Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Background
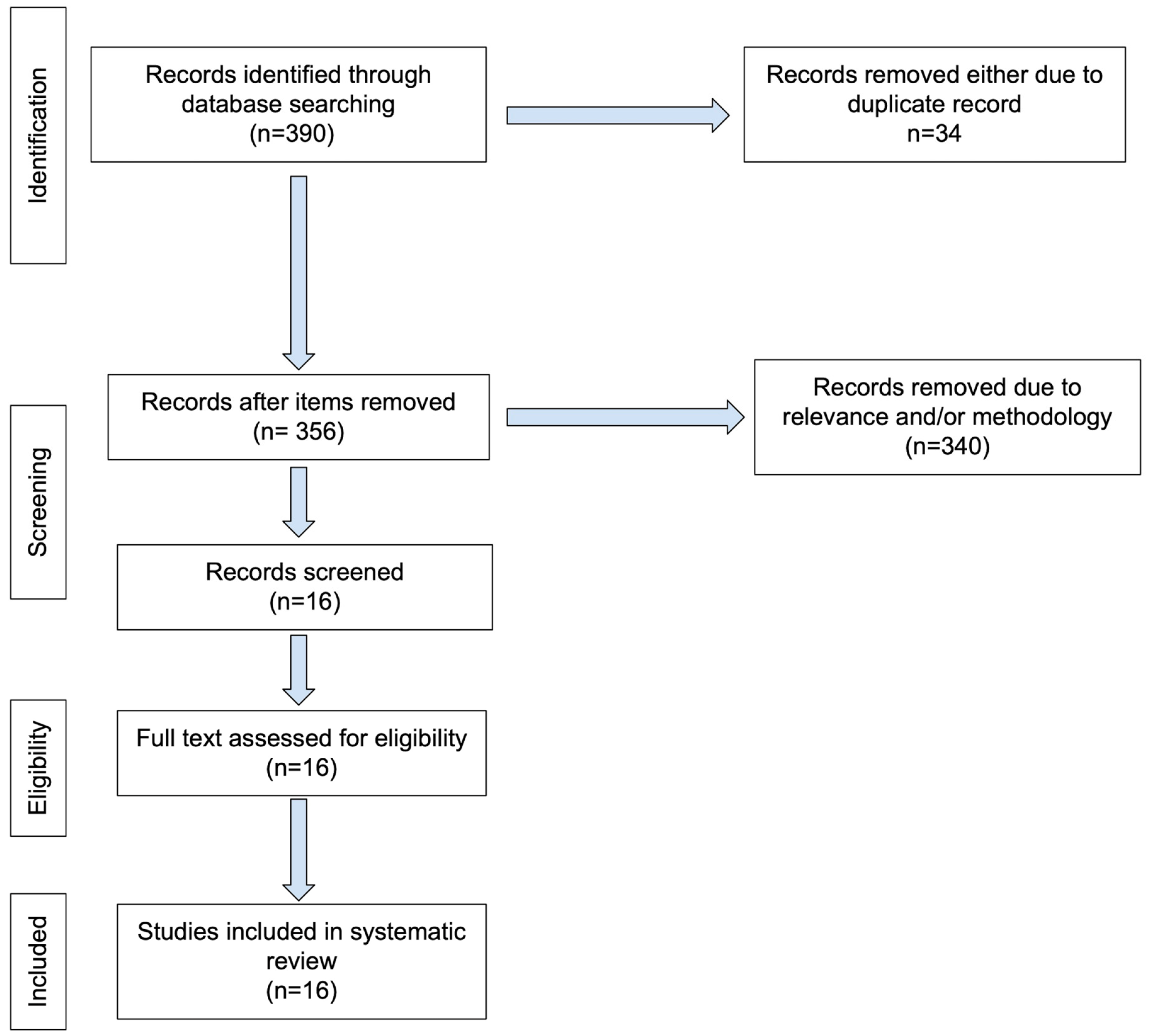
2. Materials and Methods
Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Summary of Individual Papers
4.1.1. Texture/Radiomic Features
4.1.2. Radiologist-Defined MRI Features
4.1.3. Other Methods
4.2. Summary of Lessons Learned
4.3. Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ODXRS | Oncotype DX Recurrence Score |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| DCE-MRI | Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristics |
| AUC | Area under Receiver Operating Characteristics |
References
- Kaklamani, V. A genetic signature can predict prognosis and response to therapy in breast cancer: Oncotype DX. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2006, 6, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, M.; Sangli, C.; Liu, M.L.; Pho, M.; Dutta, D.; Nguyen, A.; Jeong, J.; Wu, J.; Langone, K.C.; Watson, D. Analytical validation of the Oncotype DX genomic diagnostic test for recurrence prognosis and therapeutic response prediction in node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinsky, K.; Barlow, W.E.; Gralow, J.R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Lin, N.U.; Perez, E.A.; Goldstein, L.J.; Chia, S.K.; et al. 21-gene assay to inform chemotherapy benefit in node-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2336–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustovski, F.; Soto, N.; Caporale, J.; Gonzalez, L.; Gibbons, L.; Ciapponi, A. Decision-making impact on adjuvant chemotherapy allocation in early node-negative breast cancer with a 21-gene assay: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Q.; Xie, S.J.; Wu, S.G.; He, Z.Y. Impact of the 21-gene expression assay on treatment decisions and clinical outcomes in breast cancer with one to three positive lymph nodes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1103949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jagsi, R.; Griffith, K.A.; Harris, E.E.; Wright, J.L.; Recht, A.; Taghian, A.G.; Lee, L.; Moran, M.S.; Small, W., Jr.; Johnstone, C.; et al. Omission of Radiotherapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery for Women with Breast Cancer with Low Clinical and Genomic Risk: 5-Year Outcomes of IDEA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chevli, N.; Haque, W.; Tran, K.T.; Farach, A.M.; Schwartz, M.R.; Hatch, S.S.; Butler, E.B.; Teh, B.S. 21-Gene recurrence score predictive for prognostic benefit of radiotherapy in patients age ≥ 70 with T1N0 ER/PR + HER2− breast cancer treated with breast conserving surgery and endocrine therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 174, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, K.F.; Danciu, O.C.; Ko, N.Y.; Calip, G.S. Association of Race/Ethnicity and the 21-Gene Recurrence Score with Breast Cancer-Specific Mortality Among US Women. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saad Abdalla Al-Zawi, A.; Anichkina, K.A.; Elamass, M.; Aladili, Z. Correlation of Ki-67 proliferative index with oncotype DX recurrence score in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early breast cancer with low-burden axillary nodal disease—A review of 137 cases. Pol. J. Pathol. 