Identification of a New and Effective Marker Combination for a Standardized and Automated Bin-Based Basophil Activation Test (BAT) Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Approval, Data Sets and Study Populations
2.2. Flow Cytometric Instruments and Antibodies
2.3. Basophil Activation Test
2.4. Manual Flow Cytometry Data Analysis
2.5. Development of an Automated BAT Analysis Tool Using the PRI Approach
- Pregating:
- Basophil identification:
- User-friendly result output:
2.6. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
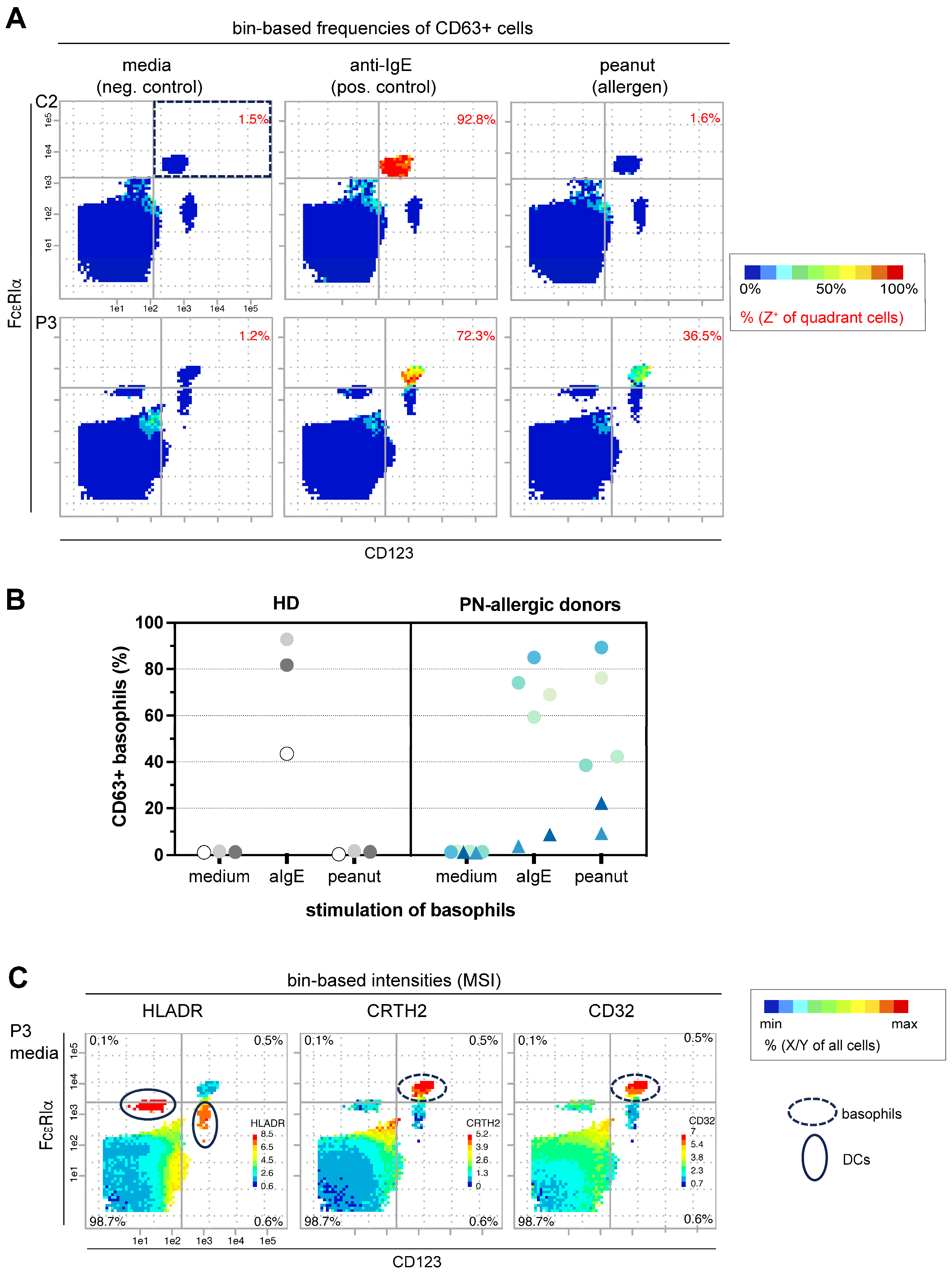
3.1. Re-Analysis of Mass Cytometry Data Sets Discovered a Useful New Marker Combination for BAT
3.1.1. PRI-Based Identification of the Best Basophile Identification Marker Combination
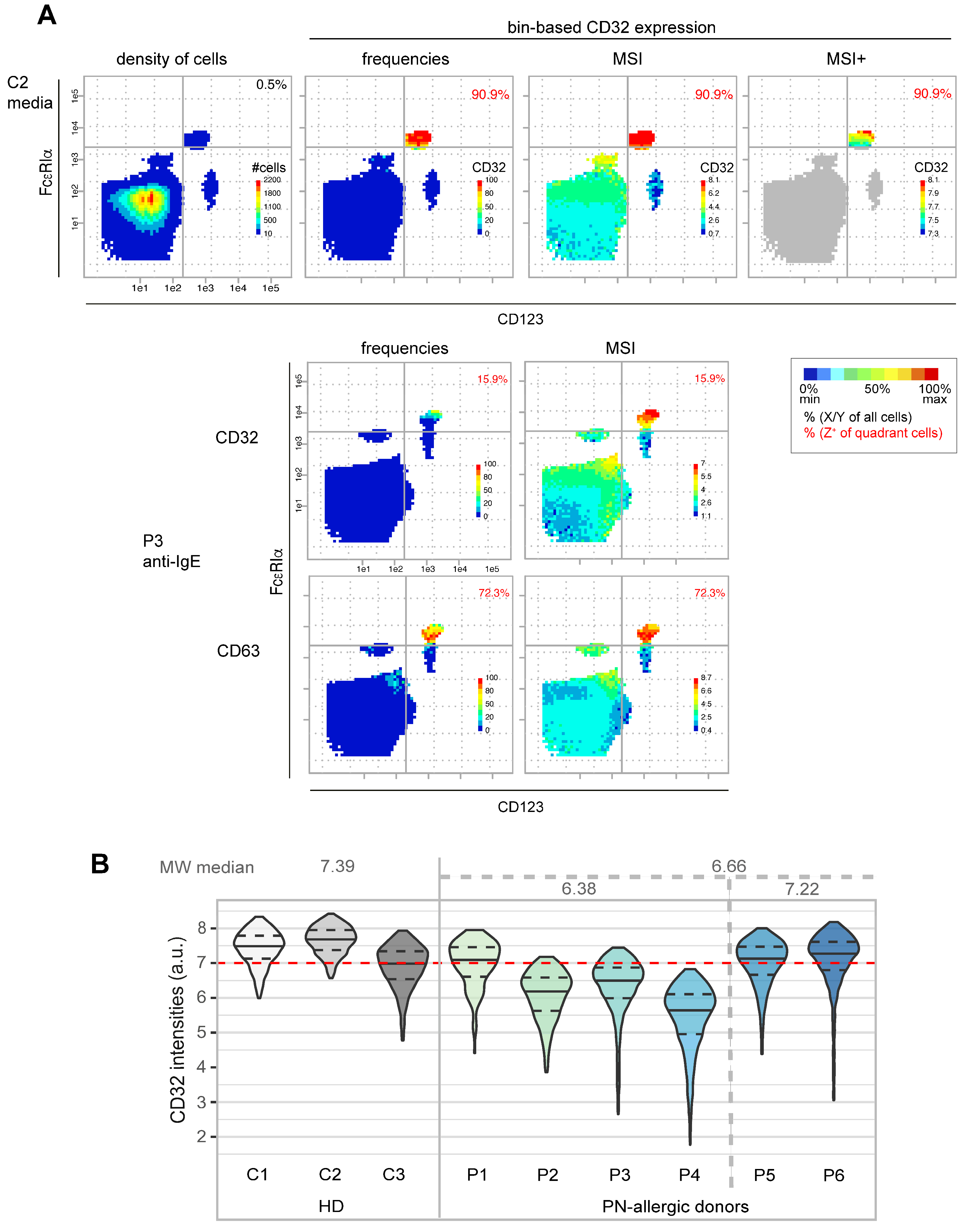
3.1.2. Characterization of CD32 Expression in Basophils
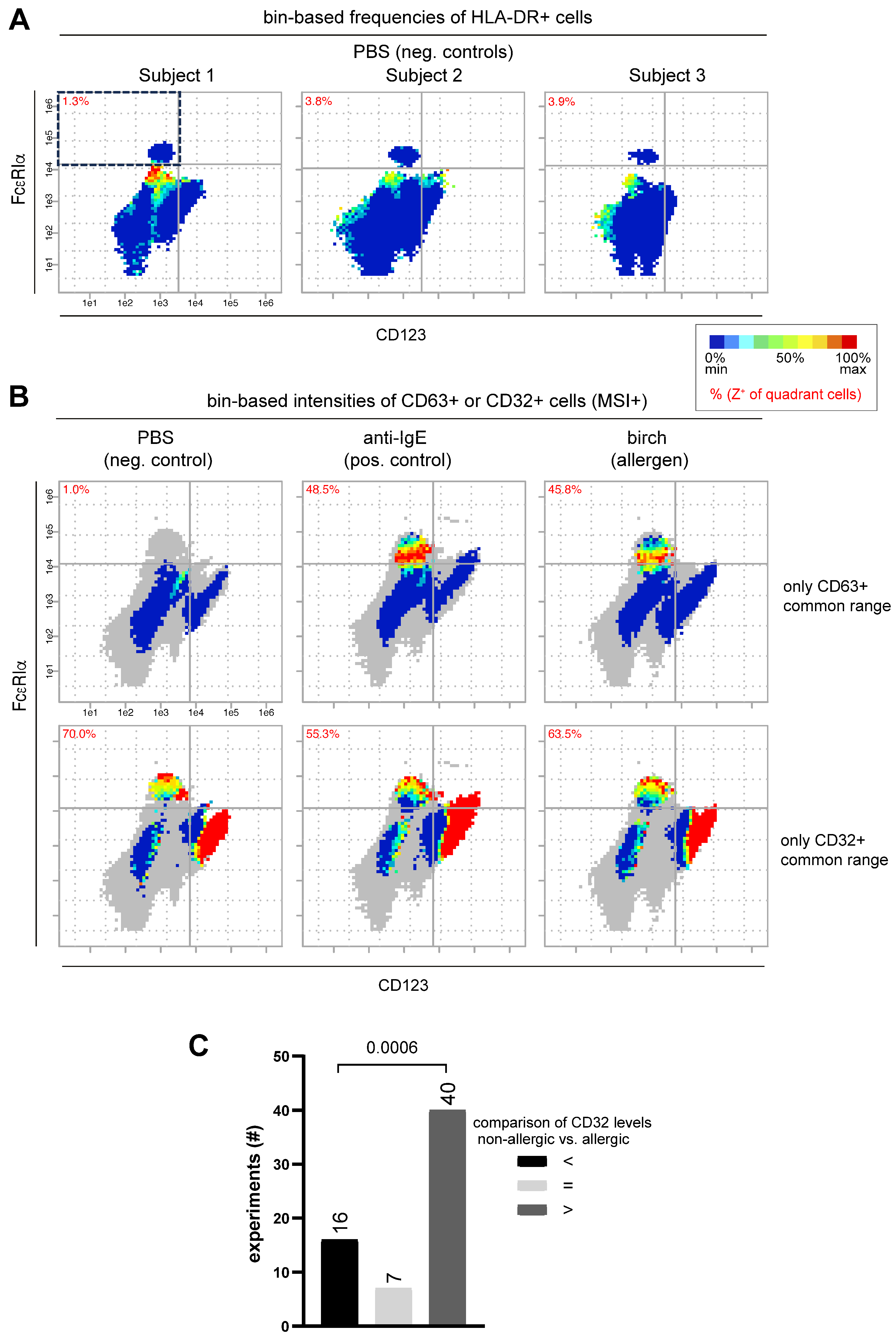
3.2. Own Flow Cytometry Data Validate Re-Analyzed Mass Cytometry Results
3.2.1. New Marker Combination Confirms Its Potential in Bin-Based BAT Analysis
3.2.2. Flow Cytometry Data Confirms Correlation of CD32, FcεRIα and CD63 Expression Patterns on Basophils
3.2.3. Tendency of Higher CD32 Expression Values on Basophils from Non-Allergic Patients Compared to Allergic Patients
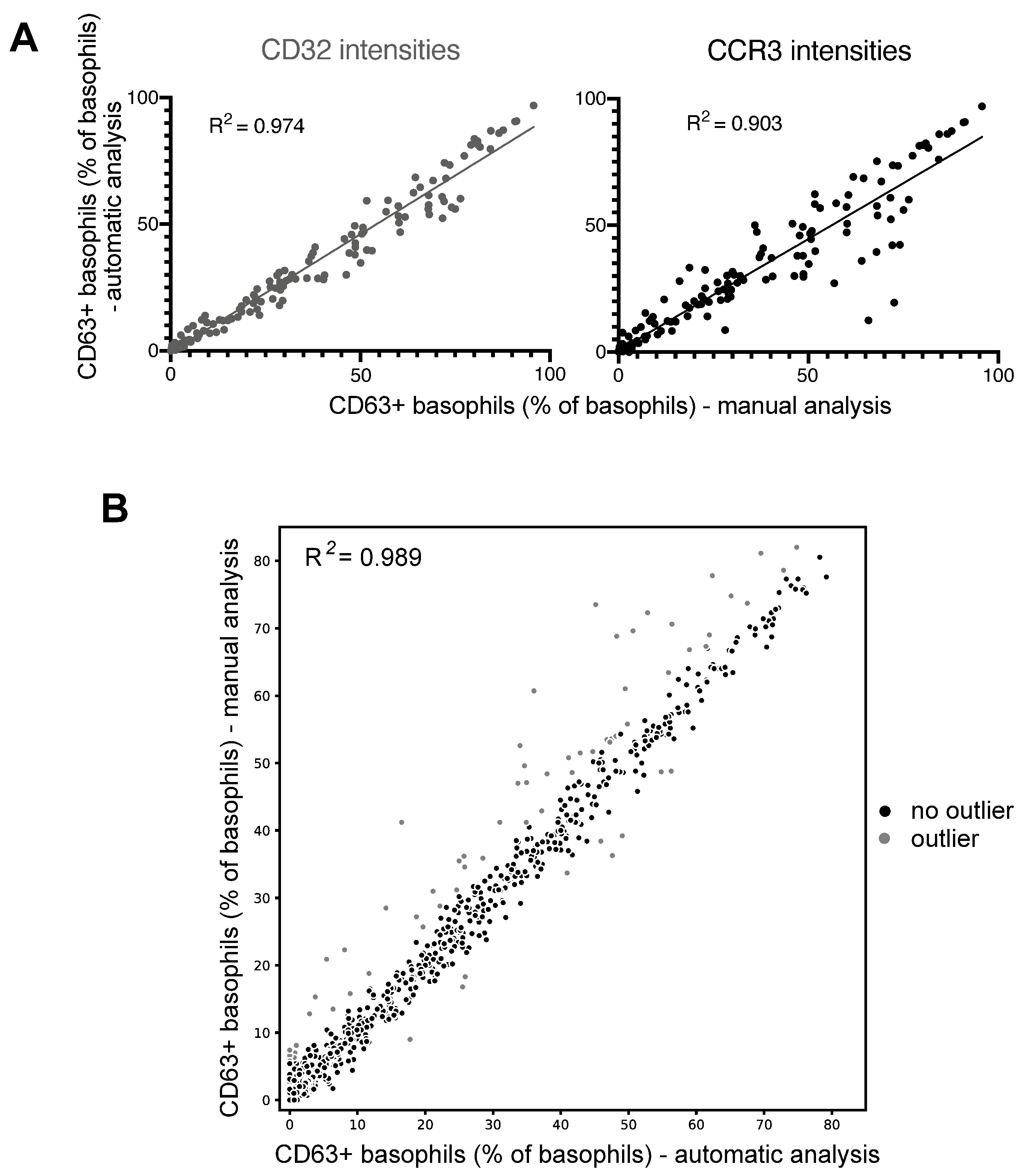
3.3. Successful Automation of BAT Analyses Using PRI Approach
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EACCI. Advocacy Manifesto—Tackling the Allergy Crisis in Europe Concerted Policy Action Needed; European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology—EU Liaison Office: Brussles, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vella, A.; Bjørklund, G.; Chirumbolo, S. Basophil Activation Test in Amiodarone Hypersensitivity and Non-IgE-Mediated Allergy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 29, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumaki, D.; Gregoriou, S.; Evangelou, G.; Katoulis, A.; Papadakis, M.; Krueger-Krasagakis, S.E.; Doxastaki, A.; Mylonakis, D.; Krasagakis, K. Real-Life Utility of Basophil Activation Test in the Diagnosis of Immediate Hypersensitivity Drug Reactions. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzaire, P.; Nosbaum, A.; Denis, L.; Bienvenu, F.; Bérard, F.; Cozon, G.; Bienvenu, J. Negativity of the basophil activation test in quinolone hypersensitivity: A breakthrough for provocation test decision-making. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, M.; Fernández-Santamaría, R.; Mayorga, C.; Barrionuevo, E.; Ariza, A.; Posadas, T.; Laguna, J.J.; Montañez, M.I.; Molina, N.; Fernández, T.D.; et al. Use of the Basophil Activation Test May Reduce the Need for Drug Provocation in Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1010–1018.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Edelman, S.M.; Nopp, A.; Möbs, C.; Geilenkeuser, W.J.; Knol, E.F.; Ebo, D.G.; Mertens, C.; Shamji, M.H.; Santos, A.F.; et al. EAACI task force report: A consensus protocol for the basophil activation test for collaboration and external quality assurance. Allergy 2024, 79, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryzik, S.; Hoang, Y.; Lischke, T.; Mohr, E.; Venzke, M.; Kadner, I.; Poetzsch, J.; Groth, D.; Radbruch, A.; Hutloff, A.; et al. Identification of a super-functional Tfh-like subpopulation in murine lupus by pattern perception. eLife 2020, 9, e53226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, Y.; Gryzik, S.; Hoppe, I.; Rybak, A.; Schädlich, M.; Kadner, I.; Walther, D.; Vera, J.; Radbruch, A.; Groth, D.; et al. PRI: Re-Analysis of a Public Mass Cytometry Dataset Reveals Patterns of Effective Tumor Treatments. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 849329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, E.; Hinnenthal, T.; Gryzik, S.; Hoang, Y.; Lischke, T.; Retzlaff, J.; Mekonnen, A.; Paul, F.; Valleriani, A.