Abstract
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is the prototype and most common autoinflammatory disease that is particularly frequent in populations originating from the Mediterranean basin. It is characterized by episodes of recurrent inflammation lasting 2–3 days. Colchicine is the mainstay therapy, which decreases the number of attacks and eventually prevents amyloidosis, the most worrisome complication of uncontrolled FMF. It is an autosomal recessive disease. The high rate of MEFV gene mutations in specific populations has been discussed as the result of an evolutionary advantage. Tel-Hashomer criteria were the first set of criteria primarily designed for adults. Recently, the Eurofever/PRINTO group has validated a new set of classification criteria for FMF, including clinical and genetic variables. Colchicine intolerance is an important problem and limits the ability to reach an effective dose. In these groups of patients, adding an alternative biological treatment (anti IL-1 agents) is recommended. Several tools such as FMF50, AIDAI, ADDI, ISSF and MASIF have been proposed to evaluate and quantify the disease activity and organ damage. Ongoing research should clarify the exact mechanisms causing FMF attacks and phenotypic variabilities between the patients; further translational research requires the implementation of proteomics and epigenetics signatures to elucidate the pathogenesis.
1. Introduction
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is the most prevalent condition among autoinflammatory diseases, characterized by recurrent fever episodes lasting no more than 3 days. Other typical manifestations include abdominal pain, chest pain, arthritis, and erysipelas-like erythema, commonly seen in lower extremities [1]. FMF is frequently seen in Turkish people, Jewish people, and Armenian people. It is a monogenic autoinflammatory condition caused by autosomal recessive mutations in the MEFV gene, which encodes the pyrin (marenostrin) protein [2,3]. Mutations in the MEFV gene cause IL-1b overproduction, which in turn results in excessive inflammation. Since 1997, when the MEFV gene was identified, many questions have arisen about the impact of these mutations. Although it is an autosomal recessive disease, some patients with a single heterozygous mutation may have the clinical phenotype, though this is still a subject of debate [4,5]. Colchicine is the first-line treatment option for reducing the number of episodes and eventually prevents amyloidosis, the most catastrophic morbidity of FMF. On the other hand, colchicine intolerance or resistance was reported in 5–10% of the patients [6]. Anti-IL1 treatment options were designed due to the pathogenesis of FMF and have since been used as satisfactory options to treat colchicine-resistant/-intolerant patients.
In this review, we evaluated recent advances in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, management, and monitoring of FMF patients and summarized recent evidence-based recommendations.
2. Pathogenesis
FMF is inherited with autosomal recessive mutations on the MEFV gene, which encodes the pyrin protein [2,3]. Pyrin is a fundamental element of the NLRP3 inflammasome complex. Mutation of this protein initiates caspase-1 activation and IL-1b production, causing excessive inflammation (Figure 1) [7].
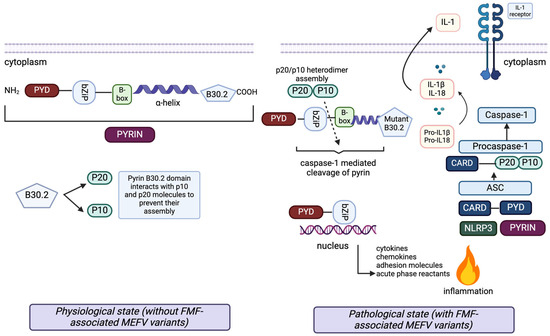
Figure 1.
The pathophysiology of the inflammatory response in FMF and the structure of pyrin with its interacting proteins. Pyrin (top left) consists of five domains: the Pyrin domain (PYD), bZip transcription factor basic domain (bZip), B-box zinc finger domain, alpha-helical (coiled coil) domain and B30.2 domain. Each domain has a regulatory role in diverse protein–protein interactions of pyrin with proteins connected to the inflammatory pathways through cell death and apoptosis, secretion of cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules, and cytoskeletal signaling. In the inflammasome (bottom right), active forms of caspase-1 subunits, p20 and p10, are produced. In the cases without any FMF-associated MEFV mutations, the pyrin B30.2 domain interacts with p20 and p10 molecules, preventing their assembly into active p20/p10 heterodimers, which activate the caspase-1 mediated cleavage of pyrin. The caspase-1 mediated cleavage site of pyrin is located between the bZip transcription factor basic domain and the B-box zinc finger domain.
Additionally, the wild-type B30.2 domain of pyrin helps to create a blockade for IL-1β secretion by interacting with proIL-1β. In the presence of FMF-associated MEFV mutations, the mutant B30.2 pyrin domain shows reduced interaction with p20 and p10, thereby allowing p20/p10 heterodimer assembly (active caspase-1), cleavage of pyrin, IL-1β activation and induction of inflammation (left). The N-terminal cleaved fragment of pyrin interacts with IκB-α, p65 and p50 molecules through the bZip domain. Subsequently, it moves into the nucleus to enhance the activation of the NF-κB transcription factor and expression of the proinflammatory genes (bottom).
