Proteomic Profiling of COVID-19 Patients Sera: Differential Expression with Varying Disease Stage and Potential Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Data Collection
2.2. Serum Preparation and Protein Extraction
2.3. Protein Characterization by Label-Free Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Studied Population
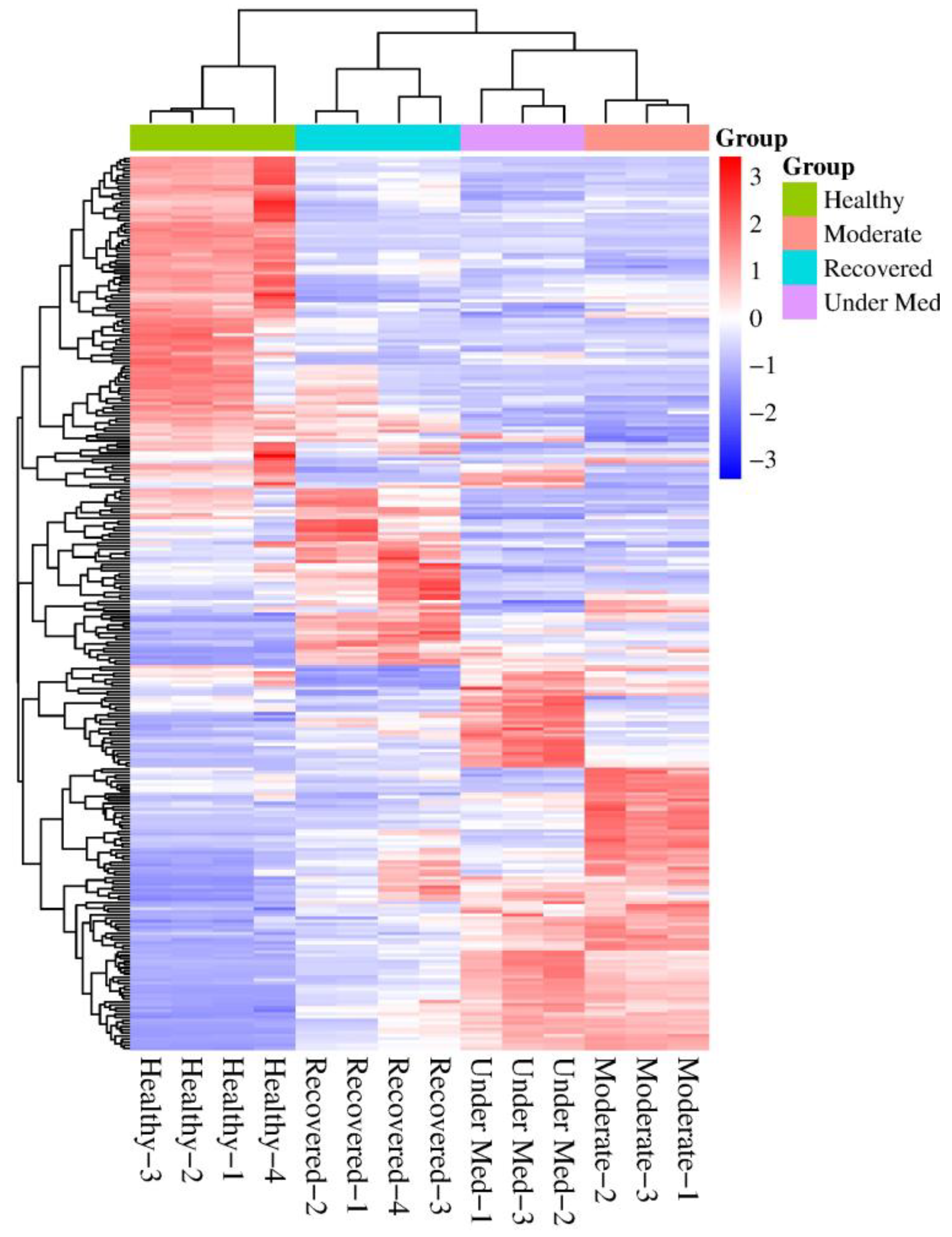
3.2. Proteomic Profiles per Disease Category
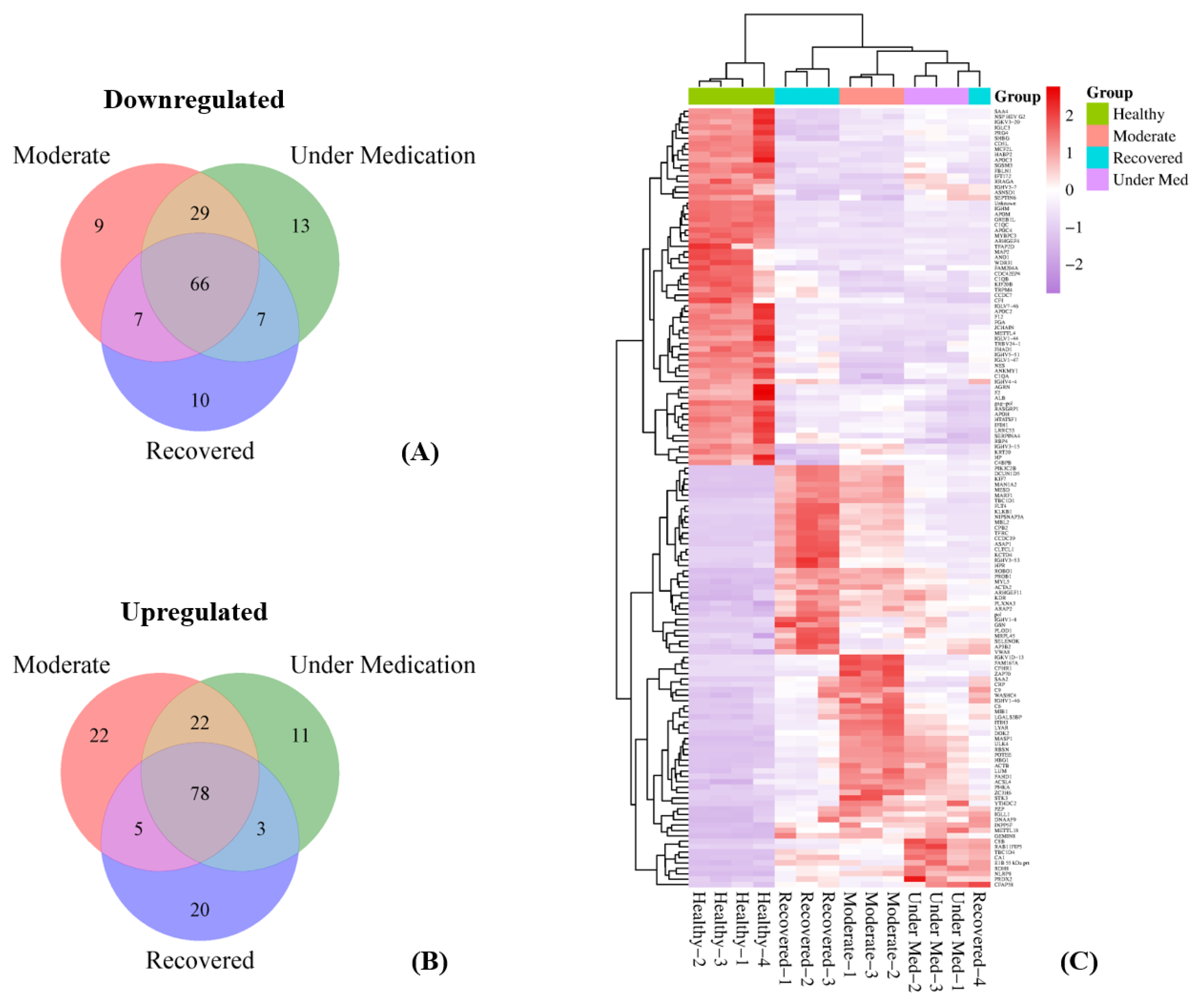
3.3. Differential Expression of Proteins per Disease Category Compared to Healthy Subjects
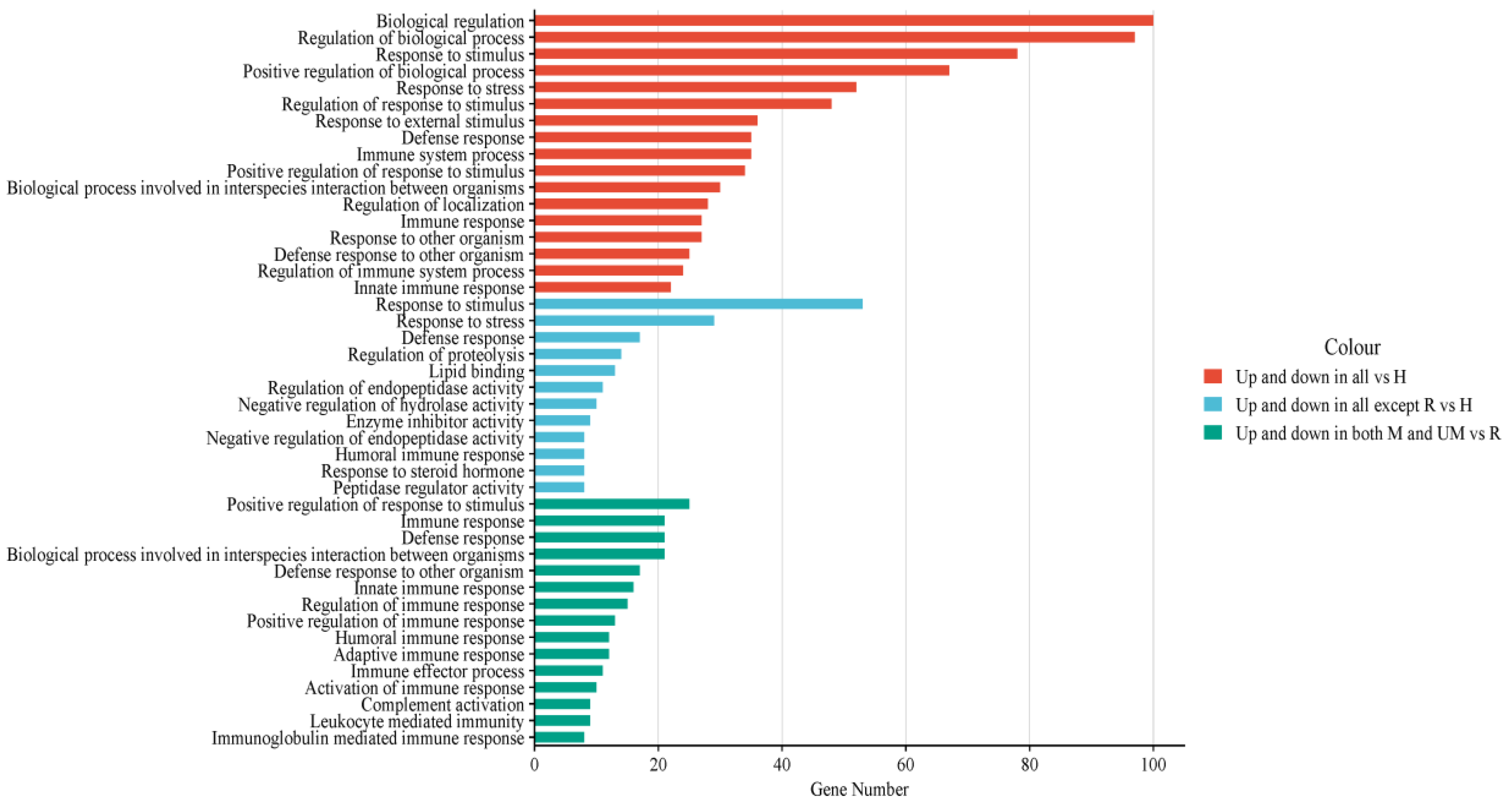
3.4. Functional Analysis of Dysregulated Proteins Compared to Healthy Subjects
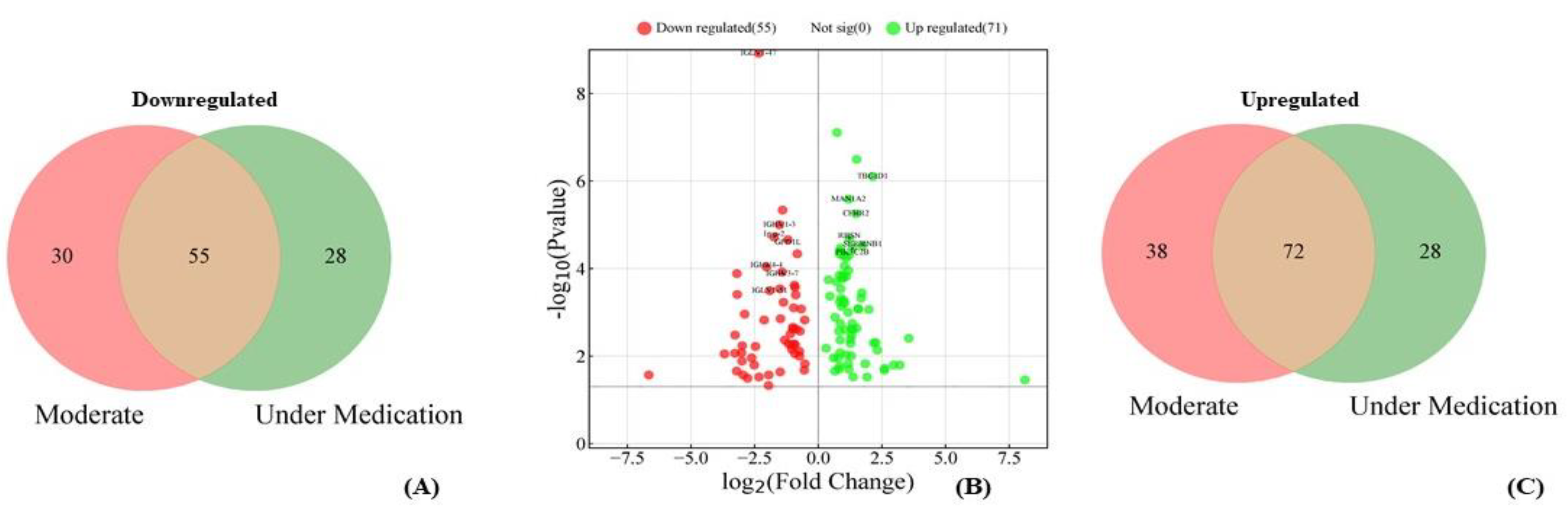
3.5. Differential Expression of Proteins in Moderate/Under Medication Patients Compared to Recovered
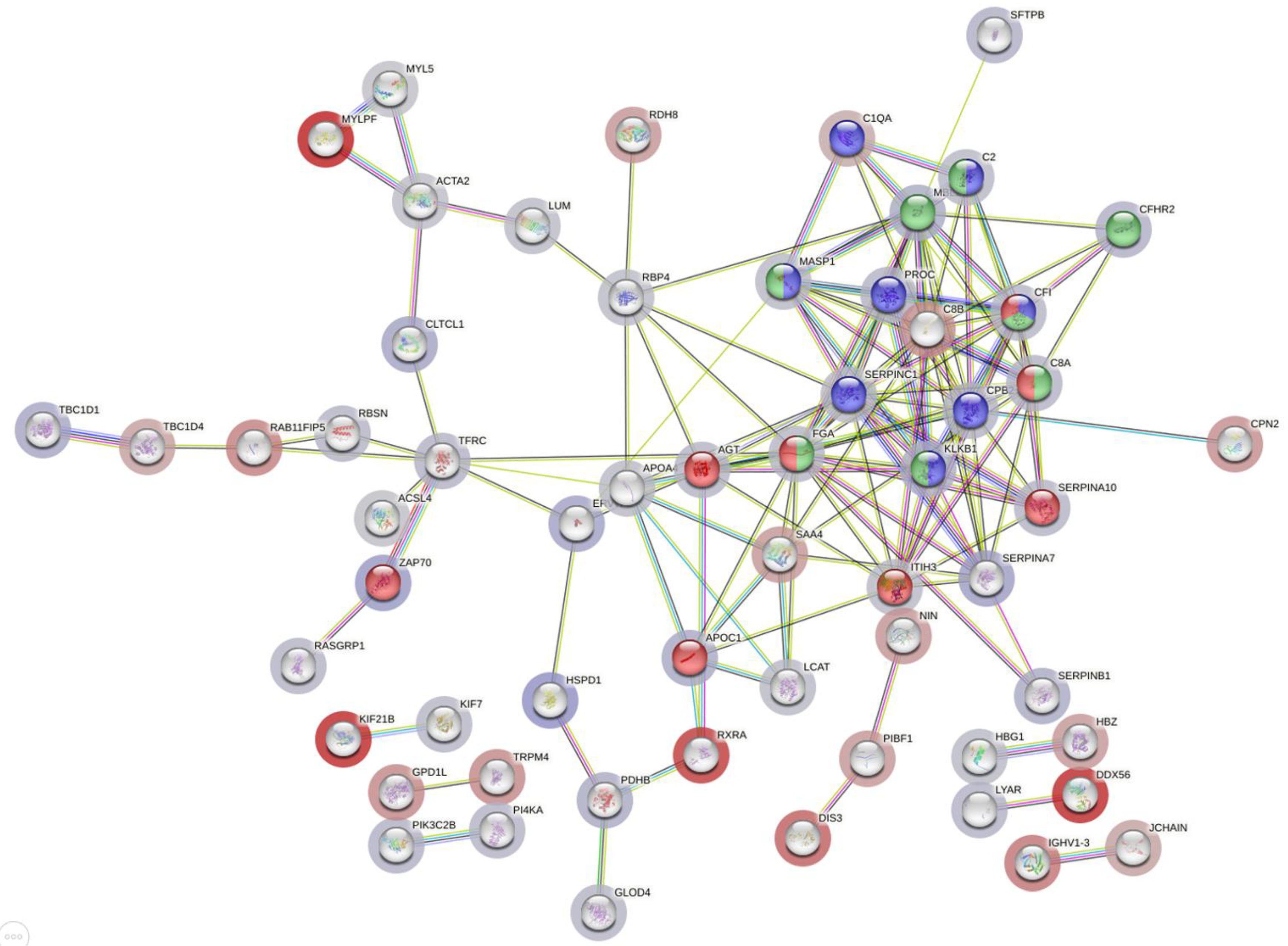
3.6. Functional Analysis of Dysregulated Proteins in Moderate/Under Medication Patients Compared to Recovered
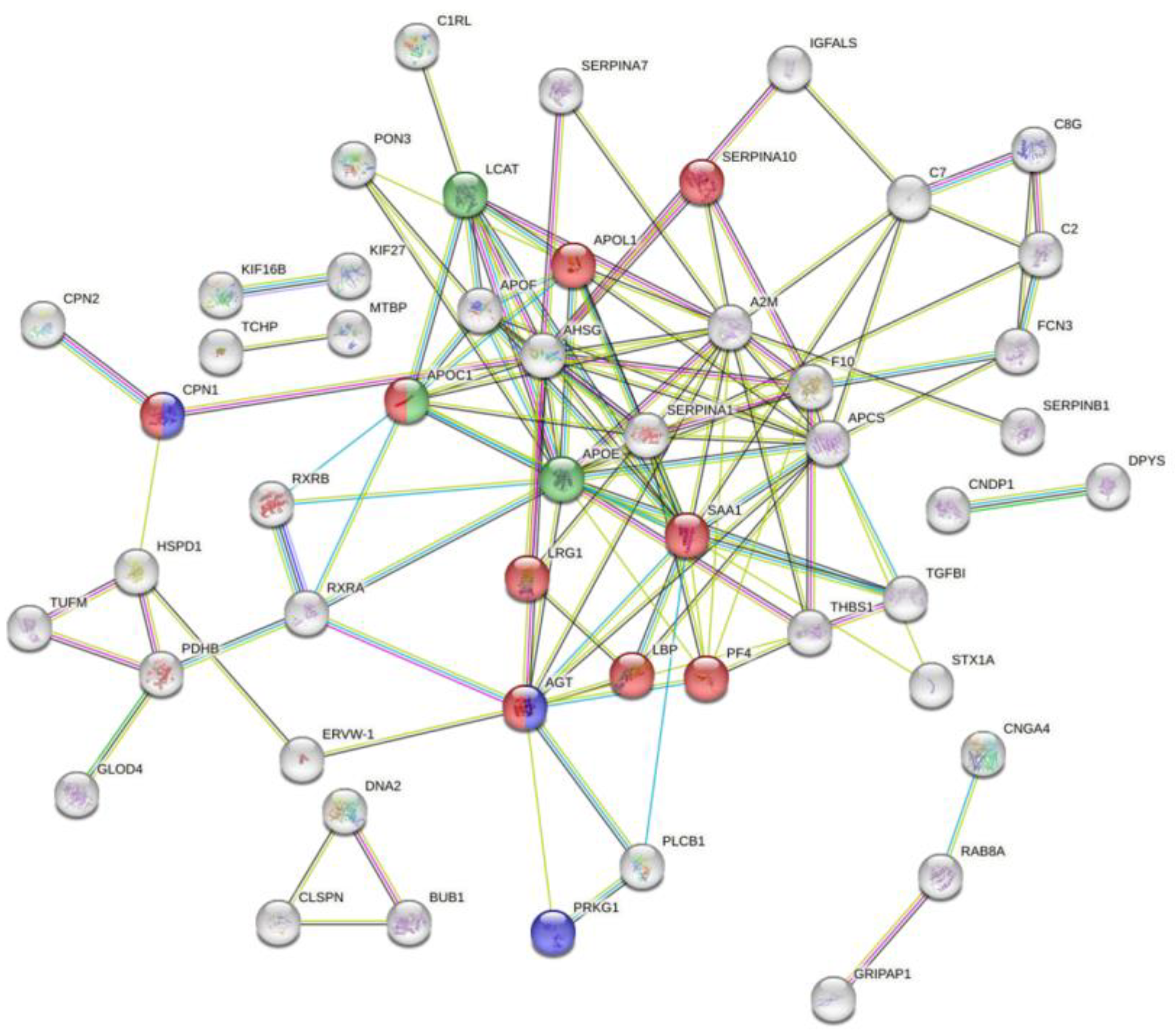
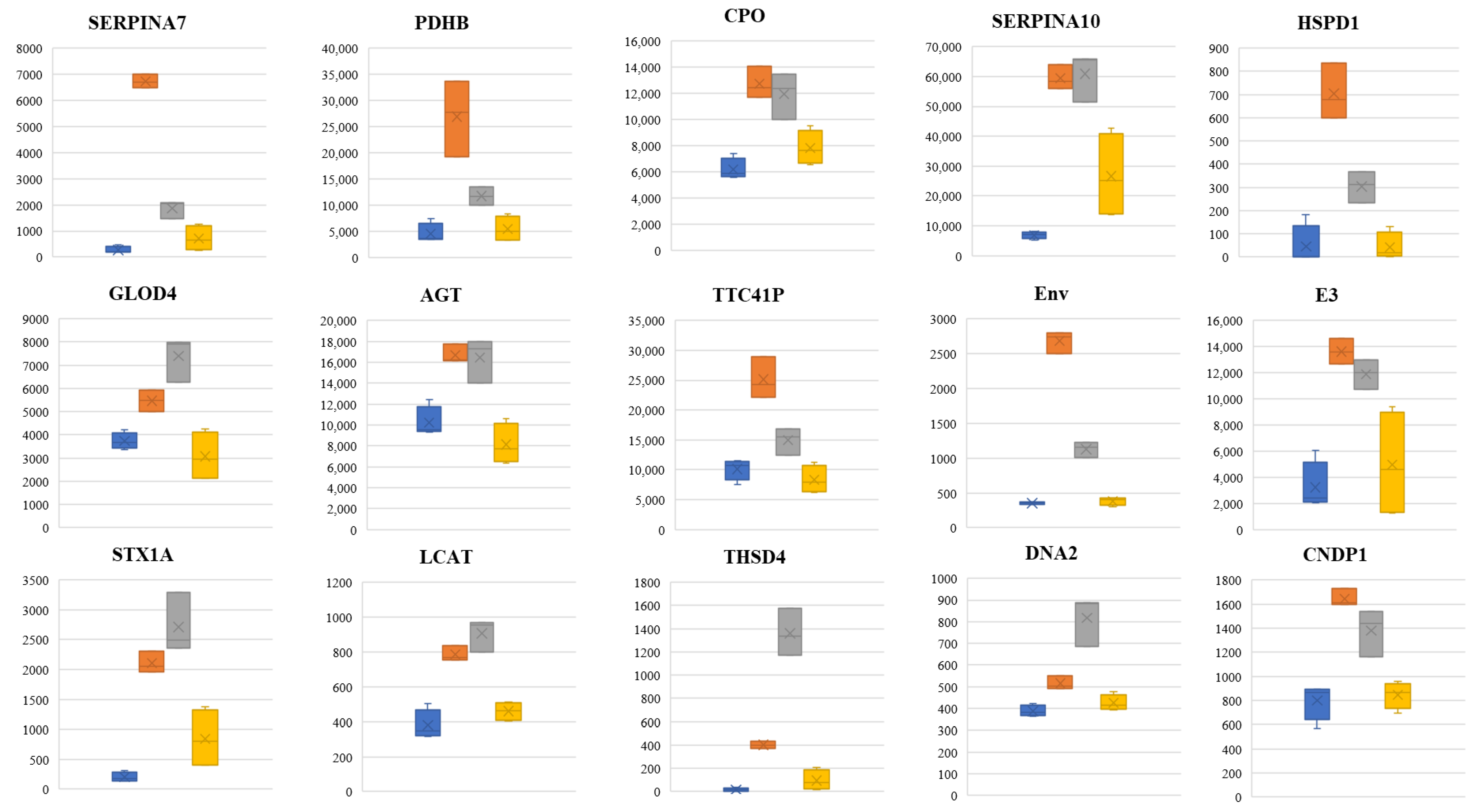
3.7. ROC Curve and Potential Biomarker Identification
3.8. Differentially Expressed Proteins Between Under Medication and Moderate Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, M.; Berhanu, G.; Desalegn, C.; Kandi, V. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update. Cureus 2020, 12, e7423. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32337143/ (accessed on 14 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, S. Family Coronaviridae. In Viruses; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 149–158. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7149805/ (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W.; Marraro, G.A.; Zeng, Y. From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: A brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 224. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32854739/ (accessed on 14 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Loeffelholz, M.J.; Tang, Y.W. Laboratory diagnosis of emerging human coronavirus infections—The state of the art. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 747–756. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32196430/ (accessed on 14 September 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, S.A.; Alhowikan, A.M.; Khlaiwi, T.A.L.; Meo, I.M.; Halepoto, D.M.; Iqbal, M.; Usmani, A.M.; Hajjar, W.; Ahmed, N. Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: Prevalence, biological and clinical characteristics comparison with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2012–2019. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32141570/ (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Zaim, S.; Chong, J.H.