Diagnostic Approach to Traumatic Axonal Injury of the Spinothalamic Tract in Individual Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
3. Statistical Analysis
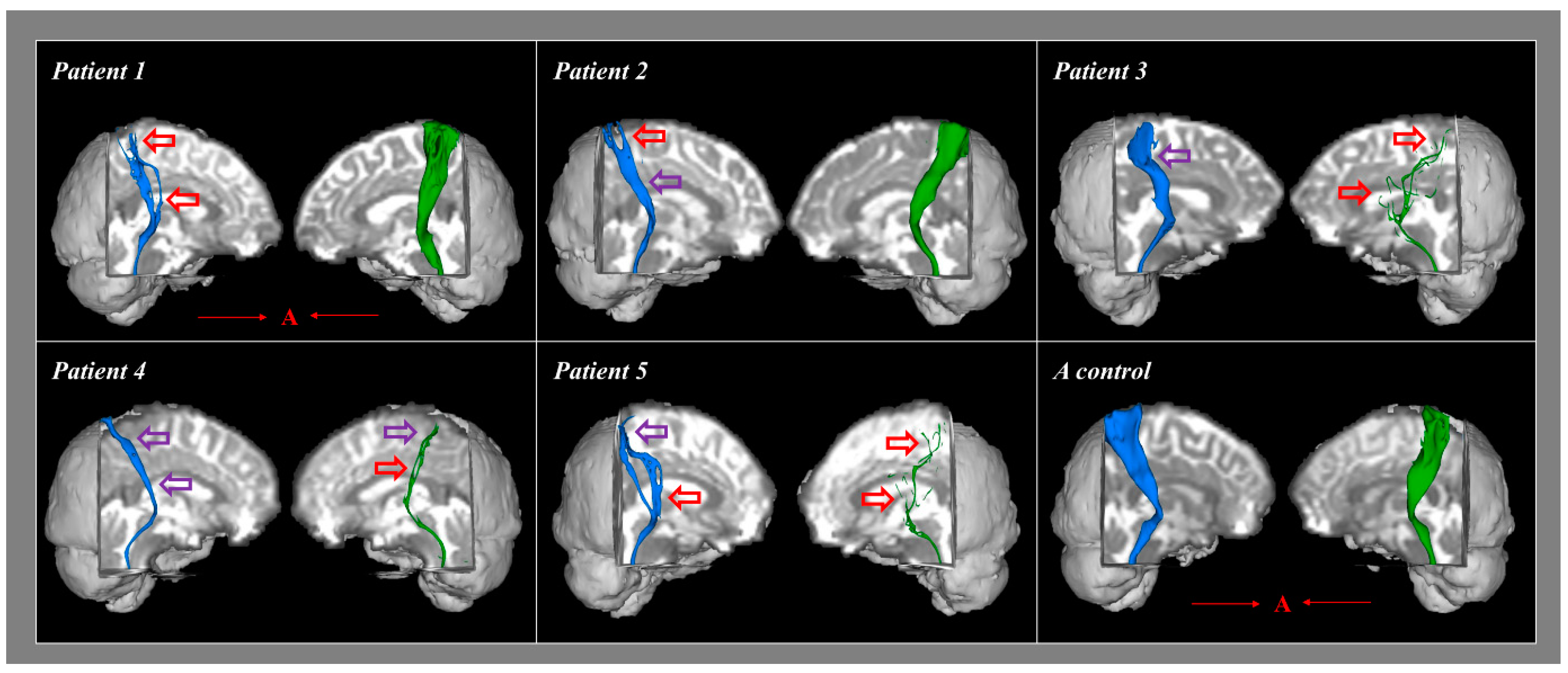
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Committee. Definition of mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 1993, 8, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.P. Mild traumatic brain injury: Pathophysiology, natural history, and clinical management. Neurology 1995, 45, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, D.R. Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1968, 31, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumbergs, P.C.; Scott, G.; Manavis, J.; Wainwright, H.; Simpson, D.A.; McLean, A.J. Staining of amyloid precursor protein to study axonal damage in mild head injury. Lancet 1994, 344, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, E.D. Neuropsychological results and neuropathological findings at autopsy in a case of mild traumatic brain injury. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2004, 10, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfanakis, K.; Haughton, V.M.; Carew, J.D.; Rogers, B.P.; Dempsey, R.J.; Meyerand, M.E. Diffusion tensor MR imaging in diffuse axonal injury. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 794–802. [Google Scholar]
- Shenton, M.E.; Hamoda, H.M.; Schneiderman, J.S.; Bouix, S.; Pasternak, O.; Rathi, Y.; Vu, M.-A.; Purohit, M.P.; Helmer, K.; Koerte, I.; et al. A review of magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging findings in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012, 6, 137–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H. Traumatic axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury. In Traumatic Brain Injury; Gorbunoy, N., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; pp. 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.H. A review of corticospinal tract location at corona radiata and posterior limb of the internal capsule in human brain. NeuroRehabilitation 2009, 24, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.P.; Kwon, Y.H.; Jang, S.H. Mini-review of studies reporting the repeatability and reproducibility of diffusion tensor imaging. Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Kwon, Y.H. Central pain due to traumatic axonal injury of the spinothalamic tract in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Neurorehabil. 2018, 11, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Kwon, H.G. Apathy due to injury of the prefrontocaudate tract following mild traumatic brain injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, e130–e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenton, M.E.; Price, B.H.; Levin, L.; Edersheim, J.G. Mild traumatic brain injury: Is DTI ready for the courtroom? Int. J. Law Psychiatry 2018, 61, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.H.; Lee, H.D. Diagnostic approach to traumatic axonal injury of the optic radiation in mild traumatic brain injury: A case report. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 98, e92–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Cho, Y.W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, S.H. The relation between injury of the spinothalamocortical tract and central pain in chronic patients with mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015, 30, E40–E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Mannion, R.J. Neuropathic pain: Aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 1999, 353, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulder, J.; Crombez, E.; Mortier, E. Central pain: An overview. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2002, 102, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Backonja, M.; Rowbotham, M.C.; Allen, R.R.; Argoff, C.R.; Bennett, G.J.; Bushnell, M.C.; Farrar, J.T.; Galer, B.S.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; et al. Advances in neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barad, M.; Greicius, M.D.; Mackey, S. Imaging the CNS correlates of neuropathic pain. Continuum 2009, 15, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klit, H.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. Central post-stroke pain: Clinical characteristics, pathophysiology, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl. 1), S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.E.; Berg, H.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Rushworth, M.F.; Woolrich, M.W. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? Neuroimage 2007, 34, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Son, S.M.; Jang, S.H. Identification of spinothalamic tract and its related thalamocortical fibers in human brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 468, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.R.; Garthwaite, P.H.; Porter, S. Point and interval estimates of effect sizes for the case-controls design in neuropsychology: Rationale, methods, implementations, and proposed reporting standards. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2010, 27, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Crain, B.J.; Chacko, V.P.; van Zijl, P.C. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Y.; Pasternak, O. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: A review. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povlishock, J.T. Traumatically induced axonal injury: Pathogenesis and pathobiological implications. Brain Pathol. 1992, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, D.S.; Mori, S. Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: A new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. Radiographics 2005, 25, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.J.; Alexander, D.C. Probabilistic anatomical connectivity derived from the microscopic persistent angular structure of cerebral tissue. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K. Diffusion tensor tractography should be used with caution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Controls (n = 12) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 42 | 48 | 42 | 48 | 45 | 45.71 ± 4.15 |
| Duration to DTT | 2 days | 14 months | 1 month | 2 months | 1 month | - |
| Central pain site (VAS) | Head (5), right arm, and leg (5) | Left head, arm, and leg (5) | Head (4), right leg (4) | Head (2), both legs (3) | Head (5), both arms and legs (4) | No pain |
