Tenascin-C-Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Phenotype and the Risk of Tendinopathy in High-Performance Athletes: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Polymorphism Genotyping and Tendon Phenotypes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
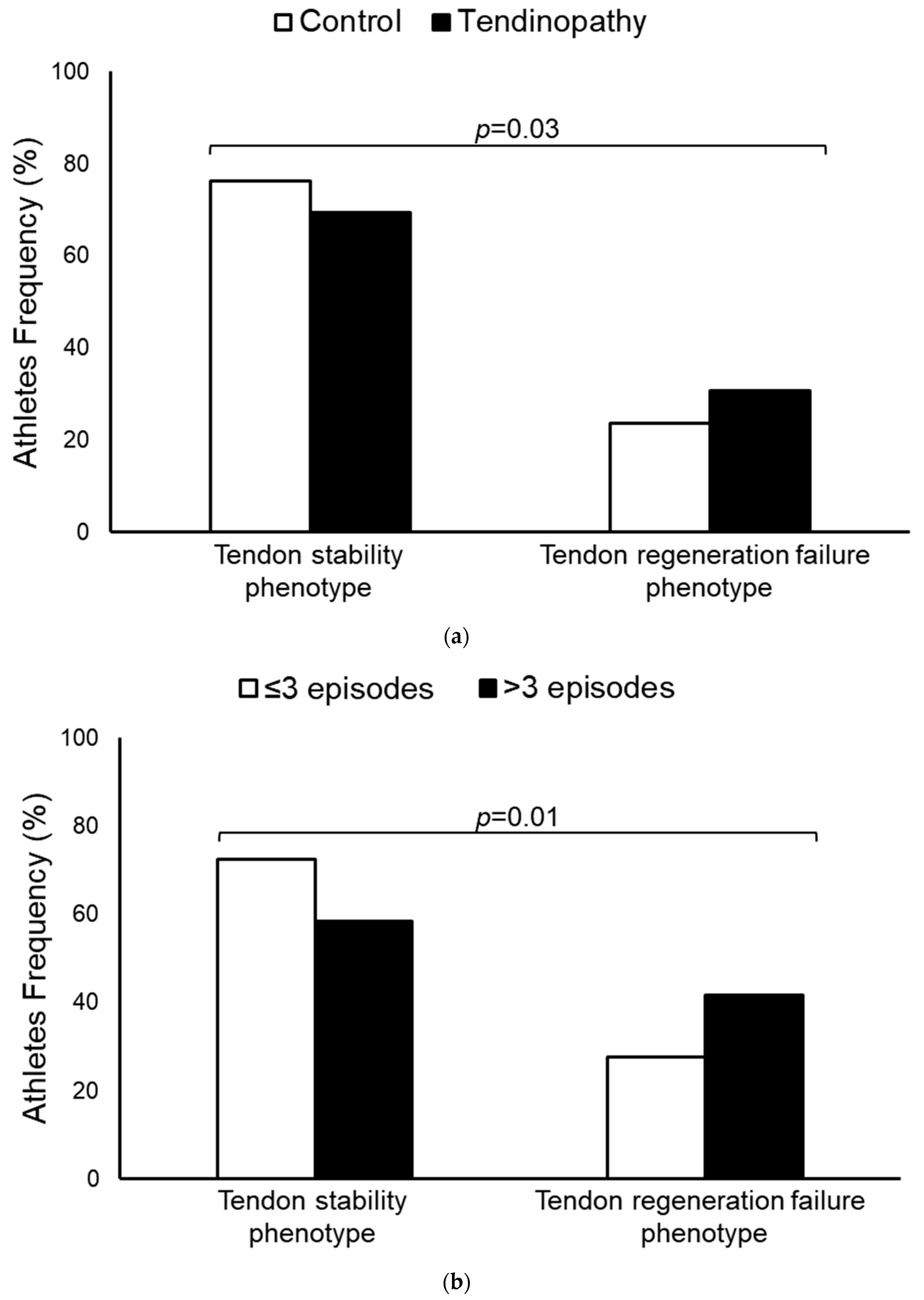
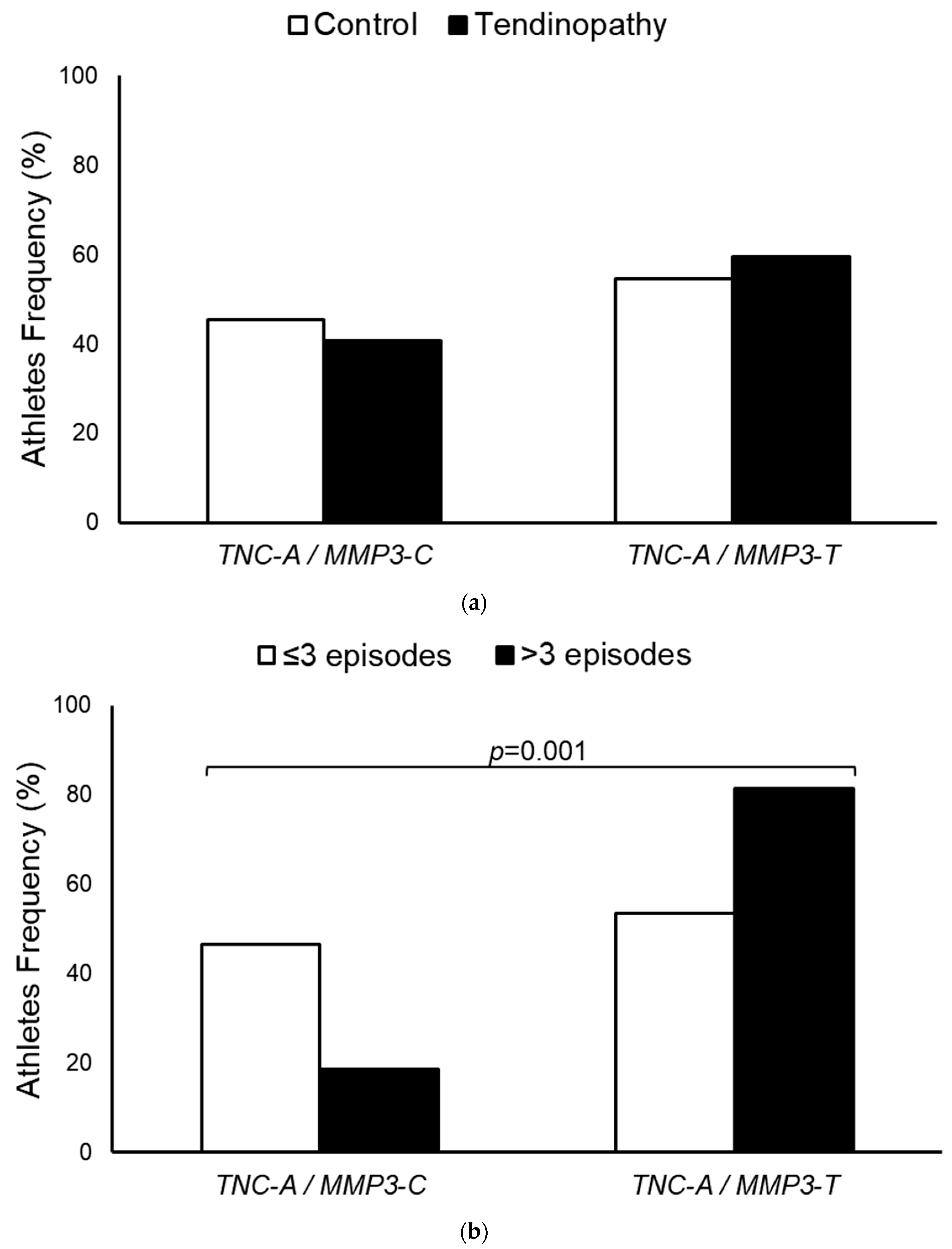
3. Results
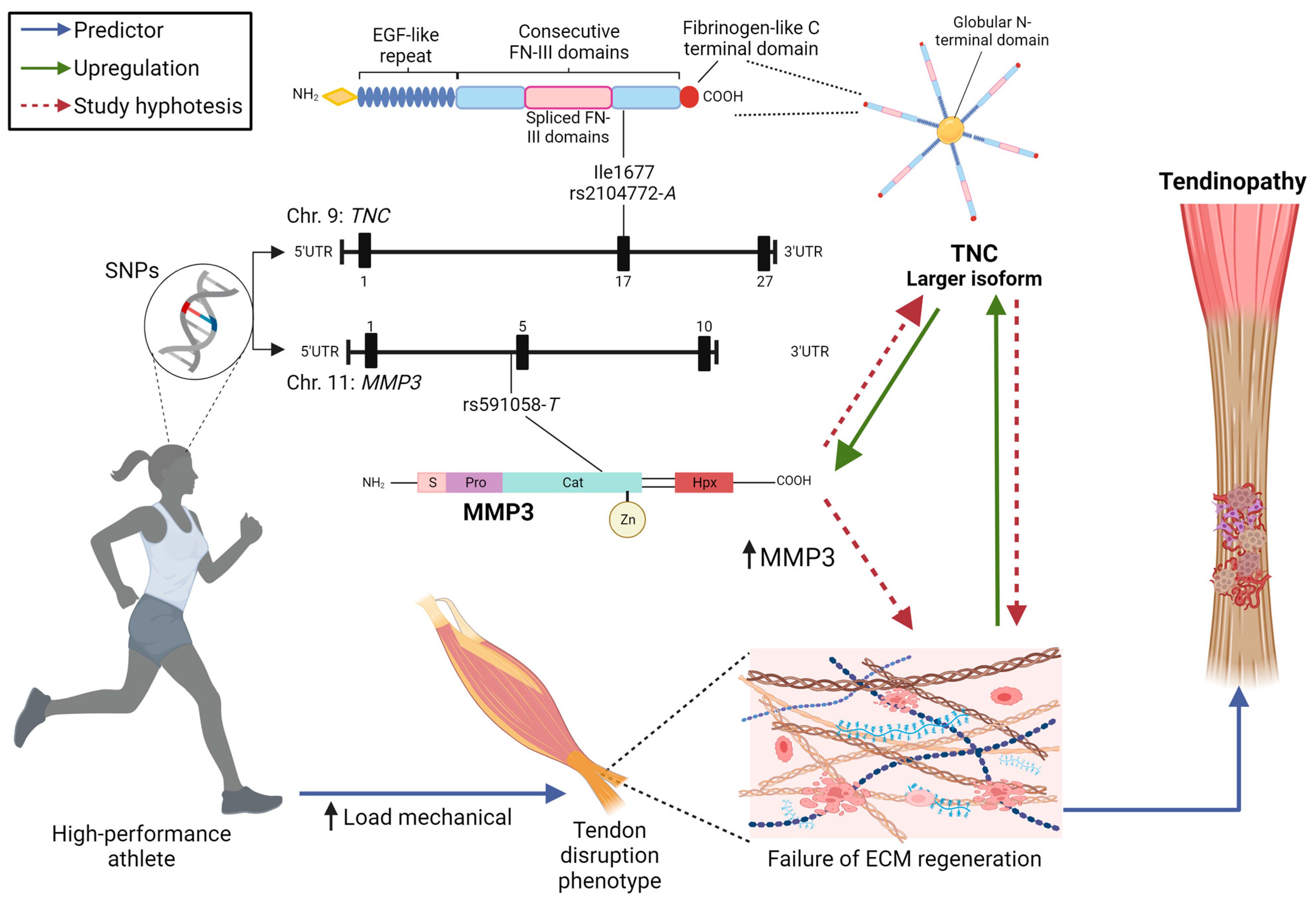
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goes, R.A.; Lopes, L.R.; Cossich, V.R.A.; de Miranda, V.A.R.; Coelho, O.N.; Bastos, R.D.C.; Domenis, L.A.M.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; Grangeiro-Neto, J.A.; Perini, J.A. Musculoskeletal injuries in athletes from five modalities: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Fu, S.C.; Chua, E.; Hu, X.; Rolf, C.; Mattila, V.M.; Qin, L.; Yung, P.S.-H.; Chan, K.-M. Critical review on the socio-economic impact of tendinopathy. Asia Pac. J. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Technol. 2016, 4, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.R.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; Amaral, M.V.G.; Pereira, C.G.; Wainchtock, V.S.; Goes, R.A.; Miranda, V.A.R.D.; Perini, J.A. Genetic Polymorphisms in COL1A2 gene and the Risk of Tendinopathy: Case-Control Study. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2023, 58, 478–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, L.R.; de Miranda, V.A.R.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; de Araujo Souza, G.G.; Wainchtock, V.S.; Grangeiro Neto, J.A.; de Araújo Goes, R.; Perini, J.A. Association of TNF-α-308G >A polymorphism with susceptibility to tendinopathy in athletes: A case-control study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.L.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Thorborg, K.; Kirwan, P.D.; Galatz, L.M.; Abrams, G.D.; Murrell, G.A.; McInnes, I.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Tendinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, J.I.; Lopes, L.R.; Duarte, M.E.L.; Morrissey, D.; Martins, M.B.; Machado, D.E.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; Perini, J.A. Fc receptor-like 3 (-169T>C) polymorphism increases the risk of tendinopathy in volleyball athletes: A case control study. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, J.I.; Duarte, M.E.; Guimarães, J.M.; Lopes, L.R.; Vilarinho Cardoso, J.; Aguiar, D.P.; Machado Neto, J.O.; Machado, D.E.; Perini, J.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 Polymorphisms Have Protective Effect against the Development of Tendinopathy in Volleyball Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.; Samiric, T.; Ilic, M.Z.; Cook, J.; Handley, C.J. Involvement of proteoglycans in tendinopathy. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2011, 11, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giantsis, I.A.; Diakakis, N.E.; Avdi, M. High Frequencies of TNC and COL5A1 Genotypes Associated With Low Risk for Superficial Digital Flexor Tendinopathy in Greek Indigenous Horse Breeds Compared With Warmblood Horses. J. Equine. Vet. Sci. 2020, 92, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, G.; Wen, X.; Liang, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, J. Additional evidence supports association of common genetic variants in MMP3 and TIMP2 with increased risk of chronic Achilles tendinopathy susceptibility. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, L.E.; Posthumus, M.; Collins, M.; van der Merwe, W.; Handley, C.; Cook, J.; Raleigh, S.M. ELN and FBN2 gene variants as risk factors for two sports-related musculoskeletal injuries. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halper, J.; Kjaer, M. Basic components of connective tissues and extracellular matrix: Elastin, fibrillin, fibulins, fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin, tenascins and thrombospondins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 802, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Helander, K.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Thomeé, R.; Faxen, E.; Olsson, N.; Eriksson, B.I.; Karlsson, J. Acute achilles tendon rupture: A randomized, controlled study comparing surgical and nonsurgical treatments using validated outcome measures. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, W.; Ramirez, F. Developmental expression of fibrillin genes suggests heterogeneity of extracellular microfibrils. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 129, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.A.; Józsa, L.; Kannus, P.; Järvinen, T.L.; Hurme, T.; Kvist, M.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Kalimo, H.; Järvinen, M. Mechanical loading regulates the expression of tenascin-C in the myotendinous junction and tendon but does not induce de novo synthesis in the skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasa-Renedo, A.; Chiquet, M. Mechanical signals regulating extracellular matrix gene expression in fibroblasts. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2005, 15, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Hirota, T.; Akahoshi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Tamari, M.; Miyatake, A.; Takahashi, A.; Nakashima, K.; Takahashi, N.; Obara, K.; et al. Coding SNP in tenascin-C Fn-III-D domain associates with adult asthma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashjian, R.Z.; Kim, S.K.; Roche, M.D.; Jones, K.B.; Teerlink, C.C. Genetic variants associated with rotator cuff tearing utilizing multiple population-based genetic resources. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, K.Y.C.; Ng, K.W.K.; Rao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Qi, S.; Tuan, R.S.; Ker, D.F.E.; Wang, D.M. Effect of Aging on Tendon Biology, Biomechanics and Implications for Treatment Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhoz, F.B.; Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Santos, M.C. MMP-3 polymorphism: Genetic marker in pathological processes (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raleigh, S.M.; van der Merwe, L.; Ribbans, W.J.; Smith, R.K.; Schwellnus, M.P.; Collins, M. Variants within the MMP3 gene are associated with Achilles tendinopathy: Possible interaction with the COL5A1 gene. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simunic-Briski, N.; Vrgoc, G.; Knjaz, D.; Jankovic, S.; Dembic, Z.; Lauc, G. MMP3 single-nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with noncontact ACL injuries in competing high-level athletes. J. Orthop. Res. 2024, 42, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, D.S.; Reiman, M.P.; Lehecka, B.J.; Naylor, A. What performance characteristics determine elite versus nonelite athletes in the same sport? Sports Health 2013, 50, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Herrmann, S.D.; Meckes, N.