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Harky, A. COVID-19 and Multiorgan Response. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100618. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32439197/ (accessed on 23 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.; Salah Eldin, H.; Taeimah, M.; Khattab, R.; Salem, R. The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1446. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32612617/ (accessed on 23 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- di Flora, D.C.; Dionizio, A.; Pereira, H.A.B.S.; Garbieri, T.F.; Grizzo, L.T.; Dionisio, T.J.; Leite, A.D.L.; Silva-costa, L.C.; Buzalaf, N.R.; Fernanda, N.R.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Proteins Involved in Inflammation, Immune Response/Complement System, and Blood Coagulation upon Admission of COVID-19 Patients to Hospital May Help to Predict the Prognosis of the Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1601. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37371071/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Shin, J.; Hara, M.; Takeda, Y.; Kubo, S.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Ino, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Moriyama, K.; et al. Identification of serum prognostic biomarkers of severe COVID-19 using a quantitative proteomic approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20638. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34667241/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñez, E.; Orera, I.; Carmona-Rodríguez, L.; Paño, J.R.; Vázquez, J.; Corrales, F.J. Mapping the Serum Proteome of COVID-19 Patients; Guidance for Severity Assessment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1690. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35884998/ (accessed on 13 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72.e15. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32492406/ (accessed on 13 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Haroun, R.A.H.; Osman, W.H.; Amin, R.E.; Eessa, A.M.; Saad, S. Increased serum interleukin-6 and lactate dehydrogenase levels among nonsurvival severe COVID-19 patients when compared to survival ones. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110626. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37459785/ (accessed on 14 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, F.R.; Nordgren, J.; Fernandez-Botran, R.; Enocsson, H.; Govender, M.; Svanberg, C.; Svensson, L.; Hagbom, M.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, A.; Nistrom, S.; et al. Pentameric C-reactive protein is a better prognostic biomarker and remains elevated for longer than monomeric CRP in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1259005. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37724104/ (accessed on 14 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaiya, A.; Alshukairi, A.; Shinwari, Z.; Al-Fares, M.; Alotaibi, J.; Alomaim, W.; Alsharif, I.; Bakheet, R.; Alharbi, L.; Allam, R.; et al. Alterations in the Plasma Proteome Induced by SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV Reveal Biomarkers for Disease Outcomes for COVID-19 Patients. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4313–4328. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34511970/ (accessed on 13 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Britto, R.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Cukura, A.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36408920/ (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37943830/ (accessed on 8 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14597658/ (accessed on 29 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Pico, A.R.; Kelder, T.; Van Iersel, M.P.; Hanspers, K.; Conklin, B.R.; Evelo, C. WikiPathways: Pathway editing for the people. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e184. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18651794/ (accessed on 4 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Balcı, H.; Hanspers, K.; Coort, S.L.; Martens, M.; Slenter, D.N.; Ehrhart, F.; Digles, D.; Waagmeester, A.; Wassink, I.; et al. WikiPathways 2024: Next generation pathway database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D679–D689. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37941138/ (accessed on 4 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Messner, C.B.; Demichev, V.; Wendisch, D.; Michalick, L.; White, M.; Freiwald, A.; Textoris-Taubet, K.; Vernardirs, S.I.; Egger, A.S.; Kreidl, M.; et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Clinical Proteomics Reveals Classifiers of COVID-19 Infection. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 11–24.e4. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32619549/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ligi, D.; Della Franca, C.; Notarte, K.I.; Goldrich, N.; Kavteladze, D.; Henry, B.M.; Mannello, F. Platelet distribution width (PDW) as a significant correlate of COVID-19 infection severity and mortality. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 62, 385–395. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37725416/ (accessed on 3 July 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.; Chourasia, N.; Bharti, V.; Singh, S.; Sarkar, P.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Pal, R.; Kanwar, J.R.; Kotnis, A.