Chae et al. have shown in MEFV knock-in mice models that gain-of-function mutations of pyrin protein led to overproduction of IL-1b via associated speck-like protein-containing CARD (ASC) and caspase-1 activation [8]. Furthermore, pyrin mediates caspase-1 activation in response to pathogen modification and inactivation of RhoA-GTPases by several bacterial toxins [9]. There is a control mechanism for pyrin inflammasome in healthy individuals. RhoA-activated serine-threonine kinases (PKN1 and PKN 2) bind and phosphorylate pyrin, which binds to regulatory 14-3-3 proteins, inhibiting pyrin inflammasome. Most of the common and severe MEFV mutations are clustered around the C terminal of the B30.2 domain, which is important for controlling pyrin phosphorylation by inhibiting the binding of PKN1, resulting in a lowered threshold for pyrin inflammasome activation. In parallel with this finding, it was shown that colchicine both activates RhoA and reverses the inhibition of RhoA by bacterial toxins [10].
A recent study by Park et al. has reported the possible selective advantage of MEFV mutations, since their carrier frequencies are very high in several Mediterranean populations. They have found that mutated pyrin interacts less with Yersinia pestis virulence factor YopM, attenuating YopM-induced IL-1b suppression. This was proven in vitro and during in vivo studies, as well. Leucocytes from patients with homozygous or compound heterozygous and asymptomatic heterozygous carriers released more IL-1b in response to Y. pestis than healthy controls. Similarly, Y. pestis-infected MEFVM680I/M680I FMF knock-in mice had IL-1-dependent increased survival relative to wild-type knock-in mice. In summary, FMF mutations in Mediterranean populations might lead to a positive selection against plague due to increased resistance to Y. pestis [11].
3. Diagnosis and Classification
A diagnosis of FMF relies on characteristic clinical features, and the presence of MEFV mutation usually supports this diagnosis. Various attempts have been made to classify FMF since 1997 (Table 1).

Table 1.
The different classification criteria of FMF.
The first criteria set for FMF was proposed mainly for adults and these criteria are referred to as Tel-Hashomer criteria [12]. Since this set of criteria is designed primarily for adults, and there are some differences between adults and children, Turkish FMF pediatric criteria, also known as Yalcinkaya-Ozen criteria, have been proposed [13]. Both these criteria sets are composed of clinical features only. They do not include the genetic variants or ethnicity data overall. Recently, the Eurofever/PRINTO group published new classification criteria, including a combination of ethnicity, clinical manifestations and genotype [14]. This new classification criteria offers two options for detecting genetic variants. The care physician can make a diagnosis based on ≥6/9 clinical criteria if MEFV variant analysis is not feasible. On the other hand, according to the MEFV genotype, one or two clinical criteria (out of four criteria) would be sufficient if genetic testing is possible. Among Turkish children, Eurofever/PRINTO criteria were the most sensitive (96% vs. 89% Tel-Hashomer; 93% Yalcinkaya-Ozen), but the least specific (73% vs. 93% Tel-Hashomer; 84% Yalcinkaya-Ozen) among these three criteria sets [15]. The combination of clinical findings and genetic testing increased the sensitivity. Although the ethnicity criteria seem to lower the specificity of the newest criteria set, having the “clinical-only” option may provide guidance which helps the physician to choose and order relevant genetic tests for patients, especially in non-endemic countries. Since 1997, the discovery of the link between the MEFV gene and FMF has increased the number of variants gradually, causing problems when it comes to deciding which variants are pathogenic. Phenotype–genotype descriptions related to the different MEFV variants are summarized and recorded in the INFEVERS database (https://infevers.umai-montpellier.fr/web/search.php?n=1 (accessed on 12 January 2025)), in which there are 401 known variants to date. These variants have been graded by an expert panel as pathogenic, likely pathogenic, benign, likely benign, and a variant of unknown significance (VUS) [16]. Screening for these 401 variants is not practical. Disease-causing pathogenic variants are commonly located in exon 10 (M694V, V726A, M680I and M694I). E148Q, which is in exon two, is the most frequent VUS in carriers. To provide clinicians, scientists, and geneticists with guidance on appropriate molecular genetic testing, an international task force developed recommendations and proposed screening a total of 14 variants for genetic confirmation of the patients (pathogenic variants: M694V, M694I, M680I, V726A, R761H, A744S, E167D, T267I and I692del VUS: K695R, E148Q, P369S, F479L, and I591T) [17]. In various studies, exon 10 mutations, specifically M694V mutations, are associated with early-onset disease with the more severe course and more frequently associated with other inflammatory comorbidities such as Behçet’s disease, inflammatory bowel diseases, vasculitis, etc. [18,19,20]. Although E148Q variants are reported as VUS and heterozygous E148Q mutations do not support the diagnosis of FMF according to the recent recommendations, in a recent study involving 169 patients (amyloidosis secondary to FMF), E148Q homozygous mutations were reported in 19 patients. In another study, 7 out of 22 FMF patients with phenotype 2 had variants in the E148Q, which was a higher number than expected [17,20,21,22]. Up-to-date recommendations for the genetic diagnosis of FMF are in Table 2.

