Identification of PECAM1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
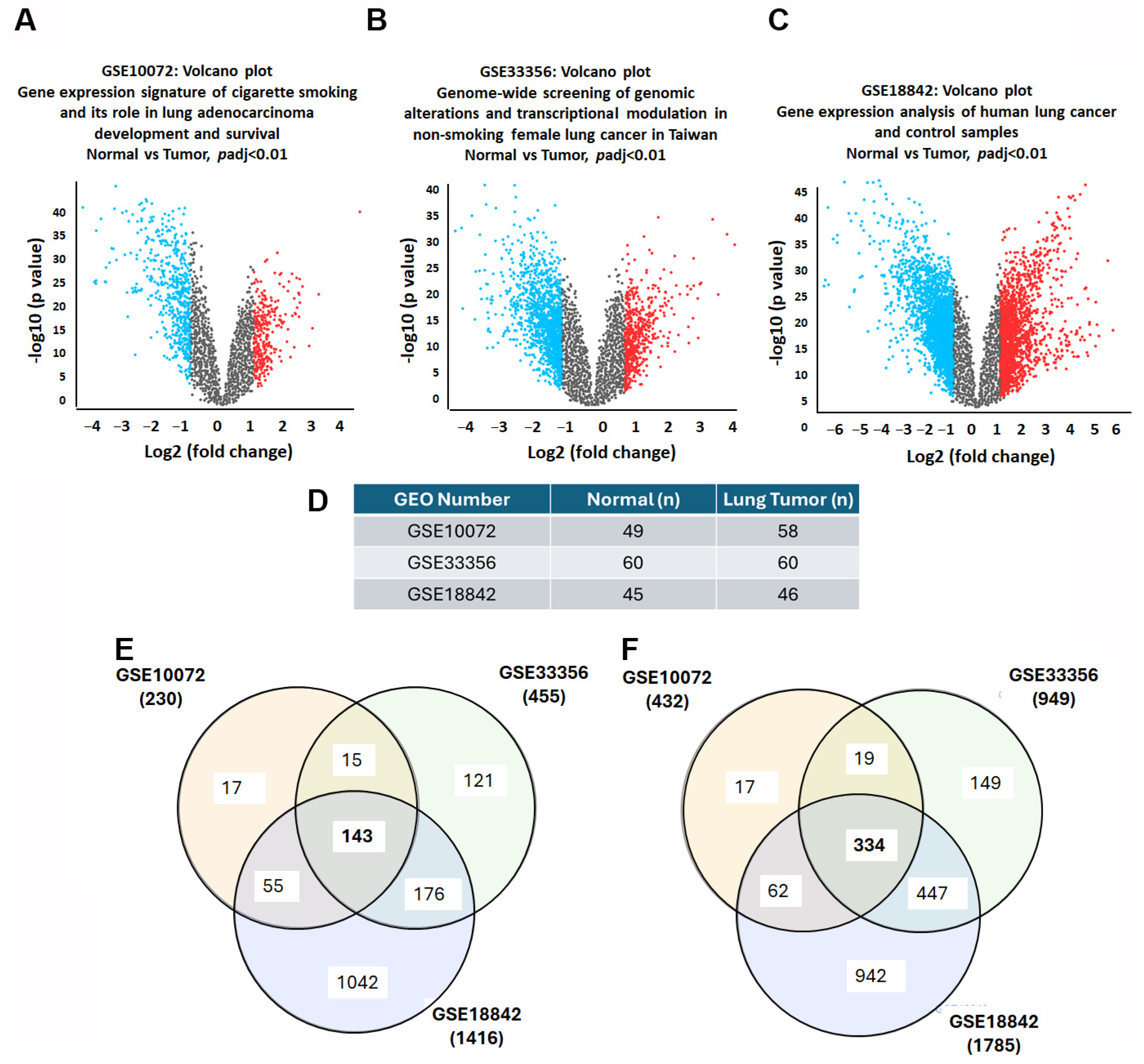
2.2. Filtering Differentially Expressed Genes in Lung Cancer
2.3. GO and KEGG Analysis of DEGs
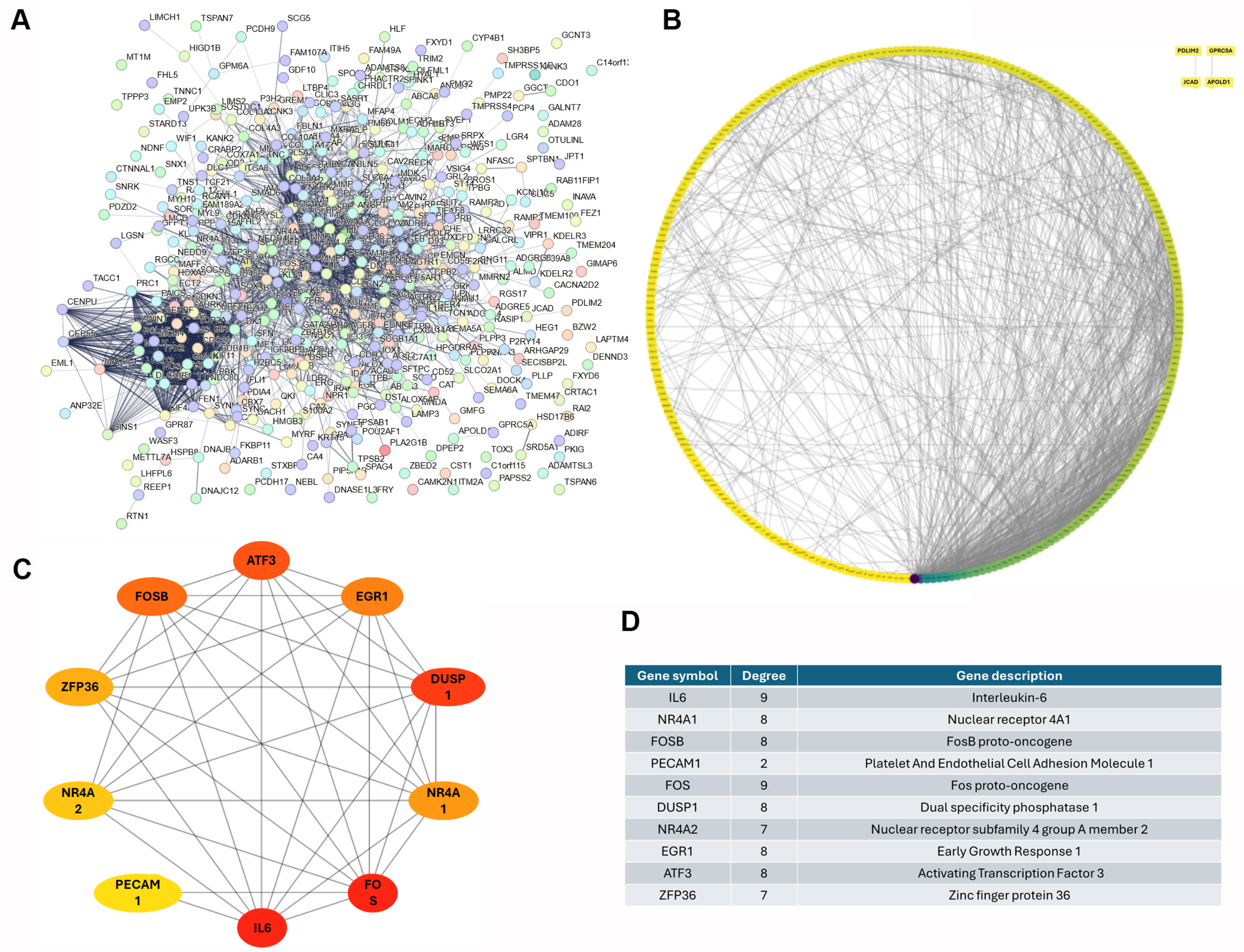
2.4. Investigation of Protein–Protein Interactions and Hub Genes
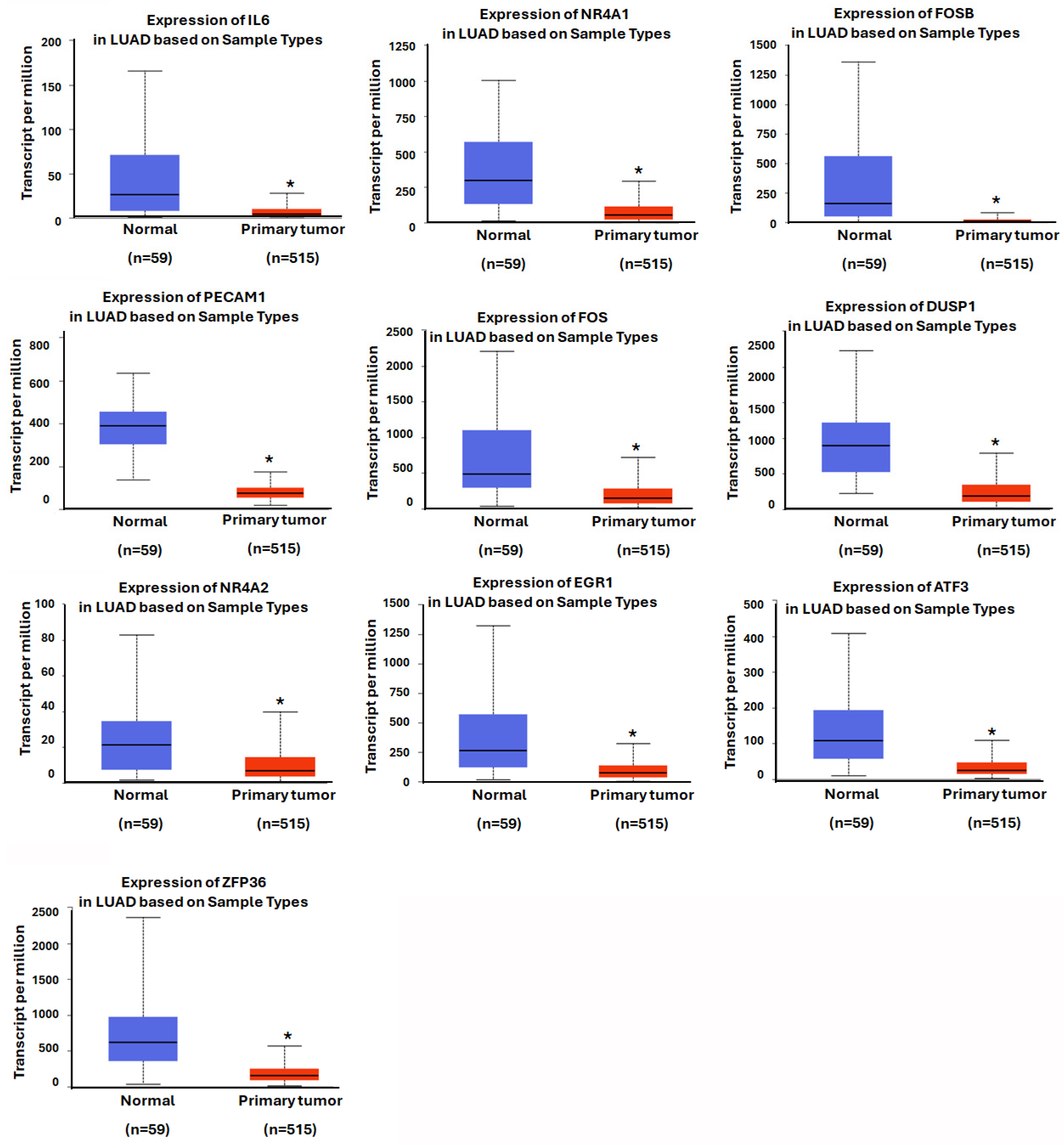
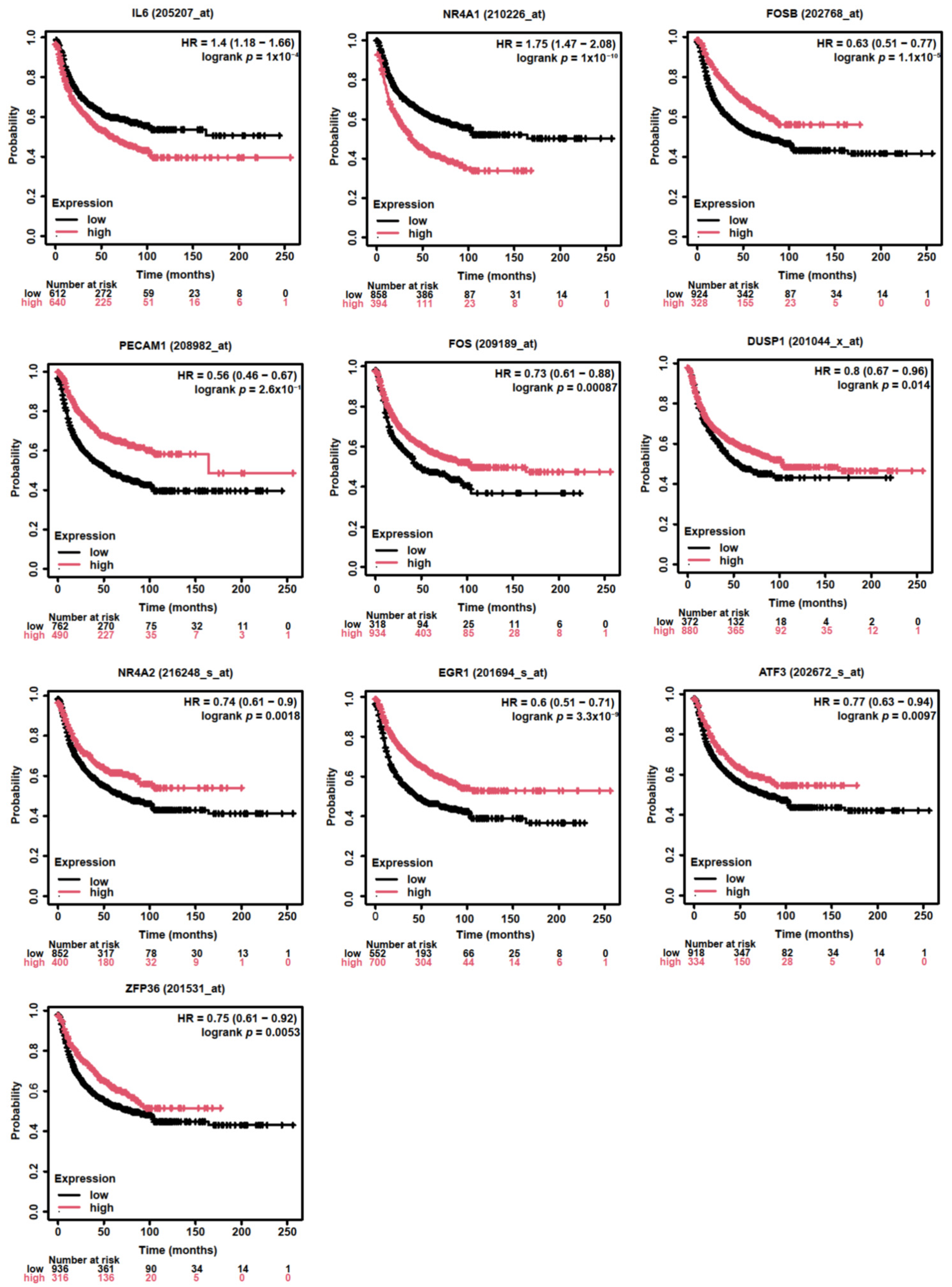
2.5. Genomic Expression and Prognosis of Hub Genes in LUAD
2.6. TIMER2.0 Analysis of DEG Expression in Pan-Cancer and Immune Cell Correlations
2.7. Analyzing Multi-Omics Data in LinkedOmics Suite
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Unveiling the Landscape of DEGs in Lung Cancer
3.2. Deciphering the Functional Roles of DEGs in Lung Cancer
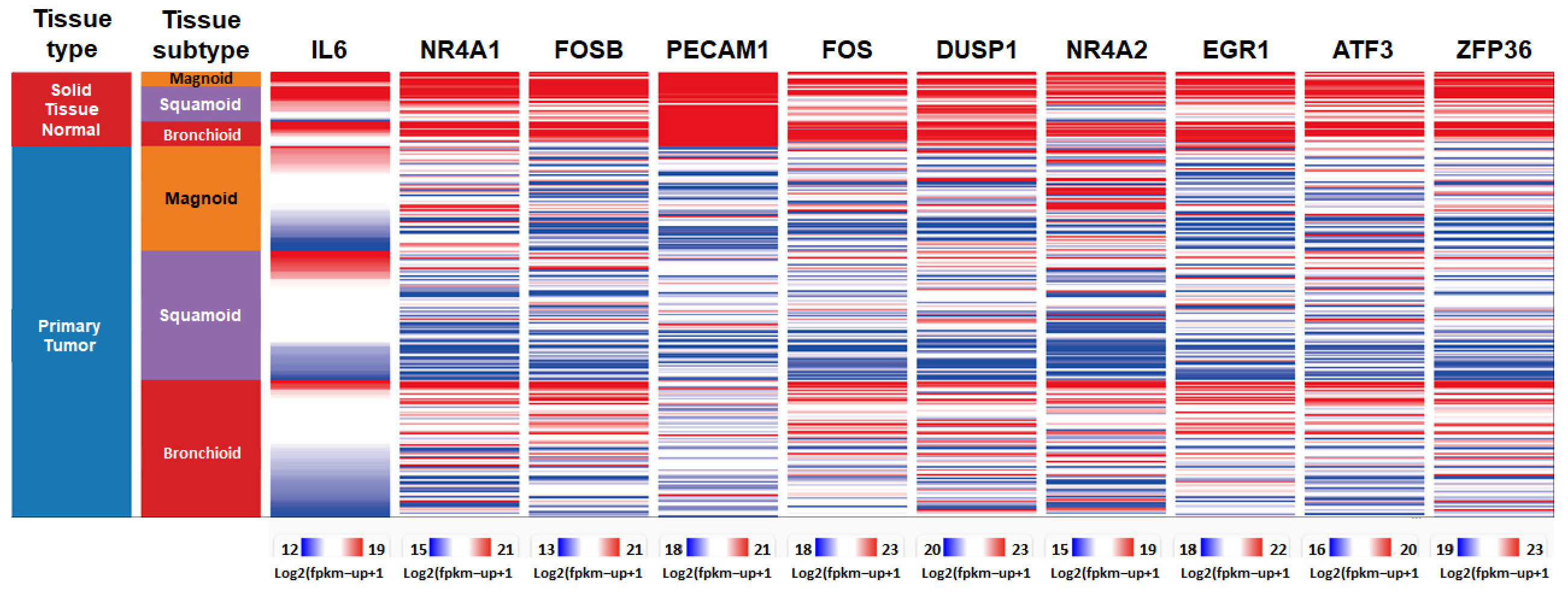
3.3. Identification of Top 10 Down-Regulated Hub Genes in Lung Cancer
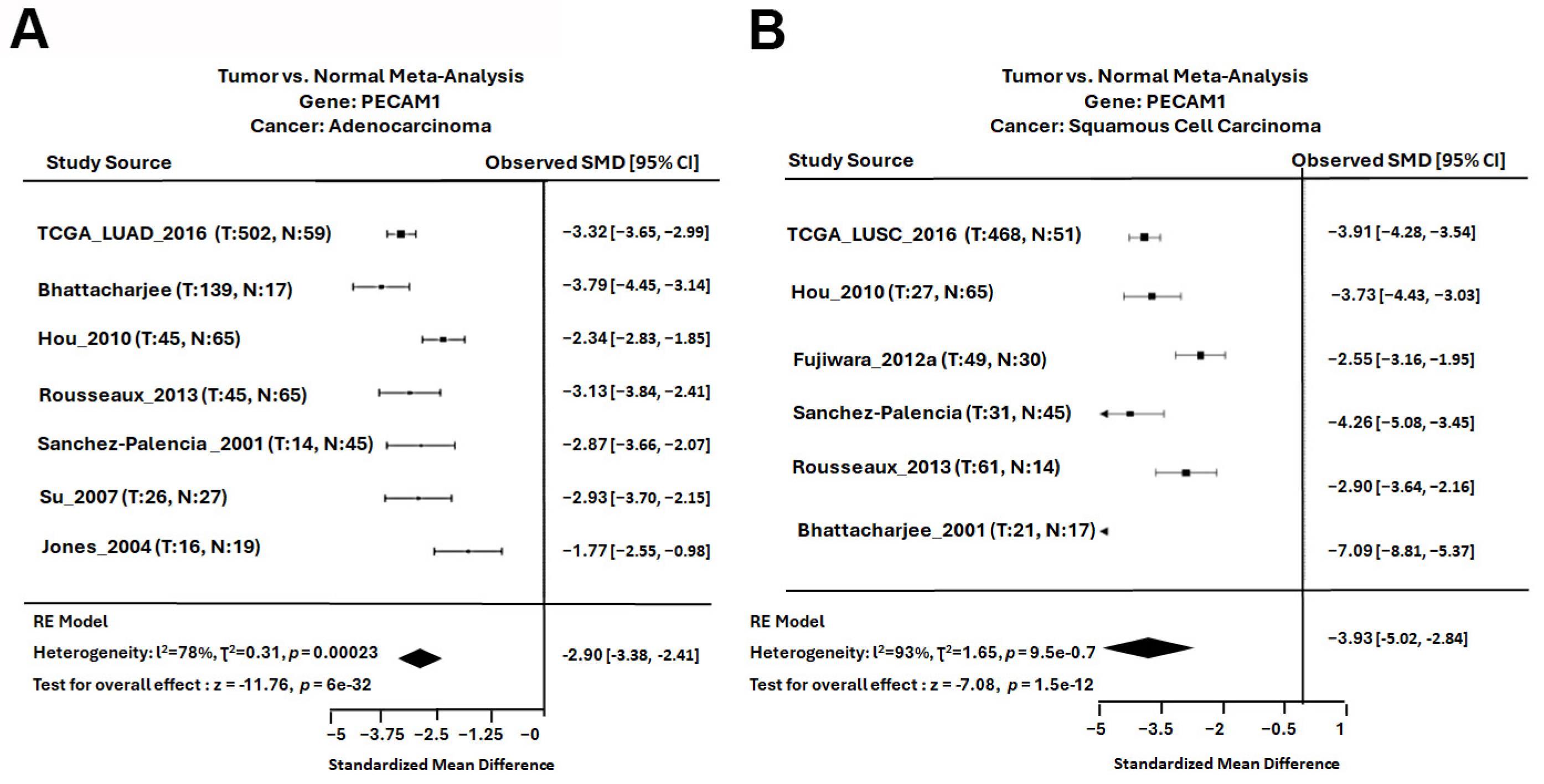
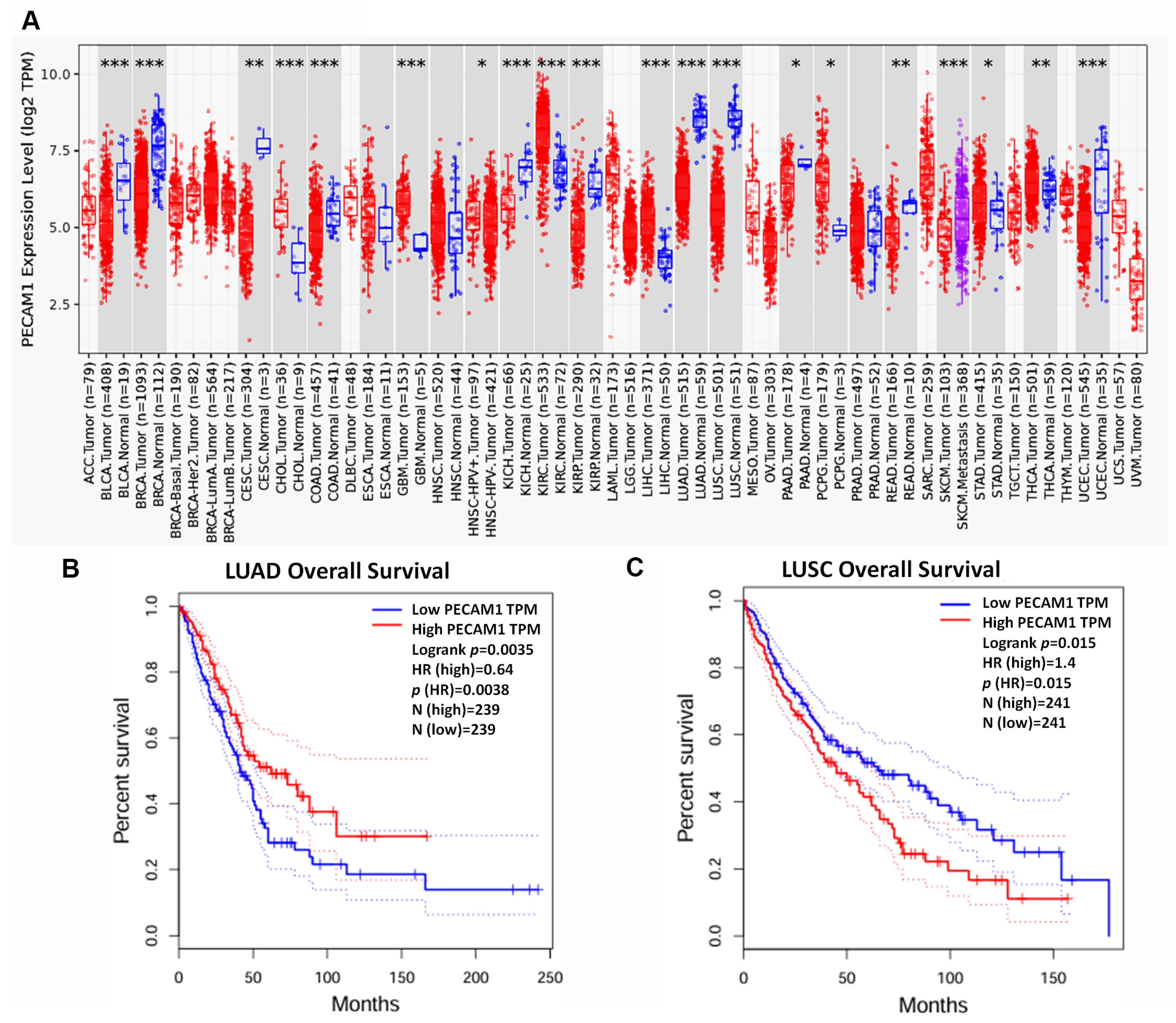
3.4. Assessing the Prognostic Value of Hub Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma
3.5. PECAM1 Was Positively Associated with NSCLC Prognosis
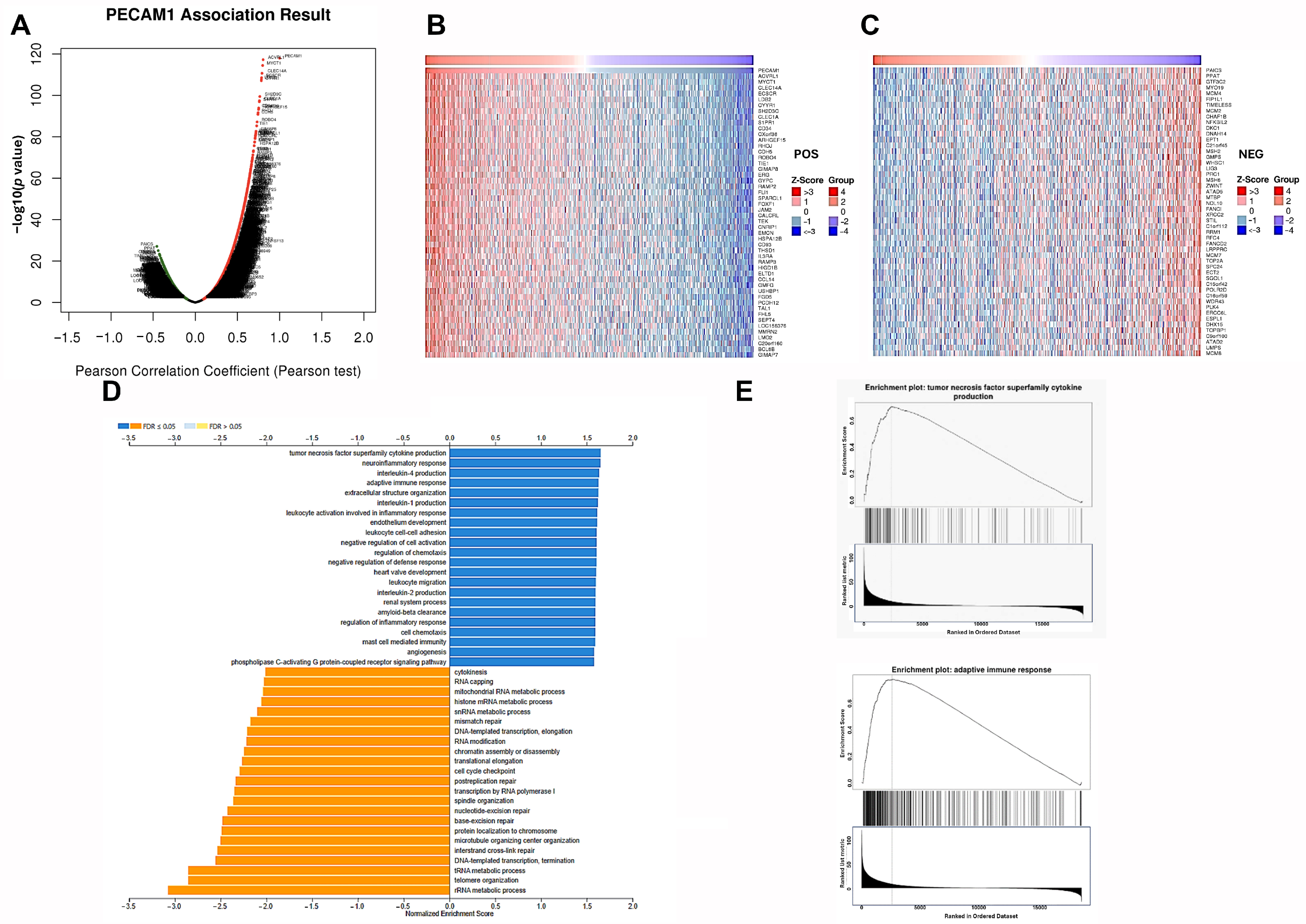
3.6. Genes Positively Correlated with PECAM1 Expression Up-Regulated Immune Function in LUAD
3.7. PECAM1 Is a Marker of Immune Infiltration in LUAD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATF3 | Activating transcription factor 3 |
| BP | Biological processes |
| CC | Cellular components |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DUSP1 | Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 |
| EGR1 | Early growth response 1 |
| FPS | First-progression survival |
| FOS | Fos proto-oncogene |
| FOSB | FosB proto-oncogene |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| MF | Molecular functions |
| NR4A1 | Nuclear receptor 4A1 |
| NR4A2 | Nuclear receptor 4 A 2 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PECAM1 | Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| STRING | Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| ZFP36 | Zinc finger protein 36 |
References
