Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal-Appearing Early Brain-CT After Cardiac Arrest and Return of Spontaneous Circulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
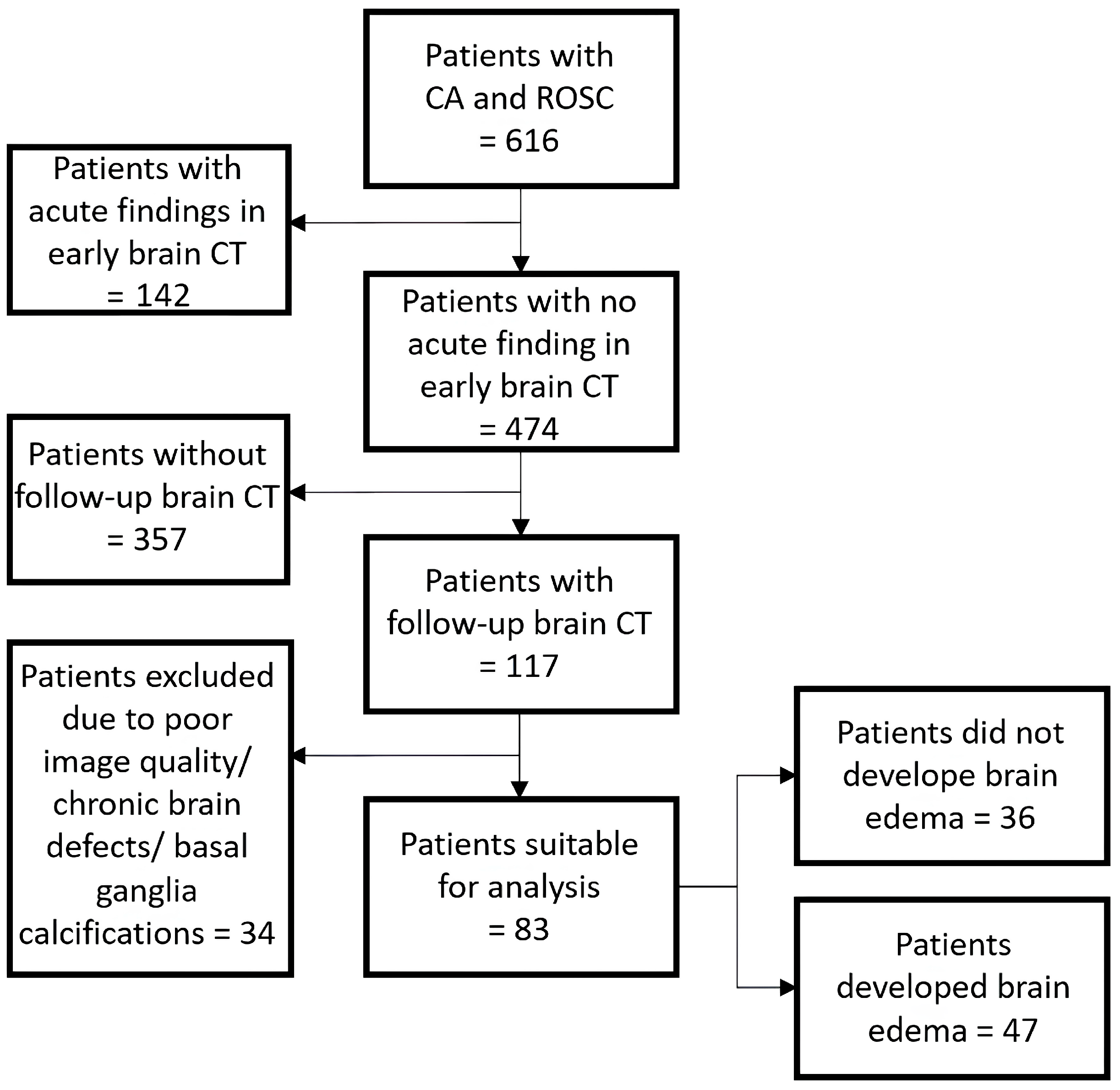
2.2. Cohort Identification
2.3. CT-Protocol
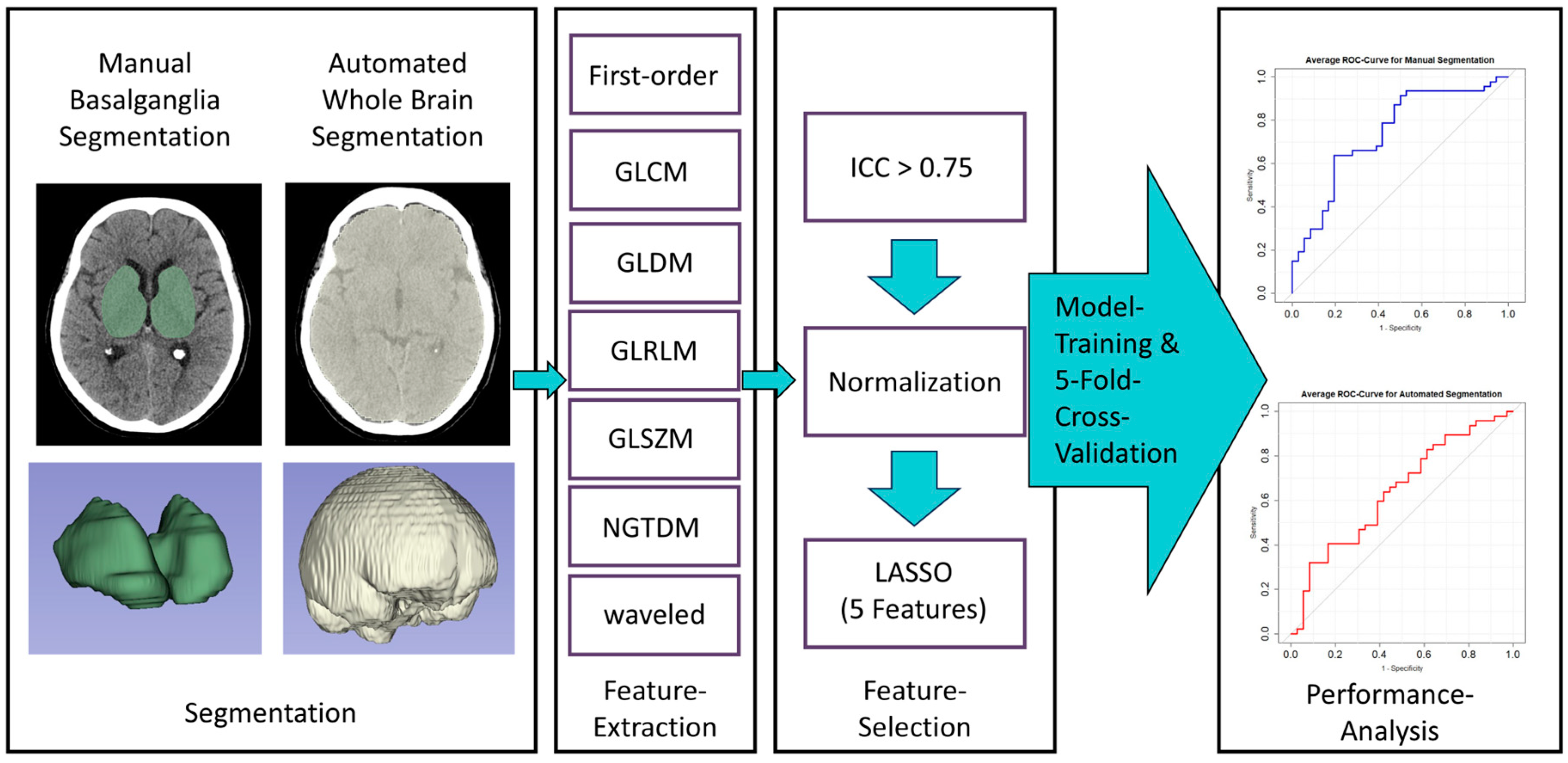
2.4. Image Segmentation and Feature Extraction
2.5. Feature Selection and Model Training
3. Results
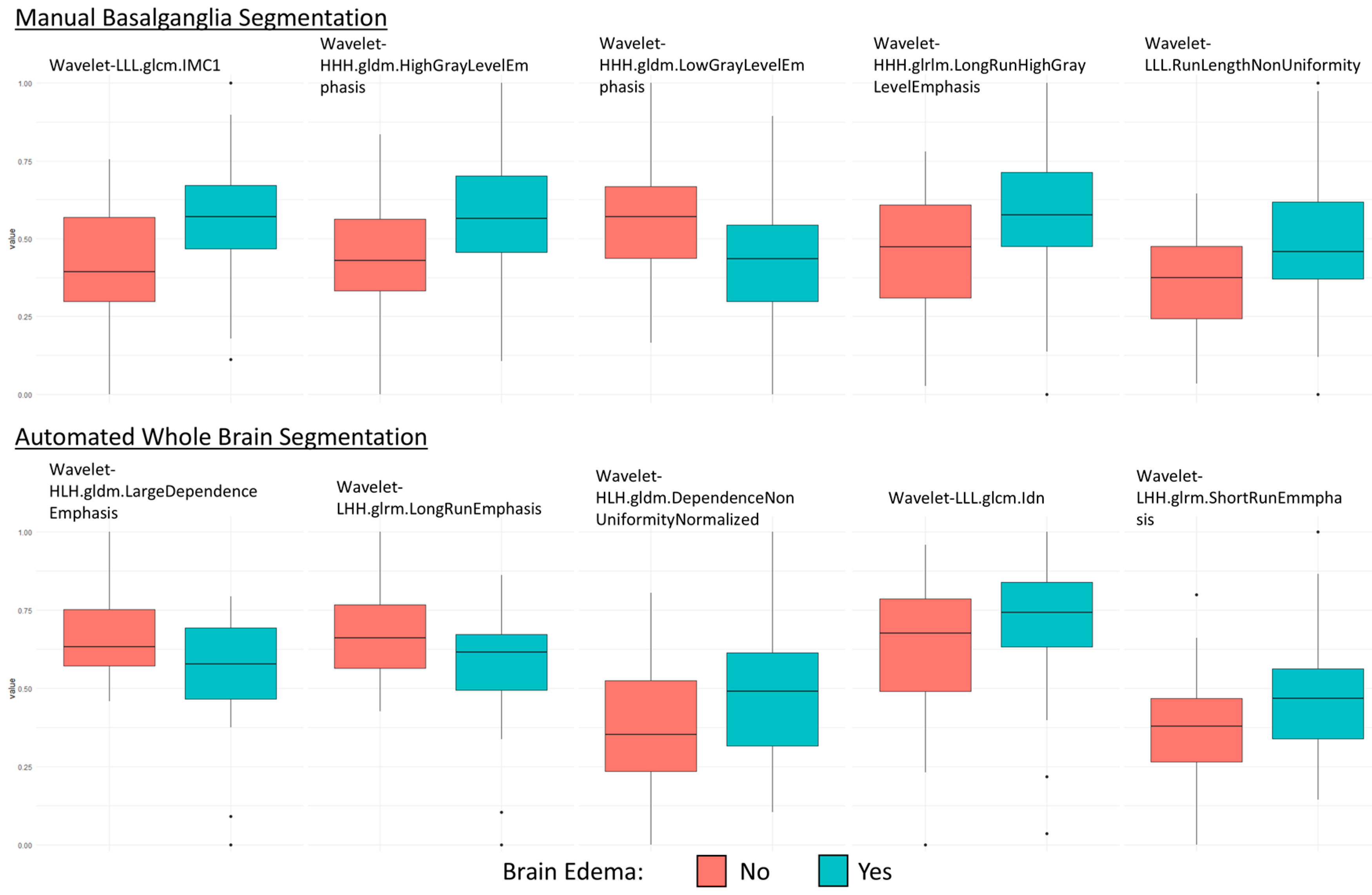
3.1. Feature Selection
3.2. Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolan, J.P.; Neumar, R.W.; Adrie, C.; Aibiki, M.; Berg, R.A.; Böttiger, B.W.; Callaway, C.; Clark, R.S.; Geocadin, R.G.; Jauch, E.C.; et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication. A Scientific Statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation; the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Stroke. Resuscitation 2008, 79, 350–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coute, R.A.; Nathanson, B.H.; Panchal, A.R.; Kurz, M.C.; Haas, N.L.; McNally, B.; Neumar, R.W.; Mader, T.J.; CARES Surveillance Group. Disability-Adjusted Life Years Following Adult Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in the United States. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e004677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragancea, I.; Rundgren, M.; Englund, E.; Friberg, H.; Cronberg, T. The influence of induced hypothermia and delayed prognostication on the mode of death after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, M.S.; Ainslie, P.N.; Griesdale, D.E. Clinical pathophysiology of hypoxic ischemic brain injury after cardiac arrest: A “two-hit” model. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmer, J.; Callaway, C. The Brain after Cardiac Arrest. Semin. Neurol. 