J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11(6), 528; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060528 - 9 Jun 2021
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4280
Abstract
Background: The effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on cell proliferation and osteogenic potential (OP) of MSCs have been frequently studied. Objective: to compare the effects of LPS on periodontal-ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells (PDLSCs) in monolayer and 3D culture. Methods: The PDLSCs were colorimetrically assessed
[...] Read more.
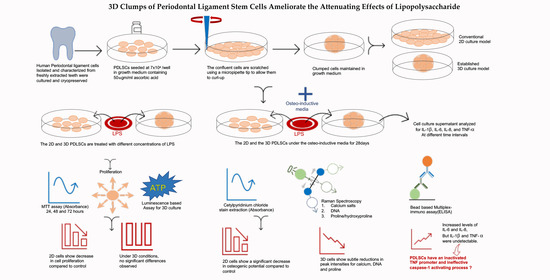
Background: The effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on cell proliferation and osteogenic potential (OP) of MSCs have been frequently studied. Objective: to compare the effects of LPS on periodontal-ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells (PDLSCs) in monolayer and 3D culture. Methods: The PDLSCs were colorimetrically assessed for proliferation and osteogenic potential (OP) after LPS treatment. The 3D cells were manually prepared by scratching and allowing them to clump up. The clumps (C-MSCs) were treated with LPS and assessed for Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and OP. Raman spectroscopy was used to analyze calcium salts, DNA, and proline/hydroxyproline. Multiplexed ELISA was performed to assess LPS induced local inflammation. Results: The proliferation of PDLSCs decreased with LPS. On Day 28, LPS-treated cells showed a reduction in their OP. C-MSCs with LPS did not show a decrease in ATP production. Principal bands identified in Raman analysis were the P–O bond at 960 cm−1 of the mineral component, 785 cm−1, and 855 cm−1 showing qualitative changes in OP, proliferation, and proline/hydroxyproline content, respectively. ELISA confirmed increased levels of IL-6 and IL-8 but with the absence of TNF-α and IL-1β secretion. Conclusions: These observations demonstrate that C-MSCs are more resistant to the effects of LPS than cells in monolayer cell culture. Though LPS stimulation of C-MSCs creates an early pro-inflammatory milieu by secreting IL-6 and IL-8, PDLSCs possess inactivated TNF promoter and an ineffective caspase-1 activating process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modulating Therapeutic Properties of Oral Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells)
►
Show Figures