Contrast Enhanced MRI in the Diagnosis of HCC
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Gadolinium Contrast Agent Selection




3. Other MRI Sequences for HCC and in Relation to GBCA
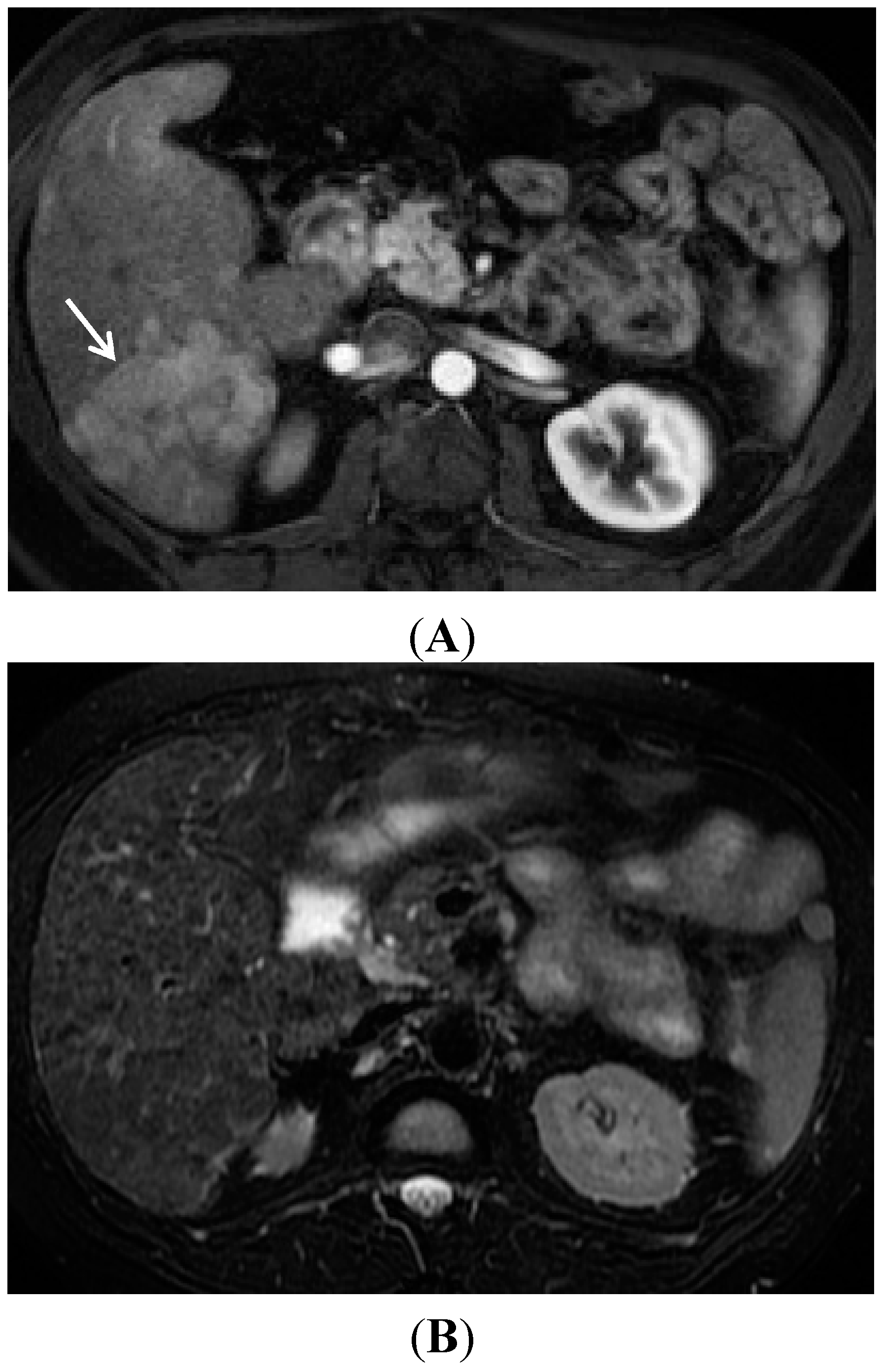
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, R.L. The radiologist as interpreter and translator. Radiology 2014, 272, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: Globocan 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Gores, G.J.; Mazzaferro, V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut 2014, 63, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willatt, J.M.; Hussain, H.K.; Adusumilli, S.; Marrero, J.A. Mr imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: Challenges and controversies. Radiology 2008, 247, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American gastroenterological association, American association for the study of liver diseases, and American college of gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Allocation of Livers. Available online: http://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/ContentDocuments/OPTN_Policies.pdf#nameddest=Policy_09 (accessed on 21 August 2015).
