The Safety and Efficacy of Hepatic Transarterial Embolization Using Microspheres and Microcoils in Patients with Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Imaging before the Procedure
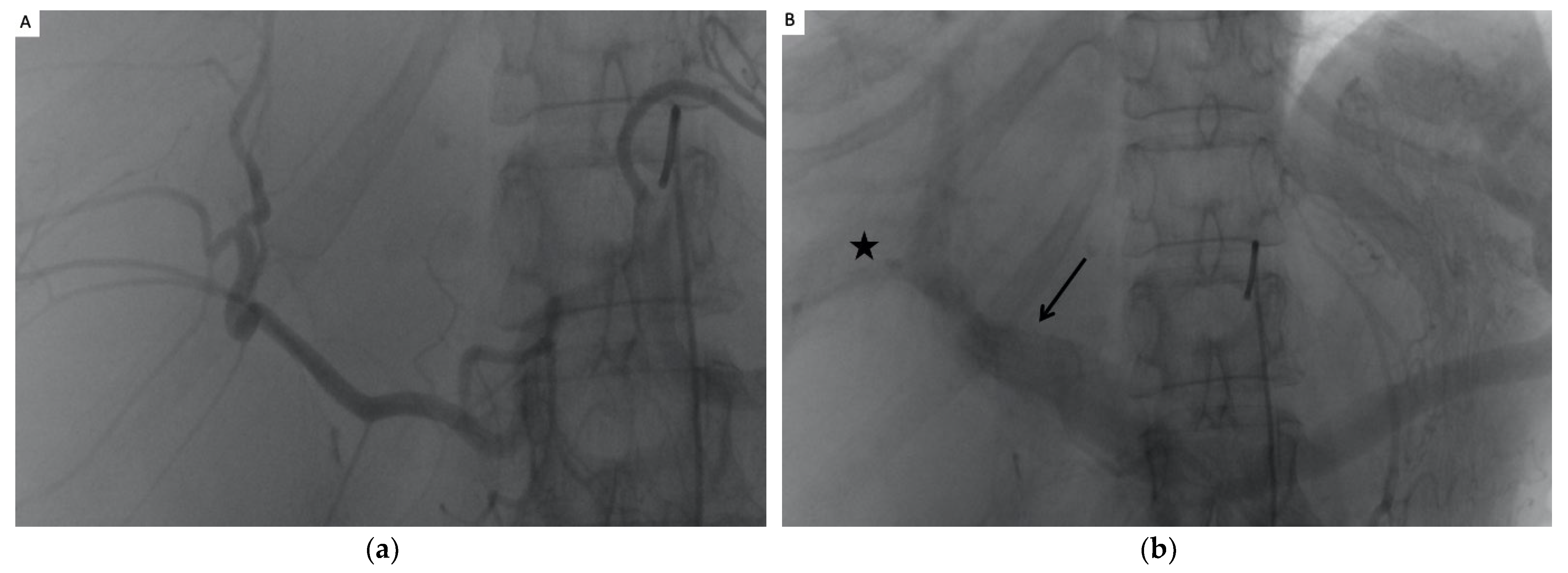
2.3. The TAE Procedure
2.4. Postprocedure Management
2.5. Endpoints
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Technical Success
3.3. Safety
3.4. Reduction in Hepatic Volume (Figure 2 and Table 3)

| Sex | Liver Volume before TAE (mL) | Liver Volume after TAE (mL) | Difference | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total liver | men | 8808.4 | 7441.1 | −15.2% | p < 0.01 | |
| women | 5672.4 | 4932.7 | −11.9% | p < 0.01 | ||
| Qobs = 0.90 IC95% [−4.1169; 10.5965] | p = 0.37 | |||||
| Embolized liver | men | 5894 | 4752 | −17.8% | p < 0.01 | |
| women | 3906 | 3234.7 | −24.3% | p < 0.01 | ||
| Qobs = −1.16 IC95% [−17.4903; 4.7764] | p = 0.25 | |||||
| Disease | ||||||
| Total liver | ADPLD | 8633 | 7174 | −16.8% | p < 0.01 | |
| ADPKD | 5597 | 4916 | −11.3% | p < 0.01 | ||
| Qobs = 1.64 IC95 [−1.3294; 12.3023] | p = 0.11 | |||||
| Embolized liver | ADPLD | 5787 | 4398 | −24% | p < 0.01 | |
| ADPKD | 3781 | 3291 | −22% | p < 0.01 | ||
| Qobs = 0.39 IC95 [−8.6315; 12.6986] | p = 0.69 | |||||
| Quality of life | ||||||
| Total liver | Improved | 6313 | 5322 | −15.7% | p < 0.01 | |
| Not improved | 6420 | 5878 | −8.1% | p = 0.03 | ||
| Qobs = −2.65 IC95 [−11.7682; −1.5267] | p < 0.01 | |||||
| Embolized liver | Improved | 4708 cc | 3811 cc | −24% | p < 0.01 | |
| Not improved | 3543 cc | 2857 cc | −12% | p < 0.01 | ||
| Qosb = −3.12 IC95 [−11.7682; −1.5267] | p < 0.01 |
| Mean Vol. before TAE (mL) | Mean Vol. after TAE (mL) | Mean Reduction of Volume | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner 3 months after TAE | ||||
| Total liver Volume | 6438 (+/−2592) | 5567 cc (+/−2122) | −12.6% (+/−8) −855 cc IC95% [570.88; 1140.55] | p < 0.01 |
| Liver embolized | 4623 (+/−2916) | 3692 cc (+/−2460) | −22.7% (+/−12.5) −930 cc IC95% [679.03; 1182.78] | p < 0.01 |
| 2+ years of follow-up | ||||
| Total Liver Volume (n = 12 patients) | 6275 (+/−2353) | 4440 cc (+/−1302) | −27.8% −1863 cc IC95% [757.7333; 2968.4889] | p < 0.01 |
| Liver embolized (n = 12 patients) | 5001(+/−2157) | 3546 cc (+/−1769) | −32.5% (+/−17) −1544 cc IC95 [841.9154; 2246.0846] | p < 0.01 |
3.5. Clinical Efficacy
3.5.1. Chronic Pain
3.5.2. Digestive Symptoms
3.5.3. Dyspnea
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cnossen, W.R.; Drenth, J.P.H. Polycystic liver disease: An overview of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, L.; Bonny, C.; Kallita, M.; Heng, A.E.; Deteix, P.; Bommelaer, G.; Abergel, A. Polycystic liver disease and its main complications. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2002, 26, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.D. Polycystic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Q. Isolated Polycystic Liver Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gigot, J.F.; Jadoul, P.; Que, F.; Van Beers, B.E.; Etienne, J.; Horsmans, Y.; Collard, A.; Geubel, A.; Pringot, J.; Kestens, P.J. Adult polycystic liver disease: Is fenestration the most adequate operation for long-term management? Ann. Surg. 1997, 225, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Laso, A.; Izquierdo-Sánchez, L.; Lee-Law, P.Y.; Perugorria, M.J.