Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy (ORG)
2.1. Overview
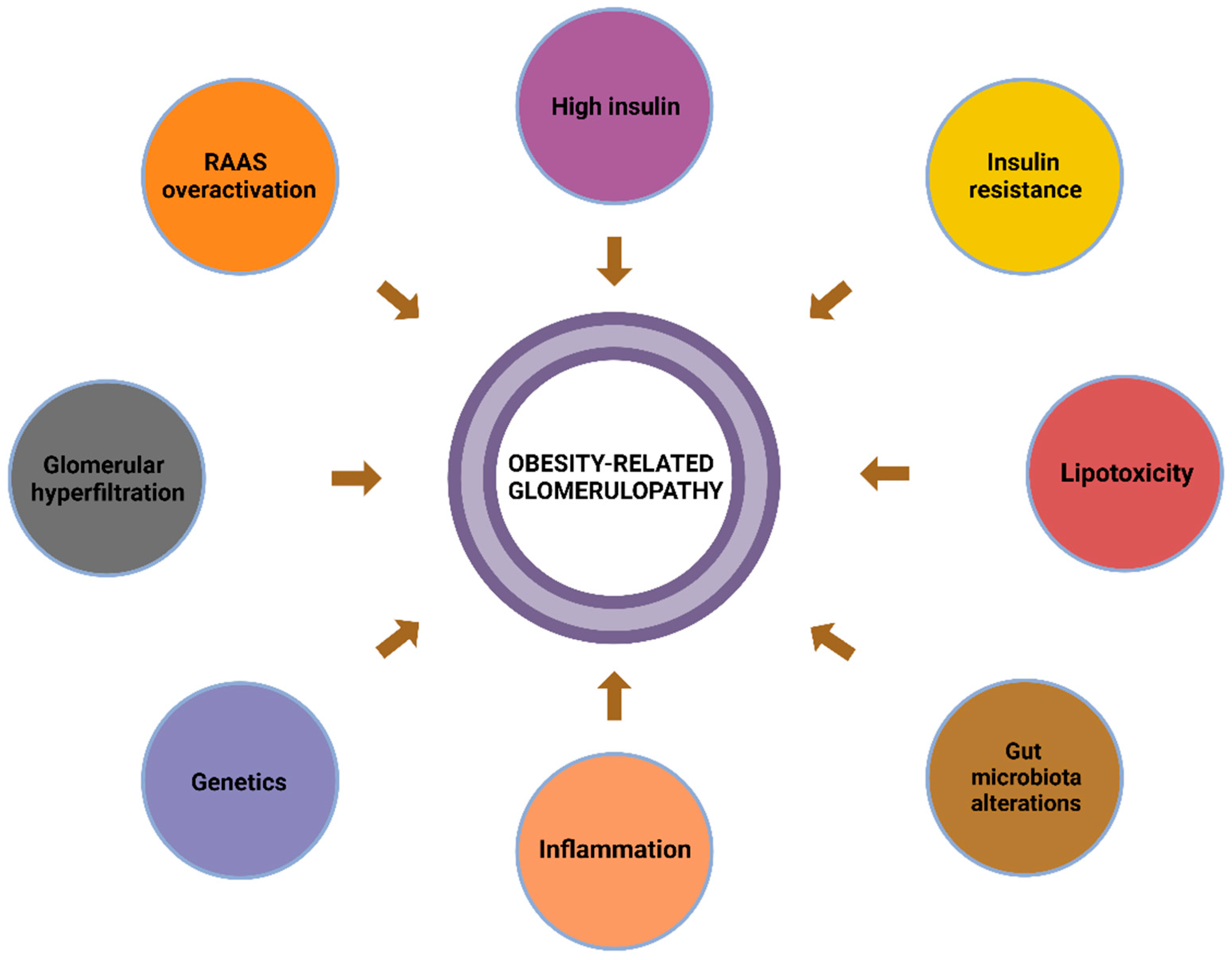
2.2. The Pathophysiology of ORG
2.2.1. Inflammation
2.2.2. Oxidative Stress
2.2.3. Insulin Resistance
2.2.4. Haemodynamic Changes
2.2.5. Lipotoxicity
2.2.6. Alterations in the Gut Microbiota
2.2.7. Genetics
2.3. Histopathology of ORG
2.4. Clinical Presentation
3. Biomarkers—Overview
3.1. Serum Creatinine (SCr)
3.2. CystatinC
3.3. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
3.4. NGAL (Neutrophil-Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin)
3.5. KIM-1 (Kidney Injury Molecule-1)
3.6. Gal-3 (Galectin-3)
NGAL, KIM-1, and Gal-3 in ORG
3.7. Klotho
3.8. The Role of MicroRNAs in ORG and CKD-Overview
3.8.1. miRNAs and Kidney Homeostasis
3.8.2. miRNAs as Predictive Markers: Diagnostic and Predictive Potential
3.8.3. Significance of miRNAs in ORG
3.8.4. The Impact of Lifestyle on miRNA Expression
3.8.5. Urinary miRNAs as Biomarkers: Challenges and Opportunities
3.9. The Role of Imaging Modalities
4. Therapeutic Approaches
4.1. Lifestyle Recommendations
4.2. Bariatric Surgery
4.3. Pharmaceutical Interventions
4.3.1. RAAS Blockade
4.3.2. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT-2)
4.3.3. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs)
4.3.4. Other Agents
4.4. Future Perspectives and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, Κ.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerte, M.; Wagner, S.; Carette, C.; Brodin-Sartorius, A.; Vilaine, E.; Alvarez, J.C.; Abe, E.; Barsamian, C.; Czernichow, S.; Massy, Z.M. The measured glomerular filtration rate (mGFR) before and 6 months after bariatric surgery: A pilot study. Nephrol. Ther. 2017, 13, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obesity in Adults: Prevalence, Screening and Evaluation, Uptodate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/obesity-in-adults-prevalence-screening-and-evaluation (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, R.F.D. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Ma, S.X.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, B.L.; Liu, Q.Q.; Zhao, Y.Y. Chronic kidney disease: Biomarker diagnosis to therapeutic targets. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 499, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, A.; Bessonny, M.; Benito, J.; Huang, K.; Parker, H.; Tyler, E.; Crawford, B.; Khan, N.; Armstrong, B.; Stamatikos, A.; et al. Urinary Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Obesity-Associated Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienaimé, F.; Muorah, M.; Metzger, M.; Broeuilh, M.; Houiller, P.; Flamant, M.; Haymann, J.P.; Vonderscher, J.; Mizrahi, J.; Friedlander, G.; et al. Combining robust urine biomarkers to assess chronic kidney disease progression. eBioMedicine 2023, 93, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Furth, S.L.; Zoccali, C. Obesity and kidney disease: Hidden consequences of the epidemic. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Khafagy, R.; Gao, Y.; Meerasa, A.; Roshandel, D.; Anvari, M.; Lin, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Farkouh, M.E.; Shah, B.R.; et al. Association Between Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease: Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Analysis and Observational Data From a Bariatric Surgery Cohort. Diabetes 2023, 72, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnoff, B.O.; Hoerger, T.J.; Shrestha, S.S.; Simpson, S.K.; Burrows, N.R.; Anderson, A.H.; Xie, D.; Chen, H.Y.; Pavkov, M.E.; CRIC Study Investigators. Modeling the impact of obesity on the lifetime risk of chronic kidney disease in the United States using updated estimates of GFR progression from the CRIC study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Minutolo, R.; Chiodini, P.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis suggests obesity predicts onset of chronic kidney disease in the general population. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Montoro, J.I.; Morales, E.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Tinahones, F.J.; Fernández-García, J.C. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Current approaches and future perspectives. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Chagnac, A.; de Vries, A.P.J.; Levi, M.; Porrini, E.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Praga, M. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Χ.; Song, Y.; Caballero, Β.; Cheskin, L.J. Association between obesity and kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathy, H.; Henriquez, G.; Abramowitz, M.K.; Kramer, H.; Rosas, S.E.; Johns, T.; Kumar, J.; Skversky, A.; Kaskel, F.; Melamed, M.L. Abdominal Obesity, Race and Chronic Kidney Disease in Young Adults: Results from NHANES 1999–2010. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Herrington, W.G.; Haynes, R.; Emberson, J.; Landray, M.J.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Woodward, M.; Baigent, C.; Lewington, S.; Staplin, N. Conventional and Genetic Evidence on the Association between Adiposity and CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Peng, T.; Zhao, K.; Zhuang, Y. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy: From Mechanism to Therapeutic Target. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounatidis, D. Primary Pathogenetic Mechanismsin the Development of Obesity-Related Glomerulopahy. 2024. Available online: www.BioRender.com (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Vallianou, V.; Dalamaga, M.; Stratigou, T.; Karampela, I.; Tsigalou, C. Do Antibiotics Cause Obesity Through Long-term Alterations in the Gut Microbiome? A Review of Current Evidence. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, I.M.; Mak, R.H. Obesity and obesity-initiated metabolic syndrome: Mechanistic links to chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourebaba, L.; Marycz, K. Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounatidis, D.; Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Voukali, M.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Kidney in Obesity: Current Evidence, Perspectives and Controversies. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 680–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaje, A.K.; Adedeji, Τ.A.; Adedoyin, A.R.; Idogun, S.E. Creatinine and cystatin C-based evaluation of renal function among obese subjects in Benin City, Nigeria. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2019, 30, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, H.; Cai, Y.; You, Q.; Fu, H.; Shao, L. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with diabetic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: Evidence from NHANES 2011–2018. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1071465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.W.; Chan, Y.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chang, S.S. Association of elevated blood serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and body composition with chronic kidney disease: A population-based study in Taiwan. Medicine 2018, 97, e11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Wei, Χ.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, P.; Luo, M. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Recent advances in inflammatory mechanisms and related treatments. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 115, 819–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, J.A.; Roshan, B.; Maski, M.; Weinrauch, L.A. Manifestation of renal disease in obesity: Pathophysiology of obesity-related dysfunction of the kidney. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2009, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. The role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in obesity-related renal diseases. Semin. Nephrol. 2012, 33, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandino, J.; Martín-Taboada, M.; Medina-Gómez, G.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Morales, E. Novel Insights in the Physiopathology and Management of Obesity-Related Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.W.; Lu, M.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, Y.; Li, W.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Chang, S.S. Combined body mass index with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as independent predictors for chronic kidney disease in a relatively healthy population in Taiwan. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou, F. Microbiota and cancer: An update. J. Chemother. 2019, 31, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Dalamaga, M. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome and Microbial Metabolites in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeni, N.; Bordiga, M.; Xu, B. A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet-Gut Microbiota-Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Panagopoulos, F.