Limitations of Semi-Automated Immunomagnetic Separation of HLA-G-Positive Trophoblasts from Papanicolaou Smears for Prenatal Genetic Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria for Patients and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Culturing and Harvesting of Cell Lines
2.4. Endocervical Sampling
2.5. Antibody Titration and Staining for FACS
2.6. Enrichment of Fetal Cells Using Cell Lines with FACS
2.7. Enrichment of Fetal Cells from Cell Line Mixtures and Endocervical Samples Using Immunomagnetic Cell Sorting
3. Results
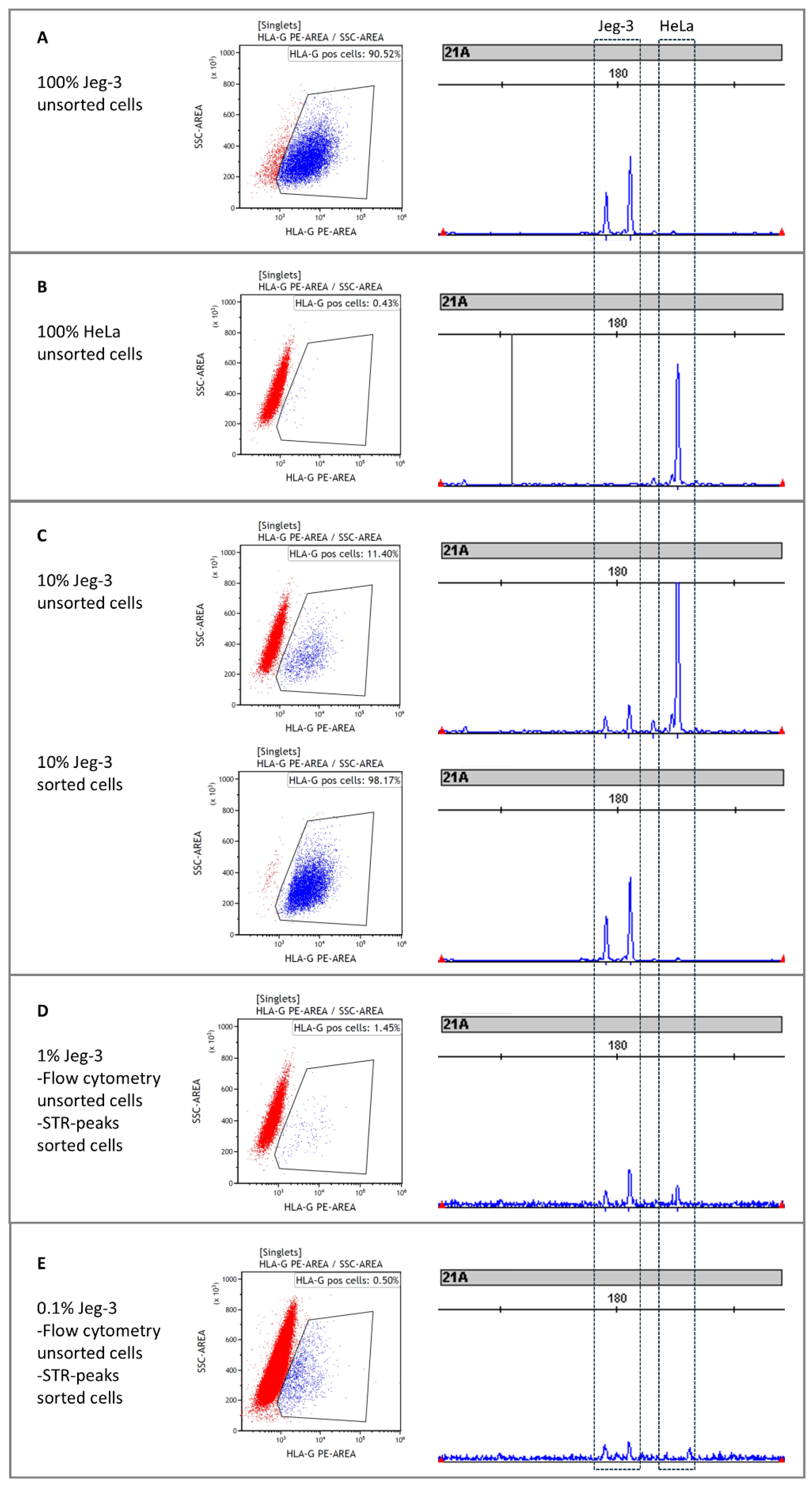
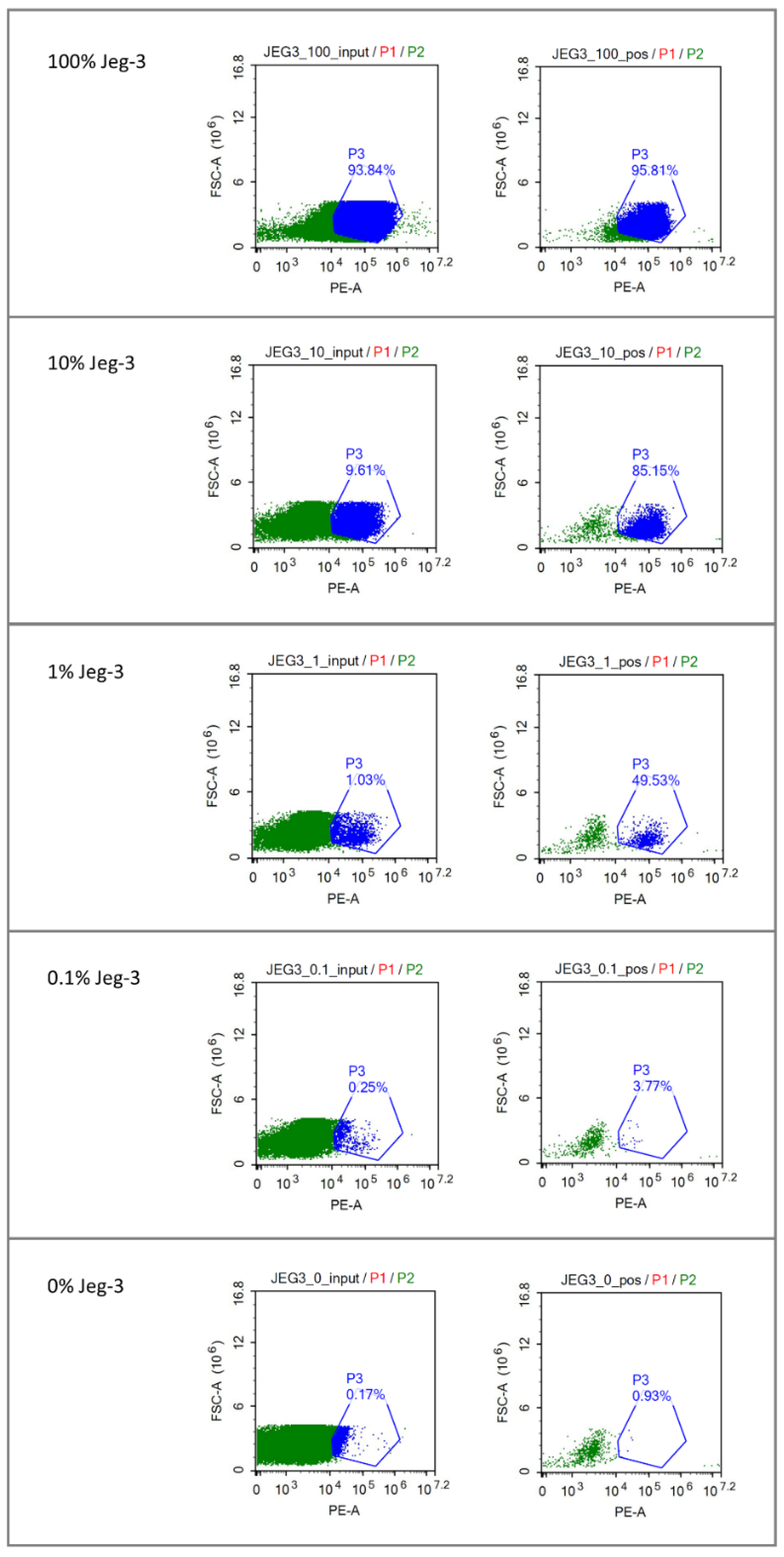
3.1. Enrichment of Fetal Cells from Cell Line Mixtures with FACS
3.2. Enrichment of Fetal Cells from Cell Lines with Immunomagnetic Cell Sorting
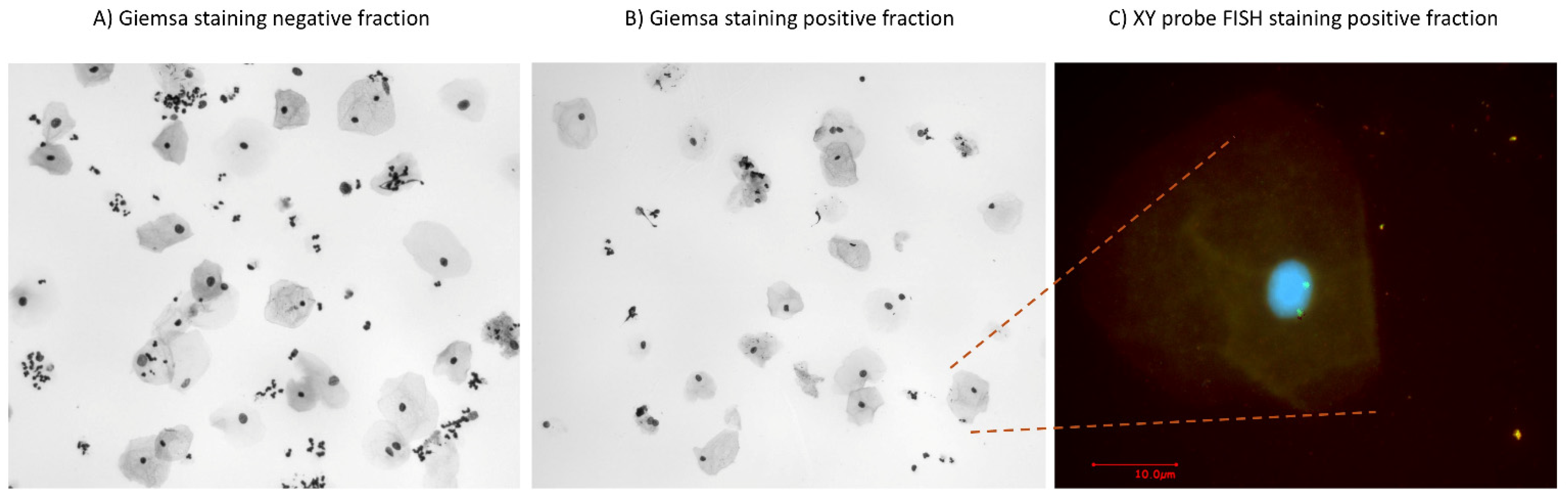
3.3. Enrichment of Fetal Cells from Endocervical Samples
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Christianson, A.; Howson, C.P.; Modell, B. March of Dimes releases premature birth report card: Kentucky receives “F’’’—KMA joins healthy babies coalition. J. Ky. Med. Assoc. 2008, 106, 557–558. [Google Scholar]
- Kypri, E.; Ioannides, M.; Achilleos, A.; Koumbaris, G.; Patsalis, P.; Stumm, M. Non-invasive prenatal screening tests - update 2022. J. Lab. Med. 2022, 46, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayashankar, S.S.; Nasaruddin, M.L.; Hassan, M.F.; Dasrilsyah, R.A.; Shafiee, M.N.; Ismail, N.A.S.; Alias, E. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Reliability, Challenges, and Future Directions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Feng, C.; Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xie, K.; Yuan, H.; Huang, S.; Yang, B.; et al. Performance of expanded non-invasive prenatal testing for fetal aneuploidies and copy number variations: A prospective study from a single center in Jiangxi province, China. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1073851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Tong, K.; Huang, D.; Tu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J. Expanding the application of non-invasive prenatal testing in the detection of foetal chromosomal copy number variations. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujezinovic, F.; Alfirevic, Z. Procedure-related complications of amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 110, 1425–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapner, R.J. Invasive prenatal diagnostic techniques. Semin. Perinatol. 2005, 29, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomaki, G.E.; Kloza, E.M.; Lambert-Messerlian, G.M.; Haddow, J.E.; Neveux, L.M.; Ehrich, M.; Van Den Boom, D.; Bombard, A.T.; Deciu, C.; Grody, W.W.; et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to detect Down syndrome: An international clinical validation study. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Jiang, P.; Wong, A.I.C.; Cheng, Y.K.Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Allen Chan, K.C.; Leung, T.Y.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Dennis Lo, Y.M. Size-tagged preferred ends in maternal plasma DNA shed light on the production mechanism and show utility in noninvasive prenatal testing. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5106–E5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceikaitė, I.; Hao, Q.; Brasch-Andersen, C.; Fagerberg, C.R.; Torring, P.M.; Kristiansen, B.S.; Ousager, L.B.; Sperling, L.; Ibsen, M.H.; Löser, K.; et al. Comprehensive Noninvasive Fetal Screening by Deep Trio-Exome Sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2017–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breman, A.M.; Chow, J.C.; U’Ren, L.; Normand, E.A.; Qdaisat, S.; Zhao, L.; Henke, D.M.; Chen, R.; Shaw, C.A.; Jackson, L.; et al. Evidence for feasibility of fetal