Lightweight and Low-Parametric Network for Hardware Inference of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
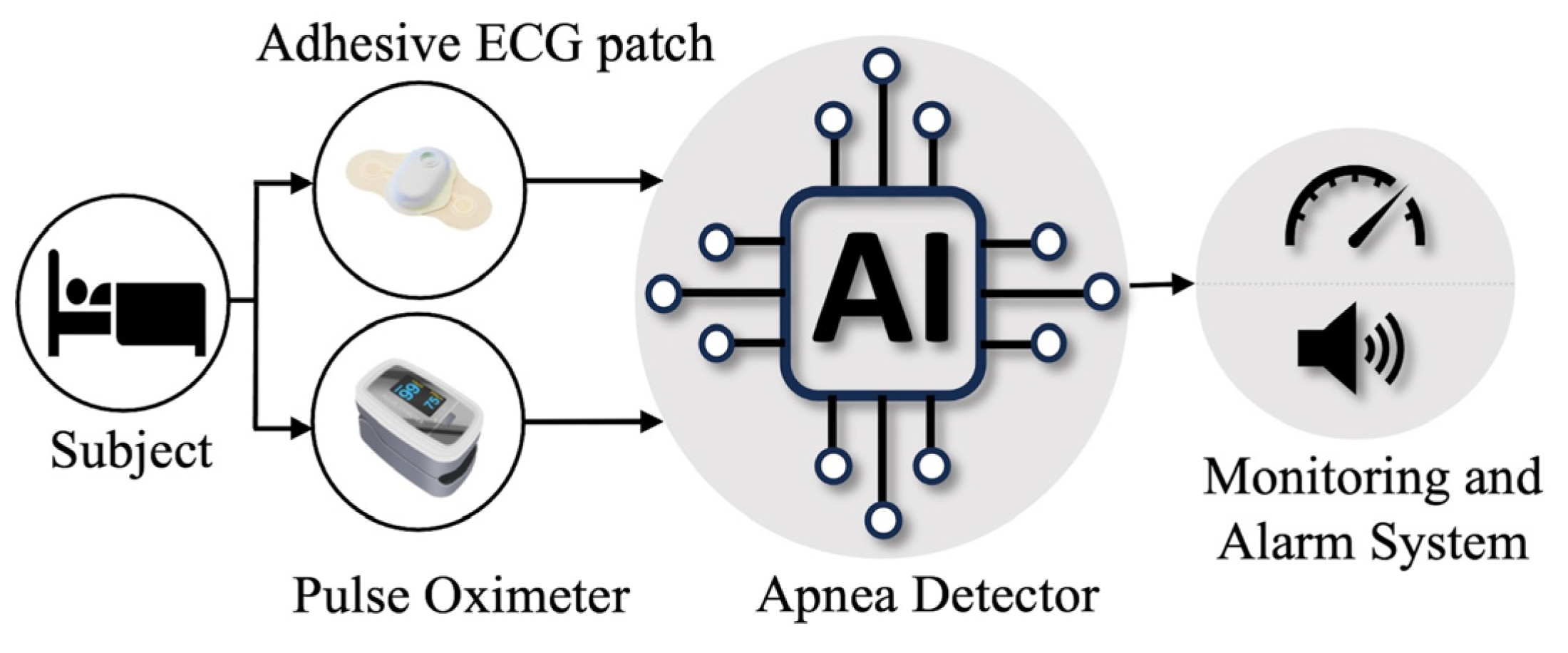
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Segmentation
2.3. Data Augmentation and Class Balancing
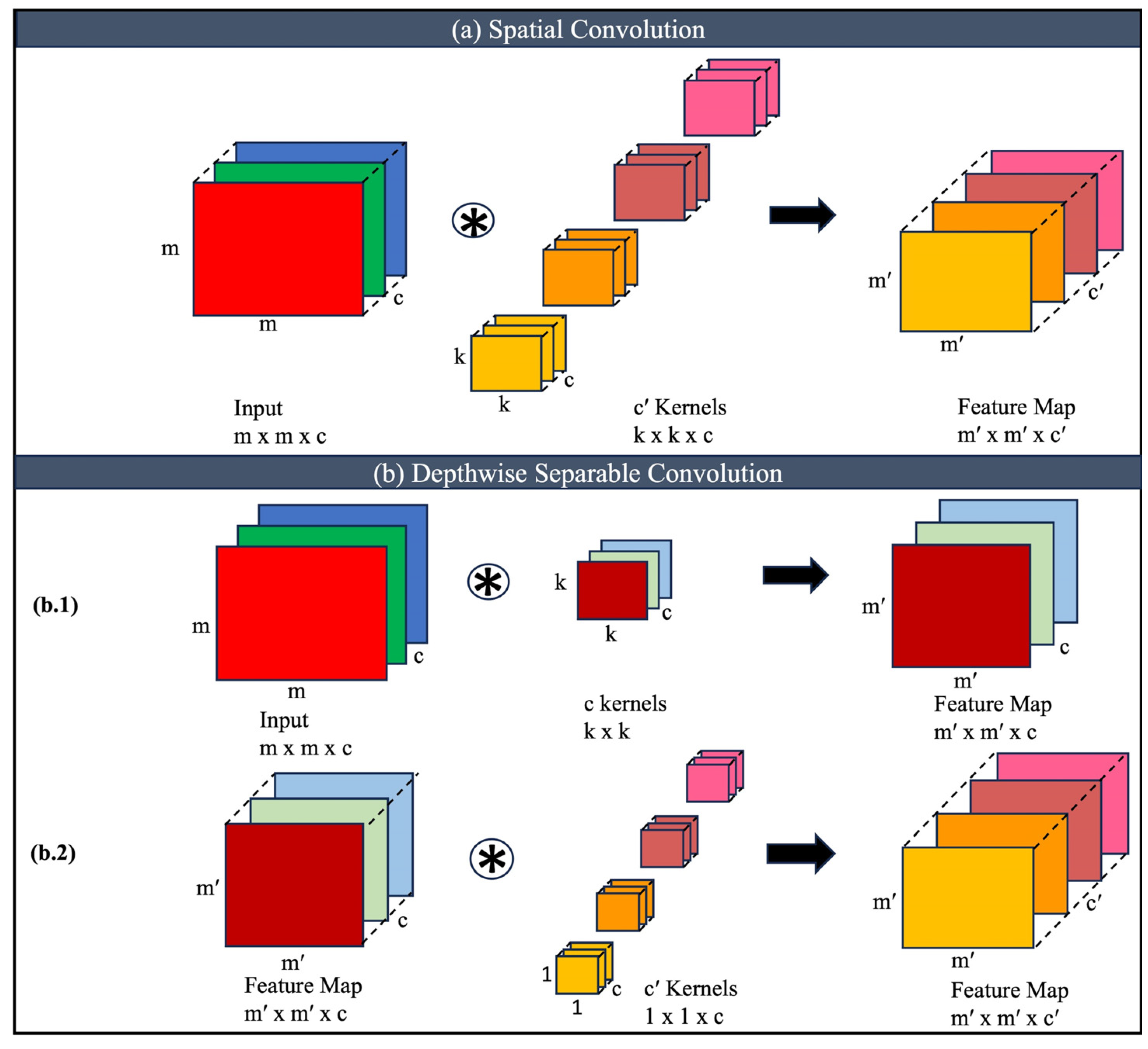
2.4. Depth-Wise Separable Convolution (DSC)
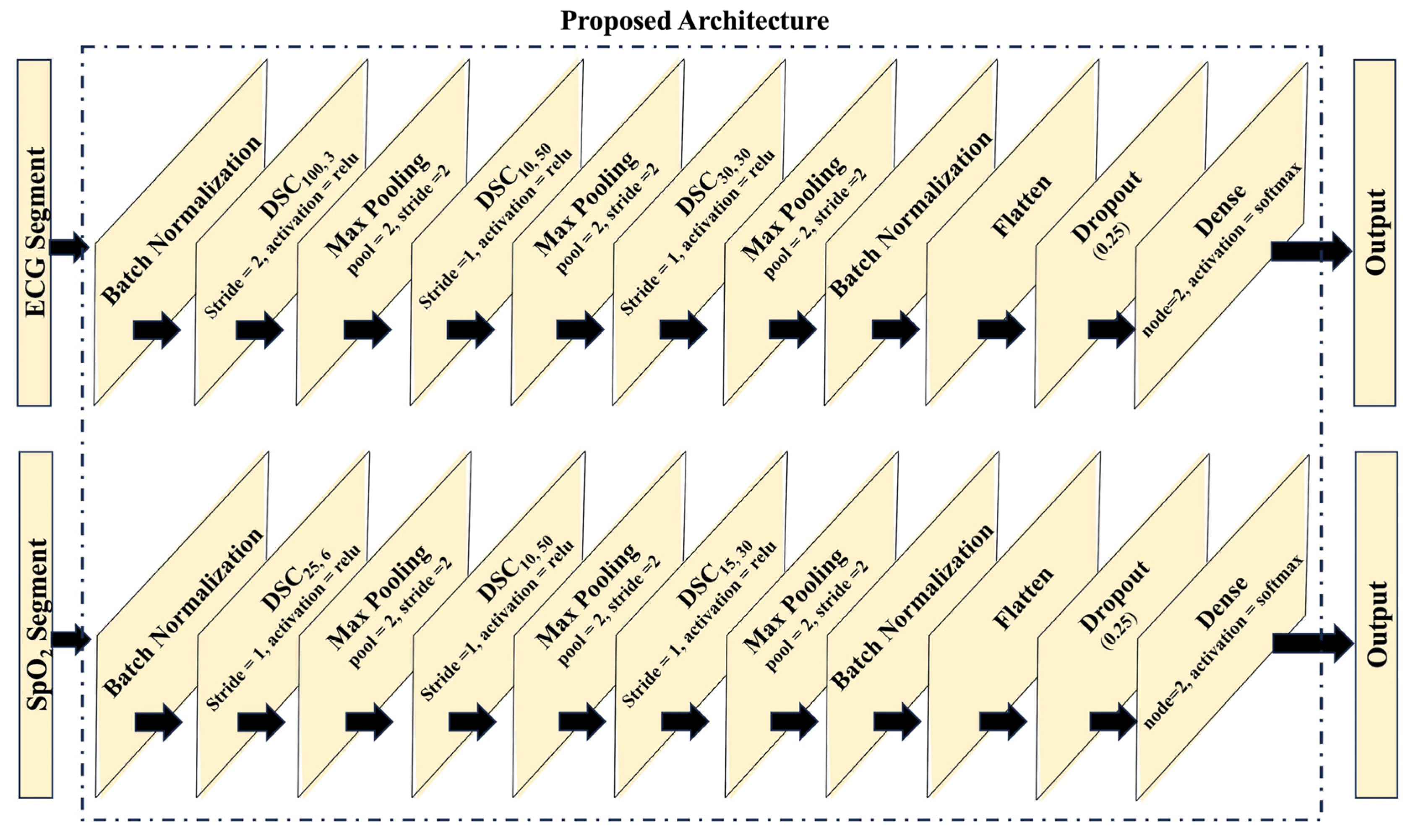
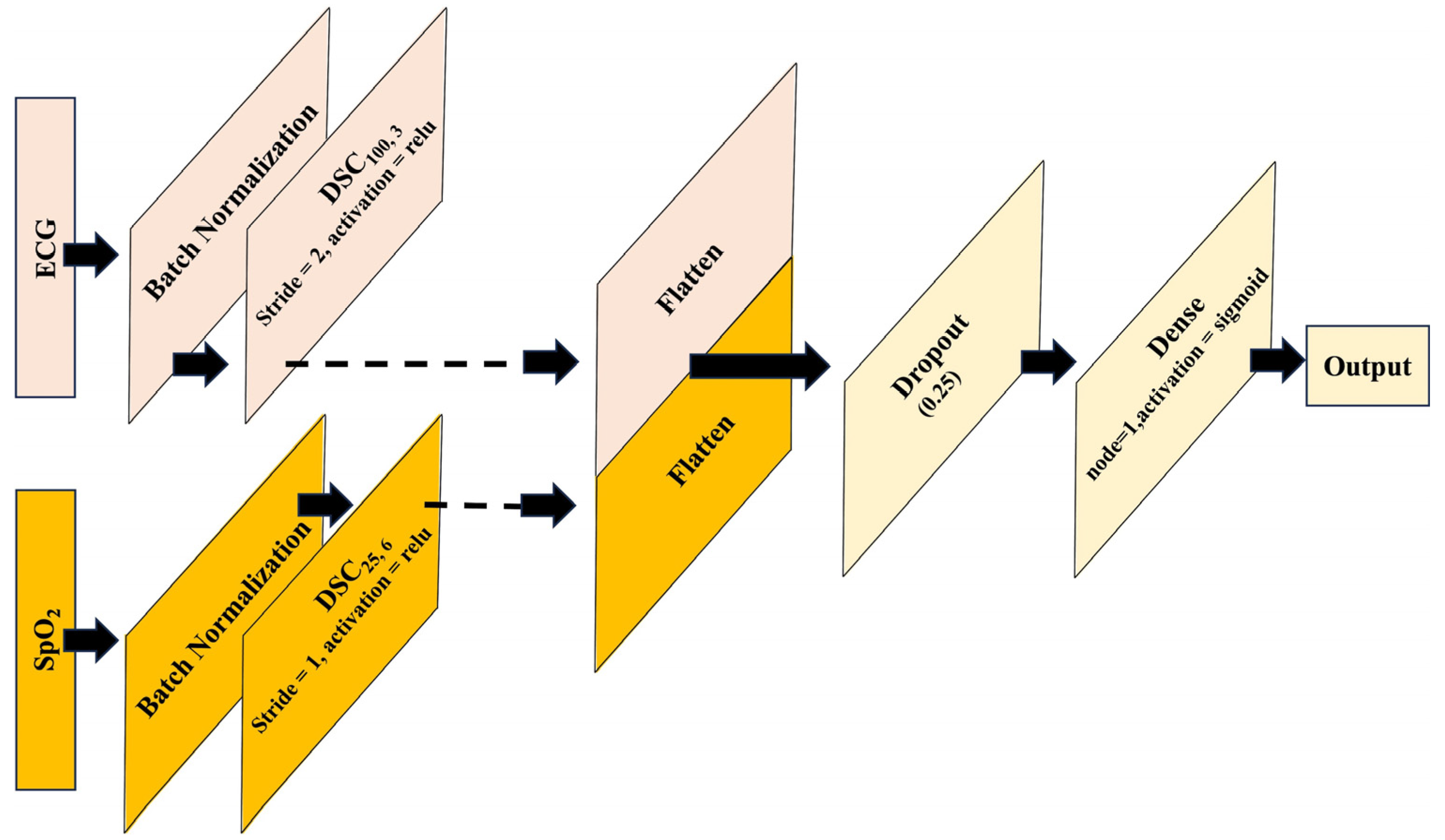
2.5. Proposed Network Architecture
