Hyperglycemia and Lung Cancer—A Possible Relationship
Abstract
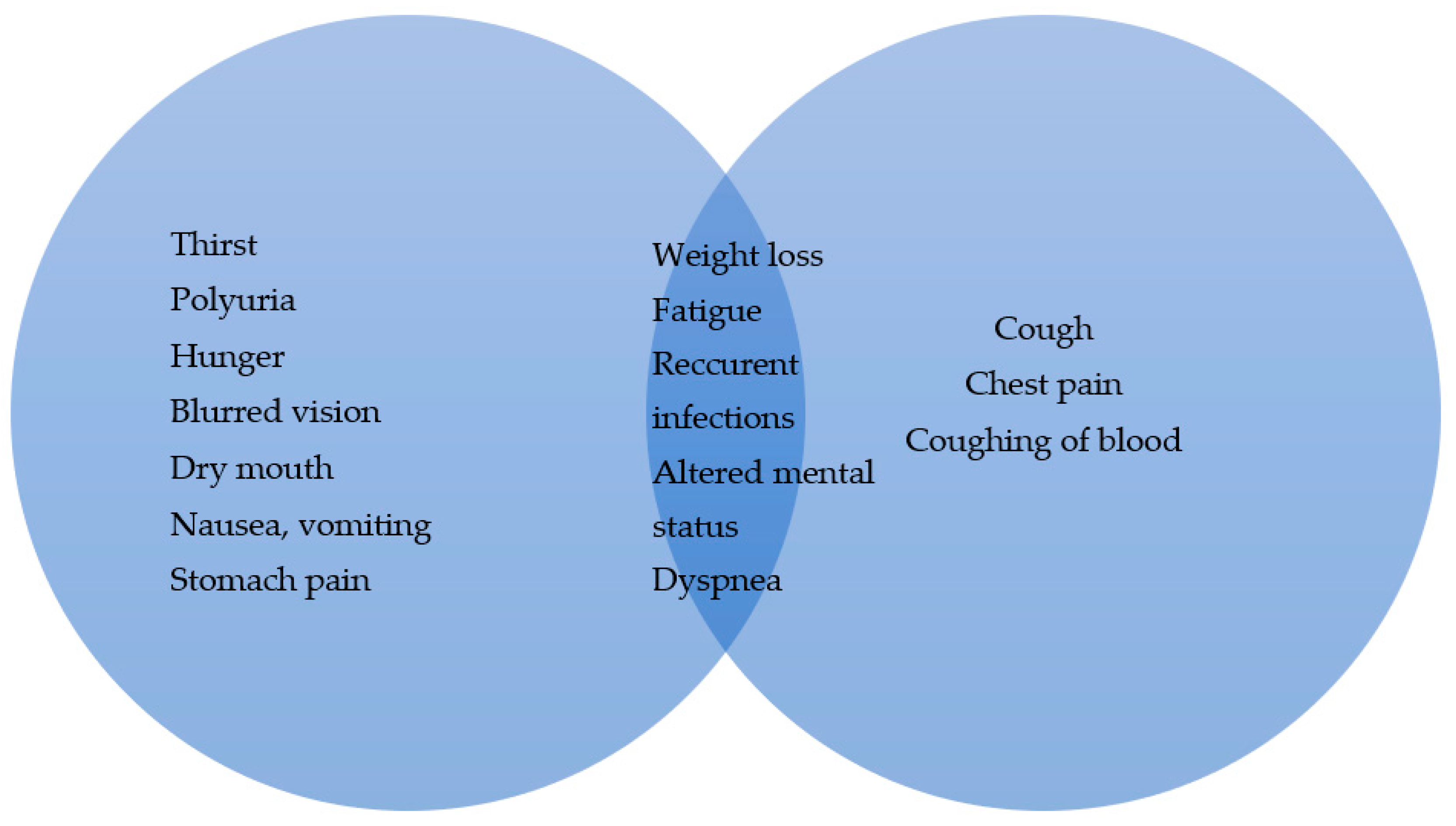
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Understanding Glucose Metabolism in Health and Disease
2.2. Lung Cancer
3. Molecular Pathways Common in Both DM and LC
3.1. Interleukin 6 (IL-6)
3.2. Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)–β
3.3. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIFs)
3.4. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
4. Effects of Hyperglycemia on Lung Cancer Treatment
5. Hyperglycemia and Chemotherapy
6. Tobacco-Induced Hyperglycemia and LC
7. Hyperglycemia, Risk of Infection and Poor-Outcome Treatment of LC Patients
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hantzidiamantis, P.J.; Awosika, A.O.; Lappin, S.L. Physiology, Glucose. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545201/ (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Mouri, M.I.; Badireddy, M. Hyperglycemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430900/ (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2461–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, F.; Henze, C.; Heidrich, K. Interleukin-6 signal transduction and lymphocyte function. Immunobiology 2000, 202, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.P.; Huang, D.; Cai, J.G.; Wang, Y. Effects of muscle derived-IL-6 on insulin resistance of skeletal muscle cells and its mechanisms. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2022, 38, 530–536. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewko, K.; Maciulewski, R.; Zielinska-Maciulewska, A.; Poplawska-Kita, A.; Szumowski, P.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Lipinska, D.; Milewski, R.; Gorska, M.; Kretowski, A.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-15 as Possible Biomarkers of the Risk of Autoimmune Diabetes Development. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 7, 4734063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cui, W.; Wu, J.; Zheng, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Shang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Blocking IL-6 signaling improves glucose tolerance via SLC39A5-mediated suppression of glucagon secretion. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshino, A.; Schechter, M.; Sen, T.; Vart, P.; Neuen, B.L.; Neal, B.; Arnott, C.; Perkovic, V.; Ridker, P.M.; Tuttle, K.R.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: New Insights From CANVAS. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Utami, A.; Putra, A.; Wibowo, J.W.; Amalina, N.D.; Satria Irawan, R.C. Hypoxic secretome mesenchymal stem cells inhibiting interleukin-6 expression prevent oxidative stress in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Med. Glas. 2023, 20, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Bai, F.; Ding, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Yue, X.; Liang, X.; et al. IL-6 promotes metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer by up-regulating TIM-4 via NF-κB. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- An, J.; Gu, Q.; Cao, L.; Yang, H.; Deng, P.; Hu, C.; Li, M. Serum IL-6 as a vital predictor of severe lung cancer. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.Q.; Huang, X.B.; Ke, S.Z.; Jiang, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, J.; Gao, F.G. Interleukin 6 augments lung cancer chemotherapeutic resistance via ataxia-telangiectasia mutated/NF-kappaB pathway activation. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caetano, M.S.; Zhang, H.; Cumpian, A.M.; Gong, L.; Unver, N.; Ostrin, E.J.; Daliri, S.; Chang, S.H.; Ochoa, C.E.; Hanash, S.; et al. IL6 Blockade Reprograms the Lung Tumor Microenvironment to Limit the Development and Progression of K-ras-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caja, L.; Dituri, F.; Mancarella, S.; Caballero-Diaz, D.; Moustakas, A.; Giannelli, G.; Fabregat, I. TGF-β and the Tissue Microenvironment: Relevance in Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heydarpour, F.; Sajadimajd, S.; Mirzarazi, E.; Haratipour, P.; Joshi, T.; Farzaei, M.H.; Khan, H.; Echeverría, J. Involvement of TGF-β and Autophagy Pathways in Pathogenesis of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review on Biological and Pharmacological Insights. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 498758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saito, A.; Horie, M.; Nagase, T. TGF-β Signaling in Lung Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel, E.E., III; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Semenza, G.L.; Agani, F.; Booth, G.; Forsythe, J.; Iyer, N.; Jiang, B.H.; Leung, S.; Roe, R.; Wiener, C.; Yu, A. Structural and functional analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrina, S.B.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in diabetes and its complications. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sena, C.M.; Matafome, P.; Crisóstomo, J.; Rodrigues, L.; Fernandes, R.; Pereira, P.; Seiça, R.M. Methylglyoxal promotes oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. Status of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmazie 2021, 76, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Ouyang, C.; Yu, B.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.F.; Ye, X.Q. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.G.; Liang, X.H.; Ke, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.K.; He, L.; Guo, Y.X.; Bian, H.; Chen, Z.N.; et al. Active demethylation upregulates CD147 expression promoting non-small cell lung cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1780–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fredriksson, L.; Li, H.; Eriksson, U. The PDGF family: Four gene products form five dimeric isoforms. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skapinker, E.; Aucoin, E.B.; Kombargi, H.L.; Yaish, A.M.; Li, Y.; Baghaie, L.; Szewczuk, M.R. Contemporaneous Inflammatory, Angiogenic, Fibrogenic, and Angiostatic Cytokine Profiles of the Time-to-Tumor Development by Cancer Cells to Orchestrate Tumor Neovascularization, Progression, and Metastasis. Cells 2024, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noskovičová, N.; Petřek, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Heinzelmann, K. Platelet-derived growth factor signaling in the lung. From lung development and disease to clinical studies. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Wang, F.; Fernandez, A.; Hu, W. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in type II diabetes mellitus and its complications. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2020, 17, 1479164120942119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Betsholtz, C.; Johnsson, A.; Heldin, C.H.; Westermark, B.; Lind, P.; Urdea, M.S.; Eddy, R.; Shows, T.B.; Philpott, K.; Mellor, A.L.; et al. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature 1986, 320, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Busund, L.T.; Bremnes, R.M. Prognostic impact of platelet-derived growth factors in non-small cell lung cancer tumor and stromal cells. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Busund, L.T.; Bremnes, R.M. Co-expression of PDGF-B and VEGFR-3 strongly correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor survival in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.; Kaira, K.; Mori, K.; Ono, A.; Akamatsu, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Taira, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Harada, H.; Naito, T.; et al. Prognostic significance of diabetes mellitus in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yi, Z.H.; Luther, Y.; Xiong, G.H.; Ni, Y.L.; Yun, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.C. Association between diabetes mellitus and lung cancer: Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Lim, Y.J. Hemoglobin A1c level is a prognostic factor for locoregional recurrence in stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lim, Y.J. Chronic hyperglycemia is an adverse prognostic factor for locoregional recurrence-free survival in small cell lung cancer patients treated with radical radiotherapy. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, L.J. Fasting blood glucose level and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.Z.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhao, T.