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Stamatopoulos, V.; Papagiorgos, A.; Geladari, E.; Dalamaga, M. Gut Microbiota and Its Role in the Brain-Gut-Kidney Axis in Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.C.; Brownlee, M.; Susztak, K.; Sharma, K.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.; Zoungas, S.; Rossing, P.; Groop, P.H.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, A.P.J.; Ruggenenti, P.; Ruan, X.Z.; Praga, M.; Cruzado, J.M.; Bajema, I.M.; D’Agati, V.D.; Lamb, H.J.; Barlovic, D.P.; Hojs, R.; et al. Fatty kidney: Emerging role of ectopic lipid in obesity-related renal disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darouich, S.; Goucha, R.; Jaafoura, M.H.; Zekri, S.; Maiz, H.B.; Kheder, A. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Obesity-associated Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2011, 35, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousa, I.; Reis, F.; Beirão, I.; Alves, R.; Belo, L.; Santos-Silva, A. New Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Management-A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.R.; Zafar, W.; Grams, M.E. Kidney Function in Obesity-Challenges in Indexing and Estimation. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.W.; Ciccia, E.A.; Devarajan, P. Cystatin C as a biomarker of chronic kidney disease: Latest developments. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, O.; Golbetz, H.; Kriss, J.P.; Myers, B.D. Limitations of creatinine as a filtration marker in glomerulopathic patients. Kidney Int. 1985, 28, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, A.Ε.; Herman, W.H. How to assess kidney outcomes in obese people with substantial weight loss: The case of GLP1- and dual-receptor agonists. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, 39, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, T.; Wiebe, N.; Culleton, B.; House, A.; Rabbat, C.; Fok, M.; McAlister, F.; Garg, A.X. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: A systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2034–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A. Estimating GFR using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) creatinine equation: More accurate GFR estimates, lower CKD prevalence estimates, and better risk predictions. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; Coresh, J.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Titan, S. Measurement and Estimation of GFR for Use in Clinical Practice: Core Curriculum 2021. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Martínez, M.; Luis-Lima, S.; Morales, E.; Navarro-Díaz, M.; Negrín-Mena, N.; Folgueras, T.; Escamilla, B.; Estupiñán, S.; Delgado-Mallén, P.; Marrero-Miranda, D.; et al. The estimation of GFR and the adjustment for BSA in overweight and obesity: A dreadful combination of two errors. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, S.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Sens, F.; Nguyen-Tu, M.S.; Juillard, L.; Dubourg, L.; Hadj-Aissa, A. Accuracy of GFR estimation in obese patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Ebert, N.; Melsom, T.; Gaspari, F.; Mariat, C.; Cavalier, E.; Björk, J.; Christensson, A.; Nyman, U.; Porrini, E.; et al. Iohexol plasma clearance for measuring glomerular filtration rate in clinical practice and research: A review. Part 1: How to measure glomerular filtration rate with iohexol? Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, T.P.; Schock-Kusch, D.; Gallo, L.A. Transdermal Measurement of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Preclinical Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2664, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Edelstein, Μ.; Weinstein, Τ.; Chagnac, A. Obesity- Related Glomerulopathy: Clinical Management. Semin. Nephrol. 2021, 41, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoula, G.V.; Kontou, P.I.; Bagos, P.G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Predicting Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 4, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Moosaie, F.; Khaloo, P.; Dehghani Firouzabadi, F.; Fatemi Abhari, S.M.; Atainia, B.; Ardeshir, M.; Nakhjavani, M.; Esteghamati, A. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Retinol-Binding Protein-4 as Biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2020, 45, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Behera, M.R.; Rai, M.K.; Mishra, P.; Bhaduaria, D.S.; Yadav, S.; Agarwal, V.; Karoli, R.; Prasad, N.; Gupta, A.