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Greer, J.L.; Vezina, J.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Leon, A.S. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larruskain, J.; Celorrio, D.; Barrio, I.; Odriozola, A.; Gil, S.M.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.R.; Nozal, R.; Ortuzar, I.; Lekue, J.A.; Aznar, J.M. Genetic Variants and Hamstring Injury in Soccer: An Association and Validation Study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.P.; Morse, C.I.; Onambele, G.L.; Williams, A.G. Variants within the MMP3 gene and patellar tendon properties in vivo in an asymptomatic population. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, C.J.; van der Merwe, L.; Posthumus, M.; Cook, J.; Handley, C.J.; Collins, M.; September, A.V. Investigation of variants within the COL27A1 and TNC genes and Achilles tendinopathy in two populations. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, R.; Burgstaller, J.; Vogl, C.; Brem, G.; Skultety, M.; Mueller, S. Candidate gene approach identifies six SNPs in tenascin-C (TNC) associated with degenerative rotator cuff tears. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlensog, M.; Ruehlmann, A.C.; Haeberle, L.; Opitz, F.; Becher, A.K.; Goering, W.; Buth, J.; Knoefel, W.T.; Ladage, D.; Meyer, A.; et al. Tenascin-C affects invasiveness of EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma through a putative paracrine loop. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnek, M.; Moreira, H.; Płaczkowska, S.; Barg, E.; Reichert, P.; Królikowska, A. Effectiveness of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy Treatment Depends on the Content of Biologically Active Compounds in Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhaimi, S.A.; Chan, S.C.; Rosli, R. Matrix Metallopeptidase 3 Polymorphisms: Emerging genetic Markers in Human Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Breast Cancer 2020, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthumus, M.; Collins, M.; van der Merwe, L.; O’cuinneagain, D.; Van Der Merwe, W.; Ribbans, W.J.; Schwellnus, M.P.; Raleigh, S.M. Matrix metalloproteinase genes on chromosome 11q22 