Table 2.
Recommendations about diagnosis, treatment, and management of FMF patients [20,23].
These recommendations are supported by “The ISAAID/EMQN Best Practice Guidelines for the genetic diagnosis of monogenic autoinflammatory disease”. These guidelines also recommend confirming the diagnosis if there are biallelic pathogenic variants. However, the decision is left to the expert clinicians if there is either one pathogenic variant + one VUS, only one pathogenic variant, or biallelic VUS mutations [24].
Although FMF is an autosomal recessive disease, some patients with heterozygous mutations also presented with typical FMF clinical features. It was reported that approximately 25% of the clinically confirmed FMF patients did not have a biallelic mutation in the MEFV gene [17]. Previously, it was thought that routine sequencing techniques had missed less common variants. However, Booty et al. [25] failed to define any intragenic genomic mutations in 46 heterozygous FMF patients with new techniques, and Marek-Yagel et al. [26] failed to define any further mutations or abnormal methylation patterns via sequencing complementary DNA in heterozygote FMF patients. On the other hand, in a recent study of 46 patients with undefined autoinflammatory diseases, a new method using an NGS-based multiplex array enabling a “long-amplicon” approach defined 46 nonsynonymous variations, 169 synonymous variations, 89 UTR variations, and 588 intronic variations in the MEFV gene, which proves that deep screening may still help to define some modifications in these groups of patients [27]. One possible explanation for carriers presenting with typical clinical features might be the effect of modifier genes related to inflammation. Certain polymorphisms in the innate immune system genes, SAA and TLR2, were shown to be linked to the development of amyloidosis [28,29,30]. Thus, if certain polymorphisms may affect the disease course, they could be the causative mechanism in heterozygote FMF patients with typical FMF phenotype [31,32].
4. Treatment
Colchicine has been the first line of treatment for FMF since 1972 [33]. It reduces the frequency of episodes and disease severity, improves quality of life, and prevents the most devastating complication, amyloidosis [34,35]. The suggested colchicine dosage for children less than five years old is ≤0.5 mg/day (≤0.6 mg/day in tablets containing 0.6 mg) and for children between five and ten years of age, it is 0.5–1.0 mg/day (1.2 mg/day if the tablets contain 0.6 mg). The recommended colchicine dosage for the pediatric age group older than 10 years and the adult population is 1.0–1.5 mg/day (1.8 mg/day if tablets contain 0.6 mg).
The maximum colchicine dosage should not exceed 3 mg/day for adults and 2 mg/day for children [6,23,36]. Historically, it was generally administered twice daily; Polat et al. showed that once-daily usage is not inferior to twice daily usage in their randomized controlled non-inferiority trial [37]. Patients should be followed at least every 6 months for disease activity, treatment adherence, and side effects. Approximately 5–10% of the patients are non-responsive or intolerant to colchicine. Recently, an expert panel reported the consensus-based definition of colchicine resistance and intolerance. Colchicine resistance was described as (if a patient is on the maximum tolerated colchicine dose) ongoing disease activity defined as recurrent clinical episodes or persistent elevation of inflammatory markers (SAA or CRP) in between episodes without any other reason [6]. Intolerance of colchicine in patients with FMF mainly presents in the form of gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea and nausea, which causes them to be unable to reach the desired or effective dosage. Colchicine toxicity is different from intolerance and is described as severe gastrointestinal involvement, bone marrow suppression, and neuromyopathy [6]. In these groups of patients, adding an alternative biological treatment is recommended. Due to the pathogenesis of FMF, pyrin inflammasome results in increased IL-1β production. Thus, anti-IL1 agents are preferred as the first-line biological treatment [23].
Anti-IL-1 therapies, including Anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) and Canakinumab (an anti-IL-1β monoclonal antibody), competitively inhibit IL-1R1 or neutralize IL-1β, thereby reducing proinflammatory cytokine production and neutrophil infiltration. These mechanisms collectively demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of IL-1 blockade in managing systemic inflammation. Anakinra and Canakinumab were reported in many publications, including six randomized controlled trials (one anakinra, four canakinumab and one rilonacept). Despite the marked heterogeneity in outcome measures across studies, the majority prioritized reductions in acute-phase reactants and attack frequency as primary endpoints, with all anti-IL-1 agents demonstrating consistent efficacy in these parameters. They demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with predominantly mild adverse events limited to injection site reactions, uncomplicated infections, transient elevations in liver enzymes, and self-limiting leukopenia [38,39,40,41,42,43]. There are also two randomized controlled trials with anti-IL6 treatment (tocilizumab). Despite both RCTs failing to achieve the primary endpoint, anti-IL6 treatments appear to be successful in reducing the frequency of attacks and acute-phase reactants while also enhancing various disease activity scores and patient-reported outcomes [44,45,46].