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin: As a Predictor of Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Indian J. Nephrol. 2018, 28, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, H. Urinary NGAL and RBP Are Biomarkers of Normoalbuminuric Renal Insufficiency in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 5063089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, K.; Joy, S.S.; George, T.P.; Mujammami, M.; Alfadda, A.A. Potential Role and Excretion Level of Urinary Transferrin, KIM-1, RBP, MCP-1 and NGAL Markers in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 5103–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Refai, A.; Tayel, S.; Ragheb, A.; Dala, A.; Zahran, A. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin as a Marker of Tubular Damage in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with and without Albuminuria. Open J. Nephrol. 2014, 4, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Timmeren, M.M.; van den Heuvel, M.C.; Bailly, V.; Bakker, S.J.L.; van Goor, H.; Stegeman, C.A. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J. Pathol. 2007, 212, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żyłka, A.; Dumnicka, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Gala-Błądzińska, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kucharz, J.; Ząbek-Adamska, A.; Maziarz, B.; Drożdż, R.; Kuźniewski, M. Markers of Glomerular and Tubular Damage in the Early Stage of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 7659243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornstad, P.; Pyle, L.; Cherney, D.; Johnson, R.; Sippl, R.; Wong, R.; Rewers, M.; Snell-Bergeon, J. Plasma biomarkers improve prediction of diabetic kidney disease in adults with type 1 diabetes over a 12-year follow-up: CACTI study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackowiak-Lewandowicz, K.; Ostalska-Nowicka, D.; Zaorska, K.; Kaczmarek, E.; Zachwieja, J.; Witt, M.; Michal Nowicki, M. Chronic kidney disease predictors in obese adolescents. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şen, S.; Özalp Kızılay, D.; Taneli, F.; Özen, Ç.; Ertan, P.; Özunan, İ.; Yıldız, R.; Ersoy, B. Urinary NGAL is a Potential Biomarker for Early Renal Injury in Insulin Resistant Obese Non-diabetic Children. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2021, 13, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, N.; Giannini, C.; Salvatore, R.; Pelliccia, P.; Parisi, A.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A. Role of urinary NGAL and KIM-1 as biomarkers of early kidney injury in obese prepubertal children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan Gayret, Ö.; Taşdemir, M.; Erol, M.; Tekin Nacaroğlu, H.; Zengi, O.; Yiğit, Ö. Are there any new reliable markers to detect renal injury in obese children? Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuguang, L.; Chang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, X. Serum klotho as a novel biomarker for metabolic syndrome: Findings from a large national cohort. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1295927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Moe, O.W. Klotho as a potential biomarker and therapy for acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mo, H.; Miao, J.; Zhou, D.; Tan, R.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Klotho Ameliorates Kidney Injury and Fibrosis and Normalizes Blood Pressure by Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, K.L.; Denby, L. MicroRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers of renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2021, 36, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicki, M.; Perco, P.; Haene, B.D.; Leierer, J.; Heinzel, A.; Mühlberger, I.; Schweibert, N.; Sunzenauer, J.; Regele, H.; Kronbichler, A.; et al. Renal microRNA- and RNA-profiles in progressive chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yu, C.; Feng, B.; Zhan, X.; Luo, N.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Q. Intrarenal microRNA signature related to the fibrosis process in chronic kidney disease: Identification and functional validation of key miRNAs. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzinger-Le Meuth, V.; Metzinger, L. miR-223 and other miRNA’s evaluation in chronic kidney disease: Innovative biomarkers and therapeutic tools. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2019, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franczyk, B.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Olszewski, R.; Parolczyk, M.; Rysz-Górzyńska, M.; Rysz, J. miRNA biomarkers in renal disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglicheau, D.; Sharma, V.K.; Ding, R.; Hummel, A.; Snopkowski, C.; Dadhania, D.; Seshan, S.V.; Suthanthiran, M. MicroRNA expression profiles predictive of human renal allograft status. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5330–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.D.; Soule, B.P.; Simone, B.A.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Jin, L.; Simone, N.L. MicroRNA expression altered by diet: Can food be medicinal? Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 17, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, A.; Marchand, L.; Thivolet, C.; Rome, S. Diagnostic Value of Cell-free Circulating MicroRNAs for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2015, 6, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serino, G.; Pesce, F.; Sallustio, F.; De Palma, G.; Cox, S.N.; Curci, C.; Zaza, G.; Lai, K.N.; Leung, J.C.K.; Tang, S.C.W.; et al. In a retrospective international study, circulating miR-148b and let-7b were found to be serum markers for detecting primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burk, U.; Schubert, J.; Wellner, U.; Schmalhofer, O.; Vincan, E.; Spaderna, S.; Brabletz, T. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chung, A.C.K.; Dong, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhong, X.; Lan, H.Y. The microRNA miR-433 promotes renal fibrosis by amplifying the TGF-β/Smad3-Azin1 pathway. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kwan, B.C.H.; Lai, F.M.M.; Choi, P.C.L.; Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.T.; Szeto, C.C. Intrarenal expression of microRNAs in patients with IgA nephropathy. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbing, M.; Kirsch, A.H.; Leber, B.; Lemesch, S.; Münzker, J.; Schweighofer, N.; Hofer, D.; Trummer, O.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Müller, H.; et al. MicroRNAs 223-3p and 93-5p in patients with chronic kidney disease before and after renal transplantation. Bone 2017, 95, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Moon, S.; Lee, K.; Park, I.B.; Lee, D.H.; Nam, S. Urinary and Blood MicroRNA-126 and -770 are Potential Noninvasive Biomarker Candidates for Diabetic Nephropathy: A Meta-Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crépin, D.; Benomar, Y.; Riffault, L.; Amine, H.; Gertler, A.; Taouis, M. The over-expression of miR-200a in the hypothalamus of ob/ob mice is linked to leptin and insulin signaling impairment. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 384, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, C.; Einhorn, D. Fatty kidney disease: The importance of ectopic fat deposition and the potential value of imaging. J. Diabetes 2022, 14, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, H.; Han, M.; Ren, X.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. Obesity and chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E24–E41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenboer, P.W.; Hobbelink, M.G.; Bosch, R.; Dik, P.; van Asbeck, F.; Beek, F.; de Kort, L. Diagnostic accuracy of Tc-99m DMSA scintigraphy and renal ultrasonography for detecting renal scarring and relative function in patients with spinal dysraphism. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, R.R.; Bolin, P.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Crow, R.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Egan, C.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.; Valero, M.A.; León, M.; Hernández, E.; Praga, M. Beneficial effects of weight loss in overweight patients with chronic proteinuric nephropathies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Xu, F.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Body mass index and proteinuria. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-López, A.; Becerra-Tomás, N.; Ruiz, V.; Toledo, E.; Babio, N.