Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Clinical Characteristics
2.3. Genetic Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Presentation
3.2. Genetic Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Glisson, F.; Bate, G. Regemorter A Pre-1801 Imprint Collection (Library of Congress). De Rachitide, Typis T. Roycrof. Londini 1660. [Google Scholar]
- Albright, F.; Butler, A.M.; Bloomberg, E. Rickets resistant to vitamin d therapy. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1937, 54, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prader, A.; Illig, R.; Heierli, E. An unusual form of primary vitamin D-resistant rickets with hypocalcemia and autosomal-dominant hereditary transmission: Hereditary pseudo-deficiency rickets. Helv. Paediatr. Acta 1961, 16, 452–468. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, M.A. Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Dependent Rickets. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, S.; Demir, K.; Shi, Y. Genetic Causes of Rickets. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Imel, E.A. Rickets, Vitamin D, and Ca/P Metabolism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2022, 95, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck-Nielsen, S.S.; Brock-Jacobsen, B.; Gram, J.; Brixen, K.; Jensen, T.K. Incidence and Prevalence of Nutritional and Hereditary Rickets in Southern Denmark. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braekeleer, M.D.; Larochelle, J. Population Genetics of Vitamin D-dependent Rickets in Northeastern Quebec. Ann. Human Genet. 1991, 55, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, D.; Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Grund, A.; Schnabel, D. Rickets Guidance: Part I—Diagnostic Workup. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 2013–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, F.; Özgürhan, G.; Kırmızıbekmez, H.; Keskin, E.; Hacıhamdioğlu, B. Genetic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1A. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2019, 11, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodamani, M.H.; Sehemby, M.; Memon, S.S.; Sarathi, V.; Lila, A.R.; Chapla, A.; Bhandare, V.V.; Patil, V.A.; Shah, N.S.; Thomas, N.; et al. Genotype and Phenotypic Spectrum of Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1A: Our Experience and Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, T.; Alos, N.; Chabot, G.; Roughley, P.; Glorieux, F.H.; Rauch, F. Short- and Long-Term Outcome of Patients with Pseudo-Vitamin D Deficiency Rickets Treated with Calcitriol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, F.; Chen, N.; Xue, S. Calcium Intake, Calcium Homeostasis and Health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwitz, C.; Jüppner, H. Regulation of Phosphate Homeostasis by PTH, Vitamin D, and FGF23. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannalire, G.; Pilloni, S.; Esposito, S.; Biasucci, G.; Di Franco, A.; Street, M.E. Alkaline Phosphatase in Clinical Practice in Childhood: Focus on Rickets. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1111445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacher, T.D.; Fischer, P.R.; Pettifor, J.M.; Lawson, J.O.; Manaster, B.J.; Reading, J.C. Radiographic Scoring Method for the Assessment of the Severity of Nutritional Rickets. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2000, 46, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaygusuz, S.B.; Alavanda, C.; Kirkgoz, T.; Eltan, M.; Yavas Abali, Z.; Helvacioglu, D.; Guran, T.; Ata, P.; Bereket, A.; Turan, S. Does Genotype-Phenotype Correlation Exist in Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type IA: Report of 13 New Cases and Review of the Literature. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.T.M.; Vu, C.D.; Dien, T.M.; Can, T.B.N.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Nguyen, H.H.; Tran, V.K.; Nguyen, N.L.; Tran, H.T.; Mai, T.T.C.; et al. Phenotypes, Genotypes, Treatment, and Outcomes of 14 Children with Sitosterolemia at Vietnam National Children’s Hospital. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chen, R.; Lin, X.; Shangguan, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Two Chinese Families with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type IA and Follow-Up. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, N.; Peña, A.S.; Perano, S.; Atkins, G.J.; Findlay, D.M.; Couper, J.J. First Australian Report of Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type I. Med. J. Aust. 2014, 201, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.; Zou, M.; Al-Rijjal, R.A.; Bircan, I.; Akçurin, S.; Meyer, B.; Shi, Y. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Patients with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 77, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Guan, Z.; Mei, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Su, L.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, R.; Liang, C.; Cai, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Long-Term Outcomes of 12 Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Retrospective Study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1007219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchlani, R.; Nemer, P.; Sinha, R.; Nemer, L.; Krishnappa, V.; Sochett, E.; Safadi, F.; Raina, R. An Overview of Rickets in Children. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, A.; Doneray, H. The Genetics and Clinical Manifestations of Patients with Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1A. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjørup, H.; Beck-Nielsen, S.S.; Haubek, D. Craniofacial and Dental Characteristics of Patients with Vitamin-D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A Compared to Controls and Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Demirbilek, H.; Ozbek, M.N.; Baran, R.T.; Tanriverdi, S.; Hussain, K. Genotype and Phenotype Characteristics in 22 Patients with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type I. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2016, 85, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiosano, D.; Hochberg, Z. Hypophosphatemia: The Common Denominator of All Rickets. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2009, 27, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, A.D. Radiology of Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Rickets and Other Bony Fragility States. Endocr. Dev. 2015, 28, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Evaluation Site | Grade | Radiographic Features |