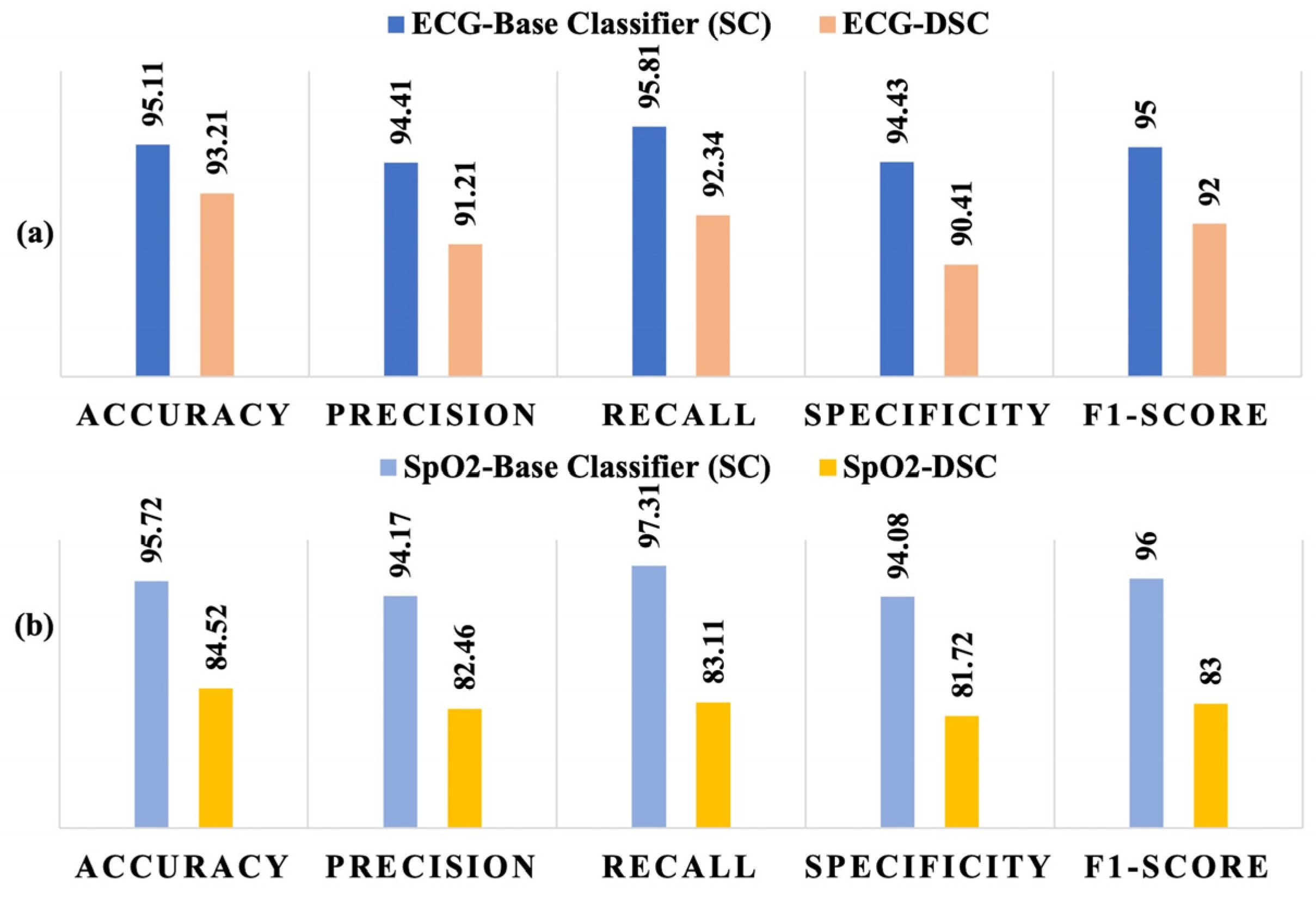
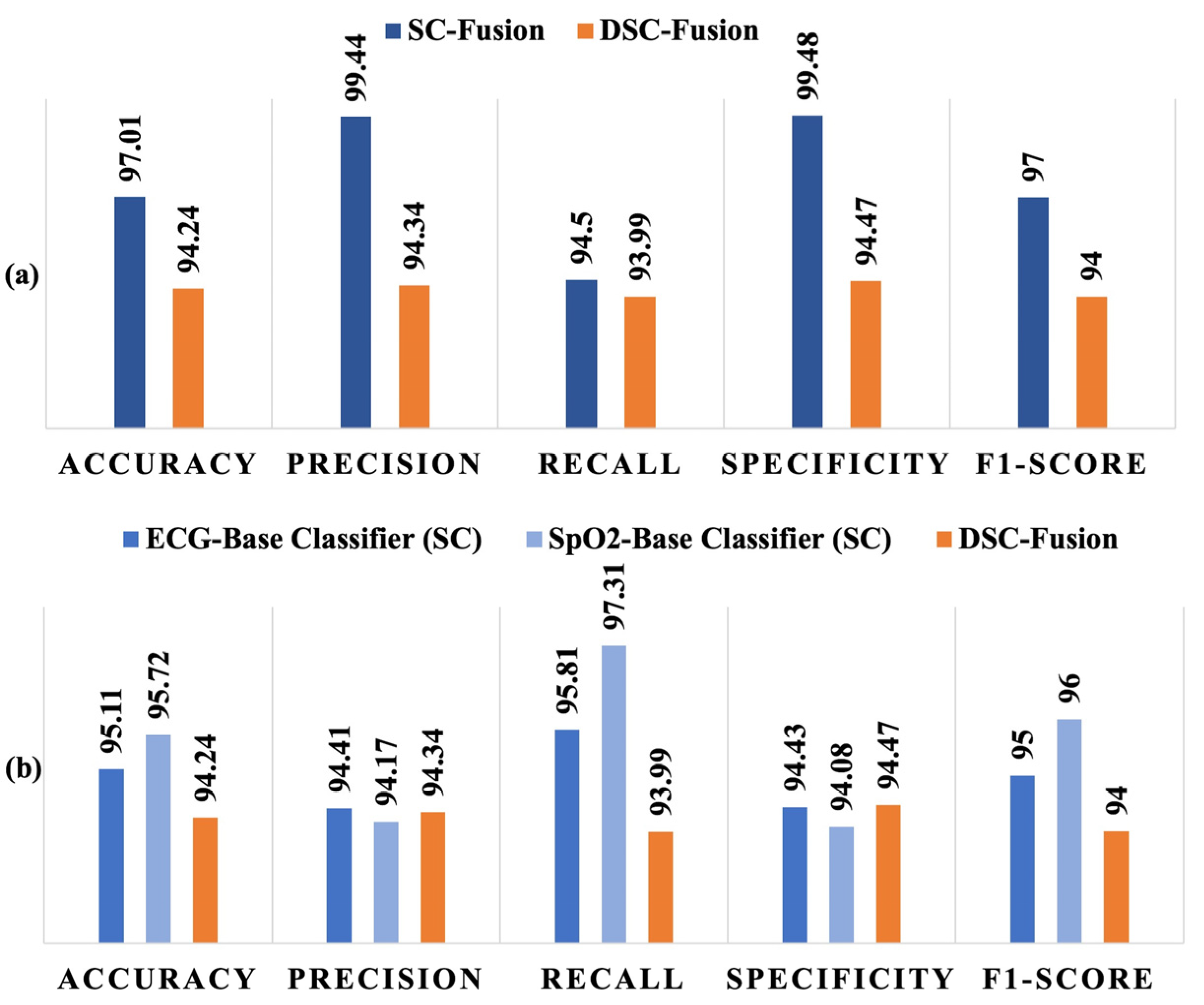
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jun, J.C.; Chopra, S.; Schwartz, A.R. Sleep Apnoea. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, V.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Punjabi, N.M.; Redline, S.; Gottlieb, D.J. Calibration Model for Apnea-Hypopnea Indices: Impact of Alternative Criteria for Hypopneas. Sleep 2015, 38, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, A.T.; Singh, P.; Ruehland, W.R.; Rochford, P.D. AASM Criteria for Scoring Respiratory Events: Interaction between Apnea Sensor and Hypopnea Definition. Sleep 2012, 35, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léger, D.; Stepnowsky, C. The Economic and Societal Burden of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 51, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, N.E.; Farrag, N.S.; Zaki, N.F.W.; Badawy, A.Y.; Abdelhafez, S.A.; El-Gilany, A.H.; El Shafey, M.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Spence, D.W.; Bahammam, A.S. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Personal, Societal, Public Health, and Legal Implications. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redline, S.; Azarbarzin, A.; Peker, Y. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Heterogeneity and Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, M.; Ayas, N.; Laher, I. Cardiovascular Complications of Sleep Apnea: Role of Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 985258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraki, I.; Wada, H.; Tanigawa, T. Sleep Apnea and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Yegneswaran, B.; Vairavanathan, S.; Zilberman, P.; Chung, F. Postoperative Complications in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Retrospective Matched Cohort Study. Can. J. Anesth. 2009, 56, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, T.S.; Grewal, R.; Doghramji, K. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Perioperative Complications: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidden Health Crisis Costing America Billions Underdiagnosing and Undertreating Obstructive Sleep Apnea Draining Healthcare System; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2016.