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Sirlin, C.B. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Part II. Extracellular agents, hepatobiliary agents, and ancillary imaging features. Radiology 2014, 273, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauthey, J.N.; Dixon, E.; Abdalla, E.K.; Helton, W.S.; Pawlik, T.M.; Taouli, B.; Brouquet, A.; Adams, R.B.; American Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association; Society of Surgical Oncology; et al. Pretreatment assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Expert consensus statement. HPB 2010, 12, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2015, 275, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirlin, C.B.; Hussain, H.K.; Jonas, E.; Kanematsu, M.; Min Lee, J.; Merkle, E.M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Reeder, S.B.; Ricke, J.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Consensus report from the 6th international forum for liver MRI using gadoxetic acid. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M.; Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1208–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialecki, E.S.; Ezenekwe, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Collins, B.T.; Ponder, T.B.; Bieneman, B.K.; di Bisceglie, A.M. Comparison of liver biopsy and noninvasive methods for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippin, J.S. Biopsy of suspicious liver nodules: Does it change management? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, W.B. Mechanisms of human hepatocarcinogenesis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2003, 3, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremidis, S.C.; Hytiroglou, P. The multistep process of hepatocarcinogenesis in cirrhosis with imaging correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, O. Imaging of multistep human hepatocarcinogenesis by CT during intra-arterial contrast injection. Intervirology 2004, 47, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Matsui, O.; Ueda, K.; Kawamori, Y.; Kadoya, M.; Yoshikawa, J.; Gabata, T.; Takashima, T.; Nonomura, A.; Nakanuma, Y.; et al. Correlation between the blood supply and grade of malignancy of hepatocellular nodules associated with liver cirrhosis: Evaluation by CT during intraarterial injection of contrast medium. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, T.; Honda, H.; Taguchi, K.; Asayama, Y.; Kuroiwa, T.; Yoshimitsu, K.; Irie, H.; Aibe, H.; Shimada, M.; Masuda, K.; et al. Sequential hemodynamic change in hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules: CT angiography and pathologic correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.N.; Yang, C.P.; Fernandez, G.J.; Cubukcu, O.; Thung, S.N.; Theise, N.D. Neoangiogenesis and sinusoidal “Capillarization” in dysplastic nodules of the liver. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1998, 22, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzawa, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nakajima, H.; Kitanaka, Y.; Omata, K.; Araki, T. Dynamic CT for detecting small hepatocellular carcinoma: Usefulness of delayed phase imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.S. Diffusion-weighted MRI of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Working Party. Terminology of nodular hepatocellular lesions. Hepatology 1995, 22, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.M.; Reinhold, C.; Mitchell, D.G. Cirrhosis and lesion characterization at MR imaging. Radiographics 2009, 29, 1637–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, M.J.; Park, C.K.; Rhim, H. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI and high-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging to distinguish well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinomas from benign nodules in patients with chronic liver disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, W868–W875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.J.; Kim, M.