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; He, X.; Xie, T.; Ye, X.Y. Recent advances of novel fourth generation EGFR inhibitors in overcoming C797S mutation of lung cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 245, 114900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Lynch, T.J. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer: An evolving story. Annu. Rev. Med. 2008, 59, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontiers Production, O. Erratum: The landscape of immunotherapy resistance in NSCLC. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1187021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, L.; Thienpont, B.; Zhao, L.; Wolf, D.; Pircher, A. Overcoming immunotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)—Novel approaches and future outlook. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashei Varnamkhasti, K.; Moghanibashi, M.; Naeimi, S. Genes whose expressions in the primary lung squamous cell carcinoma are able to accurately predict the progression of metastasis through lymphatic system, inferred from a bioinformatics analyses. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M.; Moghanibashi, M.; Naeimi, S.; Mohamadynejad, P. LINC00894, YEATS2-AS1, and SUGP2 genes as novel biomarkers for N0 status of lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Zhang, H.; Slutsky, A.S. Lung Repair and Regeneration in ARDS: Role of PECAM1 and Wnt Signaling. Chest 2019, 155, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.H.; Yu, Q. Cell aggregation induces phosphorylation of PECAM-1 and Pyk2 and promotes tumor cell anchorage-independent growth. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.M.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, X. Roles of PECAM-1 in cell function and disease progression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4082–4088. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, V.; Cao, G.; Parambath, A.; Lawal, F.; Handumrongkul, C.; Debs, R.; DeLisser, H.M. Involvement of TIMP-1 in PECAM-1-mediated tumor dissemination. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, M.T.; Dracheva, T.; Rotunno, M.; Figueroa, J.D.; Liu, H.; Dasgupta, A.; Mann, F.E.; Fukuoka, J.; Hames, M.; Bergen, A.W.; et al. Gene expression signature of cigarette smoking and its role in lung adenocarcinoma development and survival. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.P.; Hsiao, C.K.; Lai, L.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Hsu, C.P.; Lee, J.M.; Chuang, E.Y. Identification of regulatory SNPs associated with genetic modifications in lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Palencia, A.; Gomez-Morales, M.; Gomez-Capilla, J.A.; Pedraza, V.; Boyero, L.; Rosell, R.; Farez-Vidal, M.E. Gene expression profiling reveals novel biomarkers in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets—Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Brouwer, C. Pathview: An R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1830–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D561–D568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Nogare, D.E.; Clark, M.S.; Elgar, G.; Frame, I.G.; Poulter, R.T. Xena, a full-length basal retroelement from tetraodontid fish. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repecka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.X.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Wen, S. Mining expression and prognosis of topoisomerase isoforms in non-small-cell lung cancer by using Oncomine and Kaplan-Meier plotter. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorffy, B. Transcriptome-level discovery of survival-associated biomarkers and therapy targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Straub, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, G. What‘s the difference between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma? Evidence from a retrospective analysis in a cohort of Chinese patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 947443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, K.; Hirano, T. IL-6 in autoimmune disease and chronic inflammatory proliferative disease. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2002, 13, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Harada, M.; Kamimura, D.; Ogura, H.; Okuyama, Y.; Kumai, N.; Okuyama, A.; Singh, R.; Jiang, J.J.; Atsumi, T.; et al. Disease-association analysis of an inflammation-related feedback loop. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, A.; Hashemi, V.