|---|---|---|
| Radius and ulna | 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Widened growth plate, irregularity of metaphyseal margins, no concave cupping | |
| 2 | Metaphyseal concavity with fraying of margins | |
| Femur and tibia | 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Partial lucency, smooth metaphyseal margin visible | |
| 2 | Partial lucency, smooth metaphyseal margin not visible | |
| 3 | Complete lucency, epiphysis appears widely separated from distal metaphysis | |
| Multiplier | Multiplier 0.5 | |
| Multiplier 1 | ||
| Characteristics | Parameter (n = 19) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 10 (52.6%) |
| Female | 9 (47.4%) | |
| Age of diagnosis, rickets (months) | 19.2 [8.3–34.4] | |
| Time of diagnosis, VDDR1A (months) | 7.5 [1.1–148.0] | |
| Delayed walking | 11 (57.9%) | |
| Frontal bossing | 10 (52.6%) | |
| Thickened wrists and ankles | 19 (100%) | |
| Genu varum or genu valgum | 18 (94.7%) | |
| Rachitic rosary | 12 (63.2%) | |
| Bone fractures | 2 (10.5%) | |
| Seizures | 6 (31.5%) | |
| Chest deformities | 10 (52.6%) | |
| Tooth eruption (months) | 7.5 [6.0–22.0] | |
| Delayed tooth eruption | 6/17 (35.3%) | |
| Yellowish enamel or fragile teeth | 14/19 (73.7%) | |
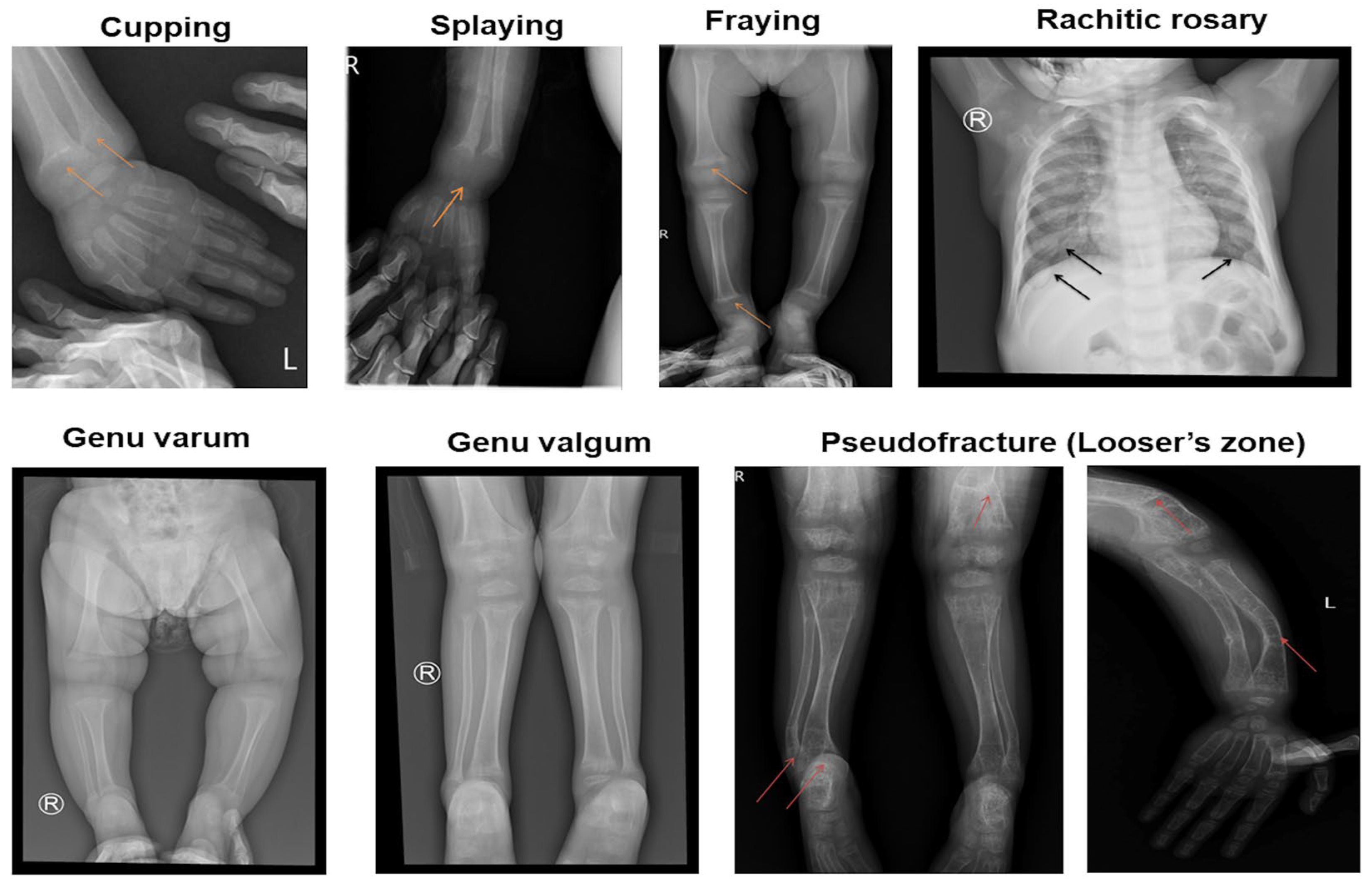
| X-ray features | Cupping and splaying | 19 (100%) |
| Fraying | 19 (100%) | |
| Rachitic rosary | 12 (63.2%) | |
| Pseudofracture (Looser’s zone) | 6 (31.6%) | |
| Rickets Severity Score = 10 | 19 (100%) | |
| Subclinical Testings | Normal Range | n | Results | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total serum calcium (mmol/L) | 2.2–2.6 | 19 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 18 hypocalcemia |
| Serum phosphate (mmol/L) | 1.05–1.95 | 19 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 11 hypophosphatemia |
| Alkaline phosphatase (UI/L) | 156–369 | 18 | 1644.2 ± 917.1 | 18 elevated |
| Parathyroid hormone (ng/L) | 11–69 | 16 | 457.7 ± 260.7 | 16 elevated |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D (nmol/L) | 50–250 | 17 | 140.5 ± 109.0 |
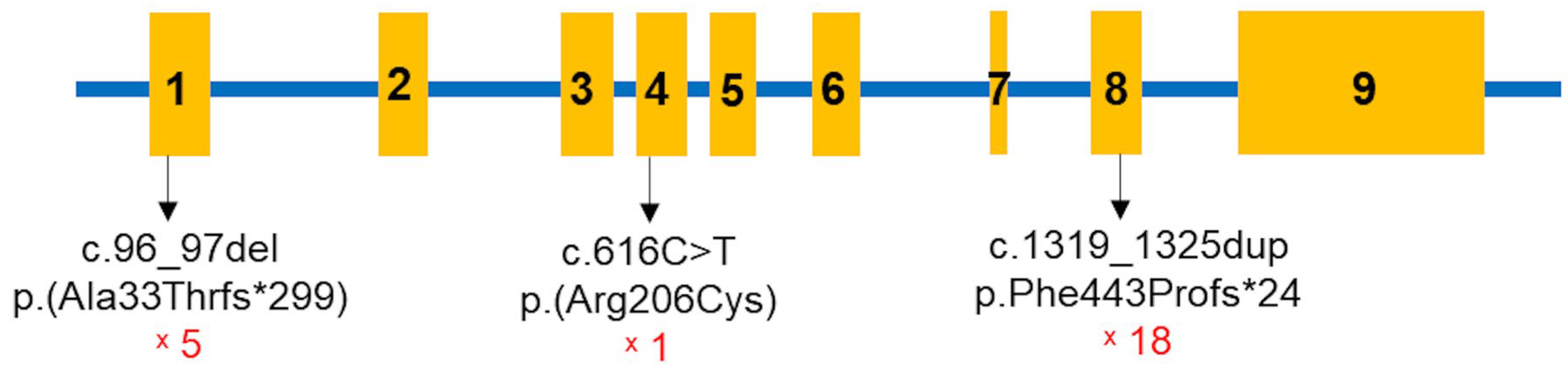
| Patient | Sex | Age of Onset (Months) | Age of Diagnosis (Months) | Exon | State in the Children | c.DNA Change | Protein Change | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 12.1 | 160.9 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 2a | M | 24.9 | 43.0 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 2b | F | 28.5 | 28.6 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 3 | M | 22.9 | 105.5 | 1/4 | Compound heterozygous | c.96_97del/ c.616C>T | p.Ala33Thrfs*299/ p.Arg206Cys | n/a |
| 4a | F | 11.1 | 11.2 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 4b | M | 17.5 | 70.4 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Paternal/Maternal |
