Clinicopathological Spectrum of Bilirubin Encephalopathy/Kernicterus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation
3. Diagnostic Testing
4. Neuroimaging
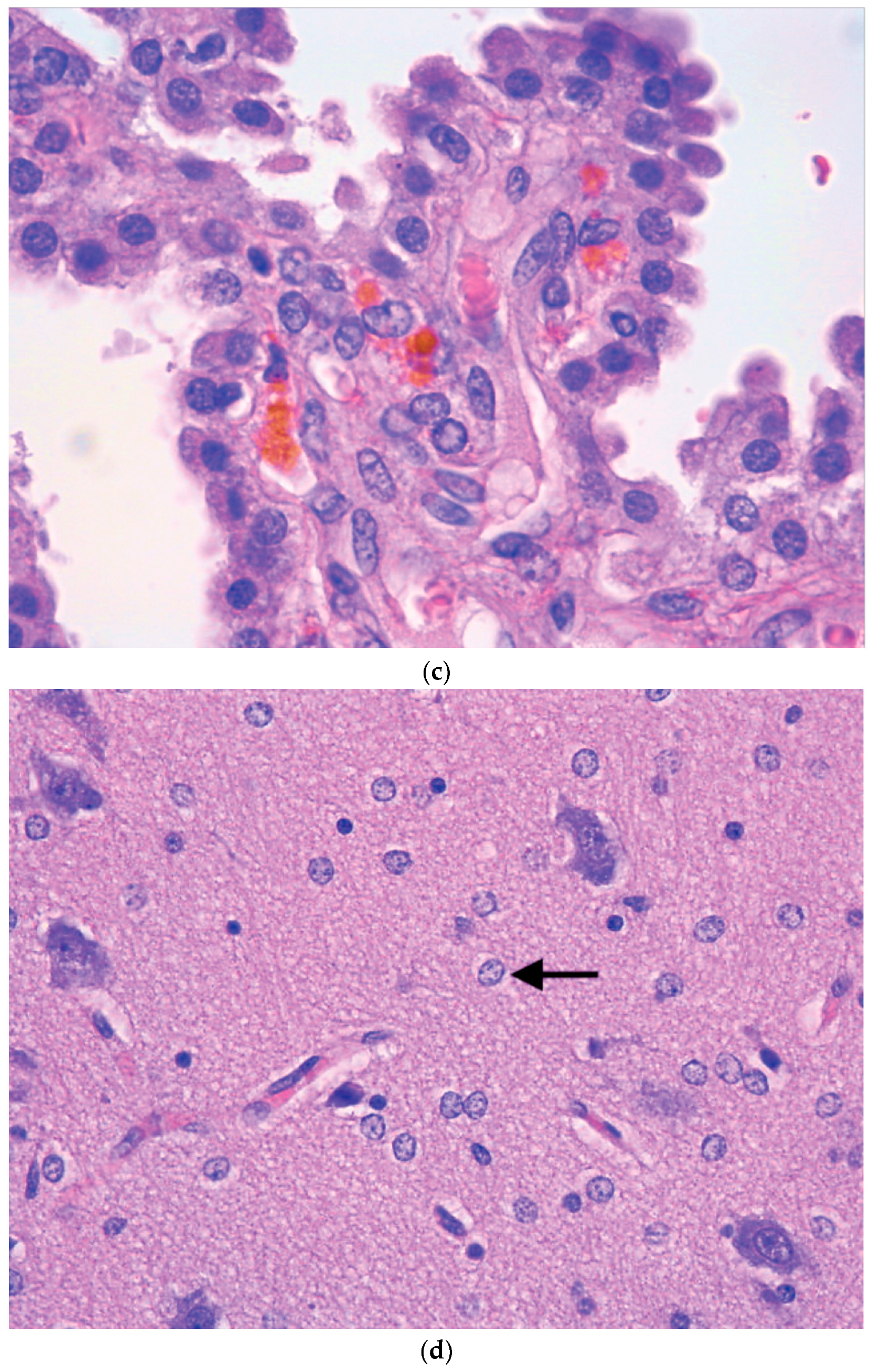
5. Neuropathology
6. Management
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olusanya, B.O.; Ogunlesi, T.A.; Slusher, T.M. Why is kernicterus still a major cause of death and disability in low-income and middle-income countries? Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchowski, K.E. Evaluation and treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 89, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Locke, T.; Biringer, A.; Booth, A.; Darling, E.K.; Dougan, S.; Harrison, J.; Hill, S.; Johnson, A.; Makin, S.; et al. Newborn Bilirubin Screening for Preventing Severe Hyperbilirubinemia and Bilirubin Encephalopathy: A Rapid Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 13, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.W.; Newman, T.B.; Maisels, M.J. Update on Predicting Severe Hyperbilirubinemia and Bilirubin Neurotoxicity Risks in Neonates. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Kaplan, M.; Hansen, W.R. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: A global perspective. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.M. Bilirubin toxicity in the developing nervous system. Pediatr. Neurol. 2003, 29, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.M. Definition of the Clinical Spectrum of Kernicterus and Bilirubin-Induced Neurologic Dysfunction (BIND). J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slusher, T.M.; Owa, J.A.; Painter, M.J.; Shapiro, S.M. The Kernicteric Facies: Facial Features of Acute Bilirubin Encephalopathy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2001, 44, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.B.; Bhutani, V.K.; Watchko, J.F. Apnea in acute bilirubin encephalopathy. Semin. Perinatal. 2014, 38, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.B.; Charafeddine, L.; Guillet, R. Transient bilirubin encephalopathy and apnea of prematurity in 28 to 32 weeks gestational age infants. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkoltsiou, K.; Tzoufi, M.; Counsell, S.; Rutherford, M.; Cowan, F. Serial brain MRI and ultrasound findings: Relation to gestational age, bilirubin level, neonatal neurologic status and neurodevelopmental outcome in infants at risk of kernicterus. Early Hum. Dev. 2008, 84, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaprio, S.M. Chronic bilirubin encephalopathy: Diagnosis and outcome. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 15, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uziel, A.; Marot, M.; Pujol, R. The Gunn rat: An experimental model for central deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 1983, 95, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olds, C.; Oghalai, J.S. Bilirubin-Induced Audiologic Injury in Preterm Infants. Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matkin, N.; Carhart, R. Auditory profiles associated with Rh incompatibility. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1966, 84, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.; Vassar, R. Movement disorders due to bilirubin toxicity. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pichon, J.B.; Riordan, S.M.; Watchko, J.; Shapiro, S.M. The Neurological Sequelae of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Definitions, Diagnosis and Treatment of the Kernicterus Spectrum Disorders (KSDs). Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 13, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Burgos, A.E.; Flaherman, V.; Chung, E.K.; Simpson, E.A.; Goyal, N.K.; Von Kohorn, I.; Dhepyasuwan, N. Discrepancies between transcutaneous and serum bilirubin measurements. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, M.A.; Silva, R.F.M.; Brites, D. Cell response to hyperbilirubinemia: A journey along key molecular events. In New Trends in Brain Research; Chen, F.J., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Odutolu, Y.; Emmerson, A.J. Low bilirubin kernicterus with sepsis and hypoalbuminemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, I.; Nakamura, H.; Koda, T.; Sakai, H.; Kurokawa, D.; Yonetani, M.; Morisawa, T.; Katayama, Y.; Wada, H.; Funato, M.; et al. Serum unbound bilirubin as a predictor for clinical kernicterus in extremely low birth weight infants at a late age in the neonatal intensive care unit. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskander, I.; Gamaleldin, R.; El Houchi, S.; El Shenawy, A.; Seoud, I.; El Gharbawi, N.; Abou-Youssef, H.; Aravkin, A.; Wennberg, R.P. Serum bilirubin and bilirubin/albumin ratio as predictors of bilirubin encephalopathy. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1330–e1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulzebos, C.V.; van Imhoff, D.E.; Bos, A.F.; Ahlfors, C.E.; Verkade, H.J.; Dijk, P.H. Usefulness of bilirubin/albumin ratio for predicting bilirubin-induced neurotoxicity in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, F384–F388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watchko, J.F. Bilirubin Induced Neurotoxicity in the Preterm Neonate. Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngashangva, L.; Bacha, V.; Goswami, P. Development of new methods for determination of bilirubin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 5, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, N.Y.; Chang, Y.F.; Leong, Y.X.; Tok, Z.Y.; Hooi, L.C.; Chee, S.C.; Latif, Z.A. The point-of-care Bilistick method has very short turn-around-time and high accuracy at lower cutoff levels to predict laboratory-measured TSB. Pediatr. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, C.; Iskander, I.F.; Akmal, D.M.; El Houchi, S.Z.; Khairy, D.A.; Bedogni, G.; Wennberg, R.P.; Tiribelli, C.; Coda Zabetta, C.D. Comparison between Bilistick System and transcutaneous bilirubin in assessing total bilirubin serum concentration in jaundiced newborns. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohsiswatmo, R.; Oswari, H.; Amandito, R.; Sjakti, H.A.; Windiastuti, E.; Roeslani, R.D.; Barchia, I. Agreement test of transcutaneous bilirubin and bilistick with serum bilirubin in preterm infants receiving phototherapy. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Houchi, S.Z.; Iskander, I.; Gamaleldin, R.; El Shenawy, A.; Seoud, I.; Abou-Youssef, H.; Wennberg, R.P. Prediction of 3- to 5-Month Outcomes from Signs of Acute Bilirubin Toxicity in Newborn Infants. J. Pediatr. 2017, 183, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; Bhutani, V.K.; Karp, K.; Sivieri, E.M.; Shapiro, S.M. Clinical report from the pilot USA Kernicterus Registry (1992 to 2004). J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, S25–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Hou, B.L.; Zhang, P.; Chineah, A.; Liu, F.; Liao, W. Studying neonatal bilirubin encephalopathy with conventional MRI, MRS, and DWI. Neuroradiology 2008, 50, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiskownski, J.L.; Panigraphy, A.; Painter, M.J.; Watchko, J.F. Magnetic resonance imaging of bilirubin encephalopathy: Current limitations and future promise. Semin. Perinatol. 2014, 38, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.M. Kernicterus. In Care of the Jaundiced Neonate; Stevenson, D.K., Maisels, M.J., Watchko, J.F., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich, A.J. MR of the normal neonatal brain: Assessment of deep structures. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wisnowski, J.L.; Panigrahy, A.; Painter, M.J.; Watchko, J.F. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities in Advanced Acute Bilirubin Encephalopathy Highlight Dentato-Thalamo-Cortical Pathways. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenendaal, F.; van der Grond, J.; de Vries, L.S. Cerebral metabolism in severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Chineah, A.; Lou, M. Usefulness of 1H-MRS in differentiating bilirubin encephalopathy from severe hyperbilirubinemia in neonates. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Corella, E.; Ibarra-González, I.; Fernández-Lainez, C.; Rodríguez-Weber, M.Á.; Guillén-Lopez, S.; Belmont-Martínez, L.; Agüero-Linares, D.; Vela-Amieva, M. Kernicterus in a boy with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: A case report. Neuropathology 2017, 37, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adle-Biassette, H.; Harding, B.; Golden, J.A. Developmental Neuropathology; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Friede, R.L. Kernicterus (Bilirubin encephalopathy). In Developmental Neuropathology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kinney, H.C.; Armstrong, D.D. Perinatal neuropathology. In Greenfield’s Neuropathology; Graham, D.I., Lantos, P.L., Eds.; Arnold: London, UK, 2002; pp. 519–606. [Google Scholar]