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Romaguera, D.; Vioque, J.; Alonso-Gómez, A.M.; et al. Effect of an Intensive Weight-Loss Lifestyle Intervention on Kidney Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients with Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Grave, R. The Benefit of Healthy Lifestyle in the Era of New Medications to Treat Obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solini, A.; Seghieri, Μ.; Santini, E.; Giannini, L.; Biancalana, E.; Taddei, S.; Volterrani, D.; Bruno, R.M. Renal Resistive Index Predicts Post-Bariatric Surgery Renal Outcome in Nondiabetic Individuals with Severe Obesity. Obesity 2019, 27, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.N.; Wahed, A.S.; Wang, J.; Courcoulas, A.P.; Dakin, G.; Hinojosa, M.W.; Kimmel, P.L.; Mitchell, J.E.; Pomp, A.; Pories, W.J.; et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on CKD Risk. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.R.; Grams, M.E.; Navaneethan, S.D. Bariatric Surgery and Kidney-Related Outcomes. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.; Mann, J. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes. Blood Pressure in CKD. KDIGO Guidelines. Available online: https://kdigo.org/guidelines/blood-pressure-in-ckd (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Tofte, N.; Lindhardt, M.; Adamova, K.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Beige, J.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Currie, G.; Delles, C.; Dimos, I.; et al. Early detection of diabetic kidney disease by urinary proteomics and subsequent intervention with spironolactone to delay progression (PRIORITY): A prospective observational study and embedded randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, E.; Gutiérrez, E.; Caro, J.; Sevillano, A.; Rojas-Rivera, J.; Praga, M. Beneficial long-term effect of aldosterone antagonist added to a traditional blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system among patients with obesity and proteinuria. Nefrologia 2015, 35, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiner, F.F.; Schytz, P.A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; von Scholten, B.J.; Idorn, T. Obesity-Related Kidney Disease: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitchett, D.; Inzucchi, S.; Cannon, C.P.; McGuire, D.K.; Scirica, B.M.; Johansen, O.E.; Sambevski, S.; Kaspers, K.; Pfarr, E.; George, J.T.; et al. Empagliflozin Reduced Mortality and Hospitalization for Heart Failure Across the Spectrum of Cardiovascular Risk in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial. Circulation 2019, 139, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: A prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolinder, J.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Kullberg, J.; Johansson, L.; Wilding, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sugg, J.; Parikh, S. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Body Weight, Total Fat Mass, and Regional Adipose Tissue Distribution in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Inadequate Glycemic Control on Metformin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Vart, P.; Jongs, N.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Quételet (body mass) index and effects of dapagliflozin in chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensterle, Μ.; Rizzo, Μ.; Haluzík, Μ.; Janež, A. Efficacy of GLP-1 RA Approved for Weight Management in Patients With or Without Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2452–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoviciu, M.S.; Păduraru, L.; Yahya, G.; Metwally, K.; Cavalu, S. Emerging Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Obesity: A Comprehensive Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Manghi, F.C.P.; Landó, L.F.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K.; SURPASS-2 Investigators. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, D.; Onishi, Y.; Norwood, P.; Huh, R.; Bray, R.; Patel, H.; Rodríguez, A. Effect of Subcutaneous Tirzepatide vs Placebo Added to Titrated Insulin Glargine on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-5 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Apperloo, E.; Davies, M.; Dicker, D.; Kandler, K.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Lawson, J.; Zeuthen, N.; Cherney, D. Effects of Semaglutide on Albuminuria and Kidney Function in People With Overweight or Obesity With or Without Type 2 Diabetes: Exploratory Analysis From the STEP 1, 2, and 3 Trials. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, A.S.; Lee, S.; Park, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, B.H.; Kim, W.; Kang, K.P. Metformin decreases high-fat diet-induced renal injury by regulating the expression of adipokines and the renal AMP-activated protein kinase/acetyl-CoA carboxylase pathway in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; Hsiao, P.J.; Lin, P.C.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, S.J. Effect of metformin on kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and moderate chronic kidney disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5416–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.C.; Chang, Y.K.; Liu, J.S.; Kuo, K.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Tarng, D.H. Metformin use and mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: National, retrospective, observational, cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y. Kidney Damage Caused by Obesity and Its Feasible Treatment Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska, M.; Niemczyk, S.; Romejko, K. Melatonin Treatment in Kidney Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Alvarez-Sánchez, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Melatonin: Buffering the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8638–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granhall, C.; Søndergaard, F.L.; Thomsen, M.; Anderson, T.W. Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Subjects with Renal Impairment. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Qiao, Q.; Tong, Q.; Bai, Q.; Huang, C.; Fan, R.; Wang, H.; Kaliannan, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Effects of exenatide on urinary albumin in overweight/obese patients with T2DM: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.; Ørsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornøe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B. for the LEADER Steering Committee and Investigators Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urva, S.; Quinlan, T.; Landry, J.; Martin, J.; Loghin, C. Effects of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of the Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Barbour, S.J.; Cattran, D.; Gafor, A.H.A.; Greasley, P.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Lim, S.K.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): A randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Chan, J.C.; Cooper, M.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Haller, H.; Remuzzi, G.; Rossing, P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Nowack, C.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2025, 314, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Chinnadurai, R.; Al-Chalabi, S.; Evans, P.; Kalra, P.A.; Syed, A.A.; Sinha, S. Obesity and chronic kidney disease: A current review. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2023, 9, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.; McCulloch, C.E.; Iribarren, C.; Darbinian, J.; Go, A.S. Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.; Aeddula, N. Chronic Kidney Disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535404/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Kambham, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Valeri, A.M.; Lin, J.; D’Agati, V.D. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: An emerging epidemic. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, M.; Samoni, S.; Petrucci, I. Imaging in Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 188, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Kidney Disorder | MiRNA |
|---|---|
| IgA nephropathy | miR-148b, miR-let-7b [80] |
| Kidney fibrosis | miR-200, miR-433, miR-21 [81,82,83] |
| Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | miR-200a/b, miR-141, miR-429, miR-192 [84] |
| Progression of CKD | miR-223-3p, miR-93-5p [85] |
| Diabetic nephropathy | miR-126, miR-770 [86] |
| Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy | miR-21, miR-29, miR-200, miR-146 [8,87] |
| Title of the study | Study Characteristics | Outcome of the Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beneficial effects of weight loss in overweight patients with chronic proteinuric nephropathies |
|
| Morales et al. [92] |
| The reno-protective effects of weight loss on patients with ORG |
|
| Shen et al. [93] |
| Effect of an Intensive Weight-Loss Lifestyle Intervention on Kidney Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial |
|
| Diaz-Lopez et al. [94] |
| Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: ASafe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients With Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure |
|
| Bruci et al. [95] |
| Renal Resistive Index Predicts Post–Bariatric Surgery Renal Outcome in Nondiabetic Individuals with Severe Obesity |
|
| Solini et al. [97] |
| Effect of Bariatric Surgery on CKD Risk |
|
| Friedman et al. [98] |
| Semaglutide and Albuminuria Reduction Trial in Obese Individuals Without Diabetes (SMART) |
|
| NCT04889183 Last update: 5 June 2024 |
| Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Subjects with Renal Impairment |
|
| Granhall et al. [120] |
| Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity (Research Study Investigating How Well Semaglutide Works in People Suffering From Overweight or Obesity: STEP-1) |
|
| Wilding et al. [121] |
| The Effect of Retatrutide Once Weekly on Cardiovascular Outcomes and Renal Function in Adults Living With Obesity (TRIUMPH-OUTCOMES) | Interventional clinical trial, phase 3 Study
|
| NCT06383390 |
| Effects of exenatide on urinary albumin in overweight/obese patients with T2DM: a randomized clinical trial | Randomized controlled trial 159 Participants
|
| Kang et al. [122] |
| Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results (LEADER®) |
|
| Mann et al. [123] |
| A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) on Renal Function in Participants With Overweight or Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease With or Without Type 2 Diabetes | Phase 2 double blind study
| Still recruiting (last update was posted on 26 September 2024) | NCT05936151 |
| Effects of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of the Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide |
|
| Urva et al. [124] |
| Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of SGLT2i and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Obese Patients With Kidney Disease |
|
| NCT06344247 |
| Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): a randomised, double-blind, crossover trial |
|
| Cherney et al. [125] |
| Effect of Dapagliflozin on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease, With and Without Cardiovascular Disease (Dapa-CKD) |
|
| Wheeler et al. [106] |
| Beneficial long-term effect of aldosterone antagonist added to a traditional blockade of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system among patients with obesity and proteinuria | Prospective cohort study
|
| Morales et al. [102] |
| Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes (FIDELIO-DKD: Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) |
|
| Bakris et al. [126] |
| Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in Patients With Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial |
|
| Bakris et al. [127] |
| Characteristic | Obesity-Related CKD | Other Causes of CKD |
|---|---|---|
| Incidence | Increasing in parallel to the incidence of obesity [14] 15–30% of patients with CKD [16] |
|
| Age at presentation | Most common in middle-aged adults (40–65 y) but may be present in children or older adults | Mainly middle-aged (40–65 y) or older adults (>65 y) |
| Clinical Presentation | Detection of proteinuria, along with normal urinary sediment in obese individuals [14] | Elevated serum creatinine, reduced eGFR |
| Clinical course |
|
|
| Serum albumin levels | Normal in most cases [15] | Usually low |
| Histology |
| Depending on the aetiology of CKD:
|
| Imaging | Glomerulomegaly (the hallmark of ORG,100% of cases) [131] |
|
| Pathophysiology |
|
|
| Therapeutic approaches |
|
RRT
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avgoustou, E.; Tzivaki, I.; Diamantopoulou, G.; Zachariadou, T.; Avramidou, D.; Dalopoulos, V.; Skourtis, A. Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020169
Avgoustou E, Tzivaki I, Diamantopoulou G, Zachariadou T, Avramidou D, Dalopoulos V, Skourtis A. Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvgoustou, Elena, Ilektra Tzivaki, Garyfalia Diamantopoulou, Tatiana Zachariadou, Despoina Avramidou, Vasileios Dalopoulos, and Alexandros Skourtis. 2025. "Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment" Diagnostics 15, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020169
APA StyleAvgoustou, E., Tzivaki, I., Diamantopoulou, G., Zachariadou, T., Avramidou, D., Dalopoulos, V., & Skourtis, A. (2025). Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Diagnostics, 15(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15020169