and the risk of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2012, 22, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briški, N.; Vrgoč, G.; Knjaz, D.; Janković, S.; Ivković, A.; Pećina, M.; Lauc, G. Association of the matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3) single nucleotide polymorphisms with tendinopathies: Case-control study in high-level athletes. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalembeyi, I.; Inada, H.; Nishiura, R.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Sakakura, T.; Yoshida, T. Tenascin-C upregulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 in breast cancer cells: Direct and synergistic effects with transforming growth factor beta1. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremble, P.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix ligands fibronectin and tenascin collaborate in regulating collagenase gene expression in fibroblasts. Mol. Biol. Cell 1994, 5, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivieso, P.; Toigo, M.; Hoppeler, H.; Flück, M. T/T homozygosity of the tenascin-C gene polymorphism rs2104772 negatively influences exercise-induced angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, A.; Knäuper, V.; Veirana, N.; Caocci, F.; Murphy, G.; Zardi, L. Different susceptibility of small and large human tenascin-C isoforms to degradation by matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8650–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Control (n = 200) | Tendinopathy (n = 197) | p-Value a,b | Crude ORs (CI 95%) | Adjusted ORs (CI 95%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) d | n (%) | ||||
| ≤23 | 124 (62.0) | 79 (40.1) | <0.01 | 1 c | 1 c |
| >23 | 76 (38.0) | 118 (59.9) | 2.44 (1.63–3.65) | 2.10 (1.37–3.23) | |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 67 (35.5) | 85 (43.1) | 0.03 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Male | 133 (66.5) | 112 (56.9) | 0.66 (0.44–0.99) | 0.60 (0.38–0.95) | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) e | |||||
| <24.9 | 131 (66.5) | 105 (53.3) | <0.01 | 1 c | 1 c |
| ≥25.0 | 66 (33.5) | 92 (46.7) | 1.74 (1.16–2.61) | 1.82 (1.16–2.88) | |
| Skin color f | |||||
