Tumor-like Lesions in Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differential Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- Collect prospective data of adequate quality to validate some findings against an updated subset of differential diagnoses;
- -
- Define clinical and neuroradiological predictors of PACNS diagnosis;
- -
- Form the basis for designing treatment trials.
2. Tumor-like Lesions in PACNS
2.1. Definition
2.2. Epidemiology
2.3. Neuroimaging
- -
- Lesion number: 8/10 (80%) patients had a single brain lesion and 2/10 (20%) patients had multifocal lesions;
- -
- Lesion location: cortex/subcortical white matter in 7/10 patients (70%), deep and/or periventricular white matter in 6/10 patients (60%), basal ganglia in 4/10 patients (40%), and brain stem in 1/10 patients (10%);
- -
- Signal features: T1-Weighted Imaging (T1-WI) hypointense signal and intermediate to hyperintense signal on T2WI without diffusion restriction; intralesional microhemorrhages (small linear or punctate patterns on either Gradient Recalled Echo (GRE-T2*) or Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI)) in 8/10 (80%) patients;
- -
- Perilesional vasogenic edema (T2-WI high signal): marked in 5/10 (50%) patients and moderate in 5/5 10 (50%) patients;
- -
- Enhancement patterns (parenchyma): all patients (10/10, 100%) had enhancing lesions with patchy parenchymal pattern in 5/10 (50%), “mottled appearance” (multiple small hypoenhancing areas within the patchy enhancing masses) in 3/10, small nodular pattern in 5/10, ring enhancement in 2/10, and linear (perivascular) enhancement pattern in 1/10 patients;
- -
- Enhancement patterns (leptomeninges): localized leptomeningeal enhancement adjacent to the dominant/largest lesions was found in 4/10 patients (40%), localized subependymal enhancement adjacent to the lesions in 3/10 patients (30%); and diffuse leptomeningeal or subependymal enhancement was not documented;
- -
- Vascular imaging (including Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA), Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), and Vessel Wall Imaging (VWI)): CTA or MRA were available in 9/10 patients (90%) of 10 patients with normal findings (notably, none of the patients underwent catheter angiography); VWI was available in 3/10 patients (30%) with normal findings on the imaged proximal large intracranial arteries.
- -
- Lesion number: two out of four patients had a single mass lesion and two out of four had multiple lesions (two hemorrhagic lesions in one case and multiple digitate-shaped enhancing lesions with edema in the second case);
- -
- Lesion location: single lesions were in the suprasellar region and in the left frontal lobe white matter; multiple lesions were in the right frontal lobe in one case and in the right frontal white matter, corpus callosum, and external capsule in the second case;
- -
- Signal features: the single lesions were an enhancing mass with edema in the suprasellar area with decreased signal on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, and a focal edematous mass-like lesion (2.1 cm) with T2-high T1-low signal lesion, gyral swelling, and increased ADC, respectively;
- -
- Enhancement patterns: they were described as variable without further details;
- -
- Vascular imaging: one patient had LV-PACNS right M1 middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion and left distal internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis on angiogram; the remaining 3/4 patients had normal vascular imaging.
2.4. Advanced MRI Findings
2.5. Pathology
3. Neuroimaging Clues in the Main Differential Diagnoses
3.1. DWI/ADC and Advanced MRI Techniques
- Dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) imaging, which is currently the most commonly used technique;
- Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) imaging (both requiring intravenous administration of a gadolinium-based contrast medium);
- Arterial spin labeling (ASL), not requiring contrast media.
3.2. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
3.3. Tumefactive Demyelination Lesions
- -
- An open-ring or incomplete-rim enhancement;
- -
- A closed ring or complete rim enhancement;
- -
- A T2 hypointense rim;
- -
- An absent or mild mass effect;
- -
- Absent or mild perilesional edema.
3.4. High-Grade Gliomas
3.5. Neurosarcoidosis
3.6. Neurotoxoplasmosis
4. MRI as a Tool for Decision Making
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, C.; Kaufmann-Bühler, A.K.; Gansukh, T.; Gansukh, A.; Schuster, S.; Bachmann, H.; Thomalla, G.; Magnus, T.; Matschke, J.; Fiehler, J.; et al. Neuroradiologic Characteristics of Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System According to the Affected Vessel Size. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2019, 29, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, L.H.; Mallek, J.A. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: Report of 8 new cases, review of the literature, and proposal for diagnostic criteria. Medicine 1988, 67, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, J.; Hellmann, D.B. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, R.; Antonenko, K.; Boulouis, G.; De Boysson, H.; Giannini, C.; Heldner, M.R.; Kargiotis, O.; Nguyen, T.N.; Rice, C.M.; Salvarani, C.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines on Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System (PACNS). Eur. Stroke J. 2023, 8, 842–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duering, M.; Biessels, G.J.; Brodtmann, A.; Chen, C.; Cordonnier, C.; de Leeuw, F.-E.; Debette, S.; Frayne, R.; Jouvent, E.; Rost, N.S.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease-advances since 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou, G.A.; El Sammak, S.; Chien, L.C.; Cavanagh, J.J.; Hutto, S.K. Tumefactive brain parenchymal neurosarcoidosis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciaguerra, L.; Morris, P.; Tobin, W.O.; Chen, J.J.; Banks, S.A.; Elsbernd, P.; Redenbaugh, V.; Tillema, J.M.; Montini, F.; Sechi, E.; et al. Tumefactive demyelination in MOG Ab–associated disease, multiple sclerosis, and AQP-4-IgG–positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurology 2023, 100, E1418–E1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthiphosuwan, S.; Bharatha, A.; Hsu, C.T.; Lin, A.W.; Maloney, J.A.; Munoz, D.G.; Palmer, C.A.; Osborn, A.G. Tumefactive primary central nervous system vasculitis: Imaging findings of a rare and underrecognized neuroinflammatory disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Gavrilova, R.H.; Metz, I.; Parisi, J.E.