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, J.T. Nodular hepatocellular carcinomas: Detection with arterial-, portal-, and delayed-phase images at spiral CT. Radiology 1997, 202, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.I.; Lee, H.J.; Han, J.K.; Choi, D.S.; Seo, J.B.; Han, M.C. Detection of hypervascular nodular hepatocellular carcinomas: Value of triphasic helical CT compared with iodized-oil CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 168, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmura, R.; Matsui, O.; Kobayashi, S.; Terayama, N.; Sanada, J.; Ueda, K.; Gabata, T.; Kadoya, M.; Miyayama, S. Cirrhotic nodules: Association between MR imaging signal intensity and intranodular blood supply. Radiology 2005, 237, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Hussain, H.K.; Nghiem, H.V.; Umar, R.; Fontana, R.J.; Lok, A.S. Improving the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with an arterially-enhancing liver mass. Liver Transpl. 2005, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimura, T.; Ueno, T.; Kin, M.; Harada, R.; Taniguchi, E.; Nakamura, T.; Sakata, R.; Hashimoto, O.; Sakamoto, M.; Kumashiro, R.; et al. Overexpression of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, C.; Andía, E.; Sánchez, A.; Moreno, V. Selective use of low-osmolality contrast media in computed tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M.; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Yoon, J.H.; Joo, I.; Woo, H.S. Recent advances in CT and MR imaging for evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2012, 1, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, K.; Yoshimitsu, K.; Nishihara, Y.; Irie, H.; Asayama, Y.; Tajima, T.; Nishie, A.; Hirakawa, M.; Ushijima, Y.; Okamoto, D.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with a pseudocapsule on gadolinium-enhanced MR images: Correlation with histopathologic findings. Radiology 2009, 250, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, A.; Marin, D.; Bae, K.T.; Lagalla, R.; Agnello, F.; Bazzocchi, M.; Brancatelli, G. Focal liver lesions hyperintense on T1-weighted magnetic resonance images. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2009, 30, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Rofsky, N.M. Dynamic subtraction mr imaging of the liver: Advantages and pitfalls. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrasegaran, K.; Tahir, B.; Nutakki, K.; Akisik, F.M.; Bodanapally, U.; Tann, M.; Chalasani, N. Usefulness of conventional MRI sequences and diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating malignant from benign portal vein thrombus in cirrhotic patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, Z.K.; McKernan, M.G.; Hahn, P.F.; Sahani, D.V. Enhancing and expansile portal vein thrombosis: Value in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with multiple hepatic lesions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellin, M.F. MR contrast agents, the old and the new. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 60, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksendal, A.N.; Hals, P.A. Biodistribution and toxicity of MR imaging contrast media. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1993, 3, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweedle, M.F. The prohance story: The making of a novel MRI contrast agent. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7 (Suppl. 5), S225–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydrychowicz, A.; Lubner, M.G.; Brown, J.J.; Merkle, E.M.; Nagle, S.K.; Rofsky, N.M.; Reeder, S.B. Hepatobiliary MR imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, C.; Russo, M.W.; Heimbach, J.K.; Hussain, H.K.; Pomfret, E.A.; Bruix, J. New OPTN/UNOS policy for liver transplant allocation: Standardization of liver imaging, diagnosis, classification, and reporting of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 2013, 266, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Izumi, N.; Kokudo, N.; Matsui, O.; Sakamoto, M.; Nakashima, O.; Kojiro, M.; Makuuchi, M.; HCC Expert Panel of Japan Society of Hepatology. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in japan: Consensus-based clinical practice guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI-RADS v2014. Available online: http://nrdr.acr.org/lirads/ (accessed on 14 September 2015).