trophoblastic cell-based noninvasive prenatal testing. Prenat. Diagn 2016, 36, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, G.; Drewlo, S.; Huppertz, B.; Randall Armant, D. Trophoblast retrieval and isolation from the cervix: Origins of cervical trophoblasts and their potential value for risk assessment of ongoing pregnancies. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravn, K.; Singh, R.; Hatt, L.; Kølvraa, M.; Schelde, P.; Vogel, I.; Uldbjerg, N.; Hindkjær, J. The Number of Circulating Fetal Extravillous Trophoblasts Varies from Gestational Week 6 to 20. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, L.D.; Lildballe, D.L.; Hatt, L.; Hedegaard, J.; Singh, R.; Toft, C.L.F.; Schelde, P.; Pedersen, A.S.; Knudsen, M.; Vogel, I. Noninvasive prenatal screening for cystic fibrosis using circulating trophoblasts: Detection of the 50 most common disease-causing variants. Prenat. Diagn 2023, 43, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, J.M.; Kilburn, B.A.; Bajpayee, S.; Reddy, N.; Jeelani, R.; Crone, B.; Simmerman, N.; Singh, M.; Diamond, M.P.; Armant, D.R. Trophoblast retrieval and isolation from the cervix (TRIC) for noninvasive prenatal screening at 5 to 20 weeks of gestation. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 135–142.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.V.; Kadam, L.; Van Dijk, M.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Kilburn, B.A.; Hartman, C.; Mazzorana, V.; Visser, A.; Hertz, M.; Bolnick, A.D.; et al. Fetal genome profiling at 5 weeks of gestation after noninvasive isolation of trophoblast cells from the endocervical canal. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, re4–re363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, M.; Boussata, S.; Janssen, D.; Afink, G.; Jebbink, J.; van Maarle, M.; Wortelboer, E.; Kooper, A.; Pajkrt, E. Tricky TRIC: A replication study using trophoblast retrieval and isolation from the cervix to study genetic birth defects. Prenat. Diagn. 