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Fu, G.M.; Wu, Q.L.; Zhou, C.W. Influence of blood glucose fluctuations on chemotherapy efficacy and safety in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients complicated with lung carcinoma. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duan, W.; Shen, X.; Lei, J.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, E.; Ma, Q. Hyperglycemia, a neglected factor during cancer progression. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 461917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hershey, D.S.; Bryant, A.L.; Olausson, J.; Davis, E.D.; Brady, V.J.; Hammer, M. Hyperglycemic-inducing neoadjuvant agents used in treatment of solid tumors: A review of the literature. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2014, 41, E343–E354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jia, B.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Qi, X. Variations of blood glucose in cancer patients during chemotherapy. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 19, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Durham, H.; Glover, L.; Ather, O.; Phillips, V.; Nemes, S.; Cousens, L.; Blomgran, P.; Ambery, P. Metabolic adverse events associated with systemic corticosteroid therapy-a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, P.L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, D.; Mao, C. Association of smoking and polygenic risk with the incidence of lung cancer: A prospective cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tyczynski, J.E.; Bray, F.; Parkin, D.M. Lung cancer in Europe in 2000: Epidemiology, prevention, and early detection. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 45–55, Erratum in Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 733–744, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornier, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Hernandez, T.L.; Lindstrom, R.C.; Steig, A.J.; Stob, N.R.; Van Pelt, R.E.; Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. The metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 777–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jang, H.J.; Min, H.Y.; Kang, Y.P.; Boo, H.J.; Kim, J.; Ahn, J.H.; Oh, S.H.; Jung, J.H.; Park, C.S.; Park, J.S.; et al. Tobacco-induced hyperglycemia promotes lung cancer progression via cancer cell-macrophage interaction through paracrine IGF2/IR/NPM1-driven PD-L1 expression. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Colao, A.; Lenzi, A.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, M.; Cao, S.M.; Dimou, N.; Wu, L.; Li, J.B.; Yang, J. Association of Metabolic Syndrome With Risk of Lung Cancer: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Chest 2024, 165, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Budisan, L.; Zanoaga, O.; Braicu, C.; Pirlog, R.; Covaliu, B.; Esanu, V.; Korban, S.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Links between Infections, Lung Cancer, and the Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. This is a Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This statement was endorsed by the Council of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. (IDSA), September 1999, and the sections of this statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161 Pt 2, S221–S247. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Rüttinger, D.; Li, R.; Si, L.S.; Wang, Y.L. Analysis of the immunological microenvironment at the tumor site in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2003, 388, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.C.; Leung, C.C. Management of co-existent tuberculosis and lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 122, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; You, N.; Pan, H.; Shen, Y.; Lu, P.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.; Zhu, L.; Martinez, L. Glycemic Trajectories and Treatment Outcomes of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Tuberculosis: A Prospective Study in Eastern China. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Lan, L.; Wu, G.; Ren, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, Q.; Peng, X.; Liu, D. Impact of diabetes itself and glycemic control status on tuberculosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1250001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rakhimov, A.Y.; Kurbanov, O.M.; Mirsoliev, S.G. The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on the Course of Purulent Thoracic Surgical Pathologies. World Bull. Public Health 2022, 15, 87–93. Available online: https://www.scholarexpress.net/index.php/wbph/article/view/1540 (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Venkataramu, V.N.; Ghotra, H.K.; Chaturvedi, S.K. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with cancer. Indian J. Psychiatry 2022, 64 (Suppl. S2), S458–S472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Tuijl, L.A.; Basten, M.; Pan, K.Y.; Vermeulen, R.; Portengen, L.; de Graeff, A.; Dekker, J.; Geerlings, M.I.; Hoogendoorn, A.; Lamers, F.; et al. Depression, anxiety, and the risk of cancer: An individual participant data meta-analysis. Cancer 2023, 129, 3287–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourpiliadis, C.; Zeng, Y.; Lovik, A.; Wei, D.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.; Song, H.; Hammar, N.; Fang, F. Metabolic Profile and Long-Term Risk of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress-Related Disorders. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e244525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Onaizi, M.; Braysh, K.; Alkafeef, S.S.; Altarrah, D.; Dannoon, S.; Alasousi, D.; Adel, H.; Al-Ajim, M.; Kandari, A.; Najem, R.; et al. Glucose intolerance induces anxiety-like behaviors independent of obesity and insulin resistance in a novel model of nutritional metabolic stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1143–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Tsai, C.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, K.C.; Lin, C.C. Randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness of home-based walking exercise on anxiety, depression and cancer-related symptoms in patients with lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hammer, M.J.; Eckardt, P.; Cartwright, F.; Miaskowski, C. Prescribed Walking for Glycemic Control and Symptom Management in Patients Without Diabetes Undergoing Chemotherapy. Nurs. Res. 2021, 70, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Transporter | Most Common Location | Type of Transport | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGLT | Renal tubules, intestinal mucosa | Secondary active transport | (Re)absorption of glucose |
| GLUT 1 | Ubiquitous | Facilitated diffusion | Basal glucose uptake |
| GLUT 2 | Pancreatic β cells, hepatocytes, intestinal mucosa, kidney | Facilitated diffusion | Regulation of blood glucose levels |
| GLUT 3 | Nervous system | Facilitated diffusion | Maintains glucose uptake in nervous system, regardless of blood glucose levels |
| GLUT 4 | Skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue, adipose tissue | Facilitated diffusion | Insulin-dependent, regulates glucose uptake in hyperglycemia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popevic, S.; Maric, N.; Ilic, B.; Belic, S.; Sekulovic Radovanovic, I.; Dimic-Janjic, S.; Stjepanovic, M. Hyperglycemia and Lung Cancer—A Possible Relationship. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060651
Popevic S, Maric N, Ilic B, Belic S, Sekulovic Radovanovic I, Dimic-Janjic S, Stjepanovic M. Hyperglycemia and Lung Cancer—A Possible Relationship. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(6):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060651
Chicago/Turabian StylePopevic, Spasoje, Nikola Maric, Branislav Ilic, Slobodan Belic, Ivana Sekulovic Radovanovic, Sanja Dimic-Janjic, and Mihailo Stjepanovic. 2025. "Hyperglycemia and Lung Cancer—A Possible Relationship" Diagnostics 15, no. 6: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060651
APA StylePopevic, S., Maric, N., Ilic, B., Belic, S., Sekulovic Radovanovic, I., Dimic-Janjic, S., & Stjepanovic, M. (2025). Hyperglycemia and Lung Cancer—A Possible Relationship. Diagnostics, 15(6), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060651






