AI-Based Noise-Reduction Filter for Whole-Body Planar Bone Scintigraphy Reliably Improves Low-Count Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
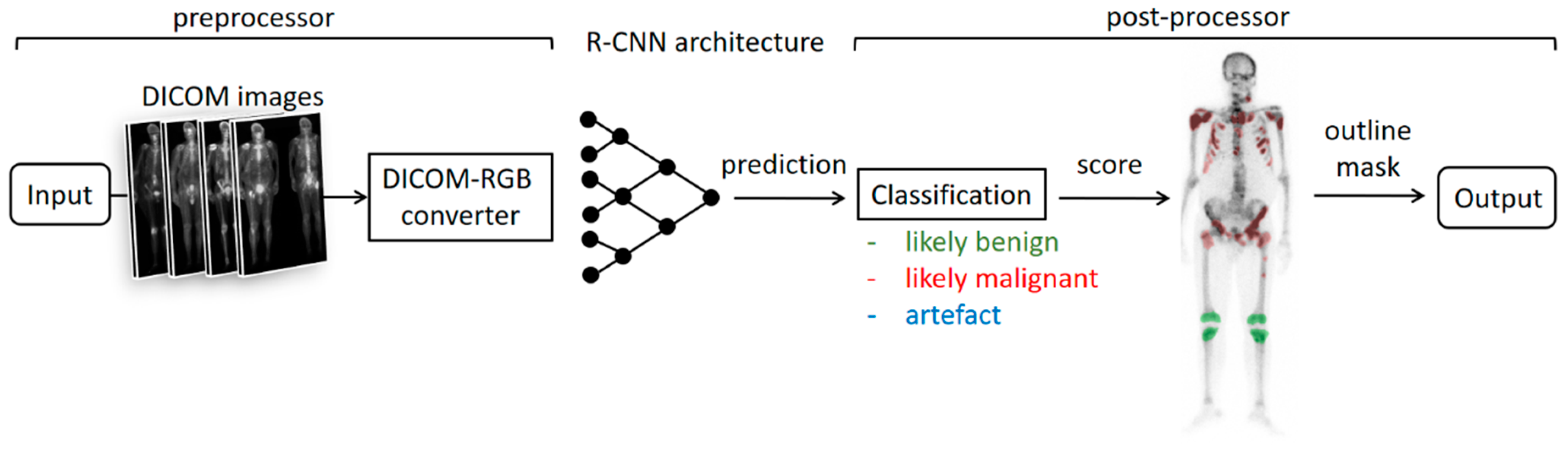
2. Methods
2.1. Data Set
- Body mass index (BMI): underweight, normal, and obese patients;
- Age: <45 years, 45–65 years, and >65 years;
- Gender: female and male;
- Lesions: normal accumulation only, ≤3 lesions, and >3 lesions (multiple metastases).
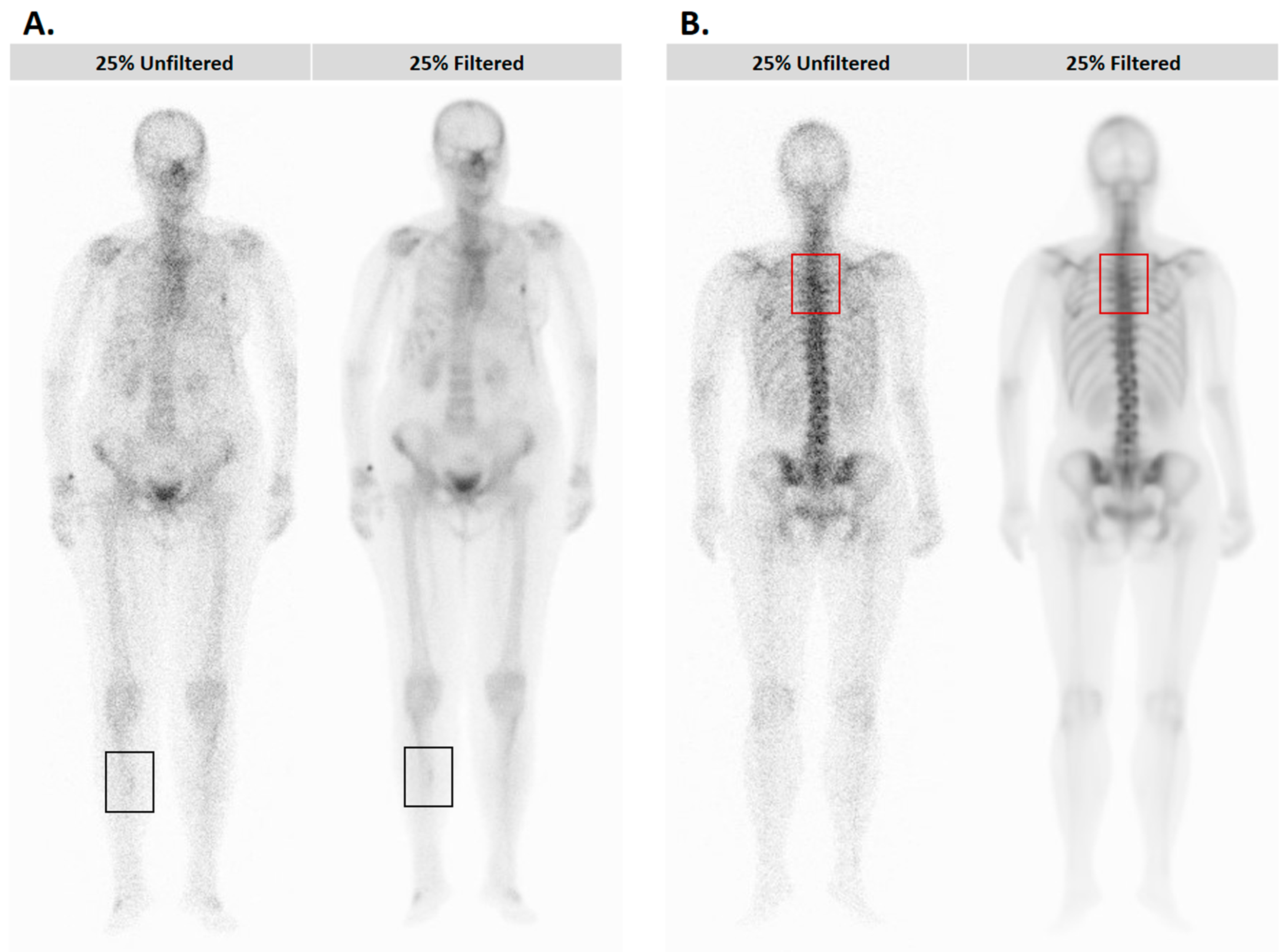
2.2. Visual Assessment
- Is there any lesion that is not visible in the original image but highlighted by the AI filter? (1: No, 2: Yes);
- Is there any lesion that is missed in the AI-filtered image? (1: No, 2: Yes);
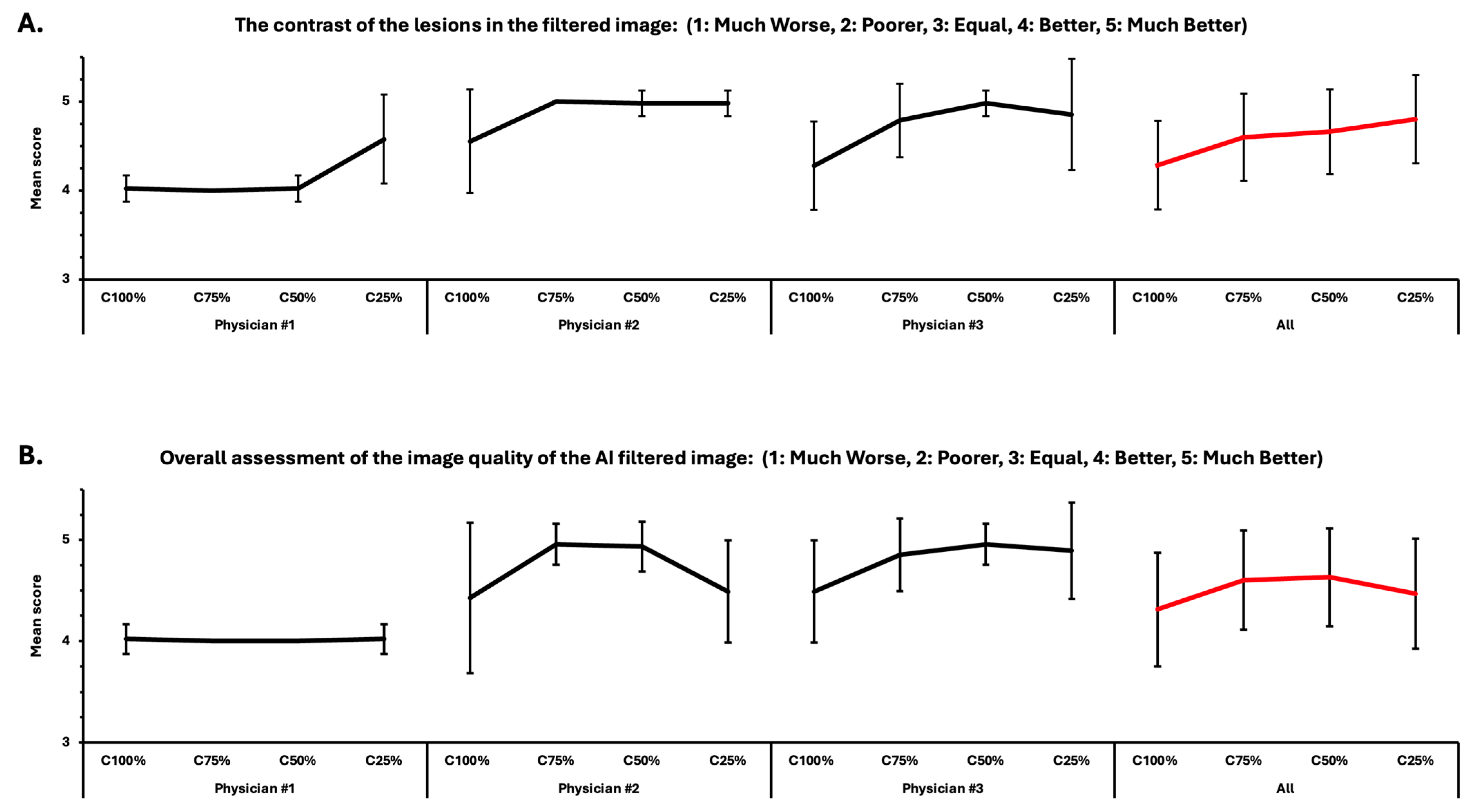
- The contrast of the lesions in the filtered image: (1: Much Worse, 2: Poorer, 3: Equal, 4: Better, 5: Much Better);
- Overall assessment of the image quality of the AI-filtered image: (1: Much Worse, 2: Poorer, 3: Equal, 4: Better, 5: Much Better).
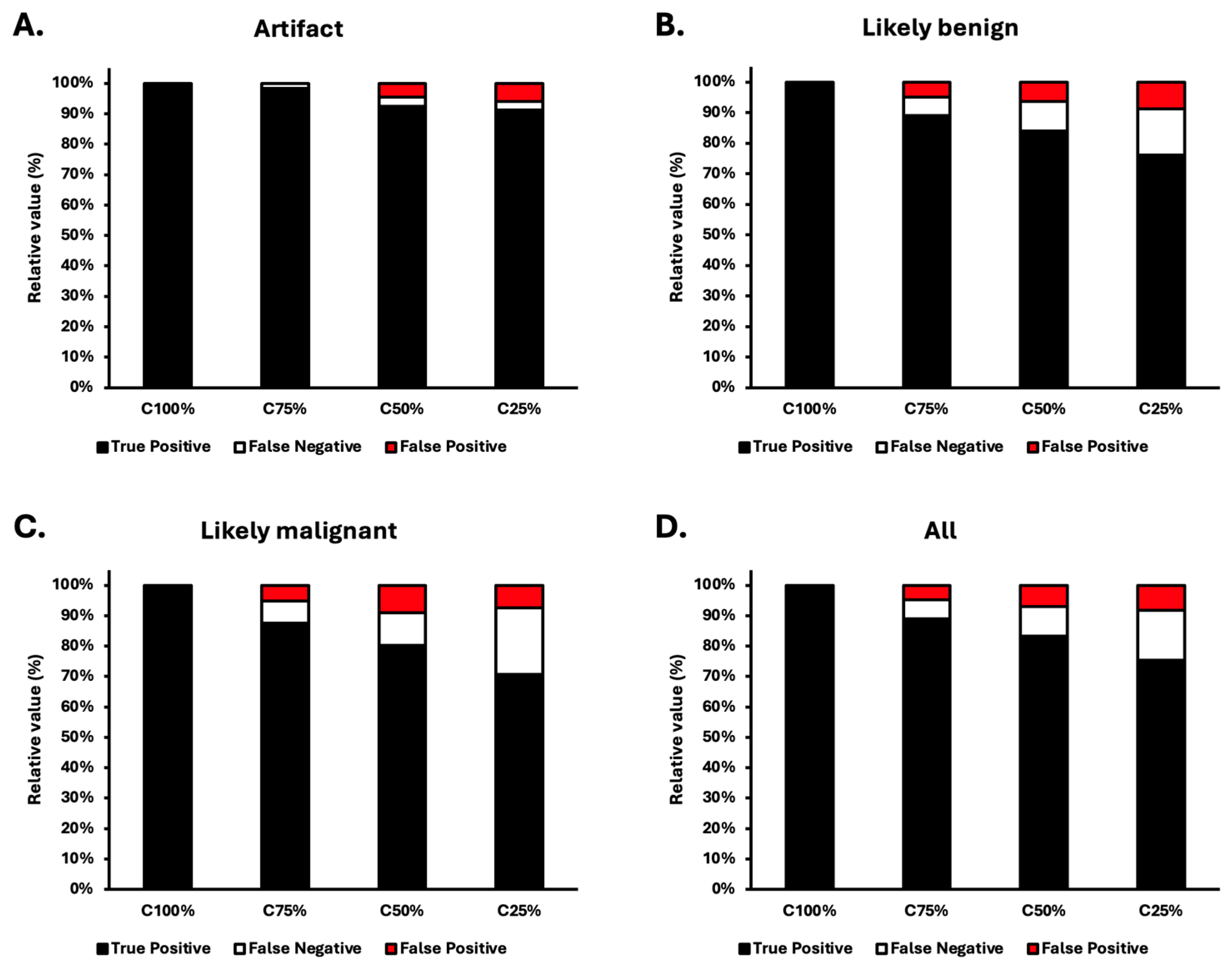
2.3. Automatic Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Visual Assessment
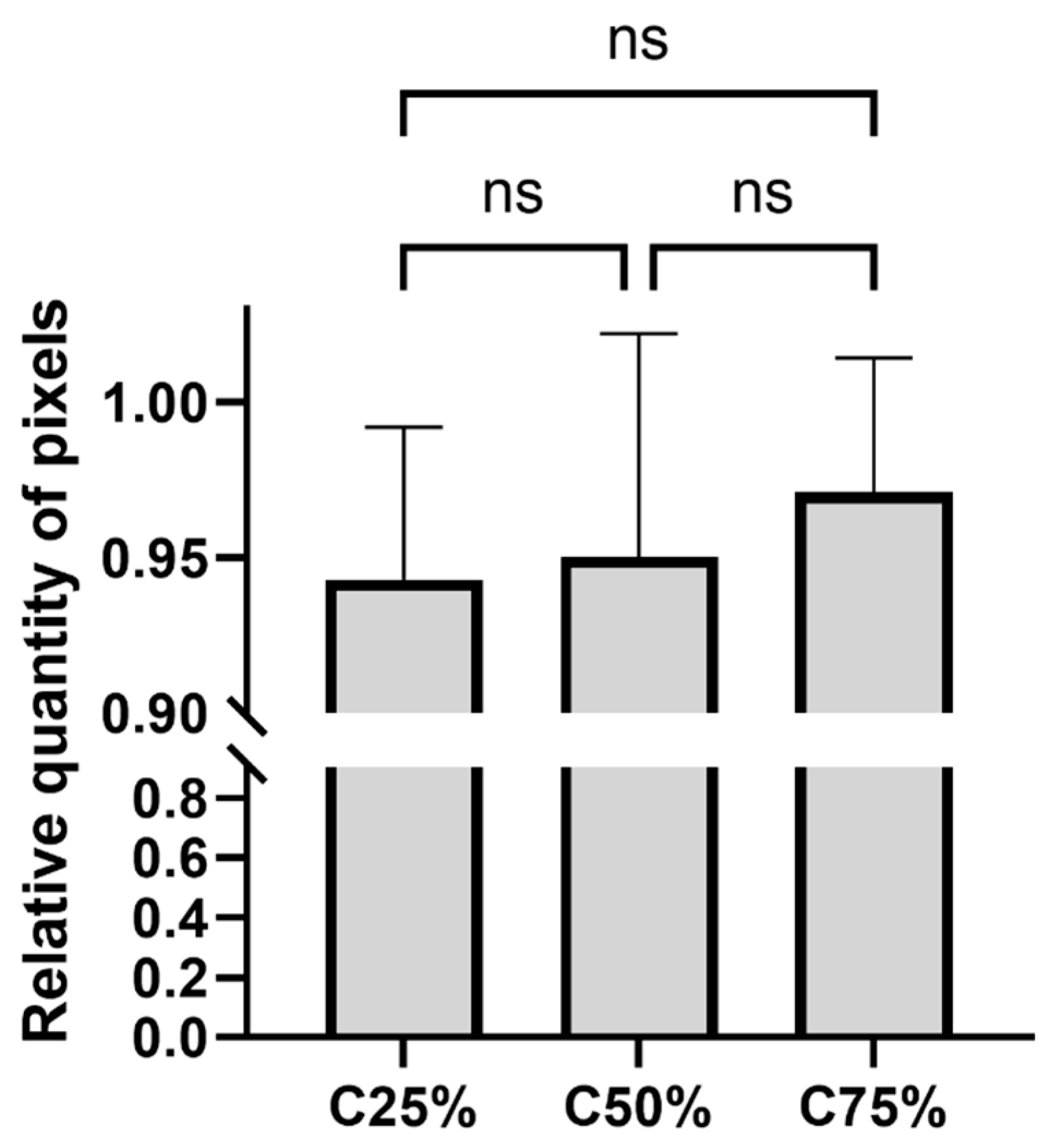
3.2. Results of the Automatic Segmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van den Wyngaert, T.; Strobel, K.; Kampen, W.U.; Kuwert, T.; van der Bruggen, W.; Mohan, H.K.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Weber, W.A.; Beheshti, M.; et al. The EANM practice guidelines for bone scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, T.B.; Kuruva, M.