2024, 75, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X. MRI-based radiomics approach for the prediction of recurrence-free survival in triple-negative breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy. Medicine 2023, 102, e35646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’Donnell, J.P.M.; Gasior, S.A.; Davey, M.G.; O’Malley, E.; Lowery, A.J.; McGarry, J.; O’Connell, A.M.; Kerin, M.J.; McCarthy, P. The accuracy of breast MRI radiomic methodologies in predicting pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 157, 110561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesapane, F.; De Marco, P.; Rapino, A.; Lombardo, E.; Nicosia, L.; Tantrige, P.; Rotili, A.; Bozzini, A.C.; Penco, S.; Dominelli, V.; et al. How Radiomics Can Improve Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Burnside, E.S.; Drukker, K.; Hoadley, K.A.; Fan, C.; Conzen, S.D.; Whitman, G.J.; Sutton, E.J.; Net, J.M.; et al. MR Imaging Radiomics Signatures for Predicting the Risk of Breast Cancer Recurrence as Given by Research Versions of MammaPrint, Oncotype DX, and PAM50 Gene Assays. Radiology 2016, 281, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Harowicz, M.R.; Wang, W.; Mazurowski, M.A. A study of association of Oncotype DX recurrence score with DCE-MRI characteristics using multivariate machine learning models. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.J.; Park, H.; Ko, E.S.; Lim, Y.; Cho, H.H.; Lee, J.E. Radiomics signature on 3T dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for estrogen receptor-positive invasive breast cancers. Medicine 2019, 98, e15871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Shen, X.; Gong, J.; Gu, Y.; Peng, W. Multiparametric MR Imaging Radiomics Signatures for Assessing the Recurrence Risk of ER+/HER2− Breast Cancer Quantified with 21-Gene Recurrence Score. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiacchiaretta, P.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Luberti, R.; Croce, P.; Sguera, M.; Torrione, C.; Marinelli, C.; Marchetti, C.; Domenico, A.; et al. MRI-Based Radiomics Approach Predicts Tumor Recurrence in ER +/HER2− Early Breast Cancer Patients. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, V.; Cuocolo, R.; Sanduzzi, L.; Carpentiero, V.; Caruso, M.; Lama, B.; Garifalos, D.; Stanzione, A.; Maurea, S.; Brunetti, A. MRI Radiomics and Machine Learning for the Prediction of Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score in Invasive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arefan, D.; Zuley, M.L.; Berg, W.A.; Yang, L.; Sumkin, J.H.; Wu, S. Assessment of Background Parenchymal Enhancement at Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI in Predicting Breast Cancer Recurrence Risk. Radiology 2024, 310, e230269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Cui, Y.; You, C.; Liu, L.; Gu, Y.; Peng, W.; Bai, Q.; Gao, X.; Li, L. Radiogenomic Signatures of Oncotype DX Recurrence Score Enable Prediction of Survival in Estrogen Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer: A Multicohort Study. Radiology 2022, 302, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, H.H.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Chae, E.Y. Association between Oncotype DX recurrence score and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI features in patients with estrogen receptor-positive HER2-negative invasive breast cancer. Clin. Imaging 2021, 75, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, F.; Magri, V.; Moffa, G.; Rizzo, V.; Botticelli, A.; Cortesi, E.; Pediconi, F. Precision Medicine in Breast Cancer: Do MRI Biomarkers Identify Patients Who Truly Benefit from the Oncotype DX Recurrence Score® Test? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialani, V.; Gaur, S.; Mehta, T.S.; Venkataraman, S.; Fein-Zachary, V.; Phillips, J.; Brook, A.; Slanetz, P.J. Prediction of Low versus High Recurrence Scores in Estrogen Receptor–Positive, Lymph Node–Negative Invasive Breast Cancer on the Basis of Radiologic-Pathologic Features: Comparison with Oncotype DX Test Recurrence Scores. Radiology 2016, 280, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, H.; Tsukada, J.; Ochi, T.; Noguchi, E.; Okamoto, T. Radiological predictive factors on preoperative multimodality imaging are related to Oncotype DX recurrence score in estrogen-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative invasive breast cancer: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2022, 36, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Hwangbo, L.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, N.K.; Nam, K.J.; Choo, K.S.; Kang, T.; Park, H.; Son, Y.; et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI of estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-negative breast cancer: Association between intratumoral heterogeneity and recurrence risk. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.B.; Durando, M.; Milans, S.; Cho, G.Y.; Gennaro, L.; Sutton, E.J.; Giri, D.; Morris, E.A. Apparent diffusion coefficient in estrogen receptor-positive and lymph node-negative invasive breast cancers at 3.0T DW-MRI: A potential predictor for an oncotype Dx test recurrence score. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sadinski, M.; Haddad, D.; Bae, M.S.; Martinez, D.; Morris, E.A.; Gibbs, P.; Sutton, E.J. Background Parenchymal Enhancement on Breast MRI as a Prognostic Surrogate: Correlation with Breast Cancer Oncotype Dx Score. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 595820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.; Chang, P.; Mutasa, S.; Karcich, J.; Goodman, S.; Blum, E.; Kalinsky, K.; Liu, M.Z.; Jambawalikar, S. Convolutional Neural Network Using a Breast MRI Tumor Dataset Can Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Adam, R.; Huang, P.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review. Tomography 2022, 8, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanmu, H.; Ren, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep learning prediction of pathological complete response, residual cancer burden, and progression-free survival in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280148. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, R.; Dell’Aquila, K.; Hodges, L.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep learning applications to breast cancer detection by magnetic resonance imaging: A literature review. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Source | Duration | # of pts | High/Mid | Low | Image Type | Method | Classifier | Cross-Validation | AUC | Accu | Sens | Spec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texture/radiomic features | |||||||||||||
| Li (2016) [13] | TCIA | 84 | DCE | Texture features | Logistic regression | LOOCV | 88% (MammaPrint) 76% (ODX) | ||||||