2022, 42, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokol’tsova, T.D.; Saburina, I.N.; Nanovskaya, T.N.; Patrikeeva, S.L.; Vernikovskaya, D.I.; Zurina, I.M.; Gorkun, A.A.; Kosheleva, N.V.; Poltavtseva, R.A.; Sukhikh, G.T. Characteristics of Trophoblasts in Long-Term Culture. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 164, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, S.H.; Jang, H.Y.; Park, H.J.; Cha, D.H. Optimization protocol of fixation method for trophoblast retrieval from the cervix (TRIC): A preliminary study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlard, L.; Manigart, Y.; Donner, C.; Smits, G.; Désir, J.; Migeotte, I.; Pichon, B. Rarity of fetal cells in exocervical samples for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. J. Perinat. Med. 2022, 50, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinillo, S.L.; Farina, A.; Sotiriadis, A.; Pozzoni, M.; Giglio, S.; Papale, M.; Candiani, M.; Cavoretto, P.I. Pregnancy outcome of confined placental mosaicism: Meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 227, 714–727.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample Number | Age of Mother | Number of Pregnancies | Gestational Age (w;d) | Number of Brushes | Number of Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 3 | 11;1 | 1 | + |
| 2 | 28 | 3 | 11;6 | 1 | − |
| 3 | 33 | 4 | 11;1 | 1 | − |
| 4 | 32 | 6 | 11;0 | 1 | + |
| 5 | 38 | 6 | 11;2 | 1 | − |
| 6 | 29 | 4 | 11;5 | 1 | + |
| 7 | 25 | 2 | 11;5 | 1 | − |
| 8 | 31 | 4 | 11;1 | 2 | + |
| 9 | 31 | 1 | 11;2 | 2 | + |
| 10 | 27 | 1 | 13;2 | 2 | − |
| 11 | 32 | 2 | 13;1 | 2 | + |
| 12 | 26 | 5 | 12;0 | 2 | + |
| 13 | 34 | 4 | 11;1 | 2 | + |
| 14 | 29 | 2 | 11;6 | 2 | + |
| 15 | 30 | 1 | 11;1 | 2 | − |
| 16 | 38 | 1 | 13;1 | 2 | + |
| 17 | 35 | 4 | 11;3 | 2 | − |
| 18 | 33 | 4 | 13;6 | 2 | − |