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. New Advances in Polycystic Liver Diseases. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoevenaren, I.A.; Wester, R.; Schrier, R.W.; McFann, K.; Doctor, R.B.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Everson, G.T. Polycystic liver: Clinical characteristics of patients with isolated polycystic liver disease compared with patients with polycystic liver and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussilhou, B.; Dokmak, S.; Dondero, F.; Joly, D.; Durand, F.; Soubrane, O.; Belghiti, J. Treatment of polycystic liver disease. Update on the management. J. Visc. Surg. 2018, 155, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aerts, R.M.; Kievit, W.; D’Agnolo, H.M.; Blijdorp, C.J.; Casteleijn, N.F.; Dekker, S.E.; de Fijter, J.W.; van Gastel, M.; Gevers, T.J.; van de Laarschot, L.F.; et al. Lanreotide Reduces Liver Growth in Patients With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Liver and Kidney Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 481–491.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.T.; Han, S.Y.; Yun, E.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Hahn, H.J.; Hahn, H.M. Recurrence after percutaneous ethanol ablation of simple hepatic, renal, and splenic cysts: Is it true recurrence requiring an additional treatment? Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenth, J.P.; Chrispijn, M.; Nagorney, D.M.; Kamath, P.S.; Torres, V.E. Medical and surgical treatment options for polycystic liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 52, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Wasel, B.; Walsh, C.; Keough, V.; Molinari, M. Pathophysiology, epidemiology, classification and treatment options for polycystic liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5775–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubara, Y.; Takei, R.; Hoshino, J.; Tagami, T.; Sawa, N.; Yokota, M.; Katori, H.; Takemoto, F.; Hara, S.; Takaichi, K. Intravascular embolization therapy in a patient with an enlarged polycystic liver. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.Q.; Duan, F.; Liu, F.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Song, P. Treatment of symptomatic polycystic liver disease: Transcatheter super-selective hepatic arterial embolization using a mixture of NBCA and iodized oil. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Kim, C.W.; Ro, H.; Moon, J.-Y.; Oh, K.-H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Yin, Y.H.; Jae, H.J.; Chung, J.W.; et al. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization Therapy for a Massive Polycystic Liver in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakuhara, Y.; Nishio, S.; Hattanda, F.; Soyama, T.; Takahashi, B.; Abo, D.; Mimura, H. Initial experience with the use of tris-acryl gelatin microspheres for transcatheter arterial embolization for enlarged polycystic liver. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpierre, F.; Cornelis, F.; Couzi, L.; Lasserre, A.S.; Tricaud, E.; Le Bras, Y.; Merville, P.; Combe, C.; Ferriere, J.M.; Grenier, N. Embolization of renal arteries before transplantation in patients with polycystic kidney disease: A single institution long-term experience. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHorney, C.A.; Ware, J.E.; Lu, J.F.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): III. Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability across diverse patient groups. Med. Care 1994, 32, 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E., Jr.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vorst, J.R.; van Dam, R.M.; van Stiphout, R.S.; van den Broek, M.A.; Hollander, I.H.; Kessels, A.G.; Dejong, C.H. Virtual Liver Resection and Volumetric Analysis of the Future Liver Remnant using Open Source Image Processing Software. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lodewick, T.M.; Arnoldussen, C.W.; Lahaye, M.J.; van Mierlo, K.M.; Neumann, U.P.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Dejong, C.H.; van Dam, R.M. Fast and accurate liver volumetry prior to hepatectomy. HPB 2016, 18, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyrwich, K.W.; Tierney, W.M.; Babu, A.N.; Kroenke, K.; Wolinsky, F.D. A Comparison of Clinically Important Differences in Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Lung Disease, Asthma, or Heart Disease. Health Serv. Res. 2005, 40, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brigden, A.; Parslow, R.M.; Gaunt, D.; Collin, S.M.; Jones, A.; Crawley, E. Defining the minimally clinically important difference of the SF-36 physical function subscale for paediatric CFS/ME: Triangulation using three different methods. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalilzadeh, O.; Baerlocher, M.O.; Shyn, P.B.; Connolly, B.L.; Devane, A.M.; Morris, C.S.; Cohen, A.M.; Midia, M.; Thornton, R.H.; Gross, K.; et al. Proposal of a New Adverse Event Classification by the Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1432–1437.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, R.; Ubara, Y.; Hoshino, J.; Higa, Y.; Suwabe, T.; Sogawa, Y.; Nomura, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Sawa, N.; Katori, H.; et al. Percutaneous Transcatheter Hepatic Artery Embolization for Liver Cysts in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ubara, Y. New Therapeutic Option for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Patients With Enlarged Kidney and Liver. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2006, 10, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, J.; Ubara, Y.; Suwabe, T.; Sumida, K.; Hayami, N.; Mise, K.; Hiramatsu, R.; Hasegawa, E.; Yamanouchi, M.; Sawa, N.; et al. Intravascular Embolization Therapy in Patients with Enlarged Polycystic Liver. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ryu, H.; Han, M.; Kim, H.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Chung, J.W.; Yi, N.-J.; Lee, K.-W.; Suh, K.-S.; Ahn, C. Comparison of volume-reductive therapies for massive polycystic liver disease in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Yuan, K.; Wang, M.Q.; Yan, J.Y.; Xin, H.N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Bai, Y.