In recent studies, JAK1/TYK2 (which act downstream of the IFN receptor) were found to be essential for regulating IL-1β-mediated inflammation by network analyses and in silico tests supported by the fact that pyrin and gasdermin-D are interferon-inducible genes [47]. Emerging clinical evidence complements preclinical findings, with three independent case series involving six FMF patients reporting that tofacitinib—a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor—demonstrated marked suppression of inflammatory biomarkers and achieved sustained clinical remission [48,49,50]. These observations, supported by a mechanistic rationale implicating JAK-STAT signaling in FMF pathogenesis, position tofacitinib as a promising therapeutic candidate warranting further investigation in larger controlled trials.
The most recent recommendations for the management and follow-up of FMF patients are given in Table 2.
5. Outcome-Measuring Tools
In parallel with a quote from economics, ‘If you cannot measure it, you cannot manage it’, physicians still debate the definition and concept of disease severity, activity, and damage. However, the ability to collect standardized data will significantly improve the care of patients with FMF.
5.1. Disease Activity
The AutoInflammatory Disease Activity Index (AIDAI) was designed to evaluate active/inactive disease for the four major hereditary recurrent fever syndromes, including FMF. It comprises 13 items, including fever, overall symptoms, abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, chest pain, painful nodes, arthralgia, or myalgia, swelling of the joints, eye manifestations, skin rash, and pain relief. This daily diary allows patients or parents to record their score as the presence or absence of the symptom (yes (1 point) or no (0 point)). In order to differentiate active disease from inactive disease, AIDAI researchers defined a cutoff score of ≥9 as having a specificity of 92% and sensitivity of 89% [51]. This score was externally validated with the colchicine-resistant FMF patients in the phase III CLUSTER trial, as well. The researchers found that AIDAI scores ≥ 12 were the optimal threshold to discriminate inactive disease with a specificity of 79% and sensitivity of 75% [52]. On the other hand, a recent study on 239 FMF patients showed that the number of episodes, rather than AIDAI, was the only key element that can be used as a valid indicator of disease activity [53].
5.2. Disease Severity
The International Severity Score for FMF (ISSF) was developed to assess the disease severity, composed of 10 different items including chronic sequela, organ dysfunction, organ failure, frequency of attacks, increased acute-phase reactants during attack-free periods, involvement of more than two sites, more than two different types of attack, duration of attacks, and exertional leg pain. According to this scoring system, patients were stratified as having severe disease (ISSF score ≥ 6), intermediate disease (ISSF score: 3–5), or mild disease (ISSF score ≤ 2) [54].
5.3. Disease Damage
The Autoinflammatory Disease Damage Index (ADDI) was developed to measure the damage caused by autoinflammatory diseases as an outcome parameter. It contains 18 items sub-categorized into eight organ systems (reproductive, renal/amyloidosis, developmental, serosal, neurological, ears, ocular and musculoskeletal damage) with different score weights. Damage was defined as “a persistent or irreversible change in structure or function that was present for at least 6 months” [55]. This score was validated by 37 experts on 110 paper clinical cases, revealing that it was strongly correlated with Physician Global Assessment of Damage and was not strongly influenced by disease activity [56].
5.4. Assessment of Treatment Outcome Indices
The FMF50 score was developed by the Turkish FMF Study group and FAVOR (FMF Arthritis Vasculitis and Orphan disease Research in pediatric rheumatology) to assess the response of the colchicine treatment. It consisted of six criteria: 1. percentage change in the frequency of attacks with the treatment; 2. percentage change in the duration of attacks with the treatment; 3. patients/parents’ global assessment of disease severity (10 cm visual analog scale (VAS)); 4. physicians’ global assessment of disease severity (10 cm VAS); 5. percentage change in arthritis attacks with the treatment; and 6. percentage change in C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or serum amyloid A level with the treatment. The response to treatment was determined to be at least a 50% improvement in five of six items among the criteria set, without worsening in any criterion, according to the original study [57]. Nonetheless, this score requires prospective validation in different cohorts to be used more widely.
The Medication Adherence Scale in Familial Mediterranean Fever (MASIF) was developed to evaluate adherence to the treatment. It comprises 18 items clustered in four domains, including knowledge about the medication, adherence to the treatment, barriers to drug use, and factors that may increase compliance. Each of these 18 items was scored 1–5 (1: strongly agree; 5: strongly disagree), resulting in a total score ranging from 18 to 90. Patients were deemed to have good medication adherence if their score was over 60 [58].
In conclusion, the availability of these scores for clinical practice and clinical trials may facilitate the long-term management of individual patients. To guide clinicians, we recommend using AIDAI and MASIF as patient-reported instruments. The AIDAI is a valid and reliable patient diary used to assess disease activity. It has been suggested that at least a three-month diary is required to decide on disease activity. However, this can be challenging in patients who experience fewer episodes during the year. In addition, MASIF may be a useful tool for identifying colchicine-resistant patients with the ability to differentiate poor adherence from nonresponse to colchicine. FMF50 is a well-performing index for measuring response to treatment in all drug studies for colchicine-resistant cases. Finally, ISSF is the most detailed tool for measuring severity scores for FMF. Close monitoring of patients with severe disease may protect them from poor prognosis.