| White | 70 (36.5) | 94 (47.7) | 0.18 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Non-white | 122 (63.5) | 103 (52.3) | 0.63 (0.41–0.94) | 0.74 (0.47–1.15) | |
| Schooling g | |||||
| University | 85 (42.9) | 121 (61.4) | 0.23 | 1 c | 1 c |
| High-school | 113 (57.1) | 76 (38.6) | 0.47 (0.32–0.71) | 0.75 (0.47–1.20) | |
| Income familiar h | |||||
| >BRL 10.000 | 47 (24.1) | 70 (36.3) | 0.09 | 1 c | 1 c |
| ≤BRL 10.000 | 148 (75.9) | 123 (63.7) | 0.56 (0.36–0.87) | 0.65 (0.40–1.06) | |
| Alcohol consumption | |||||
| No | 96 (48.0) | 71 (36.0) | 0.17 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Yes | 104 (52.0) | 126 (64.0) | 1.64 (1.10–2.45) | 1.36 (0.87–2.11) | |
| Smoking | |||||
| No | 190 (95.0) | 178 (90.4) | 0.13 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Yes | 10 (5.0) | 19 (9.6) | 2.03 (0.91–4.48) | 1.90 (0.82–4.40) | |
| Nutritional guidance | |||||
| No | 110 (55.0) | 70 (35.5) | <0.01 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Yes | 90 (45.0) | 127 (64.5) | 2.22 (1.48–3.32) | 2.24 (1.45–3.47) | |
| Continuous medication use f | |||||
| No | 173 (90.1) | 163 (82.7) | 0.74 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Yes | 19 (9.9) | 34 (17.3) | 1.90 (1.04–3.46) | 1.12 (0.57–2.21) | |
| Post-training pain | |||||
| No | 135 (67.5) | 93 (47.2) | <0.01 | 1 c | 1 c |
| Yes | 65 (32.5) | 104 (52.8) | 2.32 (1.55–3.49) | 2.07 (1.34–3.20) | |
| TEI (MET years) d,i | |||||
| ≤7.2 | 120 (60.0) | 87 (44.2) | 0.02 | 1 c | 1 c |
| >7.2 | 80 (40.0) | 110 (55.8) | 1.90 (1.27–2.83) | 1.67 (1.05–2.65) | |
| SNPs | Control (n = 200) | Tendinopathy (n = 197) | p-Value a,b | Crude ORs (CI 95%) | Adjusted ORs (CI 95%) b |
| TNC d rs2104772 (T > A) | n (%) | ||||
| TT | 61 (30.5) | 46 (23.5) | 0.04 | 1 c | 1 c |
| TA | 103 (51.5) | 98 (50.0) | 1.26 (0.79–2.02) | 1.37 (0.81–2.29) | |
| AA | 36 (18.0) | 52 (26.5) | 1.91 (1.08–3.39) | 2.22 (1.18–4.15) | |
| TA + AA | 139 (69.5) | 150 (76.5) | 0.03 | 1.43 (0.91–2.24) | 1.80 (1.07–3.04) |
| MMP3 e rs591058 (C > T) | |||||
| CC | 62 (33.0) | 59 (29.9) | 0.78 | 1 c | 1 c |
| CT | 95 (50.5) | 97 (49.2) | 1.07 (0.68–1.69) | 1.04 (0.63–1.70) | |
| TT | 31 (16.5) | 41(20.8) | 1.39 (0.77–2.50) | 1.24 (0.66–2.33) | |
| CT + TT | 126 (67.0) | 138 (70.1) | 0.72 | 1.15 (0.75–1.77) | 1.09 (0.68–1.74) |
