Could Phosphorous MR Spectroscopy Help Predict the Severity of Vasospasm? A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
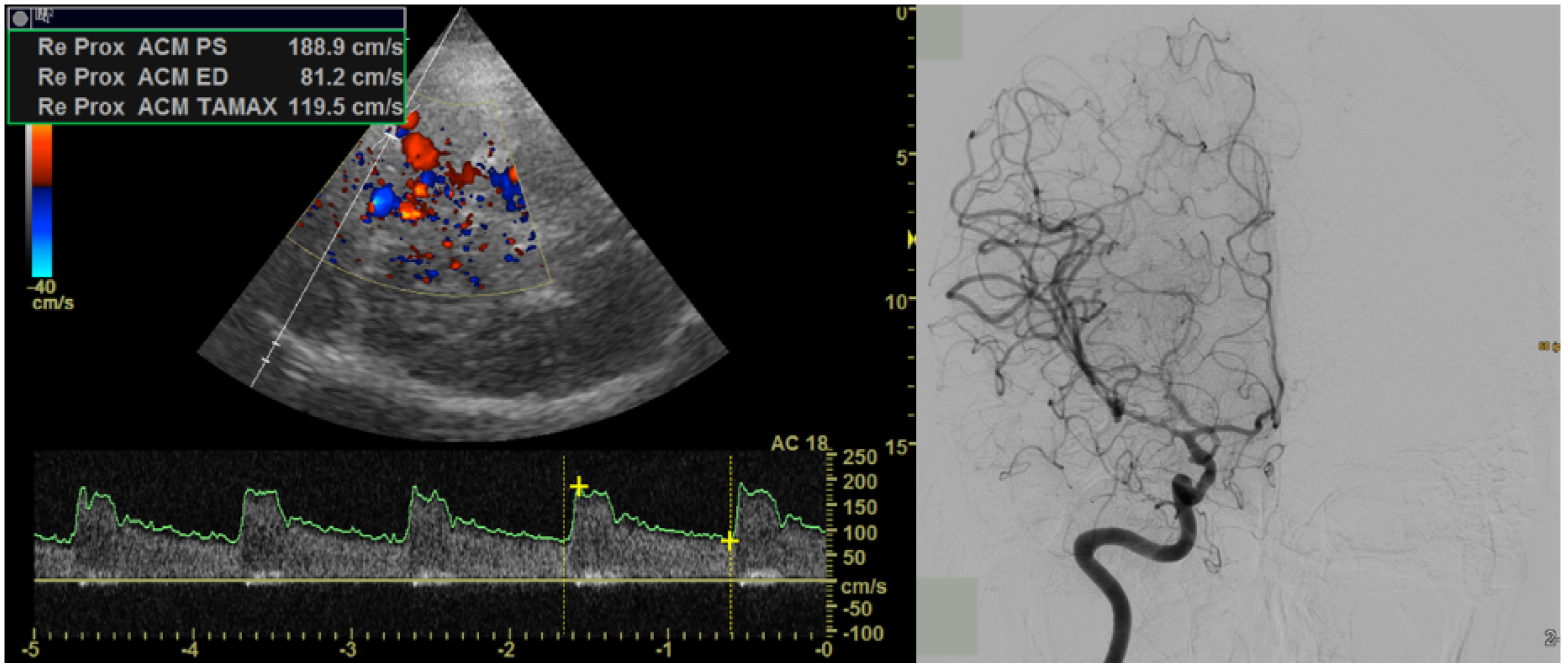
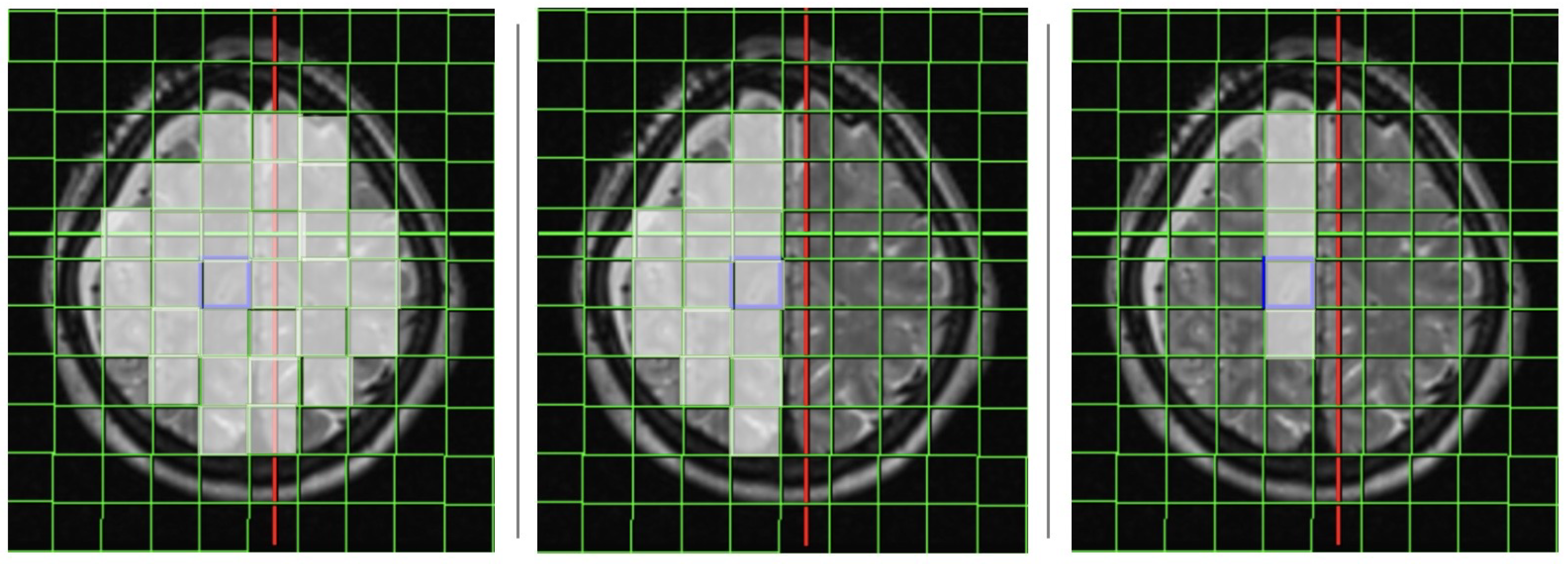
2.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Cumulative Results
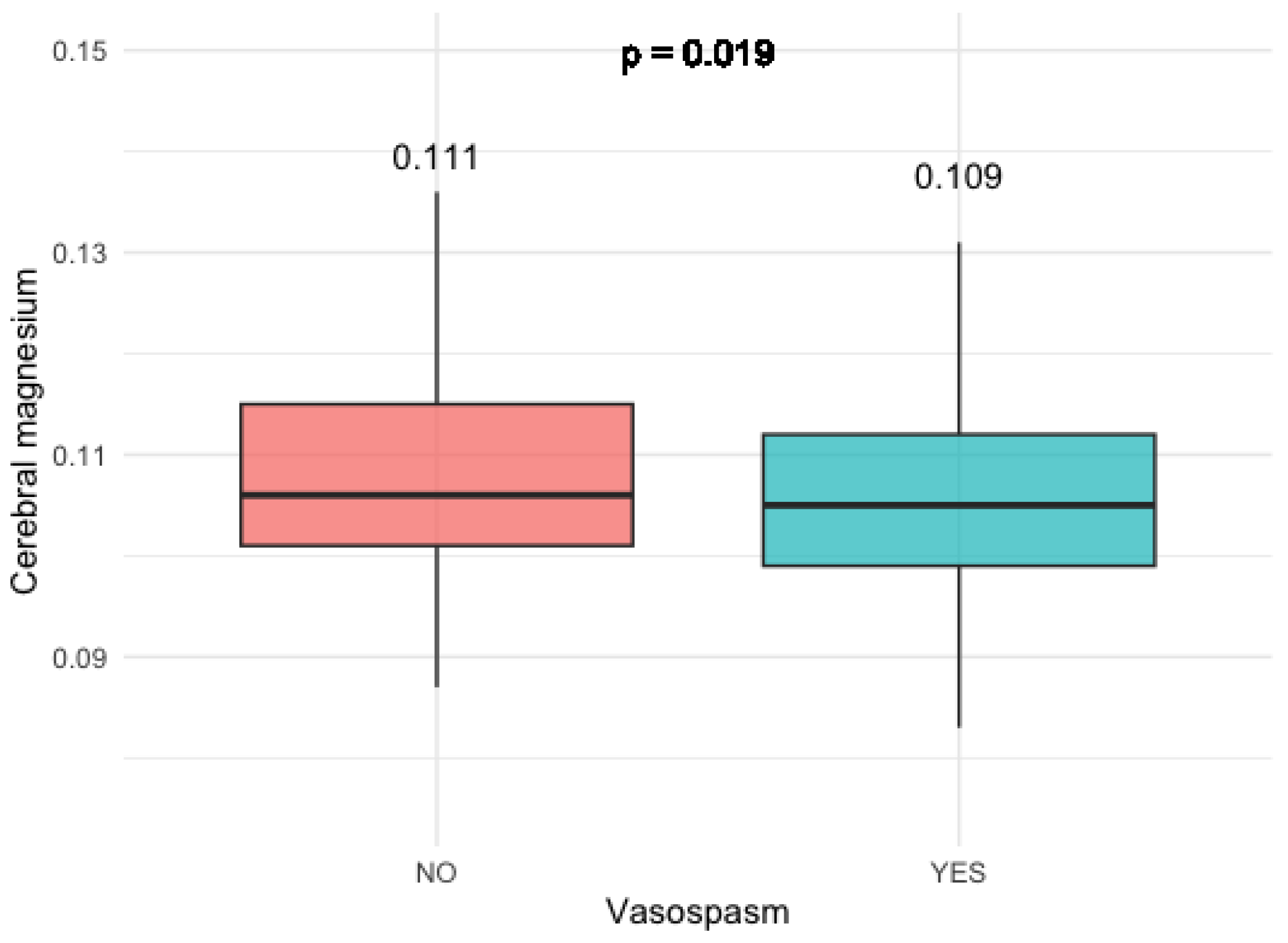
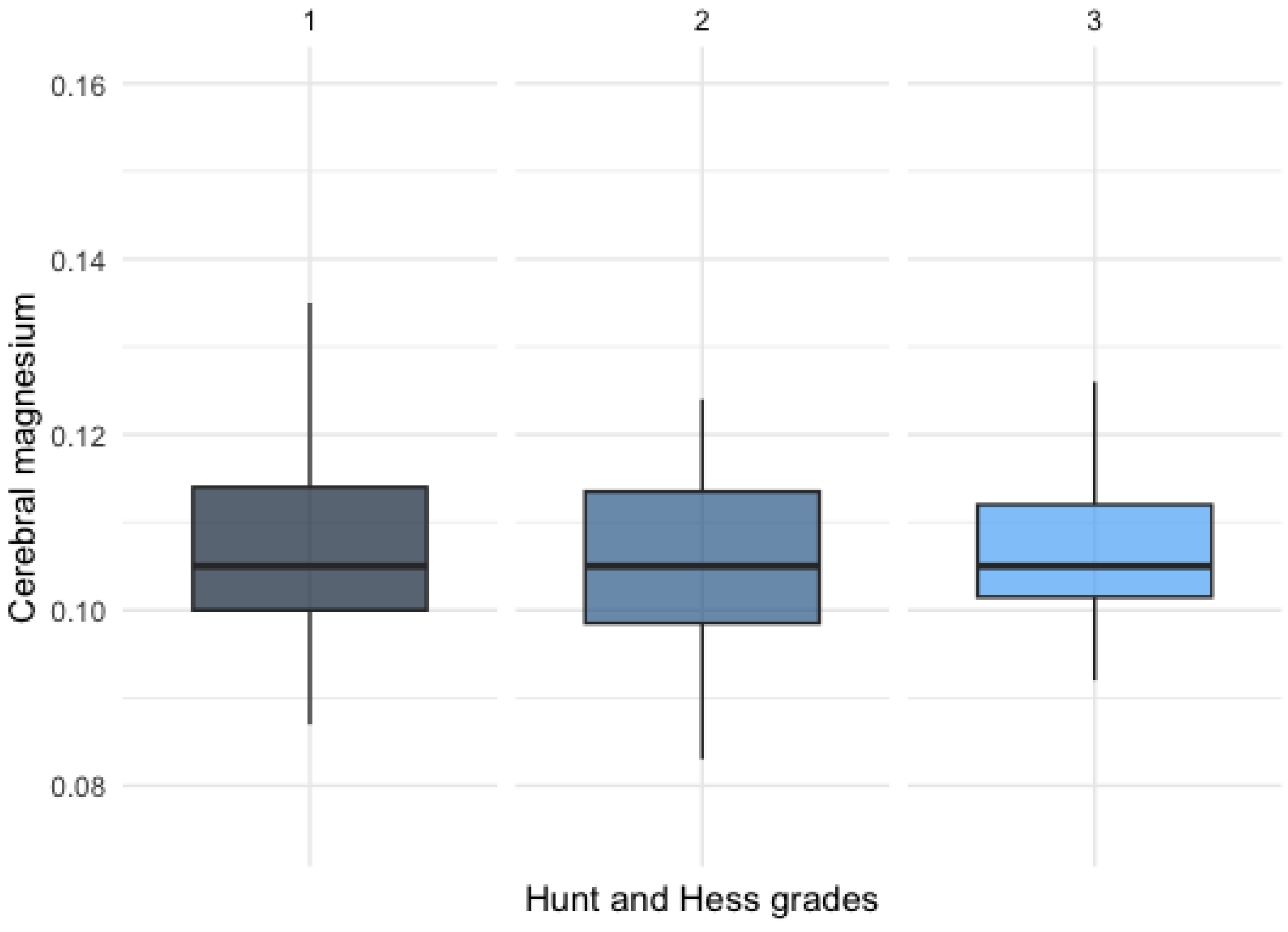
3.2.1. Magnesium Levels
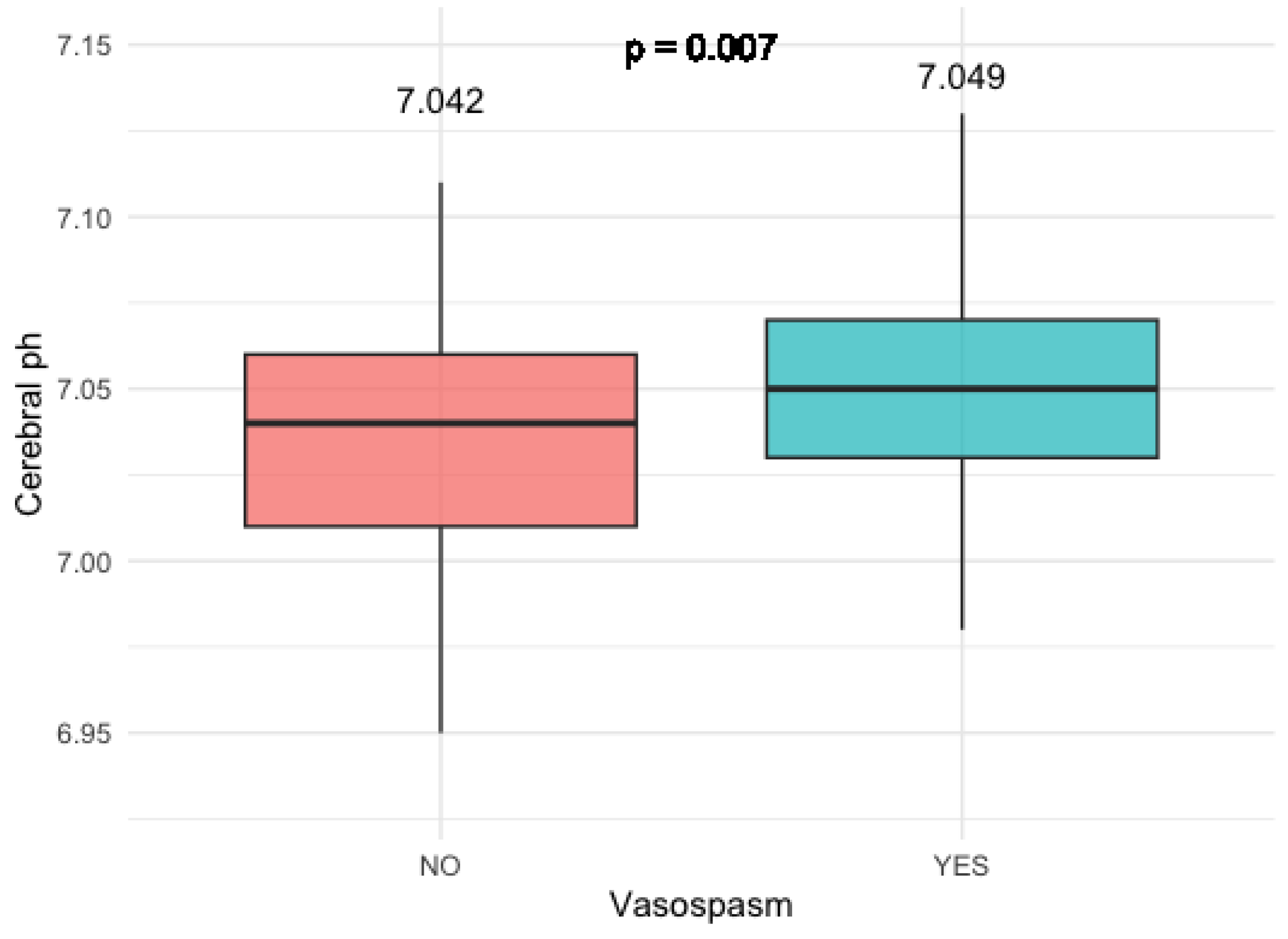
3.2.2. Cerebral pH Levels
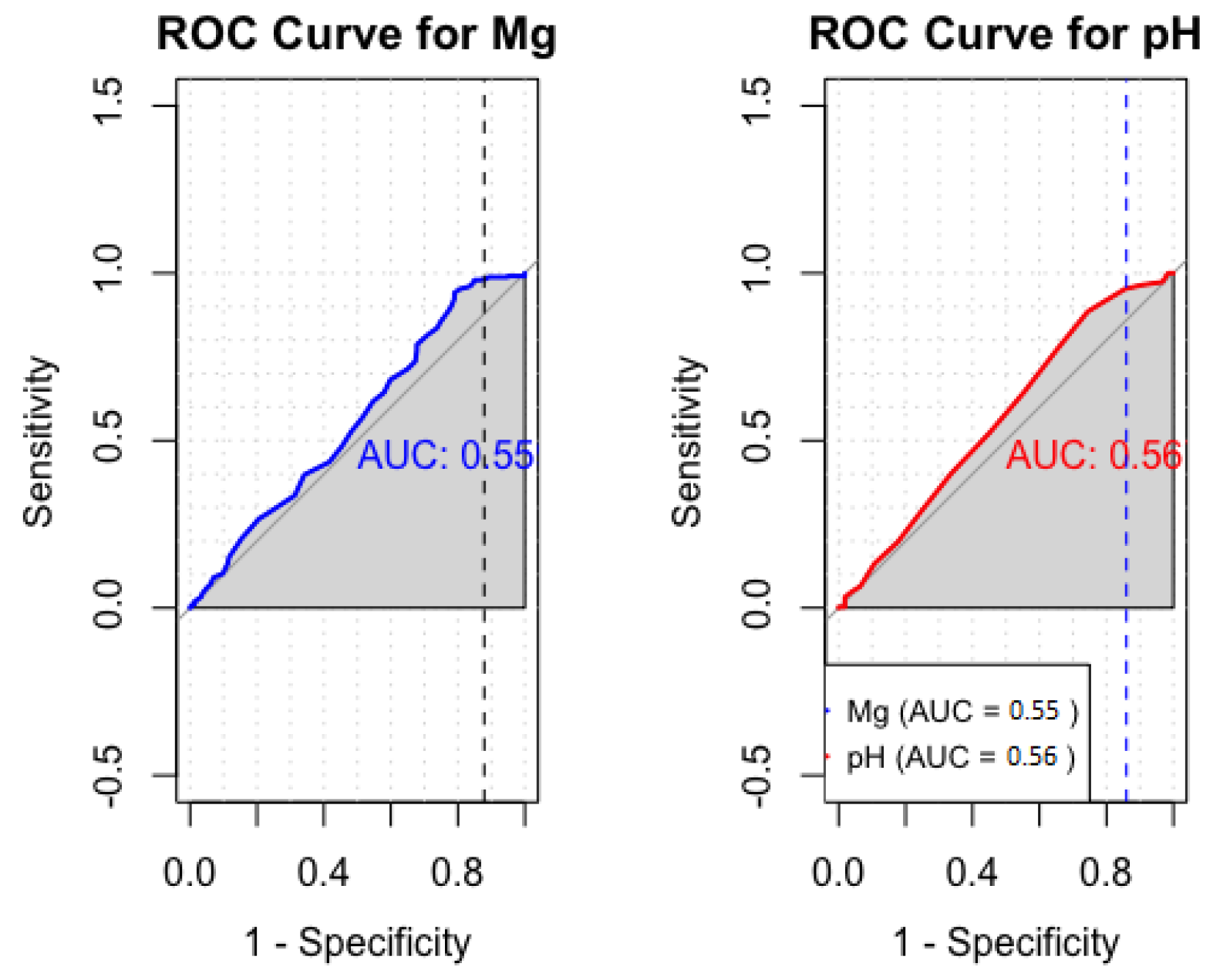
3.2.3. Sensitivity and Specificity Analysis of Cerebral Mg and pH
3.3. Results from the Affected Arterial Territory and Affected Side
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aSAH | aneurysmal subarachoidal hemorrhage |
| DCI | delayed cerebral ischemia |
| CT | computerized tomography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MISA | Monitoring and Imaging of SAH and Aneurysms |
| 31P-MRS | phosphorous magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
References
- Kassell, N.; Torner, J. The International Cooperative study on timing of aneurysm surgery. Acta Neurochir. 1982, 63, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantigua, H.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Schmidt, J.M.; Lee, K.; Badjatia, N.; Agarwal, S.; Claassen, J.; Connolly, E.; Mayer, S. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Who dies, and why? Crit. Care 2015, 19, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, M.; Hadjipavlou, G.; Kelly, M.; Westbrook, J.; Pattinson, K. Delayed cerebral ischaemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage: Looking beyond vasospasm. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, W.S.; Laurent, D.; Dumont, A.S.; Hasan, D.M.; Jabbour, P.M.; Starke, R.M.; Hosaka, K.; Polifka, A.J.; Hoh, B.L.; Chalouhi, N. Pathophysiology of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.; Claassen, J.; Schmidt, J.M.; Wartenberg, K.; Temes, R.; Connolly, E.; Mayer, S. Prediction of Symptomatic Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Modified Fisher Scale. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treichl, S.A.; Ho, W.M.; Steiger, R.; Grams, A.E.; Rietzler, A.; Luger, M.; Gizewski, E.R.; Thomé, C.; Petr, O. Cerebral energy status and altered metabolism in early brain injury after aneurysmal Subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective 31P-MRS pilot study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 831537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.B.; Harbaugh, K.S.; Hoopes, P.J.; Pikus, H.J.; Harbaugh, R.E. Neuroprotective effects of preischemia intraarterial magnesium sulfate in reversible focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 85, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, W.M.; Zuur, J.K.; Kamerling, N.A.; van Asseldonk, J.T.H.; Rinkel, G.J.; Tulleken, C.A.; Nicolay, K. Role of magnesium in the reduction of ischemic depolarization and lesion volume after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, Z.; Sadeh, M.; Shacked, I.; Sahar, A.; Hadani, M. Magnesium sulfate reverses experimental delayed cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 1991, 22, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, W.; Algra, A.; Kooten, F.; Dirven, C.; van Gijn, J.; Vermeulen, M.; Rinkel, G. Magnesium sulfate in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2005, 36, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, R.; Zohry, G. Effect of magnesium sulphate and milrinone on cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A randomized study. Rev. Bras. Anestesiol. 2018, 69, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Carter, B. Role of magnesium sulfate in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage management: A meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2011, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeon, J.; Sheen, S.; Hwang, G.; Kang, S.H.; Heo, D.; Cho, Y.J. Intravenous Magnesium Infusion for the Prevention of Symptomatic Cerebral Vasospasm after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2012, 52, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Hara, Y.; Aiko, Y.; Koike, N.; Sakamoto, S.; Nakao, Y.; Esaki, T. Effect of intrathecal magnesium sulfate solution injection via a microcatheter in the cisterna magna on cerebral vasospasm in the canine subarachnoid haemorrhage model. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 26, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossen, A.; Ernst, G.; Bauer, A. Update on intrathecal management of cerebral vasospasm: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Lobanova, I.; Huang, W.; Ishfaq, M.F.; Broderick, J.P.; Cassarly, C.N.; Martin, R.H.; Macdonald, R.L.; Suarez, J.I. Lessons learned from phase II and phase III trials investigating therapeutic agents for cerebral ischemia associated with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 36, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, W.; Albrecht, K.; Berkelbach Van Der Sprenkel, J.; Rinkel, G. Magnesium therapy after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage a dose-finding study for long term treatment. Acta Neurochir. 2003, 145, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, S.M.D.; Algra, A.; Vandertop, W.P.; van Kooten, F.; Kuijsten, H.A.; Boiten, J.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Salman, R.A.S.; Lavados, P.M.; Rinkel, G.J.; et al. Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2): A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijenaar, J.F.; Mees, S.M.D.; Algra, A.; Van Den Bergh, W.M.; Rinkel, G.J. Effect of magnesium treatment and glucose levels on delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: A substudy of the Magnesium in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage trial (MASH-II). Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Zuccarello, M.; Rapoport, R.M. pCO2 and pH regulation of cerebral blood flow. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, L.; Del Sorbo, L. Diagnosis and management of vasospasm. F1000 Med. Rep. 2009, 1, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, A.E.; Mangesius, S.; Steiger, R.; Radovic, I.; Rietzler, A.; Walchhofer, L.M.; Galijašević, M.; Mangesius, J.; Nowosielski, M.; Freyschlag, C.F.; et al. Changes in brain energy and membrane metabolism in glioblastoma following chemoradiation. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5041–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Magerkurth, J.; Pilatus, U.; Mozer, A.; Seifried, C.; Steinmetz, H.; Zanella, F.; Hilker, R. Phosphorus and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy demonstrates mitochondrial dysfunction in early and advanced Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2009, 132, 3285–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, K.J.; Hattingen, E.; Franz, K.; Steinbach, J.P.; Bähr, O.; Pilatus, U. Intracellular pH measured by 31P-MR-spectroscopy might predict site of progression in recurrent glioblastoma under antiangiogenic therapy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Jurcoane, A.; Bähr, O.; Rieger, J.; Magerkurth, J.; Anti, S.; Steinbach, J.P.; Pilatus, U. Bevacizumab impairs oxidative energy metabolism and shows antitumoral effects in recurrent glioblastomas: A 31P/1H MRSI and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walchhofer, L.M.; Steiger, R.; Rietzler, A.; Kerschbaumer, J.; Freyschlag, C.F.; Stockhammer, G.; Gizewski, E.R.; Grams, A.E. Phosphorous magnetic resonance spectroscopy to detect regional differences of energy and membrane metabolism in naïve glioblastoma multiforme. Cancers 2021, 13, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Lanfermann, H.; Menon, S.; Neumann-Haefelin, T.; DuMesnil de Rochement, R.; Stamelou, M.; Höglinger, G.; Magerkurth, J.; Pilatus, U. Combined 1H and 31P MR spectroscopic imaging: Impaired energy metabolism in severe carotid stenosis and changes upon treatment. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2009, 22, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Magerkurth, J.; Pilatus, U.; Hübers, A.; Wahl, M.; Ziemann, U. Combined 1H and 31P spectroscopy provides new insights into the pathobiochemistry of brain damage in multiple sclerosis. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, K.J.; Hattingen, E.; Franz, K.; Steinbach, J.; Bähr, O.; Pilatus, U. In vivo metabolic profiles as determined by 31P and short TE 1H MR-spectroscopy: No difference between patients with IDH wildtype and IDH mutant gliomas. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2019, 29, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galijašević, M.; Steiger, R.; Radović, I.; Birkl-Toeglhofer, A.M.; Birkl, C.; Deeg, L.; Mangesius, S.; Rietzler, A.; Regodić, M.; Stockhammer, G.; et al. Phosphorous magnetic resonance spectroscopy and molecular markers in IDH1 wild type glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, R. Issues of spectral quality in clinical 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy and a gallery of artifacts. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iotti, S.; Frassineti, C.; Alderighi, L.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A.; Barbiroli, B. In vivo assessment of free magnesium concentration in human brain by 31P MRS. A new calibration curve based on a mathematical algorithm. NMR Biomed. Int. J. Devoted Dev. Appl. Magn. Reson. Vivo 1996, 9, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Galijašević, M.; Steiger, R.; Regodić, M.; Waibel, M.; Sommer, P.J.D.; Grams, A.E.; Singewald, N.; Gizewski, E.R. Brain Energy Metabolism in Two States of