2017, 37, 019–024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çankaya Gökdere, D.; Emektar, E.; Çorbacıoğlu, Ş.K.; Yüzbaşıoğlu, Y.; Öztürk, C.; Çevik, Y. The Role of Brain CT in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Return of Spontaneous Circulation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 52, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitberger, K.J.; Endisch, C.; Ploner, C.J.; Stevens, R.; Scheel, M.; Kenda, M.; Storm, C.; Leithner, C. Timing of brain computed tomography and accuracy of outcome prediction after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 145, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.S.; Matthews, E.; Magid-Bernstein, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Park, S.; Claassen, J.; Agarwal, S. Use of early head CT following out-of-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest. Resuscitation 2017, 113, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viniol, S.; Thomas, R.P.; König, A.M.; Betz, S.; Mahnken, A.H. Early whole-body CT for treatment guidance in patients with return of spontaneous circulation after cardiac arrest. Emerg. Radiol. 2020, 27, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, Y.S. Grey-white matter ratio measured using early unenhanced brain computed tomography shows no correlation with neurological outcomes in patients undergoing targeted temperature management after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 140, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, M.; Storm, C.; Gentsch, A.; Nee, J.; Luckenbach, F.; Ploner, C.J.; Leithner, C. The prognostic value of gray-white-matter ratio in cardiac arrest patients treated with hypothermia. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2013, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Jeung, K.W.; Song, K.H.; Jung, Y.H.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, S.H.; Youn, C.S.; Cho, I.S.; Lee, D.H. Prognostic values of gray matter to white matter ratios on early brain computed tomography in adult comatose patients after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of cardiac etiology. Resuscitation 2015, 96, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.K.; Kim, W.; Lim, T.H.; Jang, B.; Cho, Y.; Choi, K.