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Azizi, G.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebe, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. STAT3, a Master Regulator of Anti-Tumor Immune Response. Cancers 2019, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.; Nilsson, M.B.; Yang, Y.; Le, X.; Tran, H.T.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, F.; Poteete, A.; Ren, X.; et al. IL6 Mediates Suppression of T- and NK-cell Function in EMT-associated TKI-resistant EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Fenoglio, S.; Gao, D.C.; Camiolo, M.; Stiles, B.; Lindsted, T.; Schlederer, M.; Johns, C.; Altorki, N.; Mittal, V.; et al. TGF-beta IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15535–15540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Bai, F.; Ding, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Yue, X.; Liang, X.; et al. IL-6 promotes metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer by up-regulating TIM-4 via NF-kappaB. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Wang, T.; Sun, B.; Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Song, H.; Guo, W.; Li, K.; Hu, M.; et al. IL6/STAT3 Signaling Orchestrates Premetastatic Niche Formation and Immunosuppressive Traits in Lung. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safe, S.; Karki, K. The Paradoxical Roles of Orphan Nuclear Receptor 4A (NR4A) in Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.O.; Li, X.; Khan, S.; Safe, S. Targeting NR4A1 (TR3) in cancer cells and tumors. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.D.; Yoon, K.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Abdelrahim, M.; Lei, P.; Hamilton, S.; Khan, S.; Ramaiah, S.K.; Safe, S. Nur77 agonists induce proapoptotic genes and responses in colon cancer cells through nuclear receptor-dependent and nuclear receptor-independent pathways. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, E.; Boisen, M.M.; Laskey, R.; Chen, R.; Song, C.; Sallit, J.; Yochum, Z.A.; Andersen, C.L.; Sikora, M.J.; Wagner, J.; et al. High expression of orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 in a subset of ovarian tumors with worse outcome. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Abdelrahim, M.; Yoon, K.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Papineni, S.; Kim, K.; Wang, H.; Safe, S. Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6824–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, A.; Rodrigues-Hoffman, A.; Safe, S. PAX3-FOXO1A Expression in Rhabdomyosarcoma Is Driven by the Targetable Nuclear Receptor NR4A1. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscat, G.E.; Eriksson, N.A.; Byth, K.; Loi, S.; Graham, D.; Jindal, S.; Davis, M.J.; Clyne, C.; Funder, J.W.; Simpson, E.R.; et al. Research resource: Nuclear receptors as transcriptome: Discriminant and prognostic value in breast cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, E.; Safe, S. Transforming Growth Factor beta/NR4A1-Inducible Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Is p38alpha (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14) Dependent. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 37, e00306-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, E.; Mohankumar, K.; Safe, S. TGFbeta-Induced Lung Cancer Cell Migration Is NR4A1-Dependent. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.; Claassen, G.; Yu, D.H.; Albers, A.; Fan, W.; Tan, P.; Grifman, M.; Hu, X.; Defife, K.; Nguy, V.; et al. Nuclear hormone receptor NR4A2 is involved in cell transformation and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8208–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tai, H.H. Activation of thromboxane A(2) receptors induces orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 expression and stimulates cell proliferation in human lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Cai, H.; Ma, L.; Ding, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, T.; Yu, Y.; Chang, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Nuclear orphan receptor NR4A2 confers chemoresistance and predicts unfavorable prognosis of colorectal carcinoma patients who received postoperative chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, K.; Li, X.; Jin, U.H.; Mohankumar, K.; Zarei, M.; Michelhaugh, S.K.; Mittal, S.; Tjalkens, R.; Safe, S. Nuclear receptor 4A2 (NR4A2) is a druggable target for glioblastomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 146, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H. EZH2 inhibitors-mediated epigenetic reactivation of FOSB inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progress. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, W.; Shi, W.; Gao, X.; Qin, W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, F.; Feng, S. Abnormal expression of FOSB correlates with tumor progression and poor survival in patients with gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, C.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Wu, S.M.; Feng, P.H.; Chan, Y.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, J.Y. FOSB(-)PCDHB13 Axis Disrupts the Microtubule Network in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.; Bhatt, M.L.B.; Singh, V.; Singh, S.; Gangwar, P.K.; Singh, U.S.; Kumar, V.; Mehrotra, D. Differential Expression of c-fos Proto-Oncogene in Normal Oral Mucosa versus Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiao, S.; Li, N.; Zhu, X. MiR-744 Functions as an Oncogene Through Direct Binding to c-Fos Promoter and Facilitates Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppstadter, J.; Ammit, A.J. Role of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 1 in Glucocorticoid-Driven Anti-inflammatory Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editors, P.O. Expression of Concern: DUSP1 Is a Novel Target for Enhancing Pancreatic Cancer Cell Sensitivity to Gemcitabine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, S.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Yu, H.; Liang, X.; Tang, J.; Yu, T.; Cai, X. DUSP1 inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis and invasion and angiogenesis in gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12133–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, Z.; Kashani, B.; Alishahi, Z.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Esmaeili, F.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Bashash, D.; Momeny, M. Dual-specificity phosphatases: Therapeutic targets in cancer therapy resistance. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, P.; Lei, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, L. DUSP1 Promotes Osimertinib Drug-Tolerant Persistence by Inhibiting MAPK/ERK Signaling in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 67, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, G. The Role of the Transcription Factor EGR1 in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ameri, A.H.; Wang, S.; Jansson, K.H.; Casey, O.M.; Yang, Q.; Beshiri, M.L.; Fang, L.; Lake, R.G.; Agarwal, S.; et al. EGR1 regulates angiogenic and osteoclastogenic factors in prostate cancer and promotes metastasis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6241–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, X.; Shuai, Y.; Wu, X.; Yan, Y.; Xing, X.; Ji, J. EGR1-mediated linc01503 promotes cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis in gastric cancer. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.C.; Cheng, C.F. Master Regulator Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) in Metabolic Homeostasis and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, S.; Fang, X.; Cao, D. Role of ATF3 as a prognostic biomarker and correlation of ATF3 expression with macrophage infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, J.; Hasim, M.S.; Baghai, T.; Niknejad, N.; Perkins, T.J.; Stewart, D.J.; Sekhon, H.S.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Dimitroulakos, J. Induction of Activating Transcription Factor 3 Is Associated with Cisplatin Responsiveness in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Yang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Ru, L.; Niu, F.; Mao, W. alpha-Hederin promotes ferroptosis and reverses cisplatin chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Aging 2024, 16, 1298–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, Y.; Chen, J.; Patial, S. The Tristetraprolin Family of RNA-Binding Proteins in Cancer: Progress and Future Prospects. Cancers 2020, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, B.H.; Park, I.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Yang, S.J.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, D.C.; Sohn, H.A.; Kim, T.W.; et al. Functional switching of TGF-beta1 signaling in liver cancer via epigenetic modulation of a single CpG site in TTP promoter. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohler, T.; Kessler, S.M.; Hosseini, K.; List, M.; Barghash, A.; Patial, S.; Laggai, S.; Gemperlein, K.; Haybaeck, J.; Muller, R.; et al. The mRNA-binding Protein TTP/ZFP36 in Hepatocarcinogenesis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Qiu, L.; Cao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; An, G.; Ni, J.; Jia, H.; Li, S.; Li, K. ZFP36 loss-mediated BARX1 stabilization promotes malignant phenotypes by transactivating master oncogenes in NSCLC. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi Sabins, N.; Taylor, J.L.; Fabian, K.P.; Appleman, L.J.; Maranchie, J.K.; Stolz, D.B.; Storkus, W.J. DLK1: A novel target for immunotherapeutic remodeling of the tumor blood vasculature. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Zhao, H. DC101, an anti-VEGFR2 agent, promotes high-endothelial venule formation and immune infiltration versus SAR131675 and fruquintinib. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 661, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutova, M.; Hibbard, J.C.; Ma, E.; Natri, H.M.; Adhikarla, V.; Chimge, N.O.; Qiu, R.; Nguyen, C.; Melendez, E.; Aguilar, B.; et al. Targeting Wnt signaling for improved glioma immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashei Varnamkhasti, K.; Moghanibashi, M.; Naeimi, S. Implications of ZNF334 gene in lymph node metastasis of lung SCC: Potential bypassing of cellular senescence. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.-S.; Hsu, P.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; You, J.-Y.; Shih, Y.-L.; Lai, H.-C. Identification of PECAM1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091094
Lin S-S, Hsu P-S, Lin Y-C, You J-Y, Shih Y-L, Lai H-C. Identification of PECAM1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shih-Sen, Pei-Sung Hsu, Ying-Chu Lin, Jie-Yu You, Yung-Leun Shih, and Hung-Chih Lai. 2025. "Identification of PECAM1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091094
APA StyleLin, S.-S., Hsu, P.-S., Lin, Y.-C., You, J.-Y., Shih, Y.-L., & Lai, H.-C. (2025). Identification of PECAM1 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091094