- Motosugi, U.; Bannas, P.; Sano, K.; Reeder, S.B. Hepatobiliary MR contrast agents in hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, T.A.; Fowler, K.J.; Sirlin, C.B.; Costa, E.A.; Yee, J.; Yeh, B.M.; Heiken, J.P. Hepatobiliary agents and their role in LI-RADS. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboyama, T.; Onishi, H.; Kim, T.; Akita, H.; Hori, M.; Tatsumi, M.; Nakamoto, A.; Nagano, H.; Matsuura, N.; Wakasa, K.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Hepatocyte-selective enhancement at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging—Correlation with expression of sinusoidal and canalicular transporters and bile accumulation. Radiology 2010, 255, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitao, A.; Matsui, O.; Yoneda, N.; Kozaka, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Koda, W.; Gabata, T.; Yamashita, T.; Kaneko, S.; Nakanuma, Y.; et al. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation between biologic features and signal intensity on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR images. Radiology 2012, 265, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.A.; Jeong, H.T.; Park, Y.N. Hyperintense HCC on hepatobiliary phase images of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: Correlation with clinical and pathological features. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3877–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.R.; Gupta, R.T.; Davenport, M.S.; Allen, B.C.; Jaffe, T.A.; Ho, L.M.; Boll, D.T.; Merkle, E.M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in a north american population: Does hepatobiliary MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA improve sensitivity and confidence for diagnosis? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, H.K.; Syed, I.; Nghiem, H.V.; Johnson, T.D.; Carlos, R.C.; Weadock, W.J.; Francis, I.R. T2-weighted MR imaging in the assessment of cirrhotic liver. Radiology 2004, 230, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, E.M.; Holland, A.E.; Israel, G.M.; Hahn, W.Y.; Kim, D.C.; West, A.B.; Babb, J.S.; Taouli, B.; Lee, V.S.; Krinsky, G.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: Gadolinium-enhanced 3D T1-weighted MR imaging as a stand-alone sequence for diagnosis. Radiology 2006, 239, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Sirlin, C.B. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Part I. Development, growth, and spread: Key pathologic and imaging aspects. Radiology 2014, 272, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhi, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Motosugi, U.; Sano, K.; Matsuda, M.; Kitamura, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Araki, T. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of hepatocellular lesions: Estimation of grade of malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motosugi, U.; Ichikawa, T.; Sou, H.; Sano, K.; Tominaga, L.; Muhi, A.; Araki, T. Distinguishing hypervascular pseudolesions of the liver from hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas with gadoxetic acid-enhanced mr imaging. Radiology 2010, 256, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Rhim, H. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma 1 cm or smaller in patients with chronic liver disease: Characterization with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI that includes diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, W758–W765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecaveye, V.; de Keyzer, F.; Verslype, C.; Op de Beeck, K.; Komuta, M.; Topal, B.; Roebben, I.; Bielen, D.; Roskams, T.; Nevens, F.; et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI provides additional value to conventional dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 2456–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, M.W.; Park, M.J.; Hwang, J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.W. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MRI with respect to the severity of liver cirrhosis. Acta Radiol. 2012, 53, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piana, G.; Trinquart, L.; Meskine, N.; Barrau, V.; Beers, B.V.; Vilgrain, V. New MR imaging criteria with a diffusion-weighted sequence for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.J.; Yan, F.H.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, J.; Ji, Y. Added value of breathhold diffusion-weighted MRI in detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma lesions compared with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 29, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, D.; Rhim, H. Small hepatocellular carcinomas: Improved sensitivity by combining gadoxetic acid-enhanced and diffusion-weighted mr imaging patterns. Radiology 2012, 264, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Sentís, M.; Zidan, A.; Donoso, L.; Puig, J.; Falcó, J.; Bella, R. Fatty metamorphosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Detection with chemical shift gradient-echo MR imaging. Radiology 1995, 195, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaran, C.; Karcaaltincaba, M.; Akata, D.; Karabulut, N.; Akinci, D.; Ozmen, M.; Akhan, O. Fat-containing lesions of the liver: Cross-sectional imaging findings with emphasis on MRI. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niendorf, E.; Spilseth, B.; Wang, X.; Taylor, A. Contrast Enhanced MRI in the Diagnosis of HCC. Diagnostics 2015, 5, 383-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics5030383
Niendorf E, Spilseth B, Wang X, Taylor A. Contrast Enhanced MRI in the Diagnosis of HCC. Diagnostics. 2015; 5(3):383-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics5030383
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiendorf, Eric, Benjamin Spilseth, Xiao Wang, and Andrew Taylor. 2015. "Contrast Enhanced MRI in the Diagnosis of HCC" Diagnostics 5, no. 3: 383-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics5030383
APA StyleNiendorf, E., Spilseth, B., Wang, X., & Taylor, A. (2015). Contrast Enhanced MRI in the Diagnosis of HCC. Diagnostics, 5(3), 383-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics5030383