-S.; Shin, H.-G.; Ahn, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.G. Gray matter to white matter ratio for predicting neurological outcomes in patients treated with target temperature management after cardiac arrest: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Resuscitation 2018, 132, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. BJR 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, V.S.; Jacobs, M.A. Deep learning and radiomics in precision medicine. Expert. Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2019, 4, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, B.; Durmaz, E.Ş.; Ateş, E.; Kılıçkesmez, Ö. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: A practical guide for beginners. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserthal, J.; Breit, H.-C.; Meyer, M.T.; Pradella, M.; Hinck, D.; Sauter, A.W.; Heye, T.; Boll, D.T.; Cyriac, J.; Yang, S.; et al. TotalSegmentator: Robust Segmentation of 104 Anatomic Structures in CT Images. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, e230024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandroni, C.; D’arrigo, S.; Cacciola, S.; Hoedemaekers, C.W.E.; Kamps, M.J.A.; Oddo, M.; Taccone, F.S.; Di Rocco, A.; Meijer, F.J.A.; Westhall, E.; et al. Prediction of poor neurological outcome in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: A systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1803–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, Y.N.; Lee, I.H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, D.M.; You, Y.; Min, J.H.; Jeong, W.; Ahn, H.J.; Kang, C.; Lee, B.K. Delayed head CT in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survivors: Does this improve predictive performance of neurological outcome? Resuscitation 2022, 172, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, R.; Hirsch, K.G. Brain imaging after cardiac arrest. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2023, 29, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Soto, C.; Dragoi, L.; Heyn, C.C.; Kramer, A.; Pinto, R.