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Duan, F.; et al. Transarterial Embolization for Treatment of Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease: More than 2-year Follow-up. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayes, K.M.; Shaaban, A.M.; Rothan, S.M.; Javadi, S.; Madrazo, B.L.; Castillo, R.P.; Casillas, V.J.; Menias, C.O. A Comprehensive Approach to Hepatic Vascular Disease. RadioGraphics 2017, 37, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollak, J.S.; White, R.I. The Use of Cyanoacrylate Adhesives in Peripheral Embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, J.B.; Cornell, C.; Worthington-Kirsch, R.; Lipman, J.C.; Benenati, J.F. Long-term Outcome from Uterine Fibroid Embolization with Tris-acryl Gelatin Microspheres: Results of a Multicenter Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, A.; Beaujeux, R.; Wassef, M.; Rüfenacht, D.; Boschetti, E.; Merland, J.J. Trisacryl gelatin microspheres for therapeutic embolization, I: Development and in vitro evaluation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1996, 17, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Neijenhuis, M.K.; Wijnands, T.F.M.; Kievit, W.; Ronot, M.; Gevers, T.J.G.; Drenth, J.P.H. Symptom relief and not cyst reduction determines treatment success in aspiration sclerotherapy of hepatic cysts. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3062–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnelldorfer, T.; Torres, V.E.; Zakaria, S.; Rosen, C.B.; Nagorney, D.M. Polycystic liver disease: A critical appraisal of hepatic resection, cyst fenestration, and liver transplantation. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwabe, T.; Ubara, Y.; Hayami, N.; Yamanouchi, M.; Hiramatsu, R.; Sumida, K.; Sawa, N.; Sekine, A.; Kawada, M.; Hasegawa, E.; et al. Factors Influencing Cyst Infection in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 141, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernts, L.H.; Neijenhuis, M.K.; Edwards, M.E.; Sloan, J.A.; Fischer, J.; Smoot, R.L.; Nagorney, D.M.; Drenth, J.P.; Hogan, M.C. Symptom relief and quality of life after combined partial hepatectomy and cyst fenestration in highly symptomatic polycystic liver disease. Surgery 2020, 168, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neijenhuis, M.K.; Gevers, T.J.; Hogan, M.C.; Kamath, P.S.; Wijnands, T.F.; Ouweland, R.C.V.D.; Edwards, M.E.; Sloan, J.A.; Kievit, W.; Drenth, J.P. Development and Validation of a Disease-Specific Questionnaire to Assess Patient-Reported Symptoms in Polycystic Liver Disease. Hepatology 2016, 64, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Patient Characteristics | Mean (Range) or N (%) |
|---|---|
| Average age in years (range) | 52.3 (33–78) |
| <50 years | 10 (39%) |
| >50 years | 16 (61%) |
| Gender | |
| -Male | 5 (19%) |
| Weight | 86.6 (+/−12.8) |
| BMI | 28.25 (+/−4.1) |
| -Female | 21 (81%) |
| Weight | 63,2 (+/−12.1) |
| BMI | 23.4 (+/−2.4) |
| Mean time follow-up (months) | 51 (6–98) |
| Type of PLD | |
| -associated with ADPK | 20 (77%) |