- Ahdab-Barmada, M.; Moossy, J. The neuropathology of kernicterus in the premature neonate: Diagnostic problems. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1984, 43, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkel, S.B. Autopsy findings associated with neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Clin. Perinatol. 1990, 17, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, J.M.; Rogers, B.B.; Burns, D. Kernicteric findings at autopsy in two sick near term infants. Pediatrics 1997, 99, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.M.; Volpe, J.J. Clinical features of bilirubin encephalopathy. Clin. Perinatol. 1990, 17, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Satoh, J.; Sakamoto, K.; Morimatsu, Y. Clinical and neuropathological findings in severe athetoid cerebral palsy: A comparative study of globo-Luysian and thalamo-putaminal groups. Brain Dev. 1991, 13, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.A.; Pereira, P.; Barroso, C.; Aronica, E.; Brites, D. New autopsy findings in different brain regions of a preterm neonate with kernicterus: Neurovascular alterations and up-regulation of efflux transporters. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 49, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watcko, J.F.; Maisels, M.J. The enigma of low bilirubin kernicterus in premature infants: Why does it still occur and is it preventable? Semin. Perinatol. 2014, 38, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, M.A.; Zurolo, E.; Pereira, P.; Barroso, C.; Aronica, E.; Brites, D. Cerebellar axon/myelin loss, axonal sprouting, and neuronal increased in vascular endothelial growth factor in a preterm infant with kernicterus. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakovic, K.; Ai, J.; D’Abbondanza, J.; Tariq, A.; Sabri, M.; Alarfaj, A.K.; Vasdev, P.; Macdonald, R.L. Bilirubin and its oxidation products damage brain white matter. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Schoor, L.W.; Dijk, P.H.; Verkade, H.J.; Kamsma, A.C.; Schreuder, A.B.; Groen, H.; Hulzebos, C.V. Unconjugated free bilirubin in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2017, 106–107, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, I. Hyperbilubinemia in preterm infants in Japan: New treatment criteria. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuntani, V.K.; Johnson, L. Synopsis report from the pilot USA Kernicterus Registry. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, S4–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Clinical Parameter | BIND Score |
|---|---|
| Mental status | |
| Normal | 0 |
| Sleep but arousable, decreased feeding | 1 |
| Lethargy, poor suck and/or irritable/jittery with strong suck | 2 |
| Semi-coma, unable to feed, seizures, coma | 3 |
| Muscle tone | |
| Normal | 0 |
| Persistent mild to moderate hypotonia | 1 |
| Hypertonia alternating with hypotonia, beginning arching of neck and trunk on stimulation | 2 |
| Persistent retrocollis and opisthotonos—bicycling or twitching of hands and feet | 3 |
| Cry pattern | |
| Normal | 0 |
| High pitched when aroused | 1 |
| Shrill, difficult to console | 2 |
| Inconsolable crying or cry weak or absent | 3 |
| TOTAL | Sum of scores from each parameter |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, S.; van Landeghem, F.K.H. Clinicopathological Spectrum of Bilirubin Encephalopathy/Kernicterus. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010024
Das S, van Landeghem FKH. Clinicopathological Spectrum of Bilirubin Encephalopathy/Kernicterus. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Sumit, and Frank K.H. van Landeghem. 2019. "Clinicopathological Spectrum of Bilirubin Encephalopathy/Kernicterus" Diagnostics 9, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010024
APA StyleDas, S., & van Landeghem, F. K. H. (2019). Clinicopathological Spectrum of Bilirubin Encephalopathy/Kernicterus. Diagnostics, 9(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9010024