Mind Measured by Phosphorous Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 686433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toi, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Yokosuka, K.; Matsubara, S.; Hirano, K.; Uno, M. Prediction of cerebral vasospasm using early stage transcranial Doppler. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2013, 53, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, C.E.; Samaniego, E.; Sam, K.; Roa, J.; Perez-Nellar, J.; Rodríguez, D. Prediction of Symptomatic Vasospasm in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Early Transcranial Doppler. J. Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2020, 11, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Souissi, R.; Boubakker, A.; Souissi, H.; Abdelrazek, A.; Badri, M.; Bziouech, S.; Jemel, H. Prediction of cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using jugular bulb oximetry monitoring: Preliminary results. Crit. Care 2010, 14, P343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heran, N.S.; Hentschel, S.J.; Toyota, B.D. Jugular bulb oximetry for prediction of vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 31, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csók, I.; Grauvogel, J.; Scheiwe, C.; Bardutzky, J.; Wehrum, T.; Beck, J.; Reinacher, P.C.; Roelz, R. Basic Surveillance Parameters Improve the Prediction of Delayed Cerebral Infarction After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.B.; Muizelaar, J.P.; Choi, S.C. Magnesium’s role in cerebral vasospasm and outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cereb. Vasospasm 1993, 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bergh, W.M.; Algra, A.; van der Sprenkel, J.W.; Tulleken, C.A.; Rinkey, G.J. Hypomagnesemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2003, 15, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipplinger, C.; Cattaneo, A.; Wipplinger, T.; Lamllari, K.; Semmler, F.; Geske, C.; Messinger, J.; Nickl, V.; Beez, A.; Ernestus, R.I.; et al. Serum concentration–guided intravenous magnesium sulfate administration for neuroprotection in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A retrospective evaluation of a 12-year single-center experience. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, B.; Weidinger, C.S.; Wolf, D.; Buchfelder, M.; Schmitt, H. Intraoperative continuous cerebral microcirculation measurement in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Preliminary data on the early administration of magnesium sulfate. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbel, F.T.; Du, X.; Hoffman, W.E.; Ausman, J.I. Brain tissue PO2, PCO2, and pH during cerebral vasospasm. Surg. Neurol. 2000, 54, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Shiba, M.; Nakatsuka, Y.; Nakano, F.; Nishikawa, H. Higher Cerebrospinal Fluid pH may Contribute to the Development of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2017, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harst, J.; Luijckx, G.J.; Elting, J.; Lammers, T.; Bokkers, R.; Bergh, W.; Eshghi, O.; Metzemaekers, J.; Groen, R.; Mazuri, A.; et al. The Predictive Value of the CTA Vasospasm Score on Delayed Cerebral Ischemia and Functional Outcome after aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 29, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, H.; Lindner, D.; Gaber, K.; Ziganshyna, S.; Jentzsch, J.; Engelmann, S.; Gerhards, T.; Sari, S.; Stock, A.; Vothel, F.; et al. Standardized Classification of Cerebral Vasospasm after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Digital Subtraction Angiography. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, A.; Holmes, J.H.; Smith, M.J.; Lee, I.; Park, S. Prediction of significant vasospasm in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using automated data. Neurocrit. Care 2014, 21, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Participants | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 13 |
| Female | 11 (84.6) |
| Male | 2 (15.4) |
| Mean age | 55 ± 9.6 |
| Applied treatment | |
| Clipping | 9 (69.2) |
| Coiling | 4 (30.8) |
| Aneurysm location | |
| ICA | 1 (7.6) |
| MCA | 2 (15.4) |
| AComm | 5 (38.4) |
| ACA | 2 (15.4) |
| PComm | 3 (23.1) |
| Patients with vasospasm | 7 (53.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galijasevic, M.; Steiger, R.; Treichl, S.A.; Ho, W.M.; Mangesius, S.; Ladenhauf, V.; Deeg, J.; Gruber, L.; Ouaret, M.; Regodic, M.; et al. Could Phosphorous MR Spectroscopy Help Predict the Severity of Vasospasm? A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080841
Galijasevic M, Steiger R, Treichl SA, Ho WM, Mangesius S, Ladenhauf V, Deeg J, Gruber L, Ouaret M, Regodic M, et al. Could Phosphorous MR Spectroscopy Help Predict the Severity of Vasospasm? A Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(8):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080841
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalijasevic, Malik, Ruth Steiger, Stephanie Alice Treichl, Wing Man Ho, Stephanie Mangesius, Valentin Ladenhauf, Johannes Deeg, Leonhard Gruber, Miar Ouaret, Milovan Regodic, and et al. 2024. "Could Phosphorous MR Spectroscopy Help Predict the Severity of Vasospasm? A Pilot Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 8: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080841
APA StyleGalijasevic, M., Steiger, R., Treichl, S. A., Ho, W. M., Mangesius, S., Ladenhauf, V., Deeg, J., Gruber, L., Ouaret, M., Regodic, M., Lenhart, L., Pfausler, B., Grams, A. E., Petr, O., Thomé, C., & Gizewski, E. R. (2024). Could Phosphorous MR Spectroscopy Help Predict the Severity of Vasospasm? A Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 14(8), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14080841