| SNPs | Tendinopathy | p-Value a,b | Crude OR (CI 95%) | Adjusted OR (CI 95%) f | |
| ≤3 Episodes (n = 154) | >3 Episodes (n = 43) | ||||
| TNC g rs2104772 (T >A) | n (%) | ||||
| TT | 38 (24.7) | 8 (19.0) | 0.32 | 1 c | 1 c |
| TA | 73 (47.4) | 25 (59.5) | 1.63 (0.67–3.95) | 1.80 (0.71–5.60) | |
| AA | 43 (27.9) | 9 (21.4) | 0.99 (0.55–2.83) | 1.05 (0.35–3.16) | |
| TA + AA | 116 (75.3) | 34 (81.0) | 0.36 | 1.39 (0.59–3.27) | 1.52 (0.62–3.72) |
| MMP3 h rs591058 (C >T) | |||||
| CC | 54 (35.1) | 5 (11.6) | 0.03 | 1 c | 1 c |
| CT | 69 (44.8) | 28 (65.1) | 3.60 (1.28–10.09) | 4.14 (1.45–11.87) | |
| TT | 31 (20.1) | 10 (23.3) | 2.79 (0.84–9.27) | 3.87 (1.15–13.02) | |
| CT + TT | 100 (64.9) | 31 (86.1) | 0.01 | 3.35 (1.23–9.10) | 4.07 (1.46– 11.36) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, L.R.; Amaral, M.V.G.; Goes, R.A.; Tavares, V.; Dias, F.; Medeiros, R.; Machado, D.E.; Perini, J.A. Tenascin-C-Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Phenotype and the Risk of Tendinopathy in High-Performance Athletes: A Case–Control Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222469
Lopes LR, Amaral MVG, Goes RA, Tavares V, Dias F, Medeiros R, Machado DE, Perini JA. Tenascin-C-Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Phenotype and the Risk of Tendinopathy in High-Performance Athletes: A Case–Control Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(22):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, Lucas Rafael, Marcus Vinícius Galvão Amaral, Rodrigo Araujo Goes, Valéria Tavares, Francisca Dias, Rui Medeiros, Daniel Escorsim Machado, and Jamila Alessandra Perini. 2024. "Tenascin-C-Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Phenotype and the Risk of Tendinopathy in High-Performance Athletes: A Case–Control Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 22: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222469
APA StyleLopes, L. R., Amaral, M. V. G., Goes, R. A., Tavares, V., Dias, F., Medeiros, R., Machado, D. E., & Perini, J. A. (2024). Tenascin-C-Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Phenotype and the Risk of Tendinopathy in High-Performance Athletes: A Case–Control Study. Diagnostics, 14(22), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222469