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Weigand, S.; Thomsen, K.; Mandrekar, J.; Altintas, A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. Clinical and radiographic spectrum of pathologically confirmed tumefactive multiple sclerosis. Brain 2008, 131, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.A.; Reddel, S.W.; Barnett, M.H.; Palace, J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G. Atypical inflammatory demyelinating syndromes of the, C.N.S. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Christianson, T.J.H.; Huston, J., 3rd; Morris, J.M.; Giannini, C.; Hunder, G.G. Primary central nervous system vasculitis mimicking brain tumor: Comprehensive analysis of 13 cases from a single institutional cohort of 191 cases. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 97, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Morris, J.M.; Giannini, C.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Christianson, T.; Hunder, G.G. Imaging Findings of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy, Aβ-Related Angiitis (ABRA), and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation: A Single-Institution 25-Year Experience. Medicine 2016, 95, e3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boysson, H.; Boulouis, G.; Dequatre, N.; Godard, S.; Néel, A.; Arquizan, C.; Detante, O.; Bloch-Queyrat, C.; Zuber, M.; Touzé, E.; et al. Tumor-Like Presentation of Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Stroke 2016, 47, 2401–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, E.S.; Singhal, A.B.; Calabrese, L.H. Tumour-like mass lesion: An under-recognised presentation of primary angiitis of the central nervous system. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, C.; Chang, J.; Yuan, X.; Bai, Y.A.; Niu, J.; Wang, M. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system mimicking a cerebellar tumor. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 35, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriel, E.; Charidimou, A.; Gurol, M.E.; Ni, J.; Van Etten, E.S.; Martinez-Ramirez, S.; Boulouis, G.; Piazza, F.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Frosch, M.P.; et al. Validation of Clinicoradiological Criteria for the Diagnosis of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, L.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Zedde, M.; Basso, G.; Arighi, A.; Shima, A.; Cagnin, A.; Caulo, M.; Carare, R.O.; Charidimou, A.; et al. Spontaneous ARIA-like Events in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation: A Multicenter Prospective Longitudinal Cohort Study. Neurology. 2021, 97, e1809–e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Qu, Y.; Guo, Z.N.; Cui, G.Z.; Yang, Y. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system mimicking glioblastoma: A case report and literature review. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.; Park, S.H.; Yim, Y.J.; Sohn, C.H.; Chang, K.H. Tumor-mimicking primary angiitis of the central nervous system: Initial and follow-up MR features. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedde, M.; Grisendi, I.; Assenza, F.; Vandelli, G.; Napoli, M.; Moratti, C.; Lochner, P.; Seiffge, D.J.; Piazza, F.; Valzania, F.; et al. The Venular Side of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: Proof of Concept of a Neglected Issue. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, P.; Absinta, M.; Grammatico, M.; Vuolo, L.; Emmi, G.; Carlucci, G.; Spagni, G.; Barilaro, A.; Repice, A.M.; Emmi, L.; et al. Central vein sign differentiates Multiple Sclerosis from central nervous system inflammatory vasculopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, F.; Caminiti, S.P.; Zedde, M.; Presotto, L.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Pascarella, R.; Giossi, A.; Sessa, M.; Poli, L.; Basso, G.; et al. Association of Microglial Activation With Spontaneous ARIA-E and CSF Levels of Anti-Aβ Autoantibodies. Neurology 2022, 99, e1265–e1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, F.; Greenberg, S.M.; Savoiardo, M.; Gardinetti, M.; Chiapparini, L.; Raicher, I.; Nitrini, R.; Sakaguchi, H.; Brioschi, M.; Billo, G.; et al. Anti-amyloid β autoantibodies in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation: Implications for amyloid-modifying therapies. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedde, M.; Pascarella, R.; Piazza, F. CAA-ri and ARIA: Two Faces of the Same Coin? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, E13–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh, W.T.; Ueda, T.; Maley, J.E. Perfusion and diffusion imaging: A potential tool for improved diagnosis of CNS vasculitis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Panchal, N.J.; Niku, S.; Imbesi, S.G. Lymphocytic vasculitis mimicking aggressive multifocal cerebral neoplasm: MR imaging and MR spectroscopic appearance. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 642–645. [Google Scholar]
- Beppu, T.; Inoue, T.; Nishimoto, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakazato, Y.; Ogasawara, K.; Ogawa, A. Primary granulomatous angiitis of the central nervous system: Findings of magnetic resonance spectroscopy and fractional anisotropy in diffusion tensor imaging prior to surgery. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, C.; Salvarani, C.; Hunder, G.; Brown, R.D. Primary central nervous system vasculitis: Pathology and mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, A.D.; Jackson, A.; Price, S.J.; Clark, C.A.; Booth, T.C.; Auer, D.P.; Tofts, P.S.; Collins, D.J.; Leach, M.O.; Rees, J.H.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers in neuro-oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, K.; Boxerman, J.; Kalnin, A.; Kaufmann, T.; Shiroshi, M.; Wintermark, M. ASFNR recommendations for clinical performance of MR dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion imaging of the brain. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, E41–E51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haacke, E.M.; Mittal, S.; Wu, Z.; Neelavalli, J.; Cheng, Y.-C.N. Susceptibility weighted imaging: Technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Ashwal, S.; Obenaus, A.; Nickerson, J.; Kido, D.; Haacke, E. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: A review of clinical applications in children. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Wu, Z.; Neelavalli, J.; Haacke, E.M. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: Technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jahng, G.-H.; Ryu, C.; Kim, S. Added value and diagnostic performance of intratumoral susceptibility signals in the differential diagnosis of solitary enhancing brain lesions: Preliminary study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Y.; She, D.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Z.; Cao, D. Differentiating intracranial solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma from meningioma using diffusion-weighted imaging and susceptibility-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, H.S.; Jahng, G.H.; Ryu, C.W.; Park, S.M.; Kim, S.Y. Semiquantitative assessment of intratumoral susceptibility signals using non-contrast-enhanced high-field high-resolution susceptibility-weighted imaging in patients with gliomas: Comparison with MR perfusion imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohile, N.A.; Abrey, L.E. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 17, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Krossnes, B.K.; Aarseth, J.H.; Scheie, D.; Johannesen, T.B.; Mella, O.; Espeland, A. Increasing incidence and continued dismal outcome of primary central nervous system lymphoma in Norway 1989–2003: Time trends in a 15-year national survey. Cancer 2007, 110, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Kråkenes, J.; Krossnes, B.K.; Mella, O.; Espeland, A. CT and MR imaging features of primary central nervous system lymphoma in Norway, 1989–2003. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Espeland, A.; Larsson, E.M. Central nervous system lymphoma: Characteristic findings on traditional and advanced imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küker, W.; Nägele, T.; Korfel, A.; Heckl, S.; Thiel, E.; Bamberg, M.; Weller, M.; Herrlinger, U. Primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL): MRI features at presentation in 100 patients. J. Neurooncol 2005, 72, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, J.L.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, P.E. Imaging of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurosurg. Focus. 2006, 21, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündüz, K.; Pulido, J.S.; McCannel, C.A.; O’Neill, B.P. Ocular manifestations and treatment of central nervous system lymphomas. Neurosurg. Focus. 2006, 21, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Kråkenes, J.; Goplen, A.K.; Dunlop, O.; Mella, O.; Espeland, A. AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma: A Norwegian national survey 1989–2003. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Escoda, A.; Naval-Baudin, P.; Velasco, R.; Vidal, N.; Majós, C. Imaging of Lymphomas Involving the CNS: An Update-Review of the Full Spectrum of Disease with an Emphasis on the World Health Organization Classifications of CNS Tumors 2021 and Hematolymphoid Tumors 2022. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Central Nervous System Tumors. WHO Classification of Tumours Online, 5th ed; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/welcome/ (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwatashi, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Moritani, T.; Wang, H.Z.; Shrier, D.A.; Numaguchi, Y.; Ekholm, S.E.; Westesson, P.L. Hypointensity on diffusion-weighted MRI of the brain related to T2 shortening and susceptibility effects. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Escoda, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.; Naval-Baudin, P.; Cos, M.; Vidal, N.; Plans, G.; Bruna, J.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Majos, C. Presurgical identification of primary central nervous system lymphoma with normalized time-intensity curve: A pilot study of a new method to analyze DSC-PWI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, A.; Nagel, I.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Klapper, W.; Vater, I.; Paulus, W.; Hans, V.; Blümcke, I.; Weis, J.; Siebert, R.; et al. Frequent triple-hit expression of, M.Y.C.; BCL2, and BCL6 in primary lymphoma of the central nervous system and absence of a favorable MYC(low)BCL2 (low) subgroup may underlie the inferior prognosis as compared to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, R.; Mercadal, S.; Vidal, N.; Alañá, M.; Barceló, M.I.; Ibáñez-Juliá, M.J.; Bobillo, S.; Caldú Agud, R.; García Molina, E.; Martínez, P.; et al. Diagnostic delay and outcome in immunocompetent patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma in Spain: A multicentric study. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, A.; Okada, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kanagaki, M.; Fushimi, Y.; Dodo, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Takahashi, J.C.; Miyamoto, S.; Togashi, K. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Is absence of intratumoral hemorrhage a characteristic finding on MRI? Radiol. Oncol. 2015, 49, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharia, T.T.; Law, M.; Naidich, T.P.; Leeds, N.E. Central nervous system lymphoma characterization by diffusion-weighted imaging and MR spectroscopy. J. Neuroimaging 2008, 18, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, P.C.; Post, M.J.; Oschatz, E.; Stadler, A.; Bruce-Gregorios, J.; Thurnher, M.M. Analysis of the utility of diffusion weighted MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient values in distinguishing central nervous system toxoplasmosis from lymphoma. Neuroradiology 2006, 48, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, C.H.; Castillo, M.; Wong, A.C.; Wei, K.C.; Wong, H.F.; Ng, S.H.; Wan, Y.L. Primary cerebral lymphoma and glioblastoma multiforme: Differences in diffusion characteristics evaluated with diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Chang, J.S.; Hwang, J.; Cha, S. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging derived apparent diffusion coefficient is predictive of clinical outcome in primary central nervous system lymphoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F., Jr.; Politi, L.S.; Anzalone, N.; Schöder, H.; Fox, C.P.; Boxerman, J.L.