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Bin-based visualization of cytokine-co-expression patterns of IL-10-producing CD4 T cell subsets. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordesillas, L.; Rahman, A.H.; Hartmann, B.M.; Sampson, H.A.; Berin, M.C. Mass cytometry profiling the response of basophils and the complete peripheral blood compartment to peanut. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1741–1744.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.H. Functional profiling of whole blood responses to allergen in healthy controls and peanut-allergic patients. Repository ID: FR-FCM-ZZTW. 2016. Available online: https://flowrepository.org/ (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Python Software Foundation. Python Language Reference, Version 3.8.5; Python Software Foundation: Wilmington, DE, USA, 2020.
- Ellis, B.H.P.; Hahne, F.; Le Meur, N.; Gopalakrishnan, N.; Spidlen, J.; Jiang, M.; Finak, G. flowcore: Basic Structures for Flow Cytometry Data, R Package Version 1.52.21; 2019. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/flowCore.html (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Hahne, F.G.N.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Wong, C.; Lee, K. flowStats: Statistical Methods for the Analysis of Flow Cytometry Data, R Package Version 4.16.0; 2024. Available online: http://www.github.com/RGLab/flowStats (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Erdmann, S.; Knol, E.F.; MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Poulsen, L.K.; Gibbs, B.F. Diagnostic tests based on human basophils: Potentials, pitfalls and perspectives. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 141, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.J.; Knol, E.F.; Ferrer, M.; Mayorga, L.; Sabato, V.; Santos, A.F.; Eberlein, B.; Nopp, A.; MacGlashan, D. Pros and Cons of Clinical Basophil Testing (BAT). Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Alpan, O.; Hoffmann, H.J. Basophil activation test: Mechanisms and considerations for use in clinical trials and clinical practice. Allergy 2021, 76, 2420–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Lack, G. Basophil activation test: Food challenge in a test tube or specialist research tool? Clin. Transl. Allergy 2016, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebo, D.G.; Bridts, C.H.; Mertens, C.H.; Sabato, V. Principles, potential, and limitations of ex vivo basophil activation by flow cytometry in allergology: A narrative review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpan, O.; Wasserman, R.L.; Kim, T.; Darter, A.; Shah, A.; Jones, D.; McNeil, D.; Li, H.; Ispas, L.; Rathkopf, M.; et al. Towards an FDA-cleared basophil activation test. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 1009437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirumbolo, S. Major pitfalls in BAT performance may be caused by gating protocols and CD63% cut off evaluation. Cytom. A 2014, 85, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonder, S.U.; Plassmeyer, M.; Loizou, D.; Alpan, O. Towards standardizing basophil identification by flow cytometry. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1133378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Kulis, M.D.; Sampson, H.A. Bringing the Next Generation of Food Allergy Diagnostics Into the Clinic. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends, J.; Schwager, C.; Hein, M.; Scholzen, T.; Kull, S.; Jappe, U. Innovative robust basophil activation test using a novel gating strategy reliably diagnosing allergy with full automation. Allergy 2021, 76, 