| 19 | 28 | 2 | 14;2 | 2 | − |
| 20 | 34 | 2 | 12;1 | 2 | − |
| 21 | 36 | 2 | 13;1 | 2 | + |
| 22 | 31 | 5 | 11;5 | 2 | − |
| 23 | 34 | 2 | 11;5 | 2 | − |
| 24 | 32 | 3 | 12;0 | 2 | − |
| 25 | 25 | 1 | 20;3 | 2 | + |
| 26 | 33 | 4 | 11;5 | 2 | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Boer, E.N.; Corsten-Janssen, N.; Wierenga, E.; Bijma, T.; Knapper, J.T.; Meerman, G.J.t.; Manten, G.T.R.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; Bouman, K.; Duin, L.K.; et al. Limitations of Semi-Automated Immunomagnetic Separation of HLA-G-Positive Trophoblasts from Papanicolaou Smears for Prenatal Genetic Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030386
de Boer EN, Corsten-Janssen N, Wierenga E, Bijma T, Knapper JT, Meerman GJt, Manten GTR, Knoers NVAM, Bouman K, Duin LK, et al. Limitations of Semi-Automated Immunomagnetic Separation of HLA-G-Positive Trophoblasts from Papanicolaou Smears for Prenatal Genetic Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030386
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Boer, Eddy N., Nicole Corsten-Janssen, Elles Wierenga, Theo Bijma, Jurjen T. Knapper, Gerard J. te Meerman, Gwendolyn T. R. Manten, Nine V. A. M. Knoers, Katelijne Bouman, Leonie K. Duin, and et al. 2025. "Limitations of Semi-Automated Immunomagnetic Separation of HLA-G-Positive Trophoblasts from Papanicolaou Smears for Prenatal Genetic Diagnostics" Diagnostics 15, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030386
APA Stylede Boer, E. N., Corsten-Janssen, N., Wierenga, E., Bijma, T., Knapper, J. T., Meerman, G. J. t., Manten, G. T. R., Knoers, N. V. A. M., Bouman, K., Duin, L. K., & Diemen, C. C. v. (2025). Limitations of Semi-Automated Immunomagnetic Separation of HLA-G-Positive Trophoblasts from Papanicolaou Smears for Prenatal Genetic Diagnostics. Diagnostics, 15(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030386