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Quarles, C.C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Auer, D.; et al. Consensus recommendations for MRI and PET imaging of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Guideline statement from the International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group (IPCG). Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Dueck, A.C.; Heiserman, J.E.; Liu, S.; Karis, J.P.; Smith, K.A.; Shapiro, W.R.; Pinnaduwage, D.S.; Coons, S.W.; et al. Correlations between perfusion MR imaging cerebral blood volume, microvessel quantification, and clinical outcome using stereotactic analysis in recurrent high-grade glioma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F., Jr.; Phillips, J.J.; Parvataneni, R.; Molinaro, A.; Essock-Burns, E.; Bourne, G.; Parsa, A.T.; Aghi, M.K.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; et al. Regional variation in histopathologic features of tumor specimens from treatment-naive glioblastoma correlates with anatomic and physiologic MR Imaging. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; Baird, G.L.; Bell, L.C.; Quarles, C.C.; Boxerman, J.L. Utility of percentage signal recovery and baseline signal in DSC-MRI optimized for relative CBV measurement for differentiating glioblastoma, lymphoma, metastasis, and meningioma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakyemez, B.; Erdogan, C.; Bolca, N.; Yildirim, N.; Gokalp, G.; Parlak, M. Evaluation of different cerebral mass lesions by perfusion-weighted MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M.; Heiland, S.; Harting, I.; Tronnier, V.M.; Sommer, C.; Ludwig, R.; Sartor, K. Distinguishing of primary cerebral lymphoma from high-grade glioma with perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 338, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Escoda, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.; Naval-Baudin, P.; Grussu, F.; Fernandez, J.J.; Simo, A.C.; Sarro, N.V.; Fernandez-Coello, A.; Bruna, J.; Cos, M.; et al. Voxel-level analysis of normalized DSC-PWI time-intensity curves: A po-tential generalizable approach and its proof of concept in discriminating glioblastoma and metastasis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3705–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Calimeri, T.; Conte, G.M.; Cattaneo, D.; Fallanca, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Scarano, E.; Curnis, F.; Nonis, A.; Lopedote, P.; et al. R-CHOP preceded by blood brain barrier permeabilization with engineered tumor necrosis factor-α in primary CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Gao, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, P.; Shi, H.; Hong, X. Utility of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating glioblastoma, primary central nervous system lymphoma and brain metastatic tumor. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofts, P.S.; Brix, G.; Buckley, D.L.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Henderson, E.; Knopp, M.V.; Larsson, H.B.; Lee, T.Y.; Mayr, N.A.; Parker, G.J.; et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced t1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: Standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 1999, 10, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.B.; Kang, X.W.; Wang, N.; Liu, T.T.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Guo, F.; Yin, H. Differentiation of primary central nervous system lymphoma from high-grade glioma and brain metastasis using arterial spin labeling and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 112, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Majós, C.; Castañer, S.; Sánchez, J.J.; Gabarrós, A.; Muntané, A.; Aguilera, C.; Arús, C. 1H-MRS is useful to reinforce the suspicion of primary central nervous system lymphoma prior to surgery. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.K.; Hoang, T.; Law, S.C.; Brosda, S.; O’Rourke, K.; Tobin, J.W.; Vari, F.; Murigneux, V.; Fink, L.; Gunawardana, J.; et al. EBV-associated primary CNS lymphoma occurring after immunosuppression is a distinct immunobiological entity. Blood 2021, 137, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, P.; Shiels, M.S.; Lynch, C.F.; Engels, E.A. Incidence and outcomes of primary central nervous system lymphoma in solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2018, 18, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaulen, L.D.; Karschnia, P.; Dietrich, J.; Baehring, J.M. Autoimmune disease-related primary CNS lymphoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, S.; Carlisi, M.; Santoro, M.; Napolitano, M.; Raso, S.; Siragusa, S. Immunosenescence and lymphomagenesis. Immun. Ageing 2018, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Escoda, A.; García-Ruíz, A.; Naval-Baudin, P.; Grussu, F.; Viveros, M.; Vidal, N.; Bruna, J.; Plans, G.; Cos, M.; Perez-Lopez, R.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell Epstein-Barr virus-positive primary CNS lymphoma in non-AIDS patients: High diagnostic accuracy of DSC perfusion metrics. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Lee, M.; Buck, O.; Woo, K.M.; Zhang, Z.; Hatzoglou, V.; Omuro, A.; Arevalo-Perez, J.; Thomas, A.A.; Huse, J.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of T1-weighted dynamic contrast enhanced-MRI and DWI-ADC for differentiation of glioblastoma and primary CNS lymphoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, N.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, C.G.; Lim, Y.M. Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps for differentiating primary CNS lymphomas from tumefactive demyelinating lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Khan, I.R.A.; Seet, Y.H.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Yu, W.Y. Atypical radiological findings of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Shin, H.J.; Chang, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Differentiation between primary cerebral lymphoma and glioblastoma using the apparent diffusion coefficient: Comparison of three different ROI methods. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bjørnerud, A.; Park, J.E.; Lee, B.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Permeability measurement using dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging enhances differential diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma from glioblastoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5539–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.A.; Chataway, J. Tumefactive demyelination: An approach to diagnosis and management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, L.; Torlone, S.; Ferrari, F.; Di Carmine, C.; Totaro, R.; di Cesare, E.; Splendiani, A. Is size an essential criterion to define tumefactive plaque? MR features and clinical correlation in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Naganawa, S.; Ouyang, M.; Jones, K.A.; Kim, J.; Capizzano, A.A.; Moritani, T. A Review of Clinical and Imaging Findings in Tumefactive Demyelination. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, P.; Meca-Lallana, V.; Barbosa, A.; Manzanares, R.; Palmí, I.; Vivancos, J. Tumefactive demyelinating lesions of 15 patients: Clinico-radiological features, management and review of the literature. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totaro, R.; Di Carmine, C.; Splendiani, A.; Torlone, S.; Patriarca, L.; Carrocci, C.; Sciamanna, S.; Marini, C.; Carolei, A. Occurrence and long-term outcome of tumefactive demyelinating lesions in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloy, G.; Pelletier, J.; Suchet, L.; Lebrun, C.; Cohen, M.; Vermersch, P.; Zephir, H.; Duhin, E.; Gout, O.; Deschamps, R.; et al. Inaugural tumor-like multiple sclerosis: Clinical presentation and medium-term outcome in 87 patients. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.S.; Khan, I.; Kandelwal, K.; Desai, T. Tumefactive demyelinating lesions (TDLs): A case series of clinicoradiological features. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 162, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabray, M.C.; Cohen, B.A.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Valles, F.E.; Barajas, R.F.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Cha, S. Performance of apparent diffusion coefficient values and conventional MRI features in differentiating tumefactive demyelinating lesions from primary brain neoplasms. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, C.H.; Wei, K.C.; Ng, S.H.; Wan, Y.L.; Castillo, M.; Lin, C.P. Differentiation of tumefactive demyelinating lesions from high-grade gliomas with the use of diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. MRI Findings in Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masdeu, J.C.; Quinto, C.; Olivera, C.; Tenner, M.; Leslie, D.; Visintainer, P. Open ring imaging sign: Highly specific for atypical brain demyelination. Neurology 2000, 54, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Given, C.A., 2nd; Stevens, B.S.; Lee, C. The MRI appearance of tumefactive demyelinating lesions. AJR 2004, 182, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Shibata, N.; Uchiyama, S. Gadolinium enhancement patterns of tumefactive demyelinating lesions: Correlations with brain biopsy findings and pathophysiology. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes-Villalba, A.A.; French, H.H.; Parratt, J.D.E. Characterisation of tumefactive demyelinating lesions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, e1.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razek, A.A.K.A.; Elsebaie, N.A. Imaging of fulminant demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner-Blazek, M.; Rovira, A.; Fillipp, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Miller, D.H.; Schmierer, K.; Frederiksen, J.; Gass, A.; Gama, H.; Tilbery, C.P.; et al. Atypical idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating lesions: Prognostic implications and relation to multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Na, D.G.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.; Yun, B.L.; Chang, K.H. Distinguishing tumefactive demyelinating lesions from glioma or central nervous system lymphoma: Added value of unenhanced CT compared with conventional contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2009, 251, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewann, A.; Enzinger, C.; Filippi, M.; Barkhof, F.; Rovira, A.; Gass, A.; Miller, D.; Montalban, X.; Thompson, A.; Yousry, T.; et al. MRI characteristics of atypical idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating lesions of the brain: A review of reported findings. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrignac, X.; Rigau, V.; Lhermitte, B.; Vincent, T.; de Champfleur, N.M.; Carra-Dalliere, C.; Charif, M.; Collongues, N.; de Seze, J.; Hebbadj, S.; et al. Pathologic and MRI analysis in acute atypical inflammatory demyelinating lesions. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelblinger, C.; Fruehwald-Pallamar, J.; Kubin, K.; Wallner-Blazek, M.; Van den Hauwe, L.; Macedo, L.; Puchner, S.B.; Thurnher, M.M. Atypical idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating lesions (IIDL): Conventional and diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI) findings in 42 cases. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1996–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, H.S.; Jain, K.K.; Agarwal, A.; Singh, M.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Husain, M.; Krishnani, N.; Gupta, R.K. Characterization of tumefactive demyelinating lesions using MR imaging and in-vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Mult. Scler. 2009, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Zeid, N.; Pirko, I.; Erickson, B.; Weigand, S.D.; Thomsen, K.M.; Scheithauer, B.; Parisi, J.E.; Giannini, C.; Linbo, L.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Diffusion-weighted imaging characteristics of biopsy-proven demyelinating brain lesions. Neurology 2012, 78, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, S.B.; Muraleedharan, A.; Kumar, S.; Nagesh, C.; Kesavadas, C.; Abraham, M.; Kapilamoorthy, T.R.; Thomas, B. Combining diffusion tensor metrics and DSC perfusion imaging: Can it improve the diagnostic accuracy in differentiating tumefactive demyelination from high-grade glioma? AJNR 2017, 38, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.B.; Huang, W.Y.; Xu, W.X.Z.; Wu, G.; Geng, D.Y.; Yin, B. Differentiating primary central nervous system lymphomas from glioblastomas and inflammatory demyelinating pseudotumor using relative minimum apparent diffusion coefficients. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2017, 41, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasel, S.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Jansen, V.; Mueller, K.; Zanella, F.; Hattingen, E. Metabolism and regional cerebral blood volume in autoimmune inflammatory demyelinating lesions mimicking malignant gliomas. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeguchi, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Abe, K.; Shimizu, S.; Maruyama, T.; Nitta, M.; Abe, K.; Kawamata, T.; Kitagawa, K. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy differentiates tumefactive demyelinating lesions from gliomas. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 26, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriyama, T.; Kataoka, H.; Taoka, T.; Tonomura, Y.; Terashima, M.; Morikawa, M.; Tanizawa, E.; Kawahara, M.; Furiya, Y.; Sugie, K.; et al. Characteristic neuroimaging in patients with tumefactive demyelinating lesions exceeding 30 mm. J. Neuroimaging 2011, 21, e69–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, T.A.; Miller, D.H. Baló’s concentric sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, E.; Trama, A.; Stiller, C.; Caldarella, A.; Soffietti, R.; Jaal, J.; Weber, D.C.; Ricardi, U.; Slowinski, J.; Brandes, A.; et al. Epidemiology of glial and non-glial brain tumours in Europe. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23 (Suppl. S2), iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cote, D.J.; Ascha, M.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Adult glioma incidence and survival by race or ethnicity in the United States from 2000 to 2014. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 who classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, F.M.; Penfold, C.; Joannides, A.; Saji, S.; Johnson, M.; Watts, C.; Brodbelt, A.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Price, S.J.; Hamilton, W.; et al. Missed opportunities for diagnosing brain tumours in primary care: A qualitative study of patient experiences. Br. J. Gen. Pr. 2019, 69, e224–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Malkin, M.G.; Rand, S.D.; Connelly, J.M.; Quinsey, C.; LaViolette, P.S.; Bedekar, D.P.; Schmainda, K.M. Validation of functional diffusion maps (fDMs) as a biomarker for human glioma cellularity. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2010, 31, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, T.; Korogi, Y.; Kochi, M.; Ikushima, I.; Shigematu, Y.; Hirai, T.; Okuda, T.; Liang, L.; Ge, Y.; Komohara, Y.; et al. Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 1999, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamecnik, J. The extracellular space and matrix of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 110, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, N.; Camby, I.; Goldman, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Balériaux, D.; Salmon, I.; Decaesteckere, C.; Kiss, R.; Metens, T. Effect of hydrophilic components of the extracellular matrix on quantifiable diffusion-weighted imaging of human gliomas: Preliminary results of correlating apparent diffusion coefficient values and hyaluronan expression level. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cheng, G.; Kang, X.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, C.; Ye, J.; Li, P.; Yin, H. Noninvasively evaluating the grading and IDH1 mutation status of diffuse gliomas by three-dimensional pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling and diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tian, J.; Shi, D.; Cheng, J.; Haacke, E.M.; Hong, X.; Ma, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M. Grading of gliomas by using monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched exponential diffusion-weighted MR imaging and diffusion kurtosis MR imaging. Radiology 2016, 278, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thust, S.C.; Hassanein, S.; Bisdas, S.; Rees, J.H.; Hyare, H.; Maynard, J.A.; Brandner, S.; Tur, C.; Jäger, H.R.; Yousry, T.A.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient for molecular subtyping of non-gadolinium-enhancing WHO grade II/III glioma: Volumetric segmentation versus two-dimensional region of interest analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Jain, R.; Radmanesh, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Guo, W.Y.; Zagzag, D.; Snuderl, M.; Placantonakis, D.G.; Golfinos, J.; Chi, A.S. Predicting genotype and survival in glioma using standard clinical MR imaging apparent diffusion coefficient images: A pilot study from the cancer genome atlas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, K.; Ott, G.A.; Lai, A.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Pope, W.B.; Yong, W.H.; Liau, L.M.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M. Perfusion and diffusion MRI signatures in histologic and genetic subtypes of WHO grade II-III diffuse gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 134, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Krejza, J.; Vossough, A.; Zhang, Y.; Kapoor, G.S.; Wang, S.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Melhem, E.R.; Poptani, H. Differentiation between oligodendroglioma genotypes using dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted imaging and proton MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Sinha, N.; Saini, J.; Mahadevan, A.; Rao, K.N.; Swaminathan, A. Assessment of tissue heterogeneity using diffusion tensor and diffusion kurtosis imaging for grading gliomas. Neuroradiology 2016, 58, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, M.; Yang, S.; Babb, J.S.; Knopp, E.A.; Golfinos, J.G.; Zagzag, D.; Johnson, G. Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced per fusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 746–755. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, R.K.; Gamal, S.A.; Essa, A.A.; Othman, M.H. Preoperative grading of glioma using dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI: Relative cerebral blood volume analysis of intra-tumoural and peri-tumoural tissue. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 167, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmainda, K.M.; Prah, M.A.; Rand, S.D.; Liu, Y.; Logan, B.; Muzi, M.; Rane, S.D.; Da, X.; Yen, Y.F.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; et al. Multisite concordance of DSC-MRI analysis for brain tumors: Results of a National Cancer Institute Quantitative Imaging Network Collaborative Project. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horská, A.; Barker, P.B. Imaging of brain tumors: MR spectroscopy and metabolic imaging. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2010, 20, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Babb, J.S.; Johnson, G.; Cha, S.; Knopp, E.A.; Zagzag, D. Glioma grading: Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bian, W.; Khayal, I.S.; Lupo, J.M.; McGue, C.; Vandenberg, S.; Lamborn, K.R.; Chang, S.M.; Cha, S.; Nelson, S.J. Multiparametric characterization of grade 2 glioma subtypes using magnetic resonance spectroscopic, perfusion, and diffusion imaging. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Xu, B. The diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in differentiating high-from low-grade gliomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 2670–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Perez, H.R.; Jacks, L.M.; Panageas, K.S.; Deangelis, D.L.M. Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 2010, 74, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathla, G.; Freeman, C.W.; Moritani, T.; Song, J.W.; Srivastava, S.; Soni, N.; Derdeyn, C.; Mohan, S. Retrospective, dual-centre review of imaging findings in neurosarcoidosis at presentation: Prevalence and imaging sub-types. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 796.e1–796.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, B.J.; Royal, W.; Gelfand, J.M.; Clifford, D.B.; Tavee, J.; Pawate, S.; Berger, J.R.; Aksamit, A.J.; Krumholz, A.; Pardo, C.A.; et al. Definition and consensus diagnostic criteria for neurosarcoidosis: From the neurosarcoidosis consortium consensus group. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Preziosa, P.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Geurts, J.J.; Paul, F.; Reich, D.S.; Toosy, A.T.; et al. Assessment of lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis: Practical guidelines. Brain 2019, 142, 1858–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchacz, K.; Baker, R.K.; Palella Jr, F.J.; Chmiel, J.S.; Lichtenstein, K.A.; Novak, R.M.; Wood, K.C.; Brooks, J.T.; HOPS Investigators. IDS-defining opportunistic illnesses in US patients, 1994–2007: A cohort study. AIDS 2010, 24, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M. Brain infections in human immunodeficiency virus positive patients, Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1994, 6, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV Infected Adults and Adolescents. 2015. Available online: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/lvguidelines/adult_oi.pdf.C1–2 (accessed on 9 November 2015).
- Antinori, A. Evaluation and management of intracranial mass lesions in AIDS: Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the american academy of neurology. Neurology 1998, 51, 1233–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R. Mass lesions of the brain in AIDS: The dilemmas of distinguishing toxoplasmosis from primary CNS lymphoma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 554–555. [Google Scholar]
- Navia, B.A.; Petito, C.K.; Gold, J.W.; Cho, E.S.; Jordan, B.D.; Price, R.W. Cerebral toxoplasmosis complicating the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: Clinical and neuropathological findings in 27 patients. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Mahadevan, A.; Guruprasad, A.S.; Kovoor, J.M.; Satishchandra, P.; Nath, A.; Ranga, U.; Shankar, S.K. Eccentric target sign in cerebral toxoplasmosis: Neuropathological correlate to the imaging feature. JMRI 2010, 31, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, R.G.; Gean, A.D. Neuroimaging of AIDS. I. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Toxoplasmosis. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 1997, 7, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Masamed, R.; Meleis, A.; Lee, E.W.; Hathout, G.M. Cerebral toxoplasmosis: Case review and description of a new imaging sign. Clin. Radiol. 2009, 64, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brightbill, T.C.; Post, M.J.; Hensley, G.T.; Ruiz, A. MR of Toxoplasma encephalitis: Signal characteristics on T2-weighted images and pathologic correlation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1996, 20, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos Miranda, T.A.; Tsuchiya, K.; Lucato, L.T. Imaging of Central Nervous System Parasitic Infections. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2023, 33, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rocha, A.J.; Sobreira Guedes, B.V.; da Silveira da Rocha, T.M.; Maia Junior, A.C.; Chiattone, C.S. Modern techniques of magnetic resonance in the evaluation of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Contributions to the diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2016, 38, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibble, E.H.; Box-erman, J.L.; Baird, G.L.; Donahue, J.E.; Rogg, J.M. Toxoplasmosis versus lymphoma: Cerebral lesion characterization using DSC-MRI revisited. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 152, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Chang, K.H.; Song, I.C.; Kim, H.D.; Seong, S.O.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, M.H. Brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumor: Discrimination with signal intensity on diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 171, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccio, C.F.; Esposito, G.; Bartolini, A.; Cerase, A. Cerebral abscesses and necrotic cerebral tumours: Differential diagnosis by perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Radiol. Med. 2008, 113, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriano, V.H.; Torres, U.S.; Spotti, A.R.; Ferraz-Filho, J.R.; Tognola, W.A. The role of dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging in differentiating between infectious and neoplastic focal brain lesions: Results from a cohort of 100 consecutive patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, A.; Husain, N.; Husain, M.; Pandey, C.M.; Srivastava, C.; Behari, S.; Rathore, R.K. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Is absence of intratumoral hemorrhage a characteristic finding on MRI? Neuroradiology 2008, 50, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.C.; Cervantes, G.; Baron, T.R.; Tyan, A.E.; Flanagan, S.; Lucato, L.T.; McKinney, A.M.; Ott, F. Imaging features of neurotoxoplasmosis: A multiparametric approach, with emphasis on susceptibility-weighted imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. Open. 2018, 17, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown Jr, R.D.; Christianson, T.J.; Huston, I.I.I.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Giannini, C.; Hunder, G.G. Primary central nervous system vasculitis associated with lymphoma. Neurology 2018, 90, e847–e855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Krawczyk, M. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Der Radiol. 2022, 62, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonduelle, T.; Stricker, J.; Minéo, J.F.; Massri, A.; Guesdon, C.; Barroso, B.; Bonnan, M. Weston-Hurst syndrome with acute hemorrhagic cerebellitis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 173, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