| -PLD isolated | 6 (23%) |
| Laboratory | |
| Creatinine | 117.3 (+/−82) |
| >60 GFR | 10 (38%) |
| <60 GFR. | 13 (50%) |
| dialysis | 3 (11%) |
| Urea | 8.1 (+/−3.6) |
| AST | 39.8 (+/−53) |
| ALT | 33.2 (+/−36.5) |
| GGT | 175.8 (+/−116.8) |
| Bilirubin | 12.3 (+/−9.2) |
| Alcaline phosphatase | 141.6 (+/−106) |
| TP | 92.1 (+/−14) |
| Hemoglobin | 12.7 (+/−1.5) |
| Platelets | 230 (+/−77) |
| Patient Characteristics | Mean (Range) or N (%) |
|---|---|
| Liver volume | |
| Total liver volume | 6436 cc (2965–13,470) |
| Right liver | 4058 cc (2073–9566) |
| Left liver | 2377 cc (848–5776) |
| Symptoms | |
| Abdominal Pain | 24 (92%) |
| Dyspnea | 21 (81%) |
| Dyspepsia | 26 (100%) |
| Previous treatment | |
| Medical treatment | 7 (27%) |
| Cyst sclerosis | 11 (42%) |
| Fenestration or hepatectomy | 0 |
| Anterior complications | 13 (50%) |
| Infection | 12 (46%) |
| Hemorrhage | 3 (11%) |
| Authors | Date | Patient | Embolic Material Used | Reduction in Liver Volume at 6 Months | Reduction in Liver Volume at 1 Year | Reduction in Liver Volume at 2 Years | Mean Liver Volume before Embolization (mL) | Clinical Success |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubara et al. [13] | 2004 | 1 | Coils | −46% | 12,364 | 100% | ||
| Takei et al. [27] | 2007 | 30 | Coils | −21.2% | 7882 | 80% | ||
| Park et al. [15] | 2009 | 3 | PVA and Coils | −15% | 9490 | 66% | ||
| Wang et al. [14] | 2012 | 21 | NBCA and lipiodol | No significative difference | −25.7% | 8270 | 85.3% | |
| Hoshino et al. [26] | 2014 | 221 | Coils | −5.3% | −9.2% | 7058 | - | |
| Yang et al. [29] | 2016 | 18 | Coils | −7.6% | 7767 | 31.4% | ||
| Zhang et al. [30] | 2017 | 23 | NBCA and lipiodol | −16.3% | −29.7% | −29.3% | 8070 | 86% |
| Sakuhara et al. [16] | 2019 | 5 | Tris Acryl Gelatin microsphere | −5.5% | −6.7% | 7406 | 60% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coussy, A.; Jambon, E.; Le Bras, Y.; Combe, C.; Chiche, L.; Grenier, N.; Marcelin, C. The Safety and Efficacy of Hepatic Transarterial Embolization Using Microspheres and Microcoils in Patients with Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101624
Coussy A, Jambon E, Le Bras Y, Combe C, Chiche L, Grenier N, Marcelin C. The Safety and Efficacy of Hepatic Transarterial Embolization Using Microspheres and Microcoils in Patients with Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(10):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoussy, Alexis, Eva Jambon, Yann Le Bras, Christian Combe, Laurence Chiche, Nicolas Grenier, and Clément Marcelin. 2022. "The Safety and Efficacy of Hepatic Transarterial Embolization Using Microspheres and Microcoils in Patients with Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 10: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101624
APA StyleCoussy, A., Jambon, E., Le Bras, Y., Combe, C., Chiche, L., Grenier, N., & Marcelin, C. (2022). The Safety and Efficacy of Hepatic Transarterial Embolization Using Microspheres and Microcoils in Patients with Symptomatic Polycystic Liver Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(10), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101624






