Detection of Acute Brain Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients on ECMO Support Using Ultra-Low-Field Portable MRI: A Retrospective Analysis Compared to Head CT
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boldt, J. Clinical Review: Hemodynamic Monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care 2002, 6, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ong, C.S.; Etchill, E.; Dong, J.; Shou, B.L.; Shelley, L.; Giuliano, K.; Al-Kawaz, M.; Ritzl, E.K.; Geocadin, R.G.; Kim, B.S.; et al. Neuromonitoring Detects Brain Injury in Patients Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 165, 2104–2110.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algethamy, H.M.; Alzawahmah, M.; Young, G.B.; Mirsattari, S.M. Added Value of MRI over CT of the Brain in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 42, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanara, B.; Manzon, C.; Barbot, O.; Desmettre, T.; Capellier, G. Recommendations for the Intra-Hospital Transport of Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmentier-Decrucq, E.; Poissy, J.; Favory, R.; Nseir, S.; Onimus, T.; Guerry, M.-J.; Durocher, A.; Mathieu, D. Adverse Events during Intrahospital Transport of Critically Ill Patients: Incidence and Risk Factors. Ann. Intensive Care 2013, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temsah, M.-H.; Al-Sohime, F.; Alhaboob, A.; Al-Eyadhy, A.; Aljamaan, F.; Hasan, G.; Ali, S.; Ashri, A.; Nahass, A.A.; Al-Barrak, R.; et al. Adverse Events Experienced with Intrahospital Transfer of Critically Ill Patients. Medicine 2021, 100, e25810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Nakagawa, N.; Kawasaki, T.; Yasuo, S.; Yoshida, T.; Ando, K.; Okamori, S.; Okada, Y. Adverse Events during Intrahospital Transport of Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, K.N.; Mazurek, M.H.; Yuen, M.M.; Cahn, B.A.; Shah, J.T.; Ward, A.; Kim, J.A.; Gilmore, E.J.; Falcone, G.J.; Petersen, N.; et al. Assessment of Brain Injury Using Portable, Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging at the Bedside of Critically Ill Patients. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 78, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberly, W.T.; Sorby-Adams, A.J.; Webb, A.G.; Wu, E.X.; Beekman, R.; Bowry, R.; Schiff, S.J.; De Havenon, A.; Shen, F.X.; Sze, G.; et al. Brain Imaging with Portable Low-Field MRI. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhat, A.M.; Crawford, A.L.; Mazurek, M.H.; Yuen, M.M.; Chavva, I.R.; Ward, A.; Hofmann, W.V.; Timario, N.; Qualls, S.R.; Helland, J.; et al. Methodology for Low-Field, Portable Magnetic Resonance Neuroimaging at the Bedside. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, K.N.; Yuen, M.M.; Mazurek, M.H.; Cahn, B.A.; Prabhat, A.M.; Salehi, S.; Shah, J.T.; By, S.; Welch, E.B.; Sofka, M.; et al. Bedside Detection of Intracranial Midline Shift Using Portable Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-M.; Wilcox, C.; Keller, S.; Acton, M.; Rando, H.; Etchill, E.; Giuliano, K.; Bush, E.L.; Sair, H.I.; Pitts, J.; et al. Assessing the SAfety and FEasibility of Bedside Portable Low-Field Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients on ECMO (SAFE-MRI ECMO Study): Study Protocol and First Case Series Experience. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuoy, E.; Glavis-Bloom, J.; Hovis, G.; Yep, B.; Biswas, A.; Masudathaya, L.-A.; Norrick, L.A.; Limfueco, J.; Soun, J.E.; Chang, P.D.; et al. Point-of-Care Brain MRI: Preliminary Results from a Single-Center Retrospective Study. Radiology 2022, 305, 211721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sien, M.E.; Robinson, A.L.; Hu, H.H.; Nitkin, C.R.; Hall, A.S.; Files, M.G.; Artz, N.S.; Pitts, J.T.; Chan, S.S. Feasibility of and Experience Using a Portable MRI Scanner in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2023, 108, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, R.; Crawford, A.; Mazurek, M.H.; Prabhat, A.M.; Chavva, I.R.; Parasuram, N.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.A.; Petersen, N.; de Havenon, A.; et al. Bedside Monitoring of Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Using Low-Field, Portable Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging after Cardiac Arrest. Resuscitation 2022, 176, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, J.; Unadkat, P.; Thomas, J.; Kleiner, N.; Khazanehdari, S.; Wanchoo, S.; Samuel, K.; Moclair, B.O.; Black, K.; Dehdashti, A.R.; et al. Portable Magnetic Resonance Imaging for ICU Patients. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, M.H.; Cahn, B.A.; Yuen, M.M.; Prabhat, A.M.; Chavva, I.R.; Shah, J.T.; Crawford, A.L.; Welch, E.B.; Rothberg, J.; Sacolick, L.; et al. Portable, Bedside, Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluation of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.M.; Prabhat, A.M.; Mazurek, M.H.; Chavva, I.R.; Crawford, A.; Cahn, B.A.; Beekman, R.; Kim, J.A.; Gobeske, K.T.; Petersen, N.H.; et al. Portable, Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Enables Highly Accessible and Dynamic Bedside Evaluation of Ischemic Stroke. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Medica 2012, 22, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalela, J.A.; Kidwell, C.S.; Nentwich, L.M.; Luby, M.; Butman, J.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Hill, M.D.; Patronas, N.; Latour, L.; Warach, S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography in Emergency Assessment of Patients with Suspected Acute Stroke: A Prospective Comparison. Lancet 2007, 369, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, H.; Kipfmueller, F.; Bagci, S.; Dresbach, T.; Grass, T.; Nitsch-Felsecker, P.; Pantazis, C.; Schmitt, J.; Schroeder, L.; Mueller, A. Feasibility of Bedside Portable MRI in Neonates and Children during ECLS. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.; Acton, M.; Rando, H.; Keller, S.; Sair, H.I.; Chinedozi, I.; Pitts, J.; Kim, B.S.; Whitman, G.; Cho, S.M. Safety of Bedside Portable Low-Field Brain MRI in ECMO Patients Supported on Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
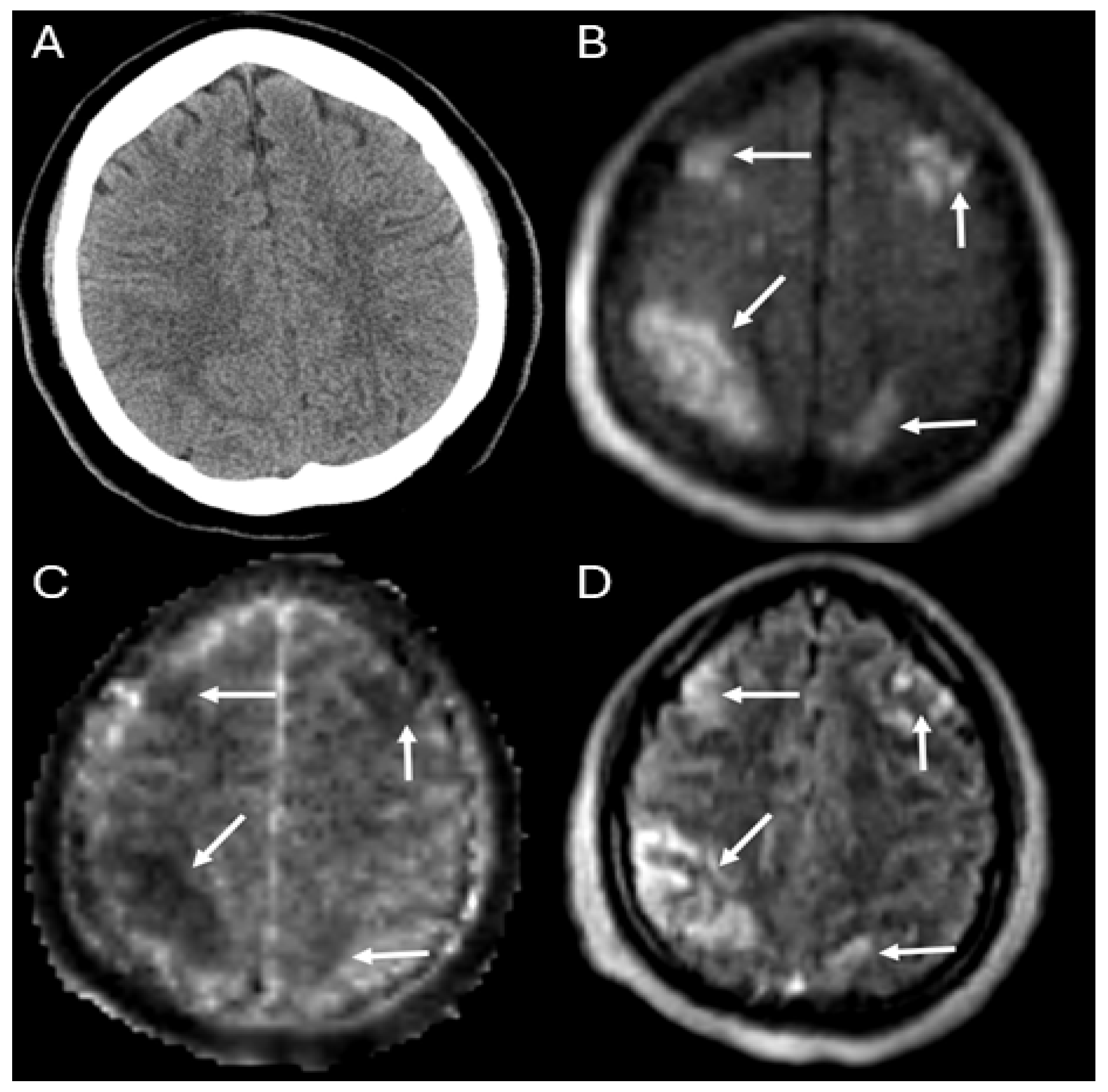
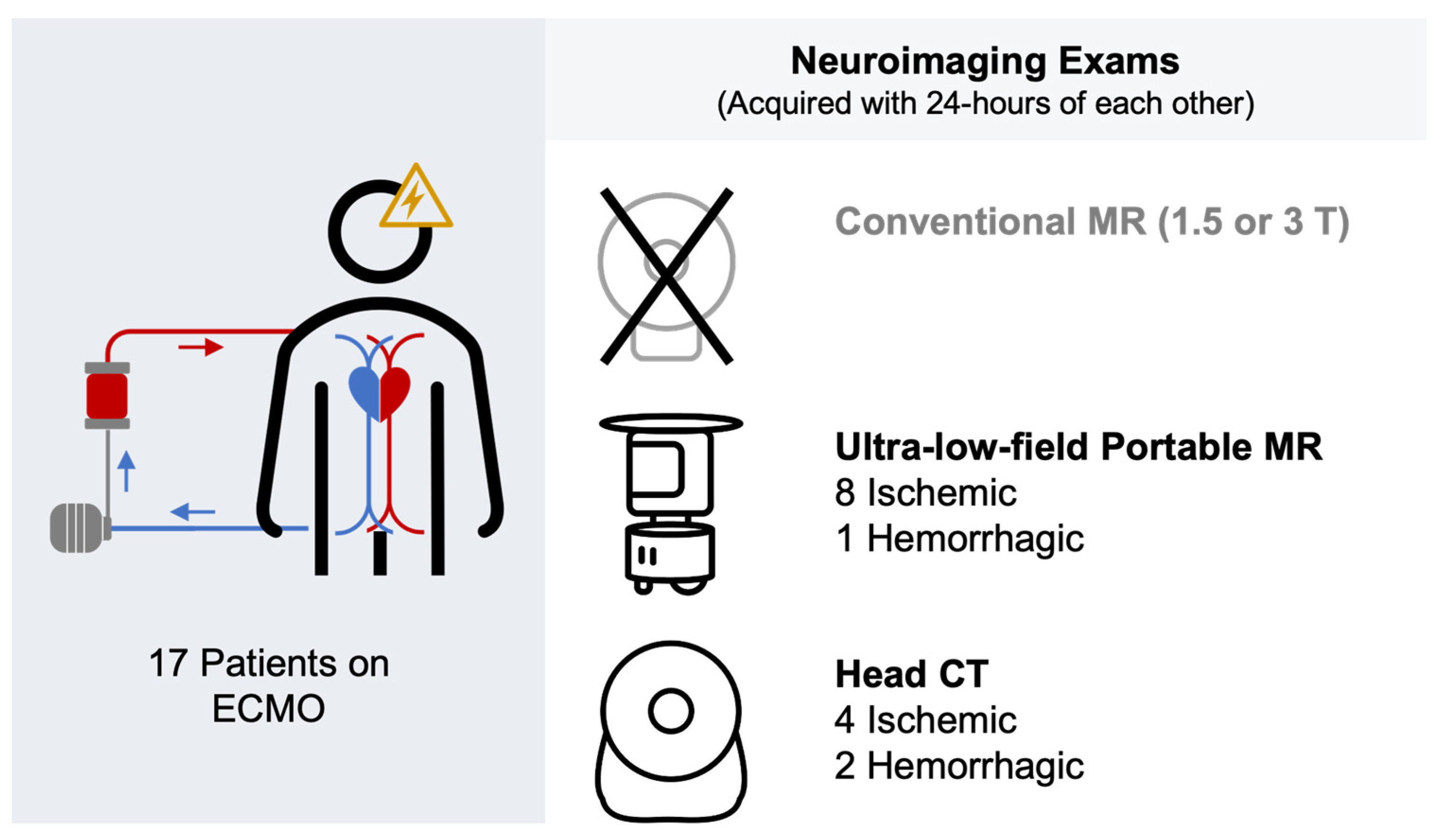
| Total (n = 17) | |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age, years (interquartile range) | 55 (41–63) |
| Male | 8 (47%) |
| Body Mass Index, kg/m2 | 31.6 (27.3–35.5) |
| Race | |
| White | 6 (35%) |
| Black | 6 (35%) |
| Hispanic | 2 (12%) |
| Asian | 2 (12%) |
| Others | 1 (6%) |
| Past medical history | |
| Ischemic stroke | 2 (12%) |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 0 (0%) |
| Hypertension | 7 (41%) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 6 (35%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (29%) |
| Heart failure | 4 (24%) |
| Chronic kidney disease | 7 (41%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (18%) |
| Pre-ECMO variables | |
| Inotropic or vasoactive support | 15 (88%) |
| Cardiac arrest | 5 (29%) |
| Glasgow Coma Scale | 6 (4–12.5) |
| SOFA score (on MRI day) | 13 (11–14) |
