Development of an Artificial Soft Solid Gel Using Gelatin Material for High-Quality Ultrasound Diagnosis
Abstract
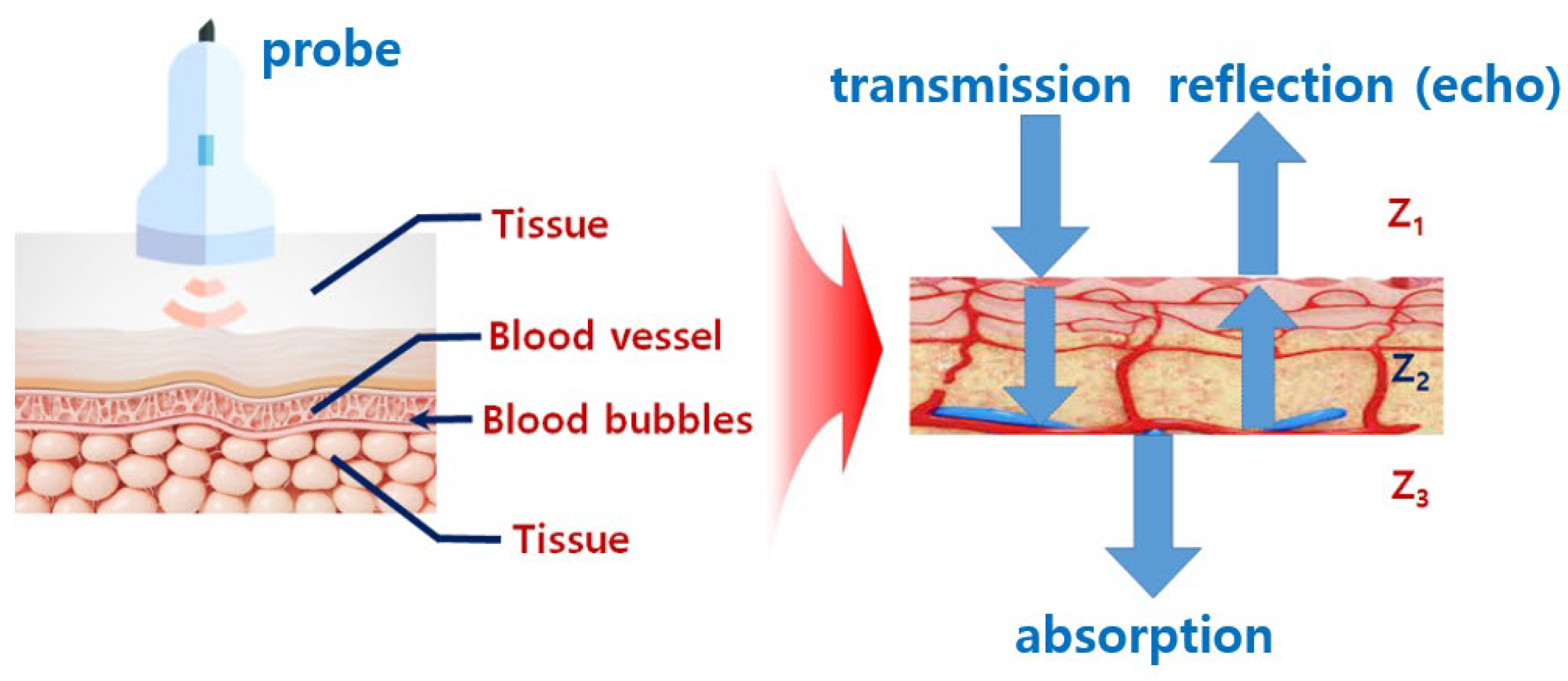
1. Introduction
2. Manufacturing Analysis and Methods
Analysis of the Ultrasonic Gel Characteristics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afzal, S.; Zahid, M.; Rehan, Z.A.; Shakir, H.M.F.; Javed, H.; Aljohani, M.M.H.; Mustafa, S.K.; Ahmad, M.; Hassan, M.M. Preparation and evaluation of polymer-based ultrasound gel and its application in ultrasonography. Gels 2022, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, W.; Shao, W.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Cui, Y. An electrical impedance matching method of dual-frequency transducers for ultrasound internal imaging. Measurement 2023, 221, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hou, L.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y. Ultrasound vibration energy harvesting from a rotary-type piezoelectric ultrasonic actuator. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.M.; Tolba, M.A.; Ismail, O.M.; Messeha, M.M. Ultrasonography versus palpation for spinal anesthesia in obese parturients undergoing cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial. Reg. Anesthesia Pain Med. 2023, 49, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown MR, D.; Farquhar-Smith, P.; Williams, J.E.; Ter Haar, G.; Desouza, N.M. The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound as a novel treatment for painful conditions—A description and narrative review of the literature. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanka, H.; Pagel Paul, S. Potential adverse ultrasound-related biological effects. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Zahid, M.; Nimra Sadia, S.; Fatima, Z.; Shakir Fayzan, H.M.; Rehan, Z.A. Ultrasound hydrogel: A review on materials and method. J. Mod. Polym. Chem. Mater. 2022, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, N.; Monnai, Y. Generating in vivo continuous ultrasound based on sub-terahertz photoacoustic effect. APL Photonics 2023, 8, 086105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, E.C.; Ware, P.J.; Bitange, P.; Cooper, G.J.; Galea, T.; Bengiamin, D.I.; Young, T.P. The “Syringe Hickey”: An Alternative Skin Marking Method for Lumbar Puncture. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 64, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaz, M. Possible long-term complications in ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty induced by sonoluminescence, sonochemistry, and thermal effect. Aesthetic Surg. J. 1998, 18, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Riis Porsborg, S.; Krzyslak, H.; Pierchala, M.K.; Trolé, V.; Astafiev, K.; Lou-Moeller, R.; Pennisi, C.P. Exploring the Potential of Ultrasound Therapy to Reduce Skin Scars: An In Vitro Study Using a Multi-Well Device Based on Printable Piezoelectric Transducers. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnle, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Kanai, H. Multi element diverging beam from a linear array transducer for transverse cross sectional imaging of carotid artery: Simulations and phantom vessel validation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 07HF05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poree, J.; Chayer, B.; Soulez, G.; Ohayon, J.; Cloutier, G. Noninvasive Vascular Modulography Method for Imaging the Local Elasticity of Atherosclerotic Plaques: Simulation and In Vitro Vessel Phantom Study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2017, 64, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingstone, L.L.; Castonguay, M.; Torres, C.; Currie, G. Carotid Artery Disease Imaging: A Home-Produced, Easily Made Phantom for Two- and Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Simulation. J. Vasc. Ultrasound 2013, 37, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.-Y.; Lin, C.-S.; Li, W.-M.; Huang, S.-H.; Cho, Y.-T.; Peng, B.-R.; Pan, L.-K.; Pan, L.-F. Optimizing the Ultrasound Image Quality of Carotid Artery Stenosis Patients via Taguchi’s Dynamic Analysis and an Indigenous Water Phantom. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, E.; Arteaga-Marrero, N.; González-Fernández, J.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Bimodal microwave and ultrasound phantoms for non-invasive clinical imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, S.; Ternifi, R.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Custom-made Flow Soft solid gels for Quantitative Ultrasound Microvessel Imaging. Ultrasonics 2023, 134, 107092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramyadevi, R. A Cost-Effective, Agar-based Soft solid gel for Thermogram-Guided Malignancy Analysis. In Computational Intelligence for Clinical Diagnosis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, M.J. Evaluating students’ conceptual understanding of balanced equations and stoichiometric ratios using a particulate drawing. J. Chem. Educ. 2005, 82, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Edwards, S.A.; Iorizzo, T.W.; Longo, B.N.; Yaroslavsky, A.N.; Kaplan, D.L.; Mallidi, S. Investigation of silk as a Soft solid gel material for ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging. Photoacoustics 2022, 28, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGibbon, C.A.; Strom, J. Numerical invariants of Soft solid gel maps. Am. J. Math. 2001, 123, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boice, E.N.; Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Knowlton, Z.J.; Berard, D.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Avital, G.; Snider, E.J. Training Ultrasound Image Classification Deep-Learning Algorithms for Pneumothorax Detection Using a Synthetic Tissue Soft solid gel Apparatus. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SONON 300C, Portable Ultrasound Device (User Manual Rev. 2); Healcerion: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013.