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and severity prediction of COVID-19: Opportunities and challenges. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 4330. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36352911/ (accessed on 7 July 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, L.; Chinello, C.; Risca, G.; Capitoli, G.; Criscuolo, L.; Lombardi, A.; Ungaro, R.; Mangioni, D.; Piga, I.; Muscatello, A.; et al. Plasma Proteomic Variables Related to COVID-19 Severity: An Untargeted nLC-MS/MS Investigation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3570. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36834989/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, H.; Zhang, N.; Wu, J.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.; Lu, X.; Cheng, L.; Luo, R.; Liang, X.; et al. Proteomic Analysis Identifies Prolonged Disturbances in Pathways Related to Cholesterol Metabolism and Myocardium Function in the COVID-19 Recovery Stage. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3463–3474. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34080435/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Shi, C.; Luo, J.; Gao, M.; et al. The E3 ligase ASB3 downregulates antiviral innate immunity by targeting MAVS for ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. Cell Death Differ. 2024. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39266719/ (accessed on 28 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, J.F.; Lo, W.L.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Shen, L.; Weiss, A. ZAP70, too little, too much can lead to autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 307, 145–160. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34923645/ (accessed on 28 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, A.T.; Yurtseven, A.; Dadmand, S.; Ozcan, G.; Akarlar, B.A.; Kucuk, N.E.O.; Senturk, A.; Ergonul, O.; Can, F.; Tuncbag, N.; et al. Plasma proteomics identify potential severity biomarkers from COVID-19 associated network. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2023, 17, 2200070. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36217943/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ran, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, B.; et al. Longitudinal Serum Proteome Characterization of COVID-19 Patients With Different Severities Revealed Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 893943. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35958562/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Sakthivadivel, V.; Bohra, G.K.; Maithilikarpagaselvi, N.; Khichar, S.; Meena, M.; Palanisamy, N.; Gaur, A.; Garg, M.K. Association of Inflammatory Markers with COVID-19 Outcome among Hospitalized Patients: Experience from a Tertiary Healthcare Center in Western India. Maedica 2021, 16, 620–627. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35261664/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. Elevated level of C-reactive protein may be an early marker to predict risk for severity of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2409–2411. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32516845/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Isakadze, N.; Engels, M.C.; Beer, D.; McClellan, R.; Yanek, L.R.; Mondaloo, B.; Hays, A.G.; Metkus, T.S.; Calkins, H.; Barth, A.S.; et al. C-reactive Protein Elevation Is Associated With QTc Interval Prolongation in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 866146. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35811700/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32845568/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasrija, R.; Naime, M. The deregulated immune reaction and cytokines release storm (CRS) in COVID-19 disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107225. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33302033/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yue, L.; Ju, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; et al. Serum Proteomic Analysis for New Types of Long-Term Persistent COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0127022. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36314975/ (accessed on 13 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32217835/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xia, Z.; Deng, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhu, C.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Z.F.; et al. Inducible LGALS3BP/90K activates antiviral innate immune responses by targeting TRAF6 and TRAF3 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008002. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31404116/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, C.; Takov, K.; Burnap, S.A.; Singh, B.; Ali, H.; Theofilatos, K.; Reed, E.; Hasman, M.; Nabeebaccus, A.; Fish, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia and proteomic trajectories inform prognostication in COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3406. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34099652/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Captur, G.; Moon, J.C.; Topriceanu, C.C.; Joy, G.; Swadling, L.; Hallqvist, J.; Doykov, I.; Patel, N.; Spiewak, J.; Baldwin, T.; et al. Plasma proteomic signature predicts who will get persistent symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection. eBioMedicine 2022, 85, 104293. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36182629/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benigni, A.; Cassis, P.; Remuzzi, G. Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 247–257. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20597104/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- El-Arif, G.; Farhat, A.; Khazaal, S.; Annweiler, C.; Kovacic, H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Fajloun, Z.; Khattar, Z.A.; Sabatier, J.M.; et al. The Renin-Angiotensin System: A Key Role in SARS-CoV-2-Induced COVID-19. Molecules 2021, 26, 6945. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34834033/ (accessed on 27 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hülsmann, S.; Khabbazzadeh, S.; Meissner, K.; Quintel, M. A Potential Role of the Renin-Angiotensin-System for Disturbances of Respiratory Chemosensitivity in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 588248. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33551831/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rousset, X.; Shamburek, R.; Vaisman, B.; Amar, M.; Remaley, A.T. Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase: An anti- or pro-atherogenic factor? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2011, 13, 249–256. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21331766/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Couret, D.; Tran-Dinh, A.; Duranteau, J.; Montravers, P.; Schwendeman, A.; Meilhac, O. High-density lipoproteins during sepsis: From bench to bedside. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 134. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32264946/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilhac, O.; Tanaka, S.; Couret, D. High-Density Lipoproteins Are Bug Scavengers. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 598. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32290632/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kow, C.S.; Hasan, S.S. The Association Between the Use of Statins and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2022, 22, 167–181. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34341972/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Permana, H.; Huang, I.; Purwiga, A.; Kusumawardhani, N.Y.; Sihite, T.A.; Martanto, E.; Wisaksana, R.; Soetedjo, N.N.M. In-hospital use of statins is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in coronavirus-2019 (COVID-19): Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 769–780. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33608850/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kollias, A.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Kyriakoulis, I.G.; Nitsotolis, T.; Poulakou, G.; Stergiou, G.S.; Syrigos, K. Statin use and mortality in COVID-19 patients: Updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2021, 330, 114–121. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34243953/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, K.; Biswas, D.; Pai, M.G.J.; Acharjee, A.; Bankar, R.; Palanivel, V.; Salkar, A.; Verma, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Choudhury, M.; et al. Proteomics and Machine Learning Approaches Reveal a Set of Prognostic Markers for COVID-19 Severity With Drug Repurposing Potential. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 652799. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33995121/ (accessed on 28 February 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Serial ID | Category | Age | Nationality | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | Healthy | 21 | Saudi | Female |
| 36 | Healthy | 21 | Saudi | Male |
| 55 | Healthy | 24 | Saudi | Male |
| 45 | Healthy | 27 | Saudi | Male |
| 25 | Healthy | 28 | Saudi | Male |
| 43 | Healthy | 38 | Saudi | Female |
| 59 | Healthy | 44 | Saudi | Male |
| 76 | Healthy | 44 | Saudi | Male |
| 56 | Healthy | 50 | Saudi | Female |
| 20 | Healthy | 57 | Saudi | Female |
| 42 | Healthy | 59 | Saudi | Female |
| 44 | Healthy | 63 | Syrian | Male |
| 7 | Healthy | 67 | Syrian | Male |
| 35 | Healthy | 28 | Yemeni | Male |
| 21 | Healthy | 34 | Yemeni | Male |
| 54 | Healthy | 28 | Indian | Female |
| 58 | Healthy | 68 | Sudanese | Male |
| 67 | Healthy | 44 | Indonesian | Male |
| 6 | Healthy | 23 | Non-Saudi | Male |
| 31 | Healthy | 22 | Non-Saudi | Male |
| 77 | Moderate | 42 | Saudi | Female |
| 72 | Moderate | 50 | Saudi | Male |
| 11 | Moderate | 58 | Saudi | Male |
| 5 | Moderate | 60 | Saudi | Male |
| 33 | Moderate | 64 | Saudi | Female |
| 2 | Moderate | 69 | Saudi | Female |
| 50 | Moderate | 38 | Syrian | Male |
| 23 | Moderate | 53 | Syrian | Male |
| 74 | Moderate | 50 | Egyptian | Male |
| 41 | Moderate | 62 | Afghan | Male |
| 53 | Moderate | 55 | Yemeni | Male |
| 29 | Moderate | 70 | Yemeni | Male |
| 66 | Moderate | 51 | Bangladesh | Male |
| 65 | Moderate | 56 | Bangladesh | Female |
| 75 | Moderate | 56 | Sudanese | Male |
| 69 | Moderate | 69 | Canadian | Male |
| 78 | Moderate | 36 | Palestinian | Female |
| 24 | Moderate | 37 | Nepalese | Female |
| 19 | Moderate | 38 | Pakistani | Male |
| 73 | Moderate | 41 | Filipino | Male |
| 32 | Under MEDS | 55 | Saudi | Female |
| 80 | Under MEDS | 56 | Saudi | Male |
| 14 | Under MEDS | 61 | Saudi | Female |
| 39 | Under MEDS | 67 | Saudi | Male |
| 48 | Under MEDS | 67 | Saudi | Male |
| 71 | Under MEDS | 73 | Saudi | Male |