| ECMO Cannulation | |
| VA-ECMO | |
| Central cannulation | 2 (12%) |
| Peripheral cannulation | 10 (59%) |
| VV-ECMO | |
| Single lumen cannulation | 4 (24%) |
| Double lumen cannulation | 1 (6%) |
| Mortality | 10 (59%) |
| ECMO duration (days) | 7 (4–14) |
| VA-ECMO duration (days) | 4.5 (2.8–8.5) |
| VV-ECMO duration (days) | 28 (11–30) |
| HCT | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ABI Present? | Yes | No | |
| ULF-pMR | Yes | 5 † | 4 ‡ |
| No | 1 * | 8 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, S.-M.; Khanduja, S.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.K.; Briscoe, J.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; Dinh, K.; Kim, B.S.; Sair, H.I.; Wandji, A.-C.N.; et al. Detection of Acute Brain Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients on ECMO Support Using Ultra-Low-Field Portable MRI: A Retrospective Analysis Compared to Head CT. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060606
Cho S-M, Khanduja S, Kim J, Kang JK, Briscoe J, Arlinghaus LR, Dinh K, Kim BS, Sair HI, Wandji A-CN, et al. Detection of Acute Brain Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients on ECMO Support Using Ultra-Low-Field Portable MRI: A Retrospective Analysis Compared to Head CT. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(6):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060606
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Sung-Min, Shivalika Khanduja, Jiah Kim, Jin Kook Kang, Jessica Briscoe, Lori R. Arlinghaus, Kha Dinh, Bo Soo Kim, Haris I. Sair, Audrey-Carelle N. Wandji, and et al. 2024. "Detection of Acute Brain Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients on ECMO Support Using Ultra-Low-Field Portable MRI: A Retrospective Analysis Compared to Head CT" Diagnostics 14, no. 6: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060606
APA StyleCho, S.-M., Khanduja, S., Kim, J., Kang, J. K., Briscoe, J., Arlinghaus, L. R., Dinh, K., Kim, B. S., Sair, H. I., Wandji, A.-C. N., Moreno, E., Torres, G., Gavito-Higuera, J., Choi, H. A., Pitts, J., Gusdon, A. M., & Whitman, G. J. (2024). Detection of Acute Brain Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients on ECMO Support Using Ultra-Low-Field Portable MRI: A Retrospective Analysis Compared to Head CT. Diagnostics, 14(6), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060606