6. Future Perspectives
Despite well-identified triggers, the exact mechanisms causing FMF attacks need better elucidation. For instance, the typical characteristics of attacks, which usually last 48–72 h followed by spontaneous resolution, remain unknown. It is still not clear why some carriers present with clinical symptoms. FMF has large phenotypic diversity even in patients with the same genotype. Identifying the factors contributing to disease variability is essential, as it will help us to understand this condition better. Epigenetic changes in MEFV have been suggested as a potential modifier of the pathogenic effect of disease-causing MEFV mutations and may explain different phenotypes or severity. This critical knowledge gap also needs to be addressed with further studies. The possible association between FMF and other diseases should be explored. For instance, patients with homozygous exon 10 mutations are more prone to sacroiliitis, vasculitis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. However, patients with less pathogenic variants or heterozygous mutations may also display these comorbidities. Further translational studies, including multi-omics approaches, are needed to shed light on these matters.
Moreover, biomarkers are needed to monitor disease progression and treatment response. Recently, Koga et al. demonstrated a significant decrease in serum CXCL1 and VEGF levels in colchicine-resistant FMF patients receiving tocilizumab treatment [59]. Therefore, levels of CXCL1 and VEGF may be used as potential biomarkers for elucidating the inflammatory state and disease progression. Further large-scale longitudinal studies with repeated measures are required to confirm the role of CRP, SAA, and S100 proteins and these recently described potential biomarkers.
The reason why FMF-related AA amyloidosis has a poor prognosis is not fully understood. One possible explanation is that once amyloid deposition starts, it causes damage, such as fibrosis, sclerosis, and kidney injury. It can continue to worsen even if the amyloid deposition stops. A recent study showed that most patients with FMF amyloidosis will experience kidney failure or die within 11 years of being diagnosed, and using IL-1 blockers after diagnosis of amyloidosis does not appear to improve outcomes [60]. Two studies from Turkey analyzed the efficacy of tocilizumab in 27 adult patients with FMF-related AA amyloidosis [61,62]. In most cases, tocilizumab effectively slowed the progression of amyloidosis and controlled the disease activity. These data confirmed the hypothesis that IL-6 inhibition is mainly effective in FMF patients with renal amyloidosis. However, further prospective studies are needed to determine if IL-1 or IL-6 blockers could be useful in improving outcomes for patients with FMF-related AA amyloidosis.
The role of anakinra in on-demand administration remains unclear. A recent article suggests that a single dose of anakinra effectively prevents disease episodes within 24 h and shortens the duration of hospitalization [63]. Future clinical trials are required to confirm these findings.
Overall, expanding and improving prospective longitudinal registries with the implementation of biobanking will contribute to research efforts aiming to validate biomarkers for monitoring, improve patient outcomes, and ultimately discover novel treatment strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S. and M.R.; methodology, D.P.; validation, M.R., D.P., O.K.C. and E.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R. and E.S.; writing—review and editing, M.R., D.P., O.K.C. and E.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FMF | Familial Mediterranean Fever. |
| YopM | Yersinia pestis virulence factor. |
| VUS | Variance of insignificance. |
| ISSAID | International Society of Autoinflammatory Diseases. |
| SAA | Serum amyloid A. |
| AIDAI | Autoinflammatory Diseases Activity Index. |
| ADDI | Autoinflammatory Disease Damage Index. |
| ISSF | International Severity Score for FMF. |
| MASIF | Medication Adherence Scale in FMF. |
| JAIMAR | Juvenile Autoinflammatory Disease Multidimensional Assessment Report. |
| FAVOR | FMF Arthritis Vasculitis and Orphan Disease Research in pediatric rheumatology. |
| VAS | Visual analog scale. |
References
- Sag, E.; Bilginer, Y.; Ozen, S. Autoinflammatory Diseases with Periodic Fevers. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, F.M.F.C. A candidate gene for familial Mediterranean fever. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International FMF Consortium. Ancient missense mutations in a new member of the RoRet gene family are likely to cause familial Mediterranean fever. Cell 1997, 90, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyoncu, M.; Acar, B.C.; Cakar, N.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Ozturk, S.; Dereli, E.; Tunca, M.; Kasapcopur, O.; Yalcinkaya, F.; Ozen, S. Are carriers for MEFV mutations “healthy”? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, S120–S122. [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann, H.J.; Sengul, B.; Yavuzsen, T.U.; Booth, D.R.; Booth, S.E.; Bybee, A.; Gallimore, J.R.; Soyturk, M.; Akar, S.; Tunca, M.; et al. Clinical and subclinical inflammation in patients with familial Mediterranean fever and in heterozygous carriers of MEFV mutations. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, S.; Sag, E.