Imaging Microstructural Parameters of Breast Tumor in Patient Using Time-Dependent Diffusion: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
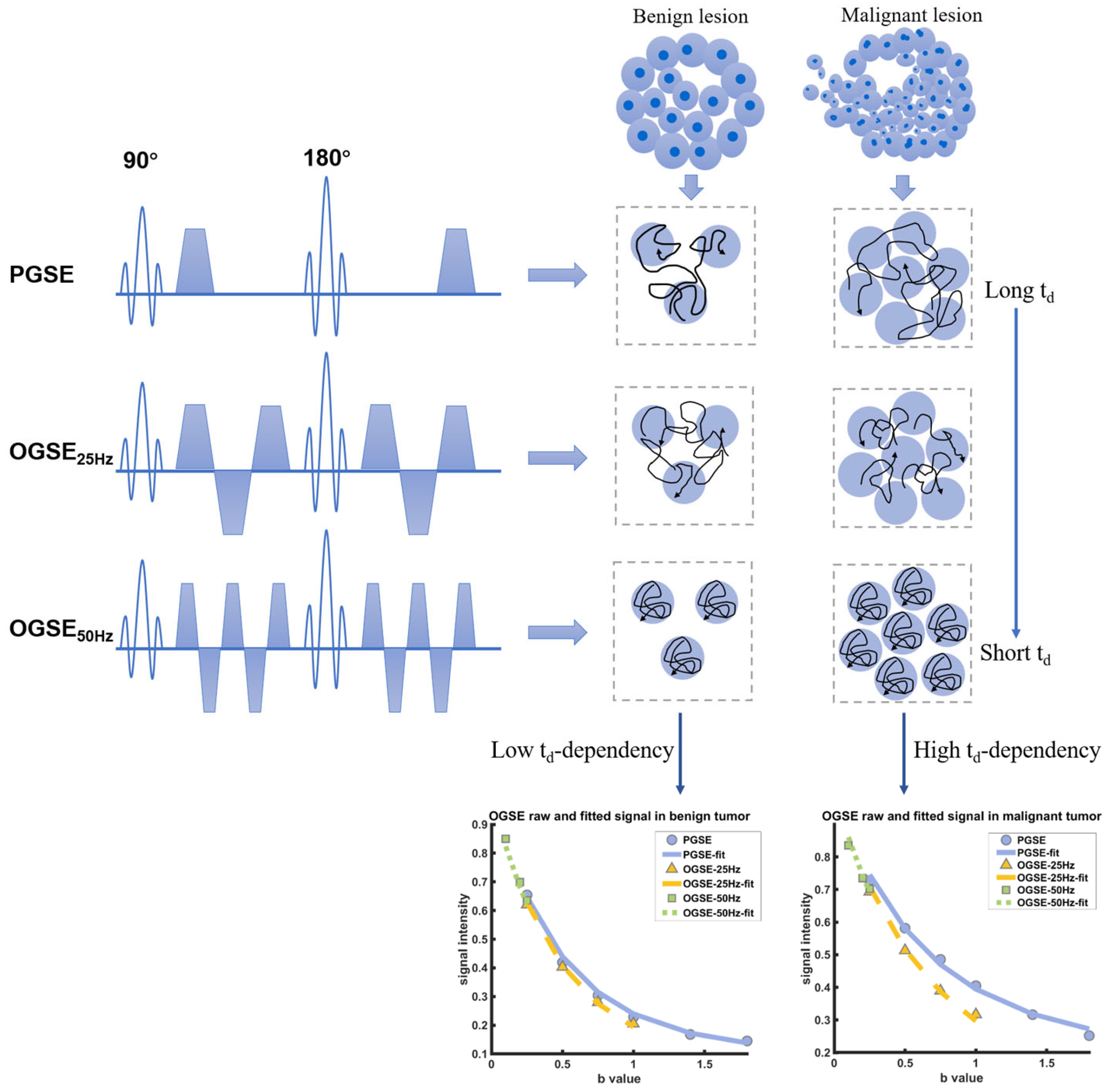
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient
2.2. MRI Data Acquisition
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Histopathologic Analysis
2.5. Statistical
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
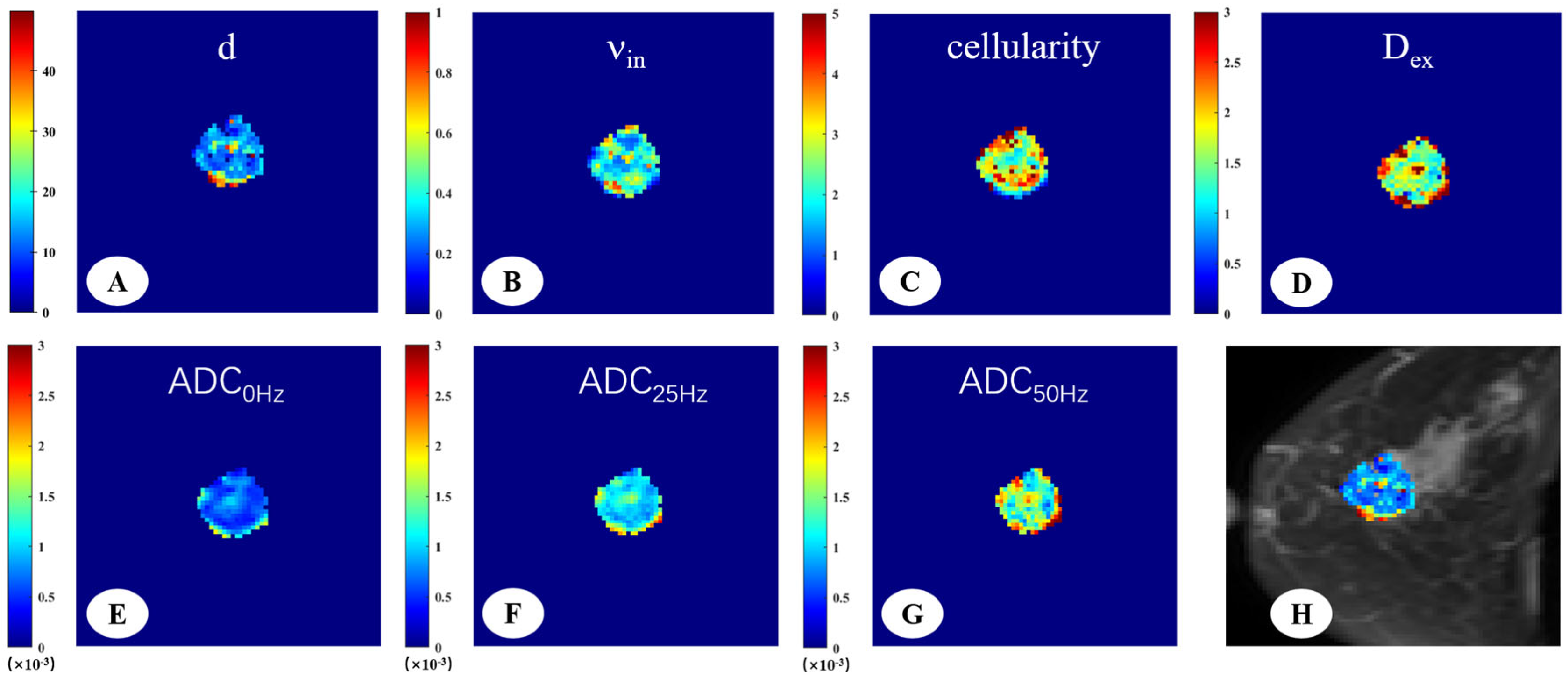
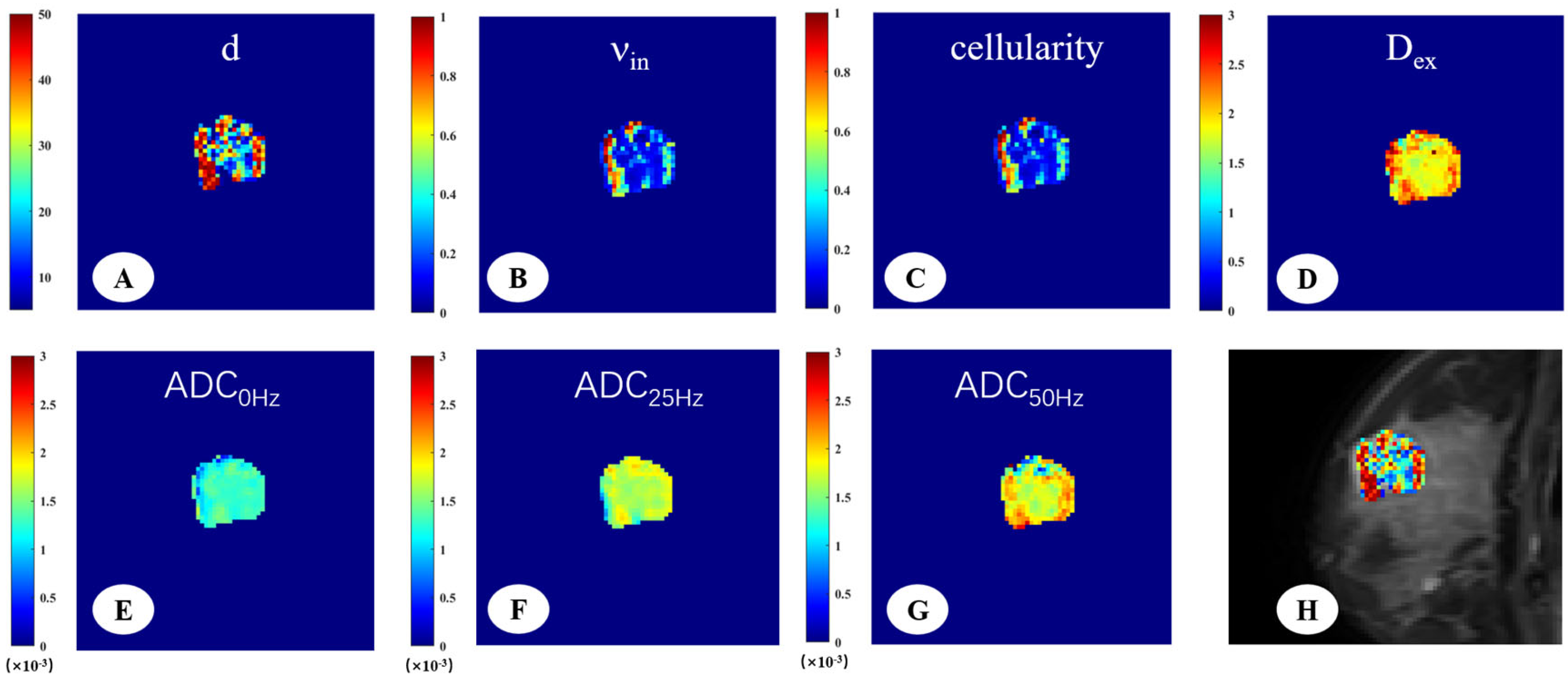
3.2. Microstructural Parameters of Malignant and Benign Breast Tumors
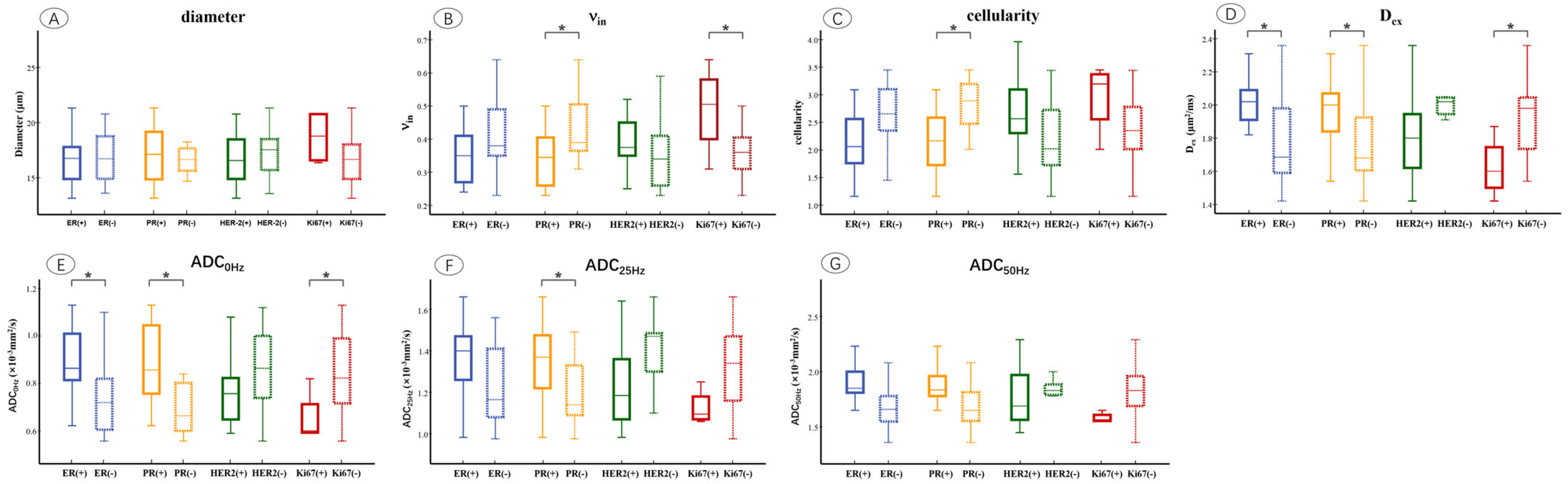
3.3. Microstructural Parameters of Different Immunohistochemical Groups in Breast Tumor
3.4. Diagnostic Performance of Microstructural Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OGSE | Oscillating Gradient Spin-Echo |
| PGSE | Pulsed Gradient Spin-Echo |
| ADC | apparent Diffusion Coefficient |
| AUC | Area Under the receiver operating characteristic Curve |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| DWI | Diffusion-Weighted Imaging |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| HER-2 | Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor-2 |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficients |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristics |
| IDC | Invasive Ductal Carcinomas |
References
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Abramson, V.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Anderson, B.; Bailey, J.; Burstein, H.J.; et al. Breast Cancer, Version 3.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, 331–357. [Google Scholar]
- Fraum, T.J.; Ludwig, D.R.; Bashir, M.R.; Fowler, K.J. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: A comprehensive risk assessment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, A.H.; Zhao, Y.; Farooq, Z.; Prince, M.R. Immediate Allergic Reactions to Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2018, 286, 731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulani, V.; Calamante, F.; Shellock, F.G.; Kanal, E.; Reeder, S.B. Gadolinium deposition in the brain: Summary of evidence and recommendations. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Amornsiripanitch, N.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Shin, H.J.; Dang, M.; Rahbar, H.; Pinker, K.; Partridge, S.C. Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Unenhanced Breast Cancer Screening. Radiology 2019, 293, 504–520. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Choi, H.Y.; Hahn, S.Y. Correlations between apparent diffusion coefficient values of invasive ductal carcinoma and pathologic factors on diffusion-weighted MRI at 3.0 Tesla. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, J.V.; Bernard-Davila, B.; Helbich, T.H.; Zhang, M.; Morris, E.A.; Thakur, S.B.; Ochoa-Albiztegui, R.E.; Leithner, D.; Marino, M.A.; Baltzer, P.A.; et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping as a quantitative imaging biomarker for prediction of immunohistochemical receptor status, proliferation rate, and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 836–846. [Google Scholar]
- Iima, M.; Honda, M.; Sigmund, E.E.; Ohno, K.A.; Kataoka, M.; Togashi, K. Diffusion MRI of the breast: Current status and future directions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 70–90. [Google Scholar]
- Partridge, S.C.; Amornsiripanitch, N. DWI in the Assessment of Breast Lesions. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, D.G.; Garroway, A.N. Measurement of translational displacement probabilities by NMR: An indicator of compartmentation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 14, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafer, A.; Zhong, J.; Gore, J.C. Theoretical model for water diffusion in tissues. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 33, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.R.; Liu, G.; Koh, D.M.; Chenevert, T.L.; Thoeny, H.C.; Takahara, T.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.; Ross, B.D.; Van Cauteren, M.; Collins, D.; et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: Consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, E.O.; Tanner, J.E. Spin diffusion measurements: Spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Xie, J.; McKinley, E.T.; Zhao, P.; Gore, J.C.; Xu, J. In vivo imaging of cancer cell size and cellularity using temporal diffusion spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.C.; Xu, J.; Colvin, D.C.; Yankeelov, T.E.; Parsons, E.C.; Does, M.D. Characterization of tissue structure at varying length scales using temporal diffusion spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, N.; Alvarez, G.A.; Frydman, L. Measuring small compartment dimensions by probing diffusion dynamics via Non-uniform Oscillating-Gradient Spin-Echo (NOGSE) NMR. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 237, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Xie, J.; Zhao, P.; Gore, J.C.; Xu, J. Quantification of cell size using temporal diffusion spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, J.; Obata, T. Oscillating-gradient spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging (OGSE-DWI) with a limited number of oscillations: I. Signal equation. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 326, 106962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Devan, S.P.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; McKinley, E.T.; Xie, J.; Zu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Wang, Y.; et al. MRI-cytometry: Mapping nonparametric cell size distributions using diffusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; McKinley, E.T.; Devan, S.P.; Hardy, B.M.; Xie, J.; Kang, H.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of mean cell size in human breast tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D. Diffusion-time dependent diffusion MRI: Effect of diffusion-time on microstructural mapping and prediction of prognostic features in breast cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 6226–6237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iima, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Kataoka, M.; Yamada, Y.; Omori, K.; Feiweier, T.; Togashi, K. Time-dependent diffusion MRI to distinguish malignant from benign head and neck tumors. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, K.; Kamimura, Y.; Nakano, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakajo, M.; Yamada, C.; Akune, K.; Ejima, F.; Ayukawa, T.; Ito, S.; et al. Differentiating brain metastasis from glioblastoma by time-dependent diffusion MRI. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura, K.; Nakano, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakajo, M.; Yamada, C.; Kamimura, Y.; Akune, K.; Ejima, F.; Ayukawa, T.; Nagano, H.; et al. Differentiating primary central nervous system lymphoma from glioblastoma by time-dependent diffusion using oscillating gradient. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, J.; Gore, J.C. Quantitative temporal diffusion spectroscopy as an early imaging biomarker of radiation therapeutic response in gliomas: A preclinical proof of concept. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, F.; Fukukura, Y.; Kamimura, K.; Nakajo, M.; Ayukawa, T.; Kanzaki, F.; Yanazume, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Kitazono, I.; Imai, H.; et al. Oscillating Gradient Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Risk Stratification of Uterine Endometrial Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Jiang, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ba, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.D. Time-Dependent Diffusion MRI for Quantitative Microstructural Mapping of Prostate Cancer. Radiology 2022, 303, 578–587. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Dudzinski, S.; Beckermann, K.E.; Young, K.; McKinley, E.; McIntyre, J.O.; Rathmell, J.C.; Xu, J.; Gore, J.C. MRI of tumor T cell infiltration in response to checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000328. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Does, M.D.; Gore, J.C. Quantitative characterization of tissue microstructure with temporal diffusion spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 200, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gore, J.C.; Xu, J. Fast and robust measurement of microstructural dimensions using temporal diffusion spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 242, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Devan, S.P.; Xie, J.; Gore, J.C.; Xu, J. Improving MR cell size imaging by inclusion of transcytolemmal water exchange. NMR Biomed. 2022, 35, e4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Anderson, B.O.; Abraham, J.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Blair, S.L.; Burstein, H.J.; Dang, C.; Elias, A.D.; et al. Breast Cancer, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 452–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Devan, S.P.; Gore, J.C.; Xu, J. MR cell size imaging with temporal diffusion spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 77, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.P.; Martins, G.; Carvalhaes, D.O.R.V. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. Magn. Reson. Imaging C 2011, 19, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasa, F.; Pinali, L.; Gasparini, A.; Toniolli, E.; Montemezzi, S. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in focal breast lesions: Analysis of 78 cases with pathological correlation. Radiol. Med. 2011, 116, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasa, F. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging: What Makes Water Run Fast or Slow? J. Clin. Imag. Sci. 2011, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, Y.; Takahashi-Taketomi, A.; Endo, K. Magnetic resonance (MR) differential diagnosis of breast tumors using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on 1.5-T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, W.; Gruber, S.; Pinker, K.; Grabner, G.; Stadlbauer, A.; Weber, M.; Moser, E.; Helbich, T.H.; Trattnig, S. Diffusion-weighted MR for differentiation of breast lesions at 3.0 T: How does selection of diffusion protocols affect diagnosis? Radiology 2009, 253, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zu, T.; Hsu, Y.C.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, R.; Zheng, T.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Inversion-Recovery-Prepared Oscillating Gradient Sequence Improves Diffusion-Time Dependency Measurements in the Human Brain. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 57, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, T.; Hori, M.; Murata, K.; Feiweier, T.; Kamiya, K.; Andica, C.; Hagiwara, A.; Fujita, S.; Kamagata, K.; Wada, A.; et al. Investigation of time-dependent diffusion in extra-axial brain tumors using oscillating-gradient spin-echo. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 96, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Strategies for subtypes—Dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M.; Livasy, C.A.; Dressler, L.G.; Cowan, D.; Conway, K.; Karaca, G.; Troester, M.A.; Tse, C.K.; Edmiston, S.; et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2006, 295, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, J.W.; Suh, H.B.; Hwangbo, L.; Son, Y.; Grimm, R. Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlations with Prognostic Factors and Molecular Subtypes. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 110–120. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | Number |
|---|---|
| Ages (years) | 45.26 ± 10.97 |
| Benign | |
| Fibroadenomas | 15 (83.3%) |
| Phyllodes | 3 (16.7%) |
| Malignant | |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 27 (100%) |
| ER status | |
| Positive | 14 (51.9%) |
| Negative | 13 (48.1%) |
| PR status | |
| Positive | 11 (40.7%) |
| Negative | 16 (59.3%) |
| HER2 status | |
| Positive | 11 (40.7%) |
| Negative | 16 (59.3%) |
| Ki67 | |
| <14% | 4 (14.8%) |
| ≥14% | 23 (85.2%) |
| Tumor subtype | |
| Luminal A | 4 (14.8%) |
| Luminal B | 10 (37.0%) |
| HER2-positive | 7 (25.9%) |
| Triple-negative | 6 (22.2%) |