| 5 | F | 19.3 | 21.8 | 8/1 | Compound heterozygous | c.1319_1325dup/ c.96_97del | p.Phe443Profs*24/ p.Ala33Thrfs*299 | Paternal/Maternal |
| 6 | F | 31.4 | 50.0 | 8/1 | Compound heterozygous | c.1319_1325dup/ c.96_97del | p.Phe443Profs*24/p.Ala33Thrfs*299 | n/a |
| 7 | F | 17.1 | 18.1 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 8 | F | 25.0 | 101.1 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 9 | F | 20.4 | 21.8 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 10 | M | 14.4 | 47.3 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 11 | M | 34.4 | 37.1 | 8/1 | Compound heterozygous | c.1319_1325dup/ c.96_97del | p.Phe443Profs*24/p.Ala33Thrfs*299 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 12 | F | 15.1 | 15.7 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | n/a |
| 13 | M | 25.2 | 110.0 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Paternal/Maternal |
| 14 | M | 13.5 | 14.6 | 8 | Compound heterozygous | c.1319_1325dup/ c.96_97del | p.Phe443Profs*24/p.Ala33Thrfs*299 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 15 | M | 20.2 | 167.3 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 16 | M | 12.3 | 13.4 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Maternal/Paternal |
| 17 | F | 8.3 | 11.1 | 8 | Homozygous | c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | n/a |
| c.DNA Change | Aa Change | Effect | Mutation Taster | dbSNP155 | ClinVar | ACMG Classification | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.96_97delAG | p.Ala33Thrfs*299 | Frameshift | Disease causing | rs1955367513 | Pathogenic | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | Novel |
| c.616C>T | p.Arg206Cys | Missense | Disease causing | Likely pathogenic (PM2, PM3, PP3, and PP4) | Novel | ||
| c.1319_1325dup | p.Phe443Profs*24 | Frameshift | Disease causing | rs780950819 | Pathogenic | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PM3, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | [10,17,20,21,22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, T.A.T.; Dien, T.M.; Nguyen, N.L.; Nguyen, K.N.; Can, T.B.N.; Thao, B.P.; Hong, N.T.T.; Tran, V.K.; Tran, T.H.; Khoa, N.X.; et al. Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070918
Tran TAT, Dien TM, Nguyen NL, Nguyen KN, Can TBN, Thao BP, Hong NTT, Tran VK, Tran TH, Khoa NX, et al. Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(7):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070918
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Thi Anh Thuong, Tran Minh Dien, Ngoc Lan Nguyen, Khanh Ngoc Nguyen, Thi Bich Ngoc Can, Bui Phuong Thao, Nguyen Thi Thuy Hong, Van Khanh Tran, Thinh Huy Tran, Ngo Xuan Khoa, and et al. 2025. "Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam" Diagnostics 15, no. 7: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070918
APA StyleTran, T. A. T., Dien, T. M., Nguyen, N. L., Nguyen, K. N., Can, T. B. N., Thao, B. P., Hong, N. T. T., Tran, V. K., Tran, T. H., Khoa, N. X., Lien, N. T. K., Tao, N. T., Nguyen, H. H., & Vu, C. D. (2025). Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam. Diagnostics, 15(7), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070918







