Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Skin Pathologies of the Breast—A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
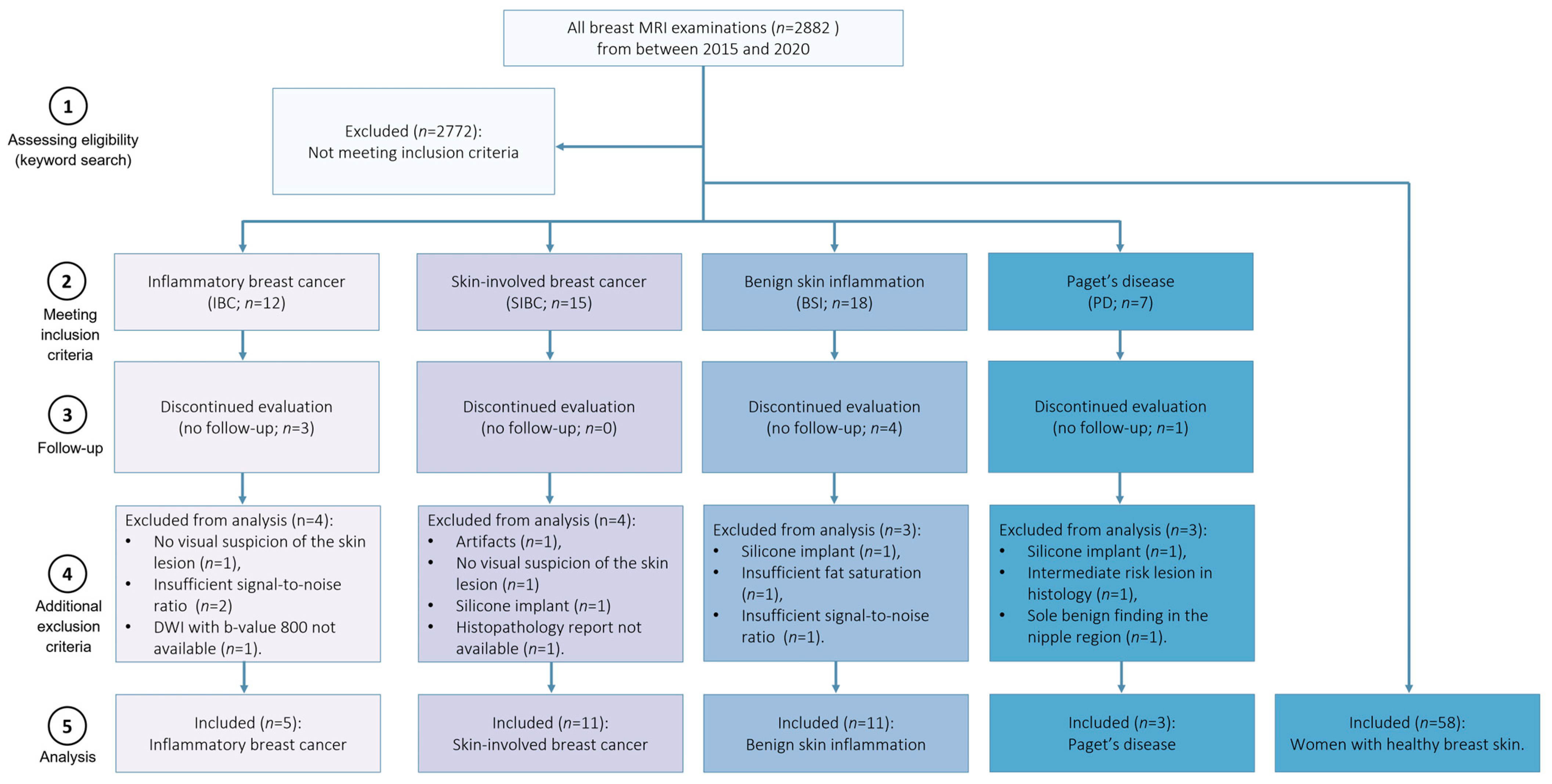
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MRI Protocol
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. ADC Calculation
2.5. SNR Estimation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
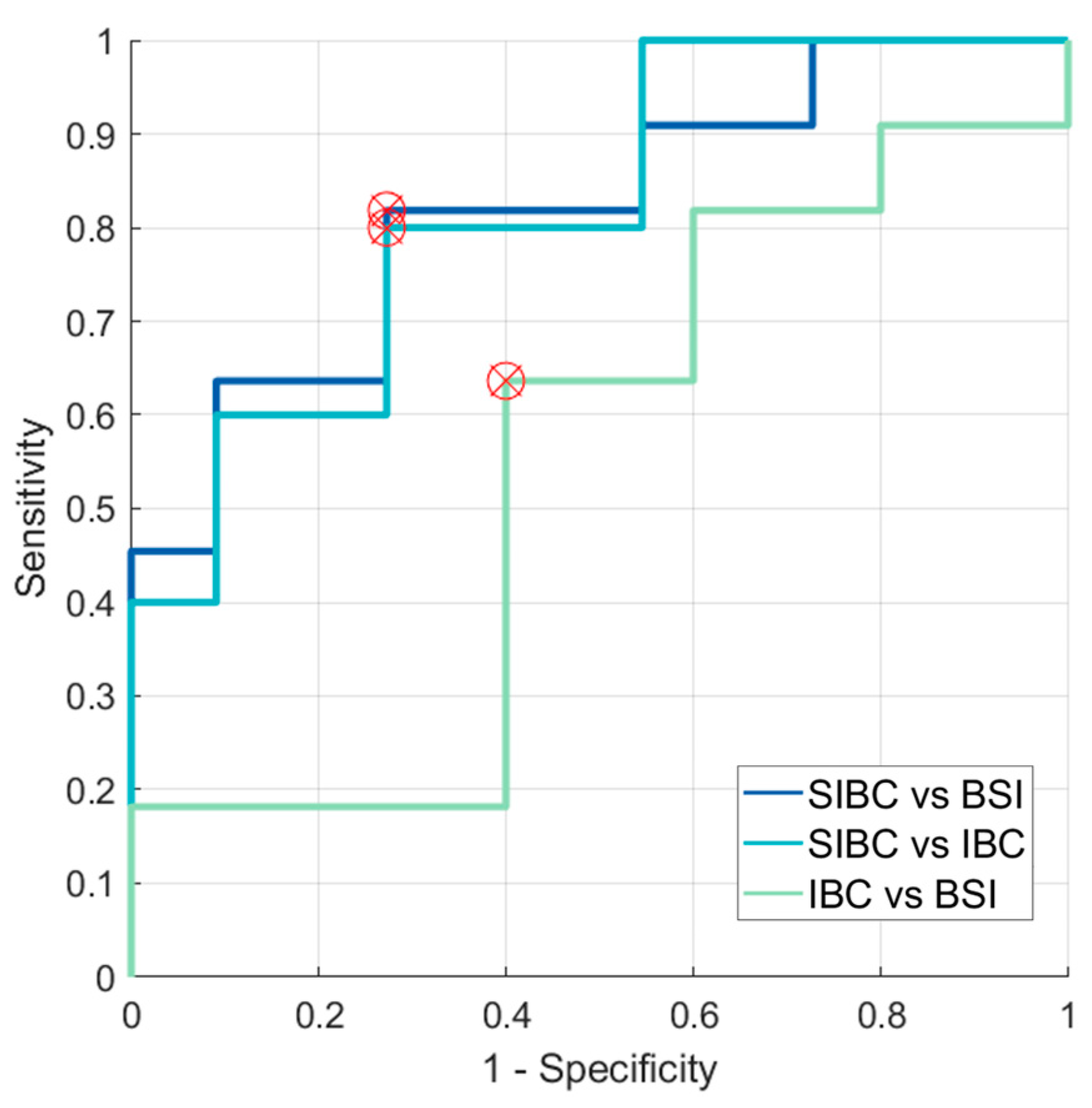
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
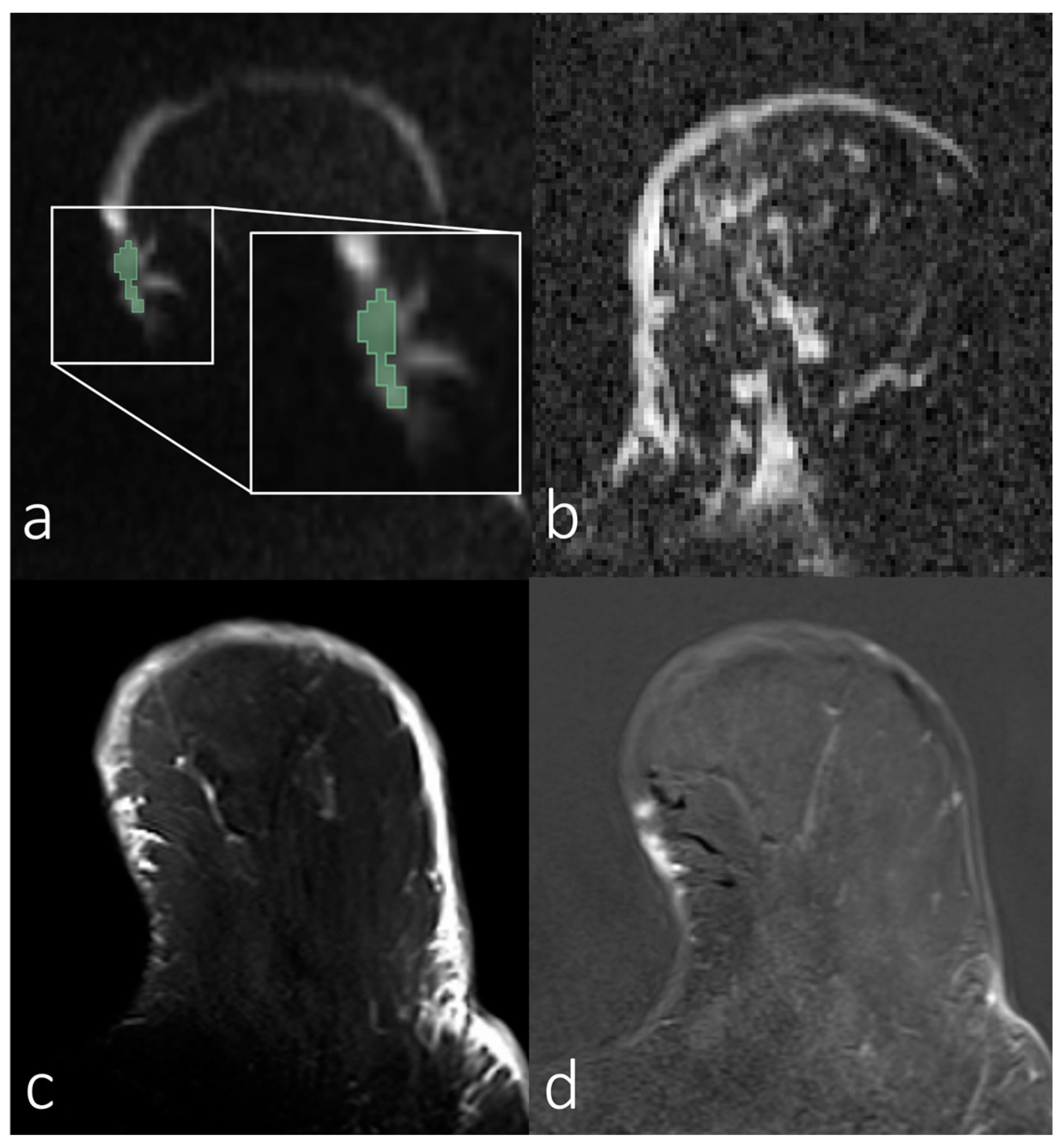
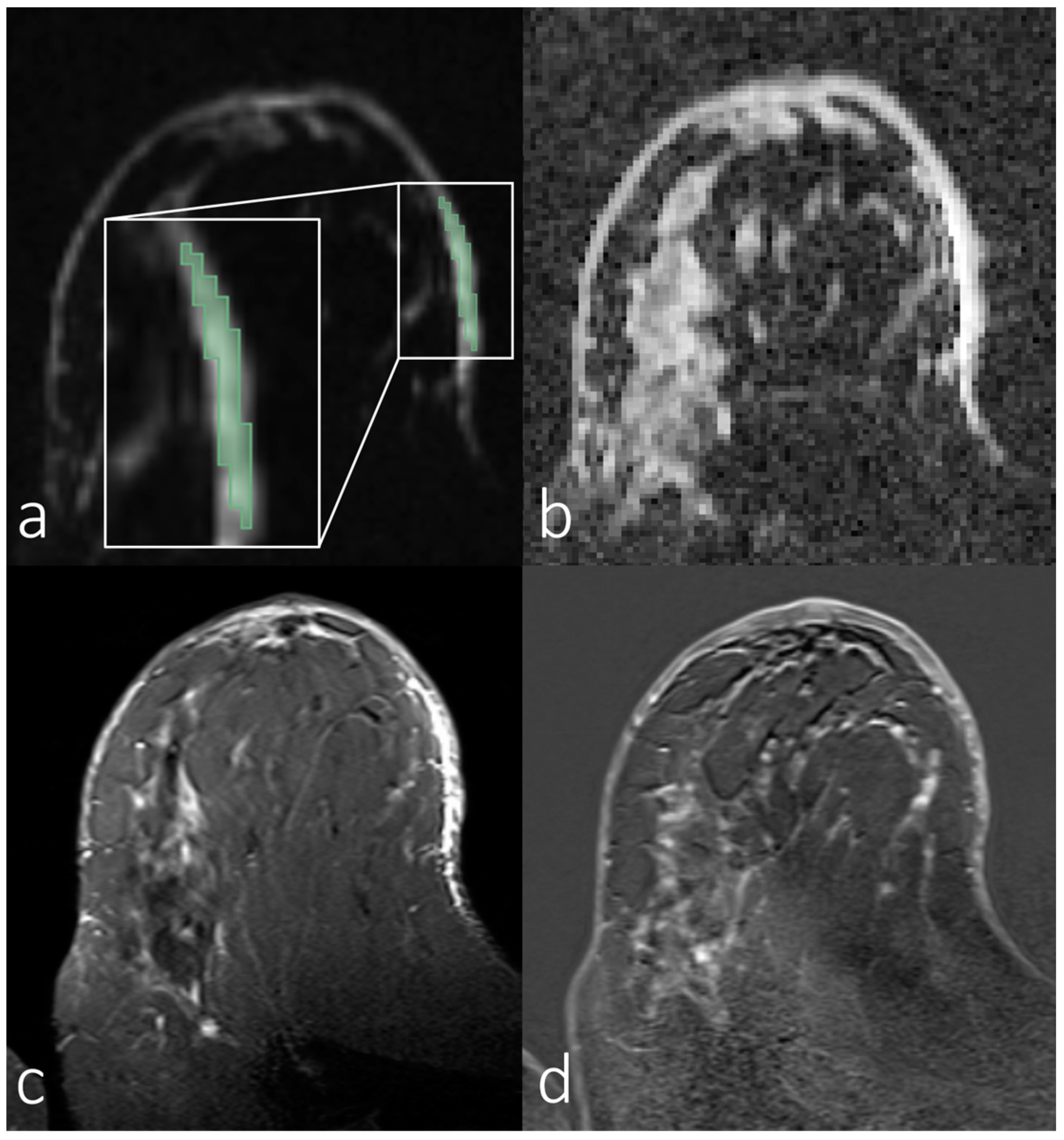
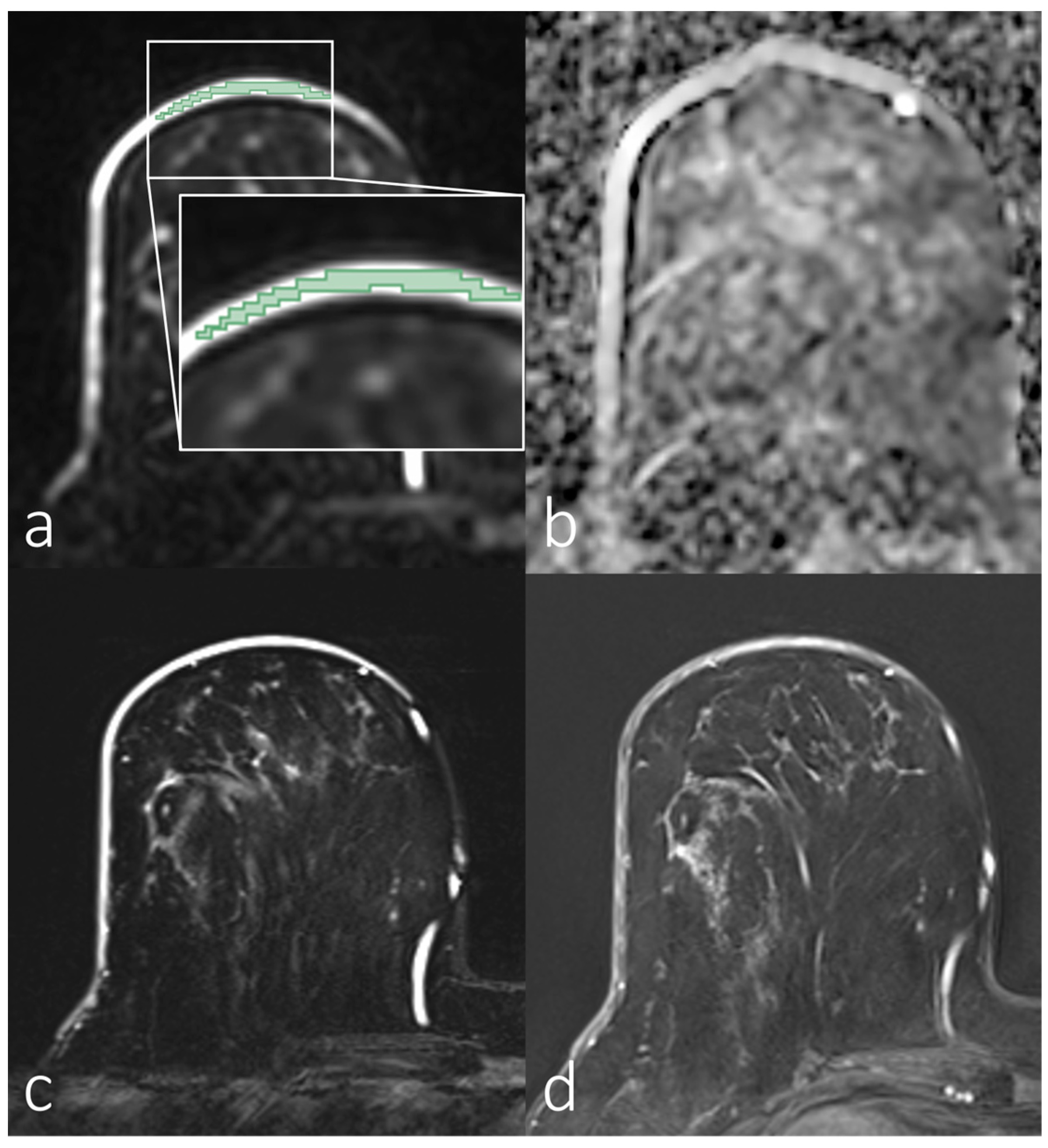
3.2. Analyses of First-Order Statistics Using the ADC
3.3. Evaluation of SNR in the Skin for Assessing ADCs in Skin Pathologies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, L.I.; Klimczak, K.; Geach, R. Breast MRI: An illustration of benign findings. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, P.; Jonasson, L.; Maeder, P.; Thiran, J.P.; Wedeen, V.J.; Meuli, R. Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: From scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 2006, 26 (Suppl. S1), S205–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, O. Time-Dependent Diffusion MRI in Cancer: Tissue Modeling and Applications. Front. Phys. 2017, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norddin, N.; Power, C.; Watson, G.; Cowin, G.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Gluch, L.; Bourne, R.M. Microscopic diffusion properties of fixed breast tissue: Preliminary findings. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iima, M.; Honda, M.; Sigmund, E.E.; Ohno Kishimoto, A.; Kataoka, M.; Togashi, K. Diffusion MRI of the breast: Current status and future directions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhani, A.R.; Liu, G.; Koh, D.M.; Chenevert, T.L.; Thoeny, H.C.; Takahara, T.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.; Ross, B.D.; Van Cauteren, M.; Collins, D.; et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: Consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltzer, P.A.T.; Bickel, H.; Spick, C.; Wengert, G.; Woitek, R.; Kapetas, P.; Clauser, P.; Helbich, T.H.; Pinker, K. Potential of Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Characterization of Breast Lesions: Intraindividual Comparison With Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2018, 53, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Hoogt, K.J.J.; Schipper, R.-J.; Wessels, R.; ter Beek, L.C.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Mann, R.M. Breast DWI Analyzed Before and After Gadolinium Contrast Administration—An Intrapatient Analysis on 1.5 T and 3.0 T. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzel, M.; Krug, B.; Clauser, P.; Burke, C.; Hellmich, M.; Maintz, D.; Uder, M.; Bickel, H.; Helbich, T.; Baltzer, P.A.T. A Multicentric Comparison of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping and the Kaiser Score in the Assessment of Breast Lesions. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlmeyer, S.; Laun, F.B.; Palm, T.; Janka, R.; Weiland, E.; Uder, M.; Wenkel, E. Simultaneous Multislice Echo Planar Imaging for Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilpert, C.; Neubauer, C.; Rau, A.; Schneider, H.; Benkert, T.; Weiland, E.; Strecker, R.; Reisert, M.; Benndorf, M.; Weiss, J.; et al. Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in 3 T Breast MRI Using a Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm With Superresolution Processing: A Prospective Comparative Study. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlmeyer, S.; Laun, F.B.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Palm, T.; Janka, R.; Weiland, E.; Uder, M.; Wenkel, E. Ultra-High b-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-Based Abbreviated Protocols for Breast Cancer Detection. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, E.; Liberman, G.; Nissan, N.; Furman-Haran, E.; Sklair-Levy, M.; Frydman, L. Diffusion-weighted breast MRI of malignancies with submillimeter resolution and immunity to artifacts by spatiotemporal encoding at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisner, D.J.; Rogers, N.; Deshpande, V.S.; Newitt, D.N.; Laub, G.A.; Porter, D.A.; Kornak, J.; Joe, B.N.; Hylton, N.M. High-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging for the separation of benign from malignant BI-RADS 4/5 lesions found on breast MRI at 3T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhan, C.; Yin, T.; Ai, T. Intraobserver and Interobserver Reproducibility of Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Quantitative Parameters: Readout-Segmented vs. Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.C.; Nissan, N.; Rahbar, H.; Kitsch, A.E.; Sigmund, E.E. Diffusion-weighted breast MRI: Clinical applications and emerging techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickelhaupt, S.; Steudle, F.; Paech, D.; Mlynarska, A.; Kuder, T.A.; Lederer, W.; Daniel, H.; Freitag, M.; Delorme, S.; Schlemmer, H.P.; et al. On a fractional order calculus model in diffusion weighted breast imaging to differentiate between malignant and benign breast lesions detected on X-ray screening mammography. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, S.; Doykova, K.; Vasilska, A.; Sapunarova, K.; Doykov, D.; Andonov, V.; Uchikov, P. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions Using ADC Values and ADC Ratio in Breast MRI. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.J.; Martin, M.; Denecke, T. DWI of the Breast—Possibilities and Limitations. Rofo 2022, 194, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Gullo, R.; Sevilimedu, V.; Baltzer, P.; Le Bihan, D.; Camps-Herrero, J.; Clauser, P.; Gilbert, F.J.; Iima, M.; Mann, R.M.; Partridge, S.C.; et al. A survey by the European Society of Breast Imaging on the implementation of breast diffusion-weighted imaging in clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6588–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, R.L.; Partridge, S.C.; Shin, H.J.; Thakur, S.B.; Pinker, K. Update on DWI for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2024, 222, e2329933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalli, S.; Freer, P.E.; Rafferty, E.A. Lesions of the Skin and Superficial Tissue at Breast MR Imaging. RadioGraphics 2010, 30, 1891–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, P.W.; Chotai, N.C.; Kulkarni, S. Imaging Features of Inflammatory Breast Disorders: A Pictorial Essay. Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardina, L.; Di Leone, A.; Magno, S.; Franco, A.; Biondi, E.; Sanchez, A.M.; D’Archi, S.; Gentile, D.; Fabi, A.; Masetti, R.; et al. Paget’s disease of the breast: Our 20 years’ experience. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 995442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menta, A.; Fouad, T.M.; Lucci, A.; Le-Petross, H.; Stauder, M.C.; Woodward, W.A.; Ueno, N.T.; Lim, B. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: What to Know About This Unique, Aggressive Breast Cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 98, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippa, V.; Barazi, H. Inflammatory Breast Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lepori, D. Inflammatory breast disease: The radiologist’s role. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 1045–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, R.H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Lim, B. Inflammatory breast cancer: Early recognition and diagnosis is critical. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Ruan, H.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Z. Application of Diffusion Weighted Imaging Techniques for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 694634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.C.; Mullins, C.D.; Kurland, B.F.; Allain, M.D.; DeMartini, W.B.; Eby, P.R.; Lehman, C.D. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values for Discriminating Benign and Malignant Breast MRI Lesions: Effects of Lesion Type and Size. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, Y.Q.; Cai, Z.L.; Gao, Y.G.; An, N.Y.; Ma, L.; Mahankali, S.; Gao, J.H. Differentiation of clinically benign and malignant breast lesions using diffusion-weighted imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 16, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.; Das, B.K.; Kapsner, L.A.; Eberle, J.; Skwierawska, D.; Folle, L.; Schreiter, H.; Laun, F.B.; Ohlmeyer, S.; Uder, M.; et al. Smart forecasting of artifacts in contrast-enhanced breast MRI before contrast agent administration. Eur. Radiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsner, L.A.; Ohlmeyer, S.; Folle, L.; Laun, F.B.; Nagel, A.M.; Liebert, A.; Schreiter, H.; Beckmann, M.W.; Uder, M.; Wenkel, E.; et al. Automated artifact detection in abbreviated dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI-derived maximum intensity projections (MIPs) of the breast. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 5997–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsner, L.A.; Balbach, E.L.; Folle, L.; Laun, F.B.; Nagel, A.M.; Liebert, A.; Emons, J.; Ohlmeyer, S.; Uder, M.; Wenkel, E.; et al. Image quality assessment using deep learning in high b-value diffusion-weighted breast MRI. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conturo, T.E.; McKinstry, R.C.; Aronovitz, J.A.; Neil, J.J. Diffusion MRI: Precision, accuracy and flow effects. NMR Biomed. 1995, 8, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, H.; Patz, S. The rician distribution of noisy mri data. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltzer, P.; Mann, R.M.; Iima, M.; Sigmund, E.E.; Clauser, P.; Gilbert, F.J.; Martincich, L.; Partridge, S.C.; Patterson, A.; Pinker, K.; et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast—A consensus and mission statement from the EUSOBI International Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging working group. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1436–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Suh, H.B.; Kang, H.J.; Shin, J.K.; Choo, K.S.; Nam, K.J.; Lee, S.W.; Jung, Y.L.; Bae, Y.T. Apparent diffusion coefficient of breast cancer and normal fibroglandular tissue in diffusion-weighted imaging: The effects of menstrual cycle and menopausal status. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 157, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittoun, J.; Querleux, B.; Darrasse, L. Advances in MR imaging of the skin. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, E.G.; Surcel, M.; Constantin, C.; Ilie, M.A.; Caruntu, A.; Caruntu, C.; Neagu, M. Skin Cancer Pathobiology at a Glance: A Focus on Imaging Techniques and Their Potential for Improved Diagnosis and Surveillance in Clinical Cohorts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornsiripanitch, N.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Shin, H.J.; Dang, M.; Rahbar, H.; Pinker, K.; Partridge, S.C. Diffusion-weighted MRI for Unenhanced Breast Cancer Screening. Radiology 2019, 293, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, H.; Pinker, K.; Polanec, S.; Magometschnigg, H.; Wengert, G.; Spick, C.; Bogner, W.