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; Gattorno, M.; Gul, A.; Hashkes, P.J.; Kone-Paut, I.; Lachmann, H.J.; Tsitsami, E.; Twilt, M.; et al. Defining colchicine resistance/intolerance in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: A modified-Delphi consensus approach. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 3799–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Bilginer, Y. A clinical guide to autoinflammatory diseases: Familial Mediterranean fever and next-of-kin. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, G.S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, P.P.; Feigenbaum, L.; Katz, S.I.; Kastner, D.L. Gain-of-function Pyrin mutations induce NLRP3 protein-independent interleukin-1beta activation and severe autoinflammation in mice. Immunity 2011, 34, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.N.; Peng, X.; Xi, J.J.; Chen, S.; et al. Innate immune sensing of bacterial modifications of Rho GTPases by the Pyrin inflammasome. Nature 2014, 513, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Wood, G.; Kastner, D.L.; Chae, J.J. Pyrin inflammasome activation and RhoA signaling in the autoinflammatory diseases FMF and HIDS. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Remmers, E.F.; Lee, W.; Ombrello, A.K.; Chung, L.K.; Shilei, Z.; Stone, D.L.; Ivanov, M.I.; Loeven, N.A.; Barron, K.S.; et al. Ancient familial Mediterranean fever mutations in human pyrin and resistance to Yersinia pestis. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, A.; Langevitz, P.; Zemer, D.; Zaks, N.; Kees, S.; Lidar, T.; Migdal, A.; Padeh, S.; Pras, M. Criteria for the diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Ozen, S.; Ozcakar, Z.B.; Aktay, N.; Cakar, N.; Duzova, A.; Kasapcopur, O.; Elhan, A.H.; Doganay, B.; Ekim, M.; et al. A new set of criteria for the diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever in childhood. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattorno, M.; Hofer, M.; Federici, S.; Vanoni, F.; Bovis, F.; Aksentijevich, I.; Anton, J.; Arostegui, J.I.; Barron, K.; Ben-Cherit, E.; et al. Classification criteria for autoinflammatory recurrent fevers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sag, E.; Demirel, D.; Demir, S.; Atalay, E.; Akca, U.; Bilginer, Y.; Ozen, S. Performance of the new ‘Eurofever/PRINTO classification criteria’ in FMF patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gijn, M.E.; Ceccherini, I.; Shinar, Y.; Carbo, E.C.; Slofstra, M.; Arostegui, J.I.; Sarrabay, G.; Rowczenio, D.; Omoyimni, E.; Balci-Peynircioglu, B.; et al. New workflow for classification of genetic variants’ pathogenicity applied to hereditary recurrent fevers by the International Study Group for Systemic Autoinflammatory Diseases (INSAID). J. Med. Genet. 2018, 55, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinar, Y.; Obici, L.; Aksentijevich, I.; Bennetts, B.; Austrup, F.; Ceccherini, I.; Costa, J.M.; De Leener, A.; Gattorno, M.; Kania, U.; et al. Guidelines for the genetic diagnosis of hereditary recurrent fevers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, K.; Coskuner, T.; Baglan, E.; Sonmez, H.E.; Yener, G.O.; Cakmak, F.; Demirkan, F.G.; Tanatar, A.; Karadag, S.G.; Ozdel, S.; et al. Real-Life Data From the Largest Pediatric Familial Mediterranean Fever Cohort. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 805919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci-Peynircioglu, B.; Kaya-Akca, U.; Arici, Z.S.; Avci, E.; Akkaya-Ulum, Z.Y.; Karadag, O.; Kalyoncu, U.; Bilginer, Y.; Yilmaz, E.; Ozen, S. Comorbidities in familial Mediterranean fever: Analysis of 2000 genetically confirmed patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancane, G.; Ter Haar, N.M.; Wulffraat, N.; Vastert, S.J.; Barron, K.; Hentgen, V.; Kallinich, T.; Ozdogan, H.; Anton, J.; Brogan, P.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for genetic diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, Z.S.; Romano, M.; Piskin, D.; Guzel, F.; Sahin, S.; Berard, R.A.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Demirkaya, E. Evaluation of E148Q and Concomitant AA Amyloidosis in Patients with Familial Mediterranean Fever. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunoğlu, A.; Erten, Ş.; Canoz, M.B.; Yuksel, A.; Ceylan, G.G.; Balci, S.; Dogan, H.T. Phenotype 2 familial mediterranean fever: Evaluation of 22 case series and review of the literature on phenotype 2 FMF. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, S.; Demirkaya, E.; Erer, B.; Livneh, A.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; Giancane, G.; Ozdogan, H.; Abu, I.; Gattorno, M.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of familial Mediterranean fever. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinar, Y.; Ceccherini, I.; Rowczenio, D.; Aksentijevich, I.; Arostegui, J.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; Boursier, G.; Gattorno, M.; Hayrapetyan, H.; Ida, H.; et al. ISSAID/EMQN Best Practice Guidelines for the Genetic Diagnosis of Monogenic Autoinflammatory Diseases in the Next-Generation Sequencing Era. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booty, M.G.; Chae, J.J.; Masters, S.L.; Remmers, E.F.; Barham, B.; Le, J.M.; Barron, K.S.; Holland, S.M.; Kastner, D.L.; Aksentijevich, I. Familial Mediterranean fever with a single MEFV mutation: Where is the second hit? Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek-Yagel, D.; Berkun, Y.; Padeh, S.; Abu, A.; Reznik-Wolf, H.; Livneh, A.; Pras, M.; Pras, E. Clinical disease among patients heterozygous for familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, F.; Romano, M.; Keles, E.; Piskin, D.; Ozen, S.; Poyrazoglu, H.; Kasapcopur, O.; Demirkaya, E. Next Generation Sequencing Based Multiplex Long-Range PCR for Routine Genotyping of Autoinflammatory Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migita, K.; Agematsu, K.; Masumoto, J.; Ida, H.; Honda, S.; Jiuchi, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Uehara, R.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. The contribution of SAA1 polymorphisms to Familial Mediterranean fever susceptibility in the Japanese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Balci, B.; Kutlay, S.; Ozen, S.; Erturk, S.; Oner, A.; Besbas, N.; Bakkaloglu, A. Analysis of the modifying effects of SAA1, SAA2 and TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms on development of amyloidosis in FMF patients. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2003, 45, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Soylu, A.; Ates, H.; Cingoz, S.; Turkmen, M.; Demir, B.K.; Tunca, M.; Sakizli, M.; Cirit, M.; Ersoy, R.; Ulgenalp, A.; et al. TLR polymorphisms in FMF: Association of TLR-2 (Arg753Gln) and TLR-4 (Asp299Gly, Thre399Ile) polymorphisms and myeloid cell TLR-2 and TLR-4 expression with the development of secondary amyloidosis in FMF. Inflammation 2011, 34, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, I.; Picot, M.C.; Domingo, C.; Notarnicola, C.; Cattan, D.; Demaille, J.; Koné-Paut, I. The MICA region determines the first modifier locus in familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazeneuve, C.; Ajrapetyan, H.; Papin, S.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Geneviève, D.; Mndjoyan, E.; Papazian, M.; Sarkisian, A.; Babloyan, A.; Boissier, B.; et al. Identification of MEFV-independent modifying genetic factors for familial Mediterranean fever. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goldfinger, S.E. Colchicine for familial Mediterranean fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 287, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, E.; Erer, B.; Ozen, S.; Ben-Chetrit, E. Efficacy and safety of treatments in Familial Mediterranean fever: A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, A.; Zemer, D.; Langevitz, P.; Shemer, J.; Sohar, E.; Pras, M. Colchicine in the treatment of AA and AL amyloidosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 23, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallinich, T.; Haffner, D.; Niehues, T.; Huss, K.; Lainka, E.; Neudorf, U.; Schaefer, C.; Stojanov, S.; Timmann, C.; Keitzer, R.; et al. Colchicine use in children and adolescents with familial Mediterranean fever: Literature review and consensus statement. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e474–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Acikel, C.; Sozeri, B.; Dursun, I.; Kasapcopur, O.; Gulez, N.; Simsek, D.; Saldir, M.; Dokurel, I.; Poyrazoglu, H.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy of once- and twice-daily colchicine dosage in pediatric patients with familial Mediterranean fever—A randomized controlled noninferiority trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Zvi, I.; Kukuy, O.; Giat, E.; Pras, E.; Feld, O.; Kivity, S.; Perski, O.; Bornstein, G.; Grossman, C.; Harari, G.; et al. Anakinra for Colchicine-Resistant Familial Mediterranean Fever: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brik, R.; Butbul-Aviel, Y.; Lubin, S.; Ben Dayan, E.; Rachmilewitz-Minei, T.; Tseng, L.; Hashkes, P.J. Canakinumab for the treatment of children with colchicine-resistant familial Mediterranean fever: A 6-month open-label, single-arm pilot study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3241–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetti, F.; Gattorno, M.; Anton, J.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; Frenkel, J.; Hoffman, H.M.; Koné-Paut, I.; Lachmann, H.J.; Ozen, S.; Simon, A.; et al. Canakinumab for the Treatment of Autoinflammatory Recurrent Fever Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1908–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashkes, P.J.; Spalding, S.J.; Giannini, E.H.; Huang, B.; Johnson, A.; Park, G.; Barron, K.S.; Weisman, M.H.; Pashinian, N.; Reiff, A.O.; et al. Rilonacept for colchicine-resistant or -intolerant familial Mediterranean fever: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, H.J.; Lauwerys, B.; Miettunen, P.; Kallinich, T.; Jansson, A.; Rosner, I.; Manna, R.; Murias, S.; Savic, S.; Smeets, S.; et al. Canakinumab improves patient-reported outcomes in children and adults with autoinflammatory recurrent fever syndromes: Results from the CLUSTER trial. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S132), 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Ben-Cherit, E.; Foeldvari, I.; Amarilyo, G.; Ozdogan, H.; Vanderschueren, S.; Marzan, K.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Dekker, E.; De Benedetti, F.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of canakinumab in patients with colchicine-resistant familial Mediterranean fever: Results from the randomized phase III CLUSTER trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henes, J.C.; Saur, S.; Kofler, D.M.; Kedor, C.; Meisner, C.; Schuett, M.; Krusche, M.; Koetter, I.; Xenitidis, T.; Schulze-Koops, H.; et al. Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Familial Mediterranean Fever-A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Sato, S.; Hagimori, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Ishimura, M.; Yasumi, T.; Kirino, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Yachie, A.; Migita, K.