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Scales, D.C. Imaging for Neuroprognostication After Cardiac Arrest: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijman, C.A.C.; Mlynash, M.; Caulfield, A.F.; Hsia, A.W.; Eyngorn, I.; Bammer, R.; Fischbein, N.; Albers, G.W.; Moseley, M. Prognostic value of brain diffusion-weighted imaging after cardiac arrest. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervós-Navarro, J.; Diemer, N.H. Selective vulnerability in brain hypoxia. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1991, 6, 149–182. [Google Scholar]
- Payabvash, S.; Souza, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Schaefer, P.W.; Furie, K.L.; Halpern, E.F.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lev, M.H. Regional Ischemic Vulnerability of the Brain to Hypoperfusion. Stroke 2011, 42, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, M.; Lindberg, E.; Englund, E. Hippocampus and basal ganglia as potential sentinel sites for ischemic pathology after resuscitated cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 139, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Fuhrman, J.D.; El Ammar, F.; Loggini, A.; Davis, J.; Lazaridis, C.; Kramer, C.; Goldenberg, F.D.; Giger, M.L. Machine Learning for Early Detection of Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury After Cardiac Arrest. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 36, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinski, N.S.; Meddeb, A.; Kenda, M.; Scheel, M. Comment on “Machine Learning for Early Detection of Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Injury After Cardiac Arrest”. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 37, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, D.M. The problem of overfitting. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Kogeichi, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Asai, H.; Fukushima, H. Explainable artificial intelligence-based prediction of poor neurological outcome from head computed tomography in the immediate post-resuscitation phase. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünser, M.W.; Hirschl, D.; Weh, B.; Meier, J.; Tschoellitsch, T. The value of a machine learning algorithm to predict adverse short-term outcome during resuscitation of patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest: A retrospective study. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 30, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheschenja, M.; Müller-Stüler, E.-M.; Viniol, S.; Wessendorf, J.; Bastian, M.B.; Jedelská, J.; König, A.M.; Mahnken, A.H. Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal-Appearing Early Brain-CT After Cardiac Arrest and Return of Spontaneous Circulation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020119
Scheschenja M, Müller-Stüler E-M, Viniol S, Wessendorf J, Bastian MB, Jedelská J, König AM, Mahnken AH. Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal-Appearing Early Brain-CT After Cardiac Arrest and Return of Spontaneous Circulation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(2):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020119
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheschenja, Michael, Eva-Marie Müller-Stüler, Simon Viniol, Joel Wessendorf, Moritz B. Bastian, Jarmila Jedelská, Alexander M. König, and Andreas H. Mahnken. 2025. "Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal-Appearing Early Brain-CT After Cardiac Arrest and Return of Spontaneous Circulation" Diagnostics 15, no. 2: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020119
APA StyleScheschenja, M., Müller-Stüler, E.-M., Viniol, S., Wessendorf, J., Bastian, M. B., Jedelská, J., König, A. M., & Mahnken, A. H. (2025). Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal-Appearing Early Brain-CT After Cardiac Arrest and Return of Spontaneous Circulation. Diagnostics, 15(2), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020119





