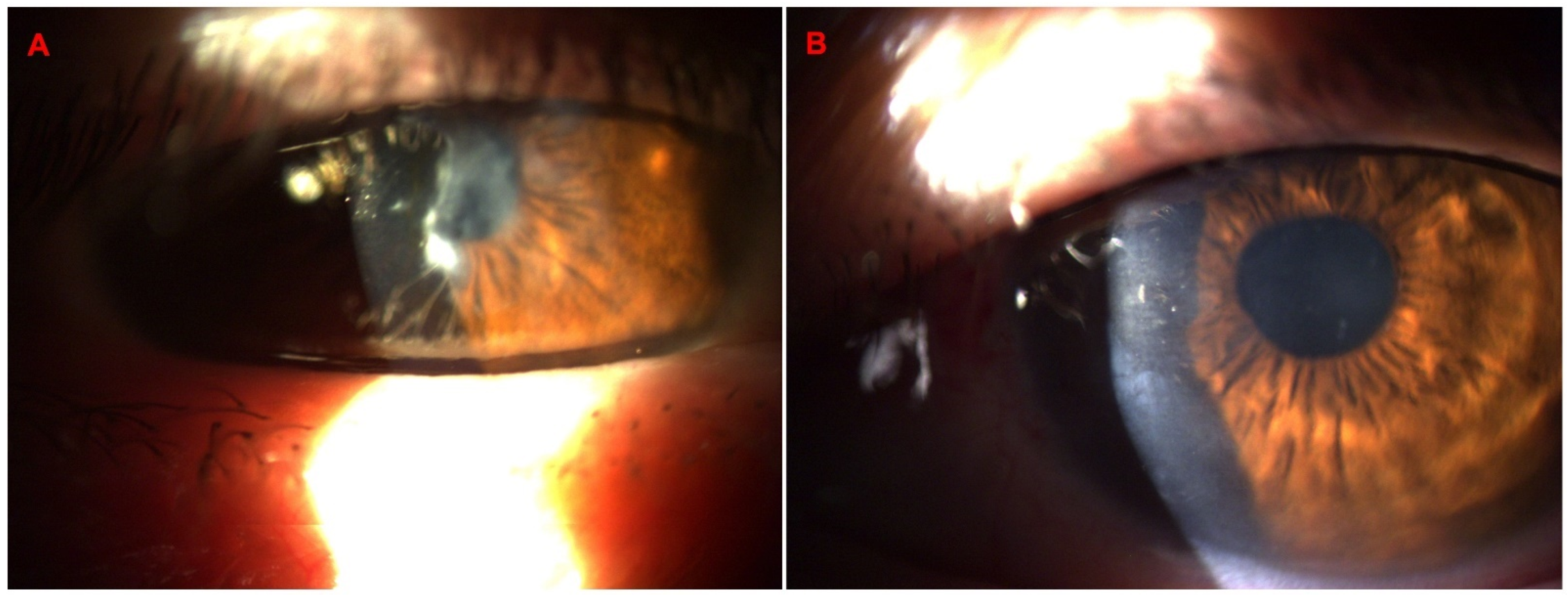
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujimoto, J.; Swanson, E. The development, commercialization, and impact of Optical Coherence Tomography–history of optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, OCT1–OCT13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, J.G.; Brezinski, M.E.; Tearney, G.J.; Boppart, S.A.; Bouma, B.; Hee, M.R.; Southern, J.F.; Swanson, E.A. Optical biopsy and imaging using optical coherence tomography. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, E.S.; Perez-Straziota, C.E.; Kim, S.W.; Santhiago, M.R.; Randleman, J.B. Distinguishing Highly Asymmetric Keratoconus Eyes Using Combined Scheimpflug and Spectral-Domain OCT Analysis. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.J.; Ruiz-Oblitas, L.; Munuera, J.M.; Aliseda, D.; Garcia-Layana, A.; Moreno-Montanes, J. Optical coherence tomography evaluation of the corneal cap and stromal bed features after laser in situ keratomileusis for high myopia and astigmatism. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 81–87; discussion 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, T.; Quurke, A.W. Iatrogenic keratectasia after LASIK in a case of forme fruste keratoconus. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 1998, 24, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Randleman, J.B. Screening for ectasia risk: What are we screening for and how should we screen for it? J. Refract. Surg. 2013, 29, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohac, M.; Koncarevic, M.; Pasalic, A.; Biscevic, A.; Merlak, M.; Gabric, N.; Patel, S. Incidence and Clinical Characteristics of Post LASIK Ectasia: A Review of over 30,000 LASIK Cases. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 33, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, A.; Lopes, B.; Hallahan, K.M.; Valbon, B.; Ramos, I.; Faria-Correia, F.; Schor, P.; Dupps, W.J.; Ambrósio, R. Enhanced Combined Tomography and Biomechanics Data for Distinguishing Forme Fruste Keratoconus. J. Refract. Surg. 2016, 32, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, M.W.; Duncan, J.K. Keratoconus: The ABCD Grading System. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2016, 233, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Salomão, M.Q.; Barros, L.; Guedes, J.; Neto, A.; Machado, A.P.; Lopes, B.T.; Sena, N., Jr.; Esporcatte, L.P.G. Multimodal diagnostics for keratoconus and ectatic corneal diseases: A paradigm shift. Eye Vis. 2023, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esporcatte, L.P.G.; Salomao, M.Q.; Neto, A.; Machado, A.P.; Lopes, B.T.; Ambrosio, R., Jr. Enhanced Diagnostics for Corneal Ectatic Diseases: The Whats, the Whys, and the Hows. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S.; McDonnell, P.J. Computer-assisted corneal topography in keratoconus. Refract. Corneal Surg. 1989, 5, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.R.; Epstein, R.J.; Randleman, J.B.; Stulting, R.D. Corneal ectasia after laser in situ keratomileusis in patients without apparent preoperative risk factors. Cornea 2006, 25, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Alonso, R.S.; Luz, A.; Velarde, L.G.C. Corneal-thickness spatial profile and corneal-volume distribution: Tomographic indices to detect keratoconus. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinstein, D.Z.; Silverman, R.H.; Rondeau, M.J.; Coleman, D.J. Epithelial and corneal thickness measurements by high-frequency ultrasound digital signal processing. Ophthalmology 1994, 101, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomão, M.Q.; Hofling-Lima, A.L.; Esporcatte, L.P.G.; Correa, F.F.; Meneses, E.F.; Li, Y.; Huang, D.; Lopes, B.; Sena, N., Jr.; Machado, A.P.; et al. Corneal Ectasia detection by epithelium pattern standard deviation from optical coherence tomography. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 49, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinstein, D.Z.; Archer, T.J.; Urs, R.; Gobbe, M.; RoyChoudhury, A.; Silverman, R.H. Detection of Keratoconus in Clinically and Algorithmically Topographically Normal Fellow Eyes Using Epithelial Thickness Analysis. J. Refract. Surg. 2015, 31, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tan, O.; Brass, R.; Weiss, J.L.; Huang, D. Corneal epithelial thickness mapping by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography in normal and keratoconic eyes. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chamberlain, W.; Tan, O.; Brass, R.; Weiss, J.L.; Huang, D. Subclinical keratoconus detection by pattern analysis of corneal and epithelial thickness maps with optical coherence tomography. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, B.T.; Ramos, I.C.; Salomao, M.Q.; Guerra, F.P.; Schallhorn, S.C.; Schallhorn, J.M.; Vinciguerra, R.; Vinciguerra, P.; Price, F.W., Jr.; Price, M.O.; et al. Enhanced Tomographic Assessment to Detect Corneal Ectasia Based on Artificial Intelligence. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 195, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalia, H.; Francis, M.; Gangil, T.; Chandapura, R.S.; Kurian, M.; Shetty, R.; Nelson, E.J.R.; Roy, A.S. Noncontact Quantification of Topography of Anterior Corneal Surface Bowman’s Layer with High-Speed, O.C.T. J. Refract. Surg. 2017, 33, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, J. Appareil de Projection Cinématographique. French Patent No. 324,823, 22 November 1901. [Google Scholar]
- Scheimplug, T. Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Photographischen Bildern und Karten. Austrian Patent No. 69,237, 23 March 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, A.; Laser-Junga, H. Photography of the anterior eye segment according to Scheimpflug’s principle: Options and limitations—A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; DeBoer, C.; Xu, B.Y. Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography: Applications for Clinical Care and Scientific Research. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 146–157. [Google Scholar]
- Leitgeb, R.A.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F.; Bajraszewski, T. Phase-shifting algorithm to achieve high-speed long-depth-range probing by frequency-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 2201–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, W.; Biedermann, B.R.; Klein, T.; Eigenwillig, C.M.; Huber, R. Multi-megahertz OCT: High quality 3D imaging at 20 million A-scans and 4.5 GVoxels per second. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 14685–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, V.; Potsaid, B.; Jiang, J.; Cole, G.D.; Robertson, M.E.; Burgner, C.B.; John, D.D.; Grulkowski, I.; Choi, W.; Tsai, T.H.; et al. High-speed ultra-broad tuning MEMS-VCSELs for imaging and spectroscopy. Smart Sens. Actuators MEMS VI 2013, 8763, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Grulkowski, I.; Liu, J.J.; Potsaid, B.; Jayaraman, V.; Lu, C.D.; Jiang, J.; Cable, A.E.; Duker, J.S.; Fujimoto, J.G. Retinal, anterior segment and full eye imaging using ultrahigh speed swept source OCT with vertical-cavity surface emitting lasers. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 2733–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povazay, B.; Bizheva, K.; Unterhuber, A.; Hermann, B.; Sattmann, H.; Fercher, A.F.; Drexler, W.; Apolonski, A.; Wadsworth, W.J.; Knight, J.C.; et al. Submicrometer axial resolution optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 1800–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizheva, K.; Tan, B.; MacLelan, B.; Kralj, O.; Hajialamdari, M.; Hileeto, D.; Sorbara, L. Sub-micrometer axial resolution OCT for in-vivo imaging of the cellular structure of healthy and keratoconic human corneas. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuk, T. The wavelength dependence of scattered light intensity in rabbit corneas. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1971, BME-18, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, T.; Tan, K. Light transmittance of the human cornea from 320 to 700 nm for different ages. Vis. Res. 1994, 34, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lawman, S.; Williams, B.M.; Ye, S.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous optical coherence tomography and Scheimpflug imaging using the same incident light. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 39660–39676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; A., Z.; Awman, S.L.; Li, X. Inventor Imaging Device. US2023.
- Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Machado, A.P.; Leao, E.; Lyra, J.M.G.; Salomão, M.Q.; Esporcatte, L.G.P.; da Fonseca Filho, J.B.; Ferreira-Meneses, E.; Sena, N.B., Jr.; Haddad, J.S.; et al. Optimized Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Ectasia Detection Using Scheimpflug-Based Corneal Tomography and Biomechanical Data. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 251, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ambrósio Jr., R.; Esporcatte, L.P.G.; de Carvalho, K.A.; Salomão, M.Q.; Pereira-Souza, A.L.; Lopes, B.T.; Machado, A.P.; Marschall, S. Combined Rotating Ultra-High-Resolution Spectral Domain OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging for In Vivo Corneal Optical Biopsy. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131455
Ambrósio Jr. R, Esporcatte LPG, de Carvalho KA, Salomão MQ, Pereira-Souza AL, Lopes BT, Machado AP, Marschall S. Combined Rotating Ultra-High-Resolution Spectral Domain OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging for In Vivo Corneal Optical Biopsy. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(13):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131455
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmbrósio Jr., Renato, Louise Pellegrino G. Esporcatte, Karolyna Andrade de Carvalho, Marcella Q. Salomão, Amanda Luiza Pereira-Souza, Bernardo T. Lopes, Aydano P. Machado, and Sebastian Marschall. 2024. "Combined Rotating Ultra-High-Resolution Spectral Domain OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging for In Vivo Corneal Optical Biopsy" Diagnostics 14, no. 13: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131455
APA StyleAmbrósio Jr., R., Esporcatte, L. P. G., de Carvalho, K. A., Salomão, M. Q., Pereira-Souza, A. L., Lopes, B. T., Machado, A. P., & Marschall, S. (2024). Combined Rotating Ultra-High-Resolution Spectral Domain OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging for In Vivo Corneal Optical Biopsy. Diagnostics, 14(13), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14131455