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial on the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, P.; Hentgen, V.; Georgin-Lavialle, S. Could tocilizumab be used in familial Mediterranean fever? A systematic review. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyssiere, M.; Sadat Aghamiri, S.; Hernandez Cervantes, A.; Henry, T.; Soumelis, V. A mathematical model of Familial Mediterranean Fever predicts mechanisms controlling inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 257, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Robledo, J.E.; Aragón, C.C.; Nieto-Aristizabal, I.; Posso-Osorio, I.; Cañas, C.A.; Tobón, G.J. Tofacitinib for familial Mediterranean fever: A new alternative therapy? Rheumatology 2019, 58, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, H.; Güler, A.A.; Atas, N.; Satış, H.; Salman, R.B.; Babaoglu, H.; Tufan, A. Tofacitinib for the treatment for colchicine-resistant familial Mediterranean fever: Case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, K.; Cengiz, G.; Erol, K.; Ozgocmen, S. Tofacitinib suppresses disease activity and febrile attacks in a patient with coexisting rheumatoid arthritis and familial Mediterranean fever. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2017, 42, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Piram, M.; Kone-Paut, I.; Lachmann, H.J.; Frenkel, J.; Ozen, S.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.; Stojanov, S.; Simon, A.; Finetti, M.; Sormani, M.P.; et al. Validation of the auto-inflammatory diseases activity index (AIDAI) for hereditary recurrent fever syndromes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koné-Paut, I.; Piram, M.; Benseler, S.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.B.; Jansson, A.; Rosner, I.; Tommasini, A.; Murias, S.; Karadag, O.; Levy, J.; et al. Use of the Auto-inflammatory Disease Activity Index to monitor disease activity in patients with colchicine-resistant Familial Mediterranean Fever, Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency, and TRAPS treated with canakinumab. Jt. Bone Spine 2022, 89, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskin, D.; Arici, Z.S.; Konukbay, D.; Romano, M.; Makay, B.; Ayaz, N.; Bilginer, Y.; Berard, R.A.; Poyrazoglu, H.; Kasapcopur, O.; et al. Number of Episodes Can Be Used as a Disease Activity Measure in Familial Mediterranean Fever. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 822473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, E.; Acikel, C.; Hashkes, P.; Gattorno, M.; Gul, A.; Ozdogan, H.; Turker, T.; Karadag, O.; Livneh, A.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; et al. Development and initial validation of international severity scoring system for familial Mediterranean fever (ISSF). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Haar, N.M.; Annink, K.V.; Al-Mayouf, S.M.; Amaryan, G.; Anton, J.; Barron, K.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Brogan, P.A.; Cantarini, L.; Cattalini, M.; et al. Development of the autoinflammatory disease damage index (ADDI). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Haar, N.M.; van Delft, A.L.J.; Annink, K.V.; van Stel, H.; Al-Mayouf, S.M.; Amaryan, G.; Anton, J.; Barron, K.S.; Benseler, S.; Brogan, P.A.; et al. In silico validation of the Autoinflammatory Disease Damage Index. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Demirkaya, E.; Duzova, A.; Erdogan, O.; Erken, E.; Gul, A.; Kasapcopur, O.; Kasifoglu, T.; Kisacik, B.; Ozdogan, H.; et al. FMF50: A score for assessing outcome in familial Mediterranean fever. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilkaya, S.; Acikel, C.; Fidanci, B.E.; Polat, A.; Sozeri, B.; Ayaz, N.A.; Makay, B.B.; Simsek, D.; Akinci, N.; Ozcelik, G.; et al. Development of a medication adherence scale for familial Mediterranean fever (MASIF) in a cohort of Turkish children. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S156–S162. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, T.; Sato, S.; Furukawa, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawakami, A. Investigating the impact of tocilizumab on serum cytokines concentrations in Japanese FMF patients: A sub-analysis of the NUH01FMF study. Immunol. Med. 2025, 48, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeri, D.J.; Bar, D.; Somech Safran, B.; Druyan, A.; Kukuy, O.L.; Giat, E.; Lidar, M.; Livneh, A. Renal outcomes and survival in amyloidosis associated with familial Mediterranean fever: A longitudinal study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2025, 71, 152642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, S.; Tekgoz, E.; Cinar, M.; Yilmaz, S. The assessment of tocilizumab therapy on recurrent attacks of patients with familial Mediterranean fever: A retrospective study of 15 patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugurlu, S.; Hacioglu, A.; Adibnia, Y.; Hamuryudan, V.; Ozdogan, H. Tocilizumab in the treatment of twelve cases with aa amyloidosis secondary to familial mediterranean fever. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebeci, S.O.; Yildiz, M.; Gunalp, A.; Cebi, M.N.; Kilinc, B.; Pinar, E.; Konte, E.K.; Aslan, E.; Haslak, F.; Adrovic, A.; et al. The efficacy of a single-dose anakinra injection during disease attack in pediatric familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).