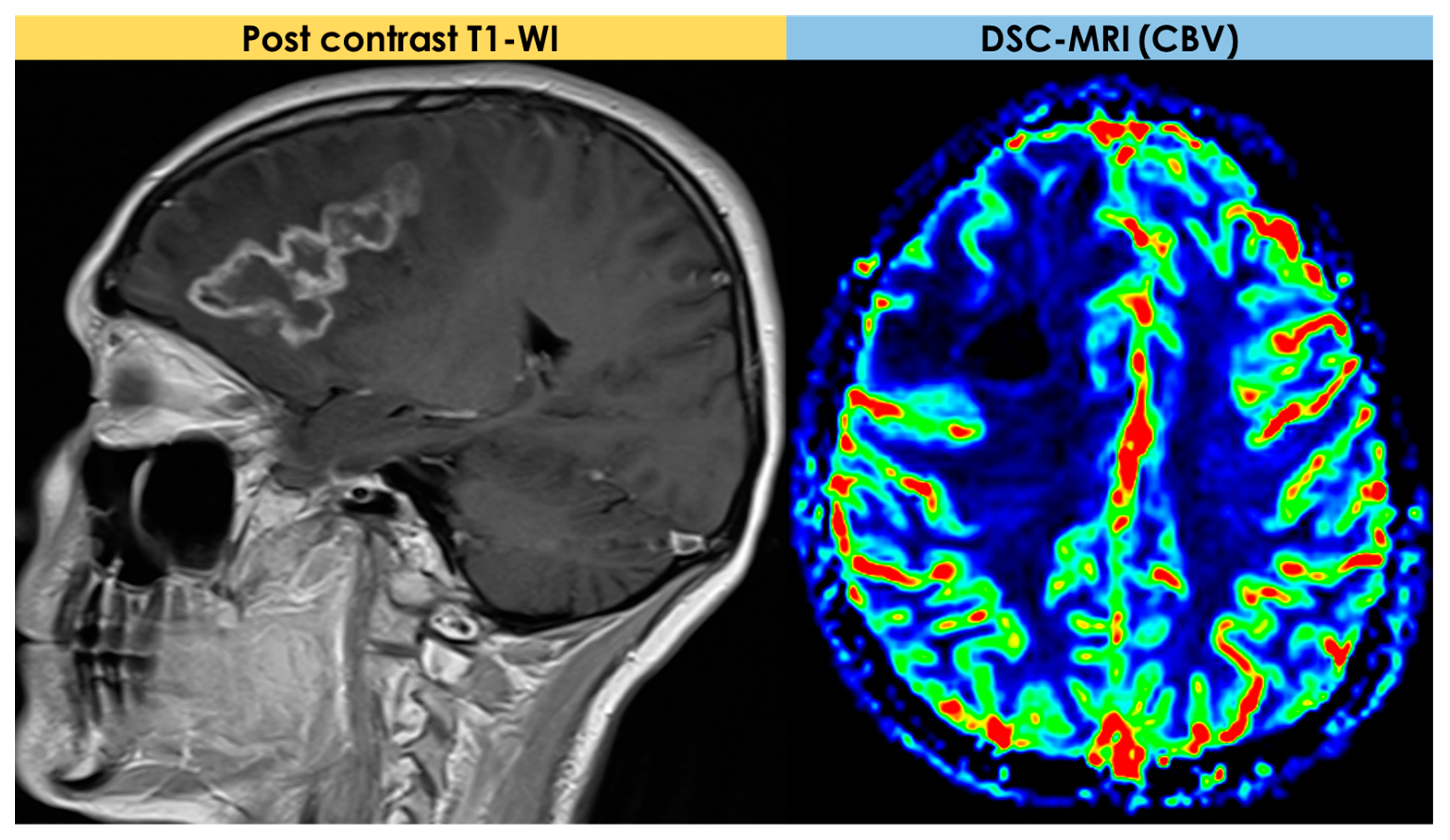
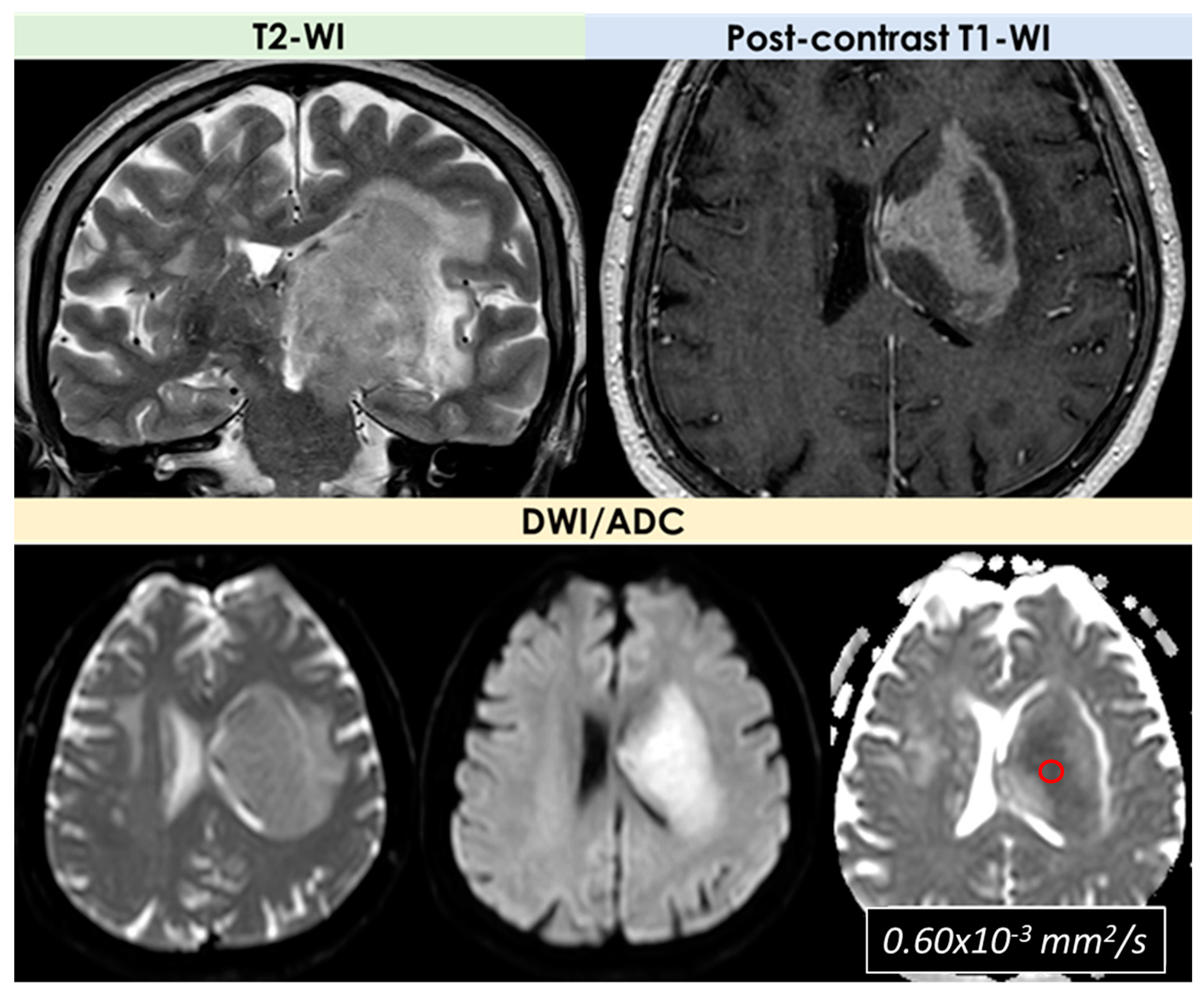

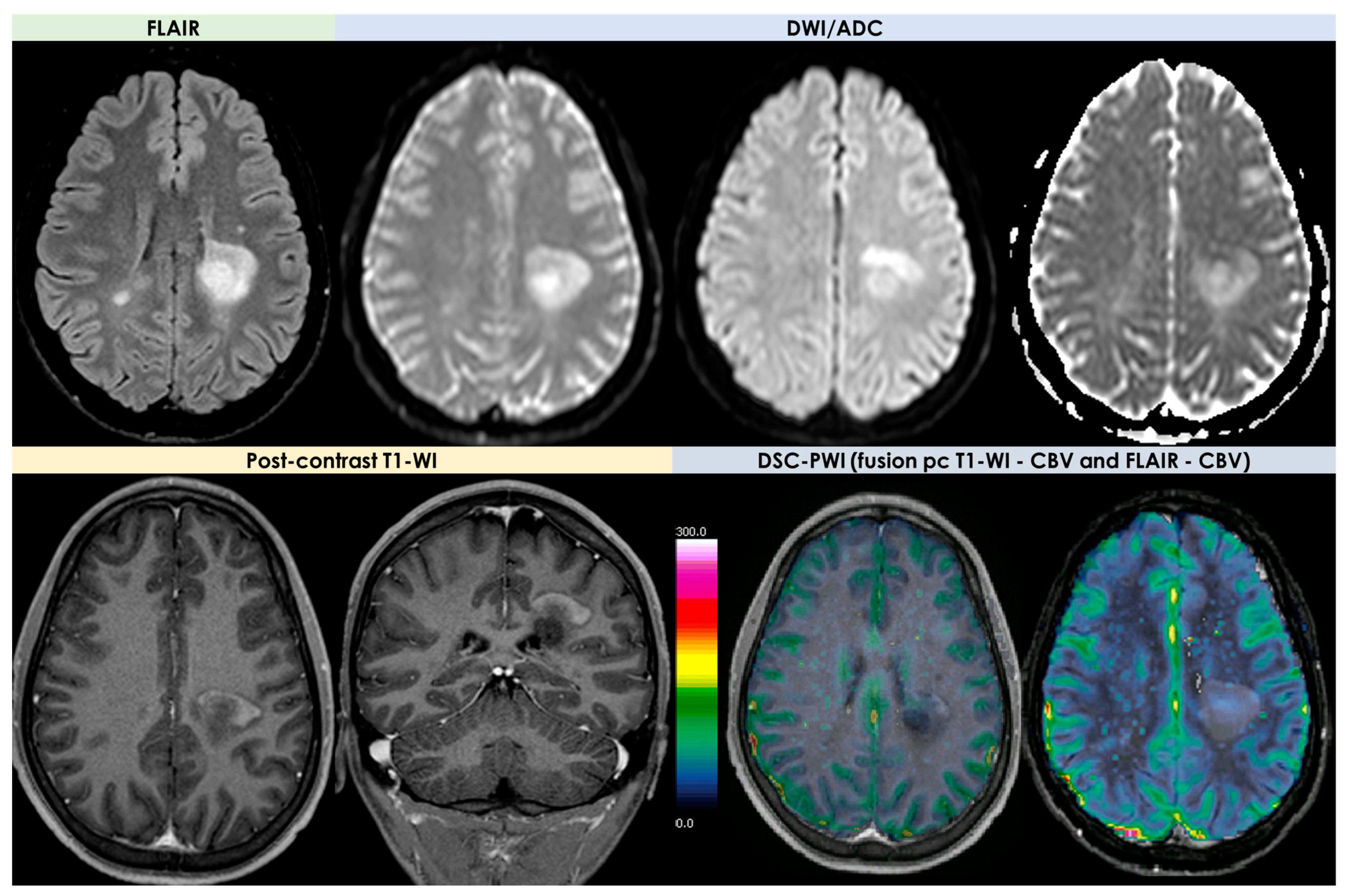
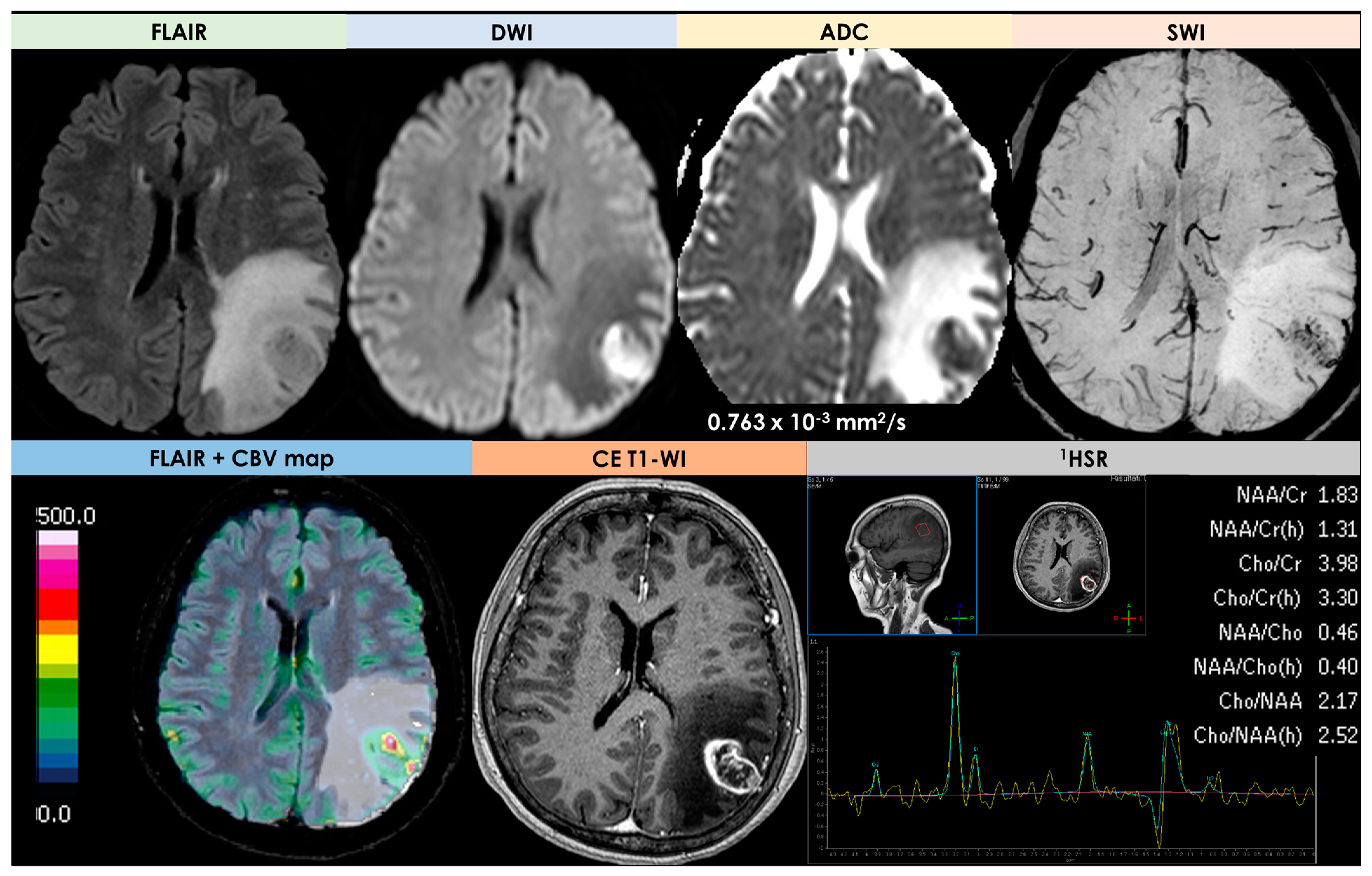
| Neuroimaging Patterns | Reported Rate |
|---|---|
| Acute intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)/subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) | 90/660 (13.6%) |
| Tumefactive (or pseudotumoral) pattern (t-PACNS) | 27/660 (4.1%) |
| Multiple acute/subacute ischemic lesions | 42/660 (6.4%) |
| Single acute/subacute ischemic lesion | 123/660 (18.6%) |
| Small vessel disease (SVD) pattern (according to the STRIVE criteria) [6,7] | 58/660 (8.8%) |
| Parenchymal contrast enhancement | 135/660 (20.4%) |
| Spinal cord involvement | 5/660 (0.8%) |
| Cohort. | Suthiphosuwan et al. [10] | Lee et al. [21] | De Boysson et al. [16] | Salvarani et al. [13] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field strength | 1.5 T and 3.0 T | 1.5-T | 1.5 T and 3.0 T | Not reported |
| Standard MRI sequences | T1-WI, T2-WI, FLAIR, and DWI. GRE-T2* or SWI Gadolinium-enhanced T1WI | Spin-echo T1-WI, fast spin-echo T2-WI, contrast-enhanced T1-WI in multiple planes, DWI with b = 1000 s/mm2 | Not detailed | Not reported |
| Vascular imaging | CTA or MRA in 9/10 pts | 3D TOF MRA DSA (high resolution matrix 1024 × 1024) in three out of four patients | MRA in all patients * | Not fully reported * Angiogram showing vasculitis was present in one out of three of the t-PACNS patients |
| Advanced MRI | DSC-MRI (3/10) 1HRS-MRI (2/10) VWI (3/10) | DSC-MRI in 3/4 patients Single-voxel 1HSR- MRS in two out of four patients | Not detailed | Not reported |
| MRI Findings | Pooled Incidence (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Open-ring or incomplete-rim enhancement | 35% (24–47%) |
| Closed-ring or complete-rim enhancement | 18% (11–29%) |
| T2 hypointense rim | 48% (36–60%) |
| Absent or mild mass effect | 67% (48–83%) |
| Absent or mild perilesional edema | 57% (36–76%) |
| MRI | PCNSL | TDLs | High Grade Glioma | Neurosarcoidosis | Toxoplasmosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preferential location | Periventricular and superficial brain regions | Mainly supratentorial (frontal and parietal lobe) | Subcortical white matter and deeper gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord | Single or multiple supratentorial lesions (spherical > stellate) with prominent perilesional edema | Usually multiple lesions, but the tumefactive form shows a single, large, necrotic lesion with extensive adjacent edema (acute necrotizing toxoplasmosis) |
| T1-WI | Hypo- or isointense | Heterogeneous with prevalent hypointensity | Hypointense | Heterogeneous with prevalent hypointensity | |
| T2-WI and FLAIR | Iso- or hypointense | Heterogeneous with hypointense rim (48%) Absent or mild mass effect (67%) Absent or mild perilesional edema (57%) | Hyperintense surrounding edema | Heterogeneous with central hypointensity Sometimes hiso-hypointensity | Concentric target sign on T2-WI/FLAIR (central hypointense lesion, hyperintense intermediate region, surrounded by a hypointense halo) |
| Contrast enhancement (CE) on T1-WI | Moderate–marked CE Non-AIDS patients: homogeneous CE, 90%; ring CE, 0–13% Leptomeningeal, subependymal, dural, or cranial nerve CE AIDS patients: irregular CE common; ring CE, 75% | Open ring (35%) Closed ring (18%) Homogeneous, heterogeneous, patchy and diffuse, cotton ball, and nodular patterns (NMOSD lesions often have absent or minimal enhancement) | Typically ring enhancement | Heterogeneous |
| MRI | PCNSL | TDLs | High Grade Glioma | Neurosarcoidosis | Toxoplasmosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWI/ADC | Hyperintense on DWI/hypointense on ADC maps Decreased FA values in lesions | High ADC values in center of lesion and relatively low ADC values in periphery of lesion Threshold for the minimum ADC value for distinguishing TDLs from PCNSL is 0.556 × 10−3 mm2/s | Hypointense in DWI and ADC | Hypointense on DWI and ADC | “Eccentric target sign” consisting of an eccentric nodule along the rim of an enhancing lesion on T1-WI ADC > 1.6 × 10−3 mm2/s suggestive of toxoplasmosis |
| DSC-MRI | rCBV lower than HGG Characteristic TIC | Few data with variable findings | rCBV usually higher than PCNSL, but variable findings | No data | rCBV lower than that in necrotic glioblastomas and metastases |
| Spectroscopy | Elevated lipid peaks and high Cho/Cr ratios | Increased Cho- peak Decreased NAA peak Increased Cho/NAA ratio | Elevated lipid peaks High Cho/Cr ratio | No data | No data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zedde, M.; Napoli, M.; Moratti, C.; Pavone, C.; Bonacini, L.; Di Cecco, G.; D’Aniello, S.; Grisendi, I.; Assenza, F.; Boulouis, G.; et al. Tumor-like Lesions in Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060618
Zedde M, Napoli M, Moratti C, Pavone C, Bonacini L, Di Cecco G, D’Aniello S, Grisendi I, Assenza F, Boulouis G, et al. Tumor-like Lesions in Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(6):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060618
Chicago/Turabian StyleZedde, Marialuisa, Manuela Napoli, Claudio Moratti, Claudio Pavone, Lara Bonacini, Giovanna Di Cecco, Serena D’Aniello, Ilaria Grisendi, Federica Assenza, Grégoire Boulouis, and et al. 2024. "Tumor-like Lesions in Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differential Diagnosis" Diagnostics 14, no. 6: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060618
APA StyleZedde, M., Napoli, M., Moratti, C., Pavone, C., Bonacini, L., Di Cecco, G., D’Aniello, S., Grisendi, I., Assenza, F., Boulouis, G., Nguyen, T. N., Valzania, F., & Pascarella, R. (2024). Tumor-like Lesions in Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 14(6), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060618