- Kim, K.; Chon, N.; Jeong, H.-W.; Lee, Y. Improvement of Ultrasound Image Quality Using Non-Local Means Noise-Reduction Approach for Precise Quality Control and Accurate Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmar, M.; Hoffmann, T.; Sauerhering, J.; Klink, F. Manufacturing process for hydrogel vessel Soft solid gels. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 5, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.; Popovics, J.S.; Struble, L.J. Using ultrasonic wave reflection to measure solution properties. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehm, K.D.; Madihally, S.V. Bioprinted chitosan-gelatin thermosensitive hydrogels using an inexpensive 3D printer. Biofabrication 2017, 10, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod Vivek, T. A Review of acoustic impedance matching techniques for piezoelectric sensors and transducers. Sensors 2020, 20, 4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.V.; Schorr, D.; Metin, J.K.; Yildirim, M.; Khan, S.A.; Schneider, M. Gelatin nanoparticles with tunable mechanical properties: Effect of crosslinking time and loading. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, M.; Sharrock, P.; Fiallo, M.; ElFeki, H. Hydroxyapatite bioceramic with large porosity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglat Ammar, A.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Suardi, N.; Oqlat Mohammad, A.; Oqlat Ahmad, A.; Abdelrahman Mostafa, A.; Farhat, O.F.; Ahmad Muntaser, S.; Alkhateb Batool, N.; Gemanam Sylvester, J.; et al. Characterization and construction of a robust and elastic wall-less flow phantom for high pressure flow rate using doppler ultrasound applications. NESciences 2018, 3, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffessi Siewe, S.; Callé, S.; Vander Meulen, F.; Valente, D.; Grégoire, J.-M.; Banquart, A.; Chevalliot, S.; Capri, A.; Levassort, F. High Acoustic Impedance and Attenuation Backing for High-Frequency Focused P (VDF-TrFE)-Based Transducers. Sensors 2023, 23, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalmans, I.; Vandewalle, E.; Anderson Douglas, R.; Costa Vital, P. Use of colour doppler imaging in ocular blood flow research. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011, 89, e609-30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H. A Class-J power amplifier implementation for ultrasound device applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Choi, H. A new approach to power efficiency improvement of ultrasonic transmitters via a dynamic bias technique. Sensors 2021, 21, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Paluska Matthew, R.; Falcon, R.; Petersen Timothy, R.; Soneru, C. Rapid Evaluation of Gastric Content With Ultrasound: An Educational Tool. Cureus 2023, 15, e49031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, T.; Kim, H.; Jo, Y.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, S.; Bae, H.M.; Lee, H.-J. Calcium-modified silk patch as a next-generation ultrasound coupling medium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55827–55839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwar, R.; Saint-Martin, L.; Avanaki, K. Couplants in acoustic biosensing systems. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Cao, X.; He, X. Theoretical and experimental studies of acoustic reflection of bubbly liquid in multilayer media. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashir, A.; Jerban, S.; Barrère, V.; Wu, Y.; Shah Sameer, B.; Andre Michael, P.; Chang Eric, Y. Skeletal Muscle assessment using quantitative ultrasound: A narrative review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, D.; Nikezic, D.; Jeremic, M.Z.; Dolicanin, E.; Miladinovic, T.B.; Zivkovic, M. Comparison between MCNP and planning system in brachytherapy of cervical cancer. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 192, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, R.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Tan, G. An Acyclic Silylone Stabilized by Mesoionic Carbene. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202200413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajest, S.S.; Shynu, T.; Regin, R. The Use of Deep Learning Methods for the Detection of Diseases in Plant Leaves. Cent. Asian J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2023, 4, 67–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kamlow, M.A. How to Formulate for Structure and Texture via 3D-Printing–Design and Characterisation of Edible Biopolymer Gels to Act as Release Vehicles. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L. Application of artificial intelligence in ultrasound imaging for predicting lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin. Imaging 2024, 106, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kor Text Version. Available online: www.jewon1986.com/m/sub/productV.php?pid=395 (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Ma, X.; Cai, J.; Liu, D. Ultrasound for pectinase modification: An investigation into potential mechanisms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4636–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]















| Type | Gray Scale [mm] | Dead Zone [mm] | Vertical Zone [mm] | Horizontal Zone [mm] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | AV * | ±SD ** | ERROR *** | AV | ±SD | ERROR | AV | ±SD | ERROR | AV | ±SD | ERROR |
| US gel | 87.0 | 4.8 | 2.4 | 44.3 | 1.01 | 0.58 | 102.1 | 0.92 | 0.5 | 83.5 | 0.65 | 0.03 |
| Soft solid gel | 102.4 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 35.4 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 140.3 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 101.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| Water soft solid gel | 80.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 30.5 | 0.83 | 0.48 | 91.8 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 60.1 | 1.7 | 1.0 |
| Silicon soft solid gel | 80.0 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 21.1 | 1.1 | 0.64 | 111.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 80.5 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Time [min/h] | Image | Significant |
|---|---|---|
| 1 min |  | |
| 30 min |  | Not dry |
| 60 min |  | |
| 6 h |  | Not dry |
| 12 h |  | |
| 24 h |  | Not dry |
| 48 h |  | |
| 72 h |  | Not dry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Yoon, K.; Lee, S.; Shin, M.-S.; Kim, K.G. Development of an Artificial Soft Solid Gel Using Gelatin Material for High-Quality Ultrasound Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030335
Kim M, Yoon K, Lee S, Shin M-S, Kim KG. Development of an Artificial Soft Solid Gel Using Gelatin Material for High-Quality Ultrasound Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030335
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minchan, Kicheol Yoon, Sangyun Lee, Mi-Seung Shin, and Kwang Gi Kim. 2024. "Development of an Artificial Soft Solid Gel Using Gelatin Material for High-Quality Ultrasound Diagnosis" Diagnostics 14, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030335
APA StyleKim, M., Yoon, K., Lee, S., Shin, M.-S., & Kim, K. G. (2024). Development of an Artificial Soft Solid Gel Using Gelatin Material for High-Quality Ultrasound Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 14(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14030335