| Saha (2018) [14] | Duke | 1 Jan 2000–23 Mar 2014 | 261 | 116 | 145 | DCE | Texture features | Logistic regression | Training, independent | 77% (high vs. mid/low) 51% (low vs. high/mid) | |||
| Nam (2019) [15] | Republic of Korea | May 2011–Mar 2016 | 67 | 3, 19 | 45 | DCE | Texture features | Logistic regression | LOOCV | 75.90% | |||
| Chen (2023) [16] | China | Apr 2017–Mar 2019 | 151 (T:106, V: 45) | 88 | 63 | T2WI, ADC, DCE | Radiomics features | Linear support vector machine | 92% (multiparametric) 83% (DCE), 78% (T2WI), 77% (ADC) | ||||
| Chiacchiaretta (2023) [17] | Italy | Jan 2016–May 2020 | 62 | 15 | 47 | DCE-MRI | Radiomics features (nCV, TST) | Partial least square (PLS) regression | nCV | 76% (nCV) 61% (TST) | |||
| Romeo (2023) [18] | Italy | 1 Jan 2000–23 Mar 2014 | 248 | 87 (+) | 161 (−) | Subtracted DCE | Radiomics features | Logistic regression | Hold-out | 66% | 63% | 80% | 45% |
| Arefan (2024) [19] | U of Pittsburgh | Jan 2007– Jan 2017 | 187 (T:127, V:60) | 16 | 44 | DCE-MRI | Tumor radiomics+ BPE | Linear discriminant analysis | 10-fold | 79% | |||
| Fan (2022) [20] | China | Aug 2015–Oct 2019 | 381 | 118 | 12 | DCE | Radiogenomic signatures (elastic net regression) | Multivariate Cox proportional hazards | 10-fold | 85% | |||
| Radiologist-defined features | |||||||||||||
| Kim (2021) [21] | Republic of Korea | Jan 2015– Dec 2018 | 473 | 197 | 288 | DCE | Radiologist-defined features; Washin/washout | Logistic regression | 84% | 52.2% | 71% | ||
| Galati (2022) [22] | Italy | Apr 2017– Jan 2018 | 58 | 23 | 35 | T2WI, ADC, DCE | Radiologist-defined MRI features | Logistic regression | |||||
| Dialani (2016) [23] | Beth Israel Deaconess | 1 Jan 2009–31 Dec 2013 | 319 | 147 | 172 | MMG, US, MRI | Radiologist-defined MRI features | Analysis of variance, Regression | None | 89% | 83% | ||
| Tsukada (2022) [24] | Japan | Jan 2007– Jan 2012 | 51 | 19 | 32 | MMG, US, DCE, PET/CT | BI-RADS, MRI, PET/CT SUV analysis | Logistic regression | 92.30% | 94.40% | 73.00% | ||
| Others | |||||||||||||
| Kim (2020) [25] | Republic of Korea | Jul 2015– Jul 2018 | 105 | 31 | 74 | ADC | ADC thresholding | Multivariate regression analysis | None | 72% | |||
| Thakur (2018) [26] | Memorial Sloan | Jan 2011–2013 | 31 | 10 | 21 | ADC | ADC thresholding | Non-parametric Mann-Whitney’s test | None | 78.5% (ADC600), 79.3% (ADC1000) | |||
| Zhang (2021) [27] | America | 2008–2010 | 80 | 34 | 46 | Post-contrast BPE | K-means (Multiple post-contrast) | Mann-Whitney U test | |||||
| Ha (2019) [28] | Columbia U | Jan 2010– Jun 2016 | 134 | 17, 40 | 77 | T1 post | Deep learning method | Convolutional Neural Network | 5-fold | 92% (3-class), 92% (2-class) | 81% (3-class), 84% (2-class) | 60% (3-class), 87% (2-class) | 90% (3-class), 81% (2-class) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Adam, R.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091054
Kim N, Adam R, Maldjian T, Duong TQ. Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091054
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nathan, Richard Adam, Takouhie Maldjian, and Tim Q. Duong. 2025. "Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091054
APA StyleKim, N., Adam, R., Maldjian, T., & Duong, T. Q. (2025). Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091054