| Characteristics of central pain | Tingling sensation & allodynia | Tingling sensation & allodynia | Electric shock-like sensation & allodynia | Tingling & electric shock-like sensations | Tingling sensation & allodynia | No pain |
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Controls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffusion Tensor Tractography Parameters | ||||||||
| [Significance] a | FA | Right | 0.44 [0.32] | 0.41 [0.38] | 0.40 [0.29] | 0.42 [0.48] | 0.45 [0.24] | 0.42 ± 0.03 |
| Left | 0.41 [0.31] | 0.39 [0.15] | 0.45 [0.26] | 0.47 [0.12] | 0.43 [0.46] | 0.42 ± 0.03 | ||
| MD | Right | 0.84 [0.31] | 0.81 [0.21] | 0.86 [0.39] | 0.79 [0.15] | 0.90 [0.42] | 0.88 ± 0.08 | |
| Left | 0.89 [0.21] | 0.80 [0.35] | 0.77 [0.22] | 0.78 [0.26] | 0.76 [0.19] | 0.82 ± 0.07 | ||
| FN | Right | 298 [0.02] c | 660 [0.04] c | 1935 [0.23] | 438 [0.02] c | 632 [0.03] c | 1576.81 ± 461.74 | |
| Left | 1824 [0.41] | 1934 [0.36] | 38 [0.01] c | 202 [0.02] c | 20 [0.01] c | 1680.90 ± 656.56 | ||
| Estimated effect size b (95% CI) | FA | Right | 0.501 (−1.913, 2.916) | −0.327 (−2.757, 2.101) | −0.598 (−3.002, 1.805) | −0.050 (−2.491, 2.389) | 0.765 (−1.614, 3.146) | |
| Left | −0.539 (−2.950, 1.871) | −1.115 (−3.425, 1.195) | 0.703 (−1.686, 3.093) | 1.303 (−1.016, 3.532) | 0.086 (−2.353, 2.526) | |||
| MD | Right | −0.533 (−2.945, 1.877) | −0.888 (−3.247, 1.470)- | −0.286 (−2.718, 2.146) | −1.110 (−3.422, 1.201) | 0.217 (−2.218, 2.653) | ||
| Left | 0.881 (−1.478, 3.242) | 0.412 (−2.836, 2.010) | 1.063 (−3.202, 1.536) | −0.676 (−3.087, 1.694) | −0.965 (−3.309, 1.378) | |||
| FN | Right | −2.001 (−3.993, −0.007) | −1.784 (−3.876, 0.307) | 0.792 (−1.584, 3.168) | −2.072 (−4.028, −0.116) | −1.824 (−3.899, 0.250) | ||
| Left | 0.228 (−2.207, 2.663) | 0.401 (−2.022, 2.825) | −2.091 (−4.037, −0.146) | −1.951 (−3.968, 0.647) | −2.106 (−4.044, −0.168) | |||
| Spinothalamic Tract Area | ||||||||
| STT area (mm) [Significance] a | Right | 12.50 [0.02] c | 9.37 [0.02] c | 18.75 [0.03] c | 11.50 [0.02] c | 16.87 [0.03] c | 98.95 ± 17.86 | |
| Left | 101.25 [0.58] | 78.12 [0.34] | 1.56 [0.04] c | 3.12 [0.04] c | 1.56 [0.04] c | 91.40 ± 9.66 | ||
| Estimated effect size b (95% CI) | Right | −2.03 (−3.97, −0.10) | −2.07 (−3.96, −0.17) | −1.96 (−4.00, 0.06) | −2.00 (−3.98, −0.020) | −1.92 (−4.01, 0.15) | ||
| Left | 1.02 (−1.78, 3.82) | −0.10 (−3.14, 2.93) | −1.52 (−4.00, 0.96) | −1.50 (−4.00, 1.00) | −1.52 (−4.00, 0.96) | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, S.H.; Lee, H.D. Diagnostic Approach to Traumatic Axonal Injury of the Spinothalamic Tract in Individual Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040199
Jang SH, Lee HD. Diagnostic Approach to Traumatic Axonal Injury of the Spinothalamic Tract in Individual Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Sung Ho, and Han Do Lee. 2019. "Diagnostic Approach to Traumatic Axonal Injury of the Spinothalamic Tract in Individual Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury" Diagnostics 9, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040199
APA StyleJang, S. H., & Lee, H. D. (2019). Diagnostic Approach to Traumatic Axonal Injury of the Spinothalamic Tract in Individual Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics, 9(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040199