3776–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.J.; Santos, A.F.; Mayorga, C.; Nopp, A.; Eberlein, B.; Ferrer, M.; Rouzaire, P.; Ebo, D.G.; Sabato, V.; Sanz, M.L.; et al. The clinical utility of basophil activation testing in diagnosis and monitoring of allergic disease. Allergy 2015, 70, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, V.; Demoly, P.; Dreborg, S.; Kalpaklioglu, A.F.; Klimek, L.; Muraro, A.; Pfaar, O.; Popov, T.A.; Hoffmann, H.J. Current practice of allergy diagnosis and the potential impact of regulation in Europe. Allergy 2018, 73, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, C.T.; Powell, M.S.; Harbeck, R.J.; Giclas, P.C.; Murphy, J.R.; Katial, R.K.; Weber, R.W.; Hogarth, P.M.; Johnson, S.; Bonvini, E.; et al. IgG antibodies produced during subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy mediate inhibition of basophil activation via a mechanism involving both FcgammaRIIA and FcgammaRIIB. Immunol. Lett. 2010, 130, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassard, L.; Jönsson, F.; Arnaud, S.; Daëron, M. Fcγ receptors inhibit mouse and human basophil activation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2995–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepley, C.L.; Cambier, J.C.; Morel, P.A.; Lujan, D.; Ortega, E.; Wilson, B.S.; Oliver, J.M. Negative regulation of FcepsilonRI signaling by FcgammaRII costimulation in human blood basophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.M.; Kepley, C.L.; Ortega, E.; Wilson, B.S. Immunologically mediated signaling in basophils and mast cells: Finding therapeutic targets for allergic diseases in the human FcvarepsilonR1 signaling pathway. Immunopharmacology 2000, 48, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekoff, M.; Möller, C.; Xiang, Z.; Nilsson, G. Coaggregation of FcepsilonRI with FcgammaRIIB Inhibits Degranulation but Not Induction of Bcl-2 Family Members A1 and Bim in Mast Cells. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, R.; Vogelsang, H.; Machnik, A.; Herrmann, D. Surface membrane antigen alteration on blood basophils in patients with Hymenoptera venom allergy under immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.U.; Calatroni, A.; Schneider, M.; Steinbrecher, J.; Smith, N.; Washburn, C.; Ma, A.; Shreffler, W.G. Data-driven programmatic approach to analysis of basophil activation tests. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Groffmann, J.; Hoppe, I.; Ahmed, W.A.N.; Hoang, Y.; Gryzik, S.; Radbruch, A.; Worm, M.; Beyer, K.; Baumgrass, R. Identification of a New and Effective Marker Combination for a Standardized and Automated Bin-Based Basophil Activation Test (BAT) Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171959
Groffmann J, Hoppe I, Ahmed WAN, Hoang Y, Gryzik S, Radbruch A, Worm M, Beyer K, Baumgrass R. Identification of a New and Effective Marker Combination for a Standardized and Automated Bin-Based Basophil Activation Test (BAT) Analysis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(17):1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171959
Chicago/Turabian StyleGroffmann, Johannes, Ines Hoppe, Wail Abbas Nasser Ahmed, Yen Hoang, Stefanie Gryzik, Andreas Radbruch, Margitta Worm, Kirsten Beyer, and Ria Baumgrass. 2024. "Identification of a New and Effective Marker Combination for a Standardized and Automated Bin-Based Basophil Activation Test (BAT) Analysis" Diagnostics 14, no. 17: 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171959
APA StyleGroffmann, J., Hoppe, I., Ahmed, W. A. N., Hoang, Y., Gryzik, S., Radbruch, A., Worm, M., Beyer, K., & Baumgrass, R. (2024). Identification of a New and Effective Marker Combination for a Standardized and Automated Bin-Based Basophil Activation Test (BAT) Analysis. Diagnostics, 14(17), 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171959