| Malignant | Benign | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| nin | 0.38 ± 0.10 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | <0.001 * |
| d (μm) | 17.26 ± 2.88 | 24.13 ± 4.54 | <0.001 * |
| Cellularity | 2.48 ± 0.68 | 1.13 ± 0.53 | <0.001 * |
| Dex (μm2/ms) | 1.88 ± 0.25 | 2.24 ± 0.17 | <0.001 * |
| ADC0Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 1.24 ± 0.21 | <0.001 * |
| ADC25Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.30 ± 0.19 | 1.77 ± 0.18 | <0.001 * |
| ADC50Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.81 ± 0.28 | 2.16 ± 0.24 | <0.001 * |
| Parameter | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microstructural parameters | |||
| nin | 0.848 (0.7009–0.937) | 0.963 | 0.667 |
| d (μm) | 0.926 (0.807–0.983) | 1.000 | 0.741 |
| Cellularity | 0.936 (0.821–0.987) | 0.926 | 0.833 |
| Dex (μm2/ms) | 0.870 (0.737–0.952) | 0.944 | 0.667 |
| ADC values | |||
| ADC0Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 0.924 (0.805–0.982) | 0.778 | 1.000 |
| ADC25Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 0.953 (0.844–0.944) | 0.926 | 0.889 |
| ADC50Hz (×10−3 mm2/s) | 0.846 (0.707–0.936) | 0.778 | 0.833 |
| Model 1 | 0.959 (0.853–0.996) | 0.889 | 0.944 |
| Model 2 | 0.969 (0.869–0.998) | 0.889 | 0.944 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, S.; Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhu, W.; Yang, F. Imaging Microstructural Parameters of Breast Tumor in Patient Using Time-Dependent Diffusion: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070823
Peng S, Sun P, Liu J, Tao J, Zhu W, Yang F. Imaging Microstructural Parameters of Breast Tumor in Patient Using Time-Dependent Diffusion: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(7):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070823
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Shuyi, Peng Sun, Jie Liu, Juan Tao, Wenying Zhu, and Fan Yang. 2025. "Imaging Microstructural Parameters of Breast Tumor in Patient Using Time-Dependent Diffusion: A Feasibility Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 7: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070823
APA StylePeng, S., Sun, P., Liu, J., Tao, J., Zhu, W., & Yang, F. (2025). Imaging Microstructural Parameters of Breast Tumor in Patient Using Time-Dependent Diffusion: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics, 15(7), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070823