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Helbich, T.H.; Baltzer, P. Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast lesions: Region-of-interest placement and different ADC parameters influence apparent diffusion coefficient values. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arponen, O.; Sudah, M.; Masarwah, A.; Taina, M.; Rautiainen, S.; Könönen, M.; Sironen, R.; Kosma, V.M.; Sutela, A.; Hakumäki, J.; et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in 3.0 Tesla Breast MRI: Diagnostic Performance and Tumor Characterization Using Small Subregions vs. Whole Tumor Regions of Interest. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iima, M.; Bihan, D.L.; Okumura, R.; Okada, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Kanao, S.; Tanaka, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Sakashita, H.; Togashi, K. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as an MR Imaging Biomarker of Low-Risk Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: A Pilot Study. Radiology 2011, 260, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanspach, J.; Nagel, A.M.; Hensel, B.; Uder, M.; Koros, L.; Laun, F.B. Sample size estimation: Current practice and considerations for original investigations in MRI technical development studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, L.; Brandão, S.; Matos, E.; Nunes, R.G.; Loureiro, J.; Ferreira, H.A.; Ramos, I. Diffusion-weighted imaging: Determination of the best pair of b-values to discriminate breast lesions. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, A. Effect of imaging parameters on the accuracy of apparent diffusion coefficient and optimization strategies. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 22, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, L.B.; Fangberget, A.; Geier, O.; Seierstad, T. Quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in malignant breast lesions using different b value combinations. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.X.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.M.; Liao, S.T.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhan, R.G.; Du, Z.L.; Yu, X.R. Diagnostic value of multiple b-value diffusion-weighted imaging in discriminating the malignant from benign breast lesions. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsche, S.; Moseley, M.E.; Stoeter, P.; Hedehus, M. Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging at 1.5 and 3.0 T: Initial Observations. Radiology 2001, 221, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, A.; Kataja, A.; Saastamoinen, A.; Ryymin, P.; Huhtala, H.; Ohman, J.; Soimakallio, S.; Dastidar, P. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain in a healthy adult population: Normative values and measurement reproducibility at 3 T and 1.5 T. Acta Radiol. 2010, 51, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-Q.; Finsterbusch, J.; Wittkugel, O.; Saager, C.; Goebell, E.; Fitting, T.; Grzyska, U.; Zeumer, H.; Fiehler, J. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Fractional Anisotropy and T2 Relaxation Time Measurement. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2007, 17, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Loenneker, T.; Barta, G.; Bellemann, M.E.; Hennig, J.; Fischer, J.E.; Il’yasov, K.A. Quantitative diffusion tensor MR imaging of the brain: Field strength related variance of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) scalars. Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fushimi, Y.; Miki, Y.; Okada, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Mori, N.; Hanakawa, T.; Urayama, S.; Aso, T.; Fukuyama, H.; Kikuta, K.; et al. Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity: Comparison between 3.0-T and 1.5-T diffusion tensor imaging with parallel imaging using histogram and region of interest analysis. NMR Biomed. 2007, 20, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, F.; Jalili, M.; Sefidbakht, S.; Channual, S.; Quane, L.; Naderi, N.; Schultze-Haakh, H.; Torrone, M. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Abdomen at 3 T: Image Quality Comparison With 1.5-T Magnet Using 3 Different Imaging Sequences. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2011, 35, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Min, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Li, B.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, P.; You, H. Effects of Echo Time on IVIM Quantification of the Normal Prostate. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Shui Yu, C.; Zhang, F.; Du, X.Y.; Jiang, H.; Xia Yan, Y.; Cheng Li, K. Effects of echo time on diffusion quantification of brain white matter at 1.5T and 3.0T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, A.; Laun, F.B.; Simon, D.; Stieltjes, B.; Schad, L.R. An in vivo verification of the intravoxel incoherent motion effect in diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.Y.; Yao, Q.Y.; Wu, L.M.; Xu, J.R. Breast Lesions: Diagnosis Using Diffusion Weighted Imaging at 1.5T and 3.0T-Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e305–e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Le Bihan, D.; Kataoka, M.; Iima, M. Diffusion kurtosis imaging as a biomarker of breast cancer. BJR Open 2023, 5, 20220038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistel, M.; Laun, F.B.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Dada, A.; Weiland, E.; Niederdränk, T.; Uder, M.; Janka, R.; Wenkel, E.; Ohlmeyer, S. Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions in Diffusion Kurtosis MRI: Does the Averaging Procedure Matter? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, J.W.; Suh, H.B.; Hwangbo, L.; Son, Y.; Grimm, R. Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlations with Prognostic Factors and Molecular Subtypes. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lv, S.; Xun, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, L. Comparison of diffusion kurtosis imaging and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI in prediction of prognostic factors and molecular subtypes in patients with breast cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 154, 110392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Soto, A.E.; Andreassen, M.M.S.; Fang, L.K.; Conlin, C.C.; Park, H.H.; Ahn, G.S.; Bartsch, H.; Kuperman, J.; Vidić, I.; Ojeda-Fournier, H.; et al. Characterization of the diffusion signal of breast tissues using multi-exponential models. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 87, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.-N.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.-L.; Zheng, D.-D.; Hu, Y. Monoexponential, Biexponential, and stretched-exponential models using diffusion-weighted imaging: A quantitative differentiation of breast lesions at 3.0T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Sequences |
|---|---|
| Total scan time | 1 min 44 s–4 min 43 s |
| Magnetic field strength | 72% 1.5 T, 28% 3 T |
| Slices, no. | 24–62 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 2.5–5 |
| Spacing between slices (mm) | 2.75–6 |
| Repetition time (ms) | 4100–9750 |
| Echo time (ms) | 54–106 |
| Inversion Time (ms) | 0–250 |
| b-values (s/mm2), [averages] | 50, 400, 800 [2, 3, 4 or 3, 4, 5 or 9, 12, 15]; 50, 750, 1500 [3, 8, 15] |
| Matrix | 128 × 80–220 × 168 |
| Percent phase field of view | 48.98–76.36 |
| Pixel spacing (mm) | 1.37–2.50 |
| Pixel bandwidth (Hz/Px) | 1263–2300 |
| Type | No. | Mean Nr of Voxels in VOI 1 | Magnetic Field Strength | b-Values (s/mm2) | Occurrence and VOI Placement | Age (Years) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 T | 3 T | 750 | 800 | Right Breast | Left Breast | ||||
| Paget’s disease of the nipple | 3 | 35 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 54 ± 8 |
| Inflammatory breast cancer | 5 | 258 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 55 ± 5 |
| Benign skin inflammation or enhancement | 11 | 197 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 59 ± 4 |
| Skin infiltration breast cancer | 11 | 46 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 61 ± 5 |
| Healthy skin | 58 | 29 | 52 | 6 | 6 | 52 | 30 | 28 | 51 ± 2 |