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Beheshti, M.; Cohen, E.J.; Weissman, A.F.; Yarbrough, T.L. SNMMI Procedure Standard for Bone Scintigraphy 4.0. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2018, 46, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.I.; Koshy, J.; Morey, J.; Lin, C.; DiPoce, J. The bone scan. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 42, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbeke, D.; Segall, G.M. Status of and trends in nuclear medicine in the United States. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52 (Suppl. S2), 24S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.I. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuni, C.C.; Hasegawa, B.H.; Hendee, W.R. Noise reduction in nuclear medicine images. J. Nucl. Med. 1983, 24, 532–534. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E.; Chang, W.; Yoo, J.; Ye, J.C. Deep Convolutional Framelet Denosing for Low-Dose CT via Wavelet Residual Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondara, L. Medical image denoising using convolutional denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Barcelona, Spain, 12–15 December 2016; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Horger, M.; Bares, R. The role of single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in benign and malignant bone disease. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 36, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Á.; Bükki, T.; Légrádi, G.; Mészáros, N.J.; Kovács, G.Z.; Prajczer, P.; Tamaga, I.; Seress, Z.; Kiszler, G.; Forgács, A.; et al. Robustness analysis of denoising neural networks for bone scintigraphy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2022, 1039, 167003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, F.; Krizsan, A.K.; Kukuts, K.; Szolikova, M.; Hascsi, Z.; Barna, S.; Acs, A.; Szabo, P.; Tron, L.; Balkay, L.; et al. Q-Bot: Automatic DICOM metadata monitoring for the next level of quality management in nuclear medicine. EJNMMI Phys. 2021, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minarik, D.; Enqvist, O.; Trägårdh, E. Denoising of Scintillation Camera Images Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network: A Monte Carlo Simulation Approach. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Onoguchi, M.; Shibutani, T.; Iimori, T.; Sawada, K.; Umezawa, T.; Masuda, Y.; Uno, T. Verification of image quality improvement of low-count bone scintigraphy using deep learning. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2024, 17, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Maeno, T.; Tsuchikame, H.; Shishido, M.; Nishi, K.; Kojima, S.; Hayashi, T.; Suzuki, K. Adapting a low-count acquisition of the bone scintigraphy using deep denoising super-resolution convolutional neural network. Phys. Med. 2022, 100, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rager, O.; Nkoulou, R.; Exquis, N.; Garibotto, V.; Tabouret-Viaud, C.; Zaidi, H.; Amzalag, G.; Lee-Felker, S.A.; Zilli, T.; Ratib, O. Whole-Body SPECT/CT versus Planar Bone Scan with Targeted SPECT/CT for Metastatic Workup. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7039406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmedo, H.; Marx, C.; Ebert, A.; Kreft, B.; Ko, Y.; Türler, A.; Vorreuther, R.; Göhring, U.; Schild, H.H.; Gerhardt, T.; et al. Whole-body SPECT/CT for bone scintigraphy: Diagnostic value and effect on patient management in oncological patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, G.J.; Carty, F.L.; Cronin, C.G. Imaging of bone metastasis: An update. World J. Radiol. 2015, 7, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyts, K.; Lasnon, C.; Ciappuccini, R.; Lequesne, J.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A.; Quak, E.; Clarisse, B.; Roussel, L.; Bardet, S.; Jaudet, C. Artificial intelligence-based PET denoising could allow a two-fold reduction in [18F]FDG PET acquisition time in digital PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3750–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Huang, H.M. Simultaneous Denoising of Dynamic PET Images Based on Deep Image Prior. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaudet, C.; Weyts, K.; Lechervy, A.; Batalla, A.; Bardet, S.; Corroyer-Dulmont, A. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence CNN Based Denoising on FDG PET Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 692973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Baratto, L.; Hawk, K.E.; Theruvath, A.J.; Pribnow, A.; Thakor, A.S.; Gatidis, S.; Lu, R.; Gummidipundi, S.E.; Garcia-Diaz, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence enables whole-body positron emission tomography scans with minimal radiation exposure. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margail, C.; Merlin, C.; Billoux, T.; Wallaert, M.; Otman, H.; Sas, N.; Molnar, I.; Guillemin, F.; Boyer, L.; Guy, L.; et al. Imaging quality of an artificial intelligence denoising algorithm: Validation in 68Ga PSMA-11 PET for patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loft, M.; Ladefoged, C.N.; Johnbeck, C.B.; Carlsen, E.A.; Oturai, P.; Langer, S.W.; Knigge, U.; Andersen, F.L.; Kjaer, A. An Investigation of Lesion Detection Accuracy for Artificial Intelligence-Based Denoising of Low-Dose 64Cu-DOTATATE PET Imaging in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quak, E.; Weyts, K.; Jaudet, C.; Prigent, A.; Foucras, G.; Lasnon, C. Artificial intelligence-based 68Ga-DOTATOC PET denoising for optimizing 68Ge/68Ga generator use throughout its lifetime. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1137514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, J.; Phulia, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Sharma, P.D.; Patel, C. Denoising Tc-99m DMSA images using Denoising Convolutional Neural Network with comparison to a Block Matching Filter. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2023, 44, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, K.; Edenbrandt, L.; Mizokami, A. Bone scan index: A new biomarker of bone metastasis in patients with prostate cancer. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Csikos, C.; Barna, S.; Kovács, Á.; Czina, P.; Budai, Á.; Szoliková, M.; Nagy, I.G.; Husztik, B.; Kiszler, G.; Garai, I. AI-Based Noise-Reduction Filter for Whole-Body Planar Bone Scintigraphy Reliably Improves Low-Count Images. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232686
Csikos C, Barna S, Kovács Á, Czina P, Budai Á, Szoliková M, Nagy IG, Husztik B, Kiszler G, Garai I. AI-Based Noise-Reduction Filter for Whole-Body Planar Bone Scintigraphy Reliably Improves Low-Count Images. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(23):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232686
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsikos, Csaba, Sándor Barna, Ákos Kovács, Péter Czina, Ádám Budai, Melinda Szoliková, Iván Gábor Nagy, Borbála Husztik, Gábor Kiszler, and Ildikó Garai. 2024. "AI-Based Noise-Reduction Filter for Whole-Body Planar Bone Scintigraphy Reliably Improves Low-Count Images" Diagnostics 14, no. 23: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232686
APA StyleCsikos, C., Barna, S., Kovács, Á., Czina, P., Budai, Á., Szoliková, M., Nagy, I. G., Husztik, B., Kiszler, G., & Garai, I. (2024). AI-Based Noise-Reduction Filter for Whole-Body Planar Bone Scintigraphy Reliably Improves Low-Count Images. Diagnostics, 14(23), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14232686