| 26 | Under MEDS | 75 | Saudi | Female |
| 18 | Under MEDS | NA | NA | NA |
| 62 | Under MEDS | 29 | Egyptian | Male |
| 57 | Under MEDS | 39 | Egyptian | Male |
| 22 | Under MEDS | 40 | Egyptian | Female |
| 64 | Under MEDS | 54 | Egyptian | Male |
| 27 | Under MEDS | 48 | Indian | Female |
| 46 | Under MEDS | 66 | Indian | Female |
| 60 | Under MEDS | 43 | Pakistani | Male |
| 17 | Under MEDS | 45 | Pakistani | Male |
| 70 | Under MEDS | 62 | Pakistani | Male |
| 63 | Under MEDS | 68 | Palestinian | Female |
| 38 | Under MEDS | 51 | Filipino | Male |
| 13 | Under MEDS | 46 | Syrian | Male |
| 12 | Recovered | 47 | Saudi | Female |
| 16 | Recovered | 60 | Saudi | Female |
| 15 | Recovered | 72 | Saudi | Male |
| 49 | Recovered | 72 | Saudi | Male |
| 68 | Recovered | 86 | Saudi | Female |
| 34 | Recovered | 91 | Saudi | Male |
| 51 | Recovered | 41 | Bangladesh | Female |
| 4 | Recovered | 44 | Bangladesh | Male |
| 10 | Recovered | 60 | Bangladesh | Male |
| 61 | Recovered | 33 | Sudanese | Male |
| 40 | Recovered | 58 | Sudanese | Male |
| 37 | Recovered | 62 | Sudanese | Female |
| 3 | Recovered | 39 | Egyptian | Male |
| 1 | Recovered | 41 | Moroccan | Female |
| 28 | Recovered | 50 | Filipino | Male |
| 79 | Recovered | 56 | Indian | Male |
| 30 | Recovered | 61 | Egyptian | Male |
| 52 | Recovered | 61 | Pakistani | Female |
| 9 | Recovered | 65 | Jordanian | Female |
| 47 | recovered | 60 | Sudanese | Male |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dandachi, I.; Alaiya, A.; Shinwari, Z.; Abbas, B.; Karkashan, A.; Al-Amari, A.; Aljabr, W. Proteomic Profiling of COVID-19 Patients Sera: Differential Expression with Varying Disease Stage and Potential Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222533
Dandachi I, Alaiya A, Shinwari Z, Abbas B, Karkashan A, Al-Amari A, Aljabr W. Proteomic Profiling of COVID-19 Patients Sera: Differential Expression with Varying Disease Stage and Potential Biomarkers. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(22):2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222533
Chicago/Turabian StyleDandachi, Iman, Ayodele Alaiya, Zakia Shinwari, Basma Abbas, Alaa Karkashan, Ahod Al-Amari, and Waleed Aljabr. 2024. "Proteomic Profiling of COVID-19 Patients Sera: Differential Expression with Varying Disease Stage and Potential Biomarkers" Diagnostics 14, no. 22: 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222533
APA StyleDandachi, I., Alaiya, A., Shinwari, Z., Abbas, B., Karkashan, A., Al-Amari, A., & Aljabr, W. (2024). Proteomic Profiling of COVID-19 Patients Sera: Differential Expression with Varying Disease Stage and Potential Biomarkers. Diagnostics, 14(22), 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14222533