| Median ADC 1 Value (µm2/s) | Max. ADC 1 Value (µm2/s) | Min. ADC 1 Value (µm2/s) | ADC 1 of Mean Signal within VOI 2 (µm2/s) | Mean of ADC 1 Values within VOI 2 (µm2/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paget’s disease of the nipple | 0.90 ± 0.26 (0.49–1.38) | 1.43 ± 0.13 (1.18–1.59) | 0.54 ± 0.23 (0.12–0.89) | 0.95 ± 0.23 (0.59–1.37) | 0.92 ± 0.24 (0.52–1.36) |
| Inflammatory breast cancer | 1.85 ± 0.17 (1.26–2.18) | 2.23 ± 0.15 (1.74–2.71) | 1.2 ± 0.21 (0.76–1.93) | 1.86 ± 0.17 (1.28–2.18) | 1.84 ± 0.16 (1.27–2.16) |
| Benign skin inflammation or enhancement | 1.88 ± 0.11 (1.03–2.31) | 2.22 ± 0.13 (1.27–2.63) | 1.46 ± 0.11 (0.73–2.06) | 1.88 ± 0.11 (1.04–2.3) | 1.87 ± 0.11 (1.03–2.3) |
| Skin infiltration breast cancer | 1.36 ± 0.13 (0.74–2.01) | 1.86 ± 0.14 (0.83–2.43) | 0.87 ± 0.14 (0.06–1.52) | 1.38 ± 0.13 (0.73–1.98) | 1.37 ± 0.13 (0.73–1.95) |
| Healthy skin | 0.48 ± 0.02 (0.22–0.84) | 0.86 ± 0.03 (0.42–1.47) | 0.18 ± 0.02 (0.01–0.63) | 0.49 ± 0.02 (0.23–0.85) | 0.48 ± 0.02 (0.23–0.84) |
| Type | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | |
|---|---|---|
| 50 s/mm2 | 800/750 s/mm2 | |
| Paget’s disease of the nipple | 36 ± 27 (4.7–54) | 14 ± 10 (2.4–22) |
| Inflammatory breast cancer | 239 ± 218 (24–588) | 59 ± 46 (4.6–117) |
| Benign skin inflammation or enhancement | 199 ± 324 (23–870) | 56 ± 101 (5.1–338) |
| Skin infiltration breast cancer | 97 ± 113 (9.2–370) | 37 ± 49 (2.9–168) |
| Healthy skin | 3.09 ± 3.71 (0.95–20) | 2.04 ± 2.97 (0.6–16) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skwierawska, D.; Laun, F.B.; Wenkel, E.; Kapsner, L.A.; Janka, R.; Uder, M.; Ohlmeyer, S.; Bickelhaupt, S. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Skin Pathologies of the Breast—A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14090934
Skwierawska D, Laun FB, Wenkel E, Kapsner LA, Janka R, Uder M, Ohlmeyer S, Bickelhaupt S. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Skin Pathologies of the Breast—A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(9):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14090934
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkwierawska, Dominika, Frederik B. Laun, Evelyn Wenkel, Lorenz A. Kapsner, Rolf Janka, Michael Uder, Sabine Ohlmeyer, and Sebastian Bickelhaupt. 2024. "Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Skin Pathologies of the Breast—A Feasibility Study" Diagnostics 14, no. 9: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14090934
APA StyleSkwierawska, D., Laun, F. B., Wenkel, E., Kapsner, L. A., Janka, R., Uder, M., Ohlmeyer, S., & Bickelhaupt, S. (2024). Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Skin Pathologies of the Breast—A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics, 14(9), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14090934