- Wickwire, E.M. Value-Based Sleep and Breathing: Health Economic Aspects of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Faculty Opinions. Fac. Rev. 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laher, I.; Faria Hirsch Allen, A.A.; Fox, N.; Ayas, N. The Public Health Burden of Obstructive Sleep Apnea REVIEWS. Sleep Sci. 2021, 14, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundo, J.V.; Downey, R. Polysomnography. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 160, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, A.L.; Berry, R.B.; Pack, A. Practice Parameters for the Use of Portable Monitoring Devices in the Investigation of Suspected Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. Sleep 2003, 26, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yan, R.; Chen, Z.; Mao, K.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.X. Deep Learning and Its Applications to Machine Health Monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2019, 115, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.; Raju, H.; Tripathy, B.K. Deep Learning in Healthcare. Stud. Big Data 2022, 91, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, S.; Basumatary, N.; Gill, S.S.; Kahani, M.; Chand Arya, R.; Singh Wander, G.; Buyya, R. HealthFog: An Ensemble Deep Learning Based Smart Healthcare System for Automatic Diagnosis of Heart Diseases in Integrated IoT and Fog Computing Environments. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 104, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Dudley, J.T. Deep Learning for Healthcare: Review, Opportunities and Challenges. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Hassan, O.; Alaboud, K.; Islam, H.; Rana, M.K.Z.; Islam, S.K.; Mosa, A.S.M. ECG and SpO2 Signal-Based Real-Time Sleep Apnea Detection Using Feed-Forward Artificial Neural Network. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2022, 2022, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Chyad, M.H.; Gharghan, S.K.; Hamood, H.Q.; Altayyar, A.S.H.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Ridha, H.M. Hybridization of Soft-Computing Algorithms with Neural Network for Prediction Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using Biomedical Sensor Measurements. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 8933–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroshana, S.M.I.; Zhu Id, X.; Nakamura, K.; Id, W.C. A Fused-Image-Based Approach to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using a Single-Lead ECG and a 2D Convolutional Neural Network. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Pinho, A.M.; Pombo, N.; Garcia, N.M. Sleep Apnea Detection Using a Feed-Forward Neural Network on ECG Signal. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathinarupothi, R.K.; Vinaykumar, R.; Rangan, E.; Gopalakrishnan, E.; Soman, K.P. Instantaneous Heart Rate as a Robust Feature for Sleep Apnea Severity Detection Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 February 2017; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcnames, J.N.; Fraser, A.M. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Classification Based on Spectrogram Patterns in the Electrocardiogram. Comput. Cardiol. 2000, 27, 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, M.M.; Alzaabi, Y.; Khandoker, A.H. Explainable Computer-Aided Detection of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Depression. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 110916–110933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.; Byun, H.; Lee, J.; Byun, J.; Rhee, H.Y.; Shin, W.; Yoon, H. Robust Method for Screening Sleep Apnea with Single-Lead ECG Using Deep Residual Network: Evaluation with Open Database and Patch-Type Wearable Device Data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Cai, W.; Gao, T.; Wang, M. A Hybrid Transformer Model for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Detection Based on Self-Attention Mechanism Using Single-Lead ECG. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2514011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, M.; Forouzanfar, M. Sleep Apnea Detection from Single-Lead ECG: A Comprehensive Analysis of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 4003011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Álvarez, D.; Del Campo, F.; Behar, J.A. Deep Learning for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Diagnosis Based on Single Channel Oximetry. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, G.; Pinheiro, L.; Fonseca Cruz, A.; Paulo, S. Validation of an Overnight Wireless High-Resolution Oximeter plus Cloud-Based Algorithm for the Diag-Nosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Clinics 2020, 75, e2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, F.; De Almeida, D.M.; Dreesen, P.; Thijs, I.; Vranken, J.; Klerkx, S. An Evaluation of the NightOwl Home Sleep Apnea Testing System. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, H.; Liu, H.; Bilodeau, M.; Wallace, B.; Bouchard, M.; Goubran, R.; Knoefel, F. Cloud Processing of Bed Pressure Sensor Data to Detect Sleep Apnea Events. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Bari, Italy, 1 June–1 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoyu, L.; Jianxing, L.; Arunkumar, N.; Hussein, A.F.; Jaber, M.M. An IoMT Cloud-Based Real Time Sleep Apnea Detection Scheme by Using the SpO2 Estimation Supported by Heart Rate Variability. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 98, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Leung, L.; Kwok, K.C.; Wu, I.C.; Folz, R.J.; Chiang, A.A. Belun Ring Platform: A Novel Home Sleep Apnea Testing System for Assessment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Nourani, M.; Gupta, G.; Tamil, L. Apnea MedAssist II: A Smart Phone Based System for Sleep Apnea Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Shanghai, China, 18–21 December 2013; pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, M.D.; Shuvo, H.; Cheng, J. Efficient Acceleration of Deep Learning Inference on Resource-Constrained Edge Devices: A Review. Proc. IEEE 2022, 111, 42–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzel, T.; Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peter, J.H. Apnea-ECG Database. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- St. Vincent’s University Hospital/University College Dublin Sleep Apnea Database v1.0.0. Available online: https://physionet.org/content/ucddb/1.0.0/ (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique. Available online: https://www.jair.org/index.php/jair/article/view/10302/24590 (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET 2017), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Member, S. A Decade Survey of Transfer Learning (2010–2020). IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Ansari, M.A.; Agrawal, R.; Anand, R.S. A Transfer Learning Approach for AI-Based Classification of Brain Tumors. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2020, 2, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Member, S.; Kumar Nundy, K.; Member, S.; Cardiff, B.; John, D. Multimodal Multiresolution Data Fusion Using Convolutional Neural Networks for IoT Wearable Sensing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2021, 15, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Panicker, R.C.; Cardiff, B.; Lian, Y.; John, D. Binary Classifiers for Data Integrity Detection in Wearable IoT Edge Devices. IEEE Open J. Circuits Syst. 2020, 1, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelouahab, K.; Pelcat, M.; Sérot, J.; Berry, F. Accelerating CNN Inference on FPGAs: A Survey. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01683. [Google Scholar]
- Taco, R.; Levi, I.; Lanuzza, M.; Member, S.; Fish, A. An 88-FJ/40-MHz [0.4 V]-0.61-PJ/1-GHz [0.9 V] Dual-Mode Logic 8 × 8 Bit Multiplier Accumulator with a Self-Adjustment Mechanism in 28-Nm FD-SOI. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyserhove, H.; Reynders, N.; Dehaene, W. Ultra-Low Voltage Datapath Blocks in 28nm UTBB FD-SOI. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), KaoHsiung, Taiwan, 10–12 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Taco, R.; Levi, I.; Lanuzza, M.; Fish, A. Evaluation of Dual Mode Logic in 28nm FD-SOI Technology. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Baltimore, MD, USA, 28–31 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, O.; Thakker, R.; Paul, T.; Parvin, D.; Saleh, A.; Mosa, M.; Islam, S.K. SABiNN: FPGA Implementation of Shift Accumulate Binary Neural Network Model for Real-Time Automatic Detection of Sleep Apnea. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–19 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, O.; Paul, T.; Amin, N.; Titirsha, T.; Thakker, R.; Parvin, D.; Saleh, A.; Mosa, M.; Kamrul Islam, S. An Optimized Hardware Inference of SABiNN: Shift-Accumulate Binarized Neural Network for Sleep Apnea Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2516311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ECG | SpO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Validation | Test | Train | Validation | Test | |
| Total | 214,264 | 8267 | 8264 | 152,364 | 5216 | 5222 |
| Apnea | 107,132 | 1572 | 1570 | 76,182 | 456 | 460 |
| Normal | 107,132 | 6695 | 6694 | 76,182 | 4760 | 4762 |
| Model | Parameters | Multiplication | Addition | Energy (μJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC-ECG | 51,389 | 6,534,116 | 6,546,647 | 2.55 |
| DSC-ECG | 7872 | 579,439 | 580,311 | 0.23 |
| SC-SpO2 | 26,702 | 1,270,016 | 1,272,876 | 0.50 |
| DSC-SpO2 | 3693 | 103,866 | 105,432 | 0.04 |
| SC-Fusion | 78,089 | 7,809,352 | 7,824,743 | 3.05 |
| DSC-Fusion | 11,563 | 683,303 | 684,721 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, T.; Hassan, O.; McCrae, C.S.; Islam, S.K.; Mosa, A.S.M. Lightweight and Low-Parametric Network for Hardware Inference of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222505
Paul T, Hassan O, McCrae CS, Islam SK, Mosa ASM. Lightweight and Low-Parametric Network for Hardware Inference of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(22):2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222505
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Tanmoy, Omiya Hassan, Christina S. McCrae, Syed Kamrul Islam, and Abu Saleh Mohammad Mosa. 2024. "Lightweight and Low-Parametric Network for Hardware Inference of Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Diagnostics 14, no. 22: 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222505
APA StylePaul, T., Hassan, O., McCrae, C. S., Islam, S. K., & Mosa, A. S. M. (2024). Lightweight and Low-Parametric Network for Hardware Inference